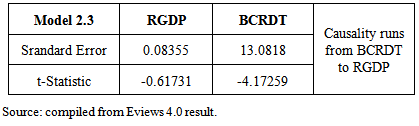
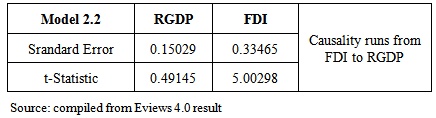
| [1] | Abdullahi, S. A. (2005). Capital Market Performance and Economic Development in Nigeria: An Empirical Analysis. Paper Presented at the Department of Business Administration, Bayero University Kano. |
| [2] | Adam, J. A., and Sanni, I. (2005). Stock Market Development and Nigeria’s Economic Growth. Journal of Economics and Allied Fields, Vol. 2 No. 2, p. 116-132. |
| [3] | Adams, J.A (1998). “Financial Intermediation and Economic Growth: Evidence from Nigeria”, Journal of Economic Management, Volume 5, N0. 2, June. |
| [4] | Agosin, M. R. and Mayer, R. (2000). “Foreign Investment in Developing Countries”, UNCTAD Discussion Papers, No. 146. |
| [5] | Agu, C.C. and J.O. Chukwu (2008) “Toda and Yamamoto causality tests between “bank based” financial deepening and economic growth in Nigeria”. European Journal of Social Science, 7(2), pp.189-98. |
| [6] | Aitken, B. and Harrison, A. (1999). “Do Domestic Firms Benefit from Foreign Investment? Evidence from Venezuela”, American Economic Review, 89, No.3. |
| [7] | Akaike, H. (1969). “Statistical predictor identification”, Annuals of the Institute o Statistical Mathematics (21), pp 207-17. |
| [8] | Amaral, P. S. and Quintin, E. (2007). Financial Intermediation and Economic Development: A Quantitative Assessment. Seminar paper at the 2004 Annual Meeting of the Society for Economic Dynamics, Arizona State University, the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis, Texas A&M, the University of Pittsburgh, the Universidad Catolica Argentina, the University of Western Ontario, Queen's University and the Universidad de Guanajuato |
| [9] | Akinlo, A. E. (2004). “Foreign Direct Investment and Growth in Nigeria: An Empirical Investigation. ”Journal of Policy Modeling. (26) 5 627-639. |
| [10] | Akinlo A. E., & Egbetunde T. (2010). Financial Development and Economic Growth: The Experiences of 10 Sub-Saharan African Countries Revisited. The Review of Finance and Banking, 02(1). |
| [11] | Alfaki, M. (2009, March 6). Explaining current situation of the Nigerian Stock Exchange. The Guardian Newspaper, p. 10. |
| [12] | Alfaro, L., Arendam, C. K., Sebrem, K. O. and Sebrem, S. (2006). “How Does Foreign Direct Investment Promote Economic Growth?” Exploring the Effects of Financial Markets on Linkages. NBER working paper No 12522. |
| [13] | Alile, H. (1997, Dec 2). “Government Must Divest” The Business Concord of Nigeria, page 8. |
| [14] | Arestis, P. and Demetriades, P. (1997). Financial Development and Economic Growth: Assessing the Evidence The Economic Journal, Volume 107, P442, 783-799. |
| [15] | Aruwa, S. A. S. (2007). “Post Consolidation Banking Crisis: Capital Assets and Deposits Nexus and Policy options”. Finance and Accounting Research Monitor (FARM), Journal of the Department of Accounting and Banking/Finance, University of Abuja. Vol. 1. No. 1, June. |
| [16] | Azege, M. (2004). The Impact of Financial Intermediation on Economic Growth: The Nigerian Perspective, Lagos State University. |
| [17] | Balasubramanyam, V. N., Salism, M. and Sapsfold, D. (1999). “Foreign Direct Investment as an Engine of Growth.” Journal of International Trade and Economic Development 8(1.) 27-40. |
| [18] | Beccalli, E., Barbara, C. B. and Girardone, C. (2006). Efficiency and Stock Performance in European Banking, Journal of Business and Accounting, 33(1-2):245-262. |
| [19] | Beckaert, G., Harvey, C. and Lundblad, C. (2005). Does Financial Liberalization Spur Growth? Journal of Financial Economics, 77, p. 3-55. |
| [20] | Beck, T., Levine, R. and Loayza, N. (2000). Finance and the sources of growth. Journal of Financial Economics, 58, 261−300. |
| [21] | Ben, N. S. and Ghazouani, S. (2007). Stock Markets, Banks and Economic Growth: Empirical Evidence from the MENA Region. Research in International Business Finance, 21, pp. 297-315. |
| [22] | Bencivenga, V. R. and Smith, B. D. (1991). Financial Intermediation and Endogenous Growth, Review of Economic Studies 58, 195-209. |
| [23] | Bencivenga, V. R., Smith, B. and Starr, R. M. (1996). Equity Markets, Transaction Costs, and Capital Accumulation: An Illustration." The World Bank Economic Review, Vol. 10: 241-65. |
| [24] | Bolbol, A., Fatheldin, A. and Omran, M. (2005). Financial Development, Structure and Economic Growth: The Case of Egypt, 1974-2002. Research in International Business Finance, 19, p. 171-194. |
| [25] | Borensztein, E., Gregorio, J. D. and Lee, W. (1998). How does foreign direct investment affect economic growth? Journal of International Economics 45, 115{135. |
| [26] | Boyd, J. H. and Smith, B. D. (1992). “Intermediation and the Equilibrium Allocation of Investment Capital: Implications for Economic Development.” Journal of Monetary Economics 30 409-432. |
| [27] | Calderón, C. & Liu, L (2002). "The Direction of Causality Between Financial Development and Economic Growth," Working Papers Central Bank of Chile 184, Central Bank of Chile. |
| [28] | Calderon, C., & Liu, L. (2003). The Direction of Causality Between Financial Development and Economic Growth. Journal of Development Economics. |
| [29] | Caporale, G. M., Howells, P., Soliman, A. M. (2005). Endogenous Growth Models and Stock Market Development: Evidence from Four Countries Review of Development Economics 9 (2), 166–176. |
| [30] | Central Bank of Nigeria Statistical Bulletin (2008).www.cenbank.org. |
| [31] | Chang, P. C., Jia, C. and Wang, Z. (2010). Bank fund reallocation and economic growth: Evidence from China, Journal of Banking & Finance, 34, 2753–2766 |
| [32] | Chee, K. C., Zulkornian, Siong, Y. H. L. and Venus, K.S. (2003). Financial Development and Economic Growth in Malaysia: The Stock Market Perspective. |
| [33] | DeMello, L. R. (1997). Foreign direct investment in developing countries: A selective survey. Journal of Development Studies, 34(1), 1–34. |
| [34] | Demetriades, P. O. and Hussain, K. A. (1996). Does Financial Development Cause Economic Growth? Time Series Evidence from 10 Countries, Journal of Development Economics 61: 387-411. |
| [35] | Demirgüç-Kunt, A. and Ross, L. (1996). "Stock Market, Corporate Finance and Economic Growth: An Overview" The World Bank Review 10(2):223-239. |
| [36] | Demirguc-Kunt, A., & Levine R. (2008). Finance, Financial Sector Policies and Long Run Growth. The World Bank Development Research Group, Policy Research Working Paper 4469. |
| [37] | Demetriades O. P., & James G. A. (2011). Finance and Growth in Africa: The Broken Link. Economic Letters, 113. |
| [38] | Estrada, G., Park, D., & Kamayandi, A. (2010). Financial Development and Economic Growth in Asia. ADB Working Paper No 233. |
| [39] | Georgellis Y., & Oluitan R. O. (2009). Bank Credit and Economic Growth: The Nigerian Experience. Paper Presented at Centre for the Study of African Economy (CSAE) Conference. Oxford University, UK. |
| [40] | Dickey, D. A. and Fuller, W. A. (1979). Distribution of Estimators for Autoregressive Time Series with a Unit Root, Journal of American Statistical Association, 74:427-431. |
| [41] | Edo, S. E. (1995). “An Estimation of a Model of Long-term Securities Investment in Nigeria” Nigerian Economic and Financial Review (N. E. F. R.) December 1995 Vol. 1 2: 45-53. |
| [42] | Emmanuel, O. O. and Adegboyega, E. (2014) Banks and Economic Growth in Nigeria: A Re-Examination of the Financial Repression Hypothesis. American Journal of Business and Management 3(1), 1-9. |
| [43] | Esso, C. (2010). Re-examining the finance growth nexus: Structural break, threshold co-integration and causality evidence from the ECOWAS. Journal of Economic Development. 35(3): 57-79. |
| [44] | Ezeoha, A., Ebele, O., and Ndi, O. O. (2009). Stock Market Development and Private Investment Growth in Nigeria. Journal of Sustainable Development in Africa, Vol.11, No.2. |
| [45] | Fadare, (2010). Recent banking sector reforms and economic growth in Nigeria. Middle Eastern Finance and Economics. Issue: 146-160. |
| [46] | Filer, R. K., Hanousek, J., and Campo, N. F. (2000). Do Stock Markets Promote Economic Growth? William Davidson Institute at the University of Michigan, Working Paper No. 151. |
| [47] | Francis, X. and Raja, A.V. (2007). Stock Market and Shareholder Protection: Are They Important for Economic Growth?. |
| [48] | Goldsmith, R.W. (1969). “Financial Structure and Development,” Yale Univ. Press, New Haven CN. |
| [49] | Granger, C. W. J. (1980). Long memory relationships and the aggregation of dynamic models. Journal of Econometrics. 14, 227-38. |
| [50] | Granger, C. W. J. (1969). Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica, 35, 424–438. |
| [51] | Granger, C. W. J. (1981). Some properties of time series data and their use in econometric model specification. Journal of Econometrics 16, 121-30. |
| [52] | Greenwoood, J. and Smith, B. (1996). Financial Markets in Development and the Development of Financial Markets, Journal of Economic Dynamic and Control, 21:145-81. |
| [53] | Gurley, J. and Shaw, E. (1967). “Financial Structure and Economic Development”, Economic Development and Cultural Change, 34(2), 333-346. |
| [54] | Gursoy, C. T. and Muslumov, A. (1999). Stock Markets and Economic Growth: A Causality Test. MBA Thesis Submitted to the Institute of Social Sciences, Istanbul Technical University Turkey, pp. 124-131. |
| [55] | Guryay, E., Safakli, O. V. and Tuzel, B. (2007). “Financial Development and Economic Growth: Evidence from Northern Cyprus”, International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, ISSN 1450-2887 Issue 8. |
| [56] | Hakeem, M. I. (2009). Banking development, human capital and economic growth in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). Journal of Economic Studies. 37(5): 557-577. |
| [57] | Hamid, M. and Sumit, A. (1998). Stock Market Development and Economic Growth: Evidence from Developing Countries. |
| [58] | Hicks, J. A. (1969). A Theory of Economic History. Clarendon Press Oxford, U.K. |
| [59] | Ho, N.W. (2002). “Financial Development and Economic Growth in Macau,” AMCM Quarterly Bulletin, Issue No.3, April, 15-30. |
| [60] | Hondroyiannis, G., Lolos, S. and Papapetrou, E. (2005). Financial Market and Economic Growth in Greece, 1986-1999. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 15, pp. 173-188. |
| [61] | IMF (1993). "Balance of Payments Manual" Fifth Edition (Washington, D.C., International Monetary Fund, 1993) |
| [62] | Inanga, I. L. and Chidozie, E. (1997). “Institutional, Traditional and Asset Pricing Characteristics of the Nigerian Stock Exchange” African Economic Research Consortium Research paper 60 march 1997. |
| [63] | Johannes, T. A., Njong, A. M., & Cletus N. (2011). Financial Development and Economic Growth in Cameroon, 1970 – 2005. Journal of Economics & International Finance, 3(6), 367-375. |
| [64] | Johansen, S. (1988). “Statistical Analysis of Cointegrating Vectors”, Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 12, 231-254. |
| [65] | Johansen, S. (1992). “Testing Weak Exogeneity and Order of Cointegration in UK Money Demand Data”, Journal of Policy Modeling, 14, 313-334. |
| [66] | Johansen, S. and Juselius, K. (1990). “Maximum Likelihood Estimation and Inference on Cointegration with Applications to Demand for Money.” Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics, Vol.52, May, pp. 169 – 210. |
| [67] | Jung, W. S. (1986). Financial development and economic growth: International evidence. Economic Development and Cultural Change 34, 336–346. |
| [68] | Khan, A. (2000). The Finance and Growth Nexus.” FRBP Business Review, January/February, 3-14. |
| [69] | King, R. and Levine, R. (1993). Stock Market Development and Long-run Growth. World Bank Economic Review, 10:323-339. |
| [70] | Krugman, P. (1998). “Fire Sale FDI”, Working paper, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. |
| [71] | Kumar, R. R. (2011). Do Remittances, Exports and Financial Development Matter for Economic Growth? A Case Study of Pakistan Using Bounds Approach. Journal of International Academic Research, 11(1). |
| [72] | Levine, R. (1991). Stock Markets, Growth and Tax Policy. Journal of Finance, Vol. XLV1, pp.1445-1465. |
| [73] | Levine, R. and Zervos, S. (1996). “Stock Market Development and Long-Run Growth”, The World Bank Economic Review 10, 323-339. |
| [74] | Levine, R. and Zervos, S. (1998). “Stock Markets, Banks and Economic Growth”, American Economic Review 88, 537-558. |
| [75] | Levine, R., Loayza, N. and Beck, T. (1999). “Financial Intermediation and Growth: Causality and Causes”, www.worldbank.org/research. |
| [76] | Levine, R. Loayza, N. and Beck, T. (2000). Financial intermediation and growth: Causality and causes, Journal of Monetary Economics, 46, 31−77 |
| [77] | Lipsey, R. (1999). The location and characteristics of U.S. affiliates in Asia. NBER Working Paper No. 6876. Cambridge, MA |
| [78] | Liu, W. and Hsu, C. (2006). The Role of Financial Development in Economy: The Experiences of Taiwan, Korea and Japan. Journal of Asian Economies, 17, p. 667-690. |
| [79] | Luintel, K. and Khan, M. (1999). A Quantitative Reassessment of the Finance-Growth Nexus: Evidence form a Multivariate VAR, Journal of Development Economics. 60: 381-405. |
| [80] | Mainoma, M. A. (2010). “Towards I-Theory of Bank Failure in Nigeria”. Conference proceeding on the theme ” Managing the Challenges of Global Financial Crisis in Developing Economies.” Organized by Faculty of Administration, Nasarawa State Univevrsity, Keffi between March 9-11, 2010. Vol. 2. p. 20-30 |
| [81] | McKinnon, R. (1973). Money and Capital in Economic Development, the Brookings Institute, Washington. |
| [82] | Miller, R. L. (1998). Economics Today, Addison-Wesley Longman, Reading. |
| [83] | Minier, J. (2003). Are Small Stock Markets Different?. Journal of Monetary Economics, 50, p. 1593-1602. |
| [84] | Mohammed, S.E. and Sidiropoulos, M. (2006). Finance-Growth Nexus in Sudan: Empirical Assessment Based on an Application of the ARDL Model. |
| [85] | Mohtadi, H. and Agarwal, S. (2004). Stock Market Development and Economic Growth: Evidence from Developing Countries, Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [86] | Muhammed, S., Nadeem, A. and Liaquat, A. (2008). Stock Market Development and Economic Growth: ARDL Causality in Pakistan. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, Issue 14, p.183-195. |
| [87] | Ndebbio, J. E. U. (2004). Financial Deepening, Economic Growth and Development: Evidence from Selected SSA Countries, AERC RP 142. |
| [88] | Neusser, K. and Kugler, M. (1998). “Manufacturing Growth and Financial Development: Evidence from OECD Countries”, Review of Economics and Statistics, 80 (4): 638-646. |
| [89] | Nieuwerburgh, S., Buelens, F. and Cuyvers, L. (2005). Stock Market Development and Economic Growth in Belgium. NYU Working Paper 05-024. |
| [90] | Nunnenkamp, P. and Spatz, J. (2003). “Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth in Developing Countries: How Relevant are Host – country and Industry characteristics?” Kiel working paper no. 1176. |
| [91] | Nurudeen, A. (2009) Does Stock Market Development Raise Economic Growth? Evidence from Nigeria. The Review of Finance and Banking, 1(1)15–26 |
| [92] | Nyong, M. O. (1997). Capital Market Development and Long-run Economic Growth: Theory, Evidence and Analysis. First Bank Review, p. 13-38. |
| [93] | Obadan, M. I. (2004). Foreign Capital Flows and External Debt: Perspectives on Nigeria and the LDCs Group. Broadway Press Limited, Lagos |
| [94] | Obademi, O. E. and Elumaro, A. (2014). Banks and Economic Growth in Nigeria: A Re-Examination of the Financial Repression Hypothesis. American Journal of Business and Management, 3(1). |
| [95] | Obamiro, J. K. (2005). Nigerian Economy: Growth and the Role of Stock Market. Journal of Economic and Financial Studies Vol. 2 No. 2. |
| [96] | Obreja, B., Dragota, L., Catarama, V. D. and Semenescu, A. (2008). Correlations between Capital Market Development and Economic Growth: The Case of Romania. Journal of Applied and Quantitative Methods, Vol. 3 No. 1, p. 64-75, Spring. |
| [97] | Obwona, M. B. (2001). “Determinants of FDI and their Impact on Economic Growth in Uganda”, African Development Bank, 2201, 46-81. |
| [98] | Ogbokor, A. C. (2005). “Macroeconomic Impact of Trade on Namibian Growth: An Empirical Illustration.” Journal of social sciences 1(1) 57-60. |
| [99] | Ogwumike, F. O. and Omole, D.A. (1996). The Stock Exchange and Domestic Resource Mobilization In Nigeria. S. Mensah Ed. Rector Press Ltd, Massachusetts, p. 230-251. |
| [100] | Okereke-Onyuike, N. (2009). The Nigerian Stock Exchange. A review of Market Performance in 2008 and the outlook for 2009. C: /users/HPUSER/Document/Nigeria Stock Exchange-official 2008 Review and Outlook for 2009. Retrieved on 25/03/2009. |
| [101] | Oluitan, R. O. (2012). Bank Credit and Economic Growth: Evidence from Nigeria. International Business and Management .5(2), 102-110. |
| [102] | Onuorah, A. C. & Ozurumba, B. A. (2013). Bank Credits: An Aid to Economic Growth In Nigeria, Information and Knowledge Management, 3(3). |
| [103] | Osinubi, T. S., and Amaghionyeodiwe, L.A. (2003). Stock Market Development and Long-run Growth in Nigeria. Journal of African Business, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 103-129. |
| [104] | Otepola, A. (2002). “Foreign Direct Investment as a factor of Economic Growth in Nigeria.” Africa Institute for Economic Development and Planning (IDEP), Dakar, Seregal. |
| [105] | Oyejide, T. A. (2005). Capital Flows and Economic Transformation: A Conceptual Framework on Proceedings of Central Bank of Nigeria 5th Annual Monetary Policy Conference with the theme “Capital Flows and Economic Transformation in Nigeria.” Held at the CBN Conference Hall, Abuja. November 10th to 11th. |
| [106] | Patrick, H. T. (1966). Financial development and economic growth in underdeveloped countries. Economic Development and Cultural Change, 14, 174-189. |
| [107] | Romer, P. (1993). Idea gaps and object gaps in economic development. Journal of Monetary Economics 32, 543{573. |
| [108] | Saltz, I. S. (1992). “The Negative Correlation between Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth in the Third World: Theory and Evidence”, Rivista Internationale Di Scienz Economiche e Commerciale, 19(7), 617-633. |
| [109] | Sanusi, J.O. (2002). The Evolution of Monetary Management in Nigeria and Its Impact on Economic Development. CBN Bullion, Volume 26, p1, 1-11. |
| [110] | Sanusi, L. S. (2009). ‘The Nigerian Banking Industry: What Went Wrong and Way Forward’; A Pre-convocation Lecture delivered at Bayero University, Kano. |
| [111] | Sanusi, L. S. (2010). International Financial Structure and the Nigerian Banking System. Conference proceeding on the theme ” Managing the Challenges of Global Financial Crisis in Developing Economies.” Organized by Faculty of Administration, Nasarawa State Univevrsity, Keffi between March 9-11, 2010. Vol. 2. pp. 8-19 |
| [112] | Shaw, E. S. and Gurley, J. G. (1955). Financial Aspect of the Economic Development. The American Economic Review. Xlv(4). |
| [113] | Shaw, E.S. (1973). Financial Deepening in Economic Development, New York, Oxford University Press, London and New York. |
| [114] | Schumpeter, J.A. (1911). The Theory of Economic Development, Harvard University Press. |
| [115] | Soludo, C. C. (2009). Global Financial and Economic Crisis: How Vulnerable is Nigeria, www.cenbank.org. |
| [116] | Soyode, A. (1990). ‘The Role of Capital in Economic Development” Security Market Journal Nigeria Vol.6. |
| [117] | Stern, N. (1985). The Economics of Development: A Survey. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 17(2), pp. 133-152, May. |
| [118] | Tang, S., Selvanathan, E. A. and Selvanathan, S. (2008). “Foreign Direct Investment, Domestic Investment, and Economic Growth in China.” UNU-WIDER Research Paper No. 2008/19. |
| [119] | Ted, A., Lazar, D. and Jeyapaul, J. (2005). Is the Indian Stock Market A Casino? Journal of Business and Economic Research, Vol. 3 No. 4, pp. 63-72. |
| [120] | Tharavanij, P. (2007). Capital Market, Severity of Business Cycle, and Probability of Economic Downturn. MPRA Paper No. 4953. |
| [121] | Thornton, J. (1995). Financial Deepening and Economic Growth in Developing Countries. Economia Internationale, 48(3), pp.423-4. |
| [122] | Unalmis, D. (2002). “The Causality between Financial Development and Economic Growth: The Case of Turkey”; Research Department, Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey, 06100, Ankara. |
| [123] | UNCTAD, Foreign Direct Investment Data Base, www.unctad.org. |
| [124] | Wadud, M. A. (2005). “Financial Development and Economic Growth: A Cointegration and ECM Approach for South Asian Countries”, Paper presented at International Conference of the Asian Law and Economics Association at Seoul National University, South Korea on 24-25 June, 2005. |
| [125] | Waqabaca, C. (2004). “Financial Development and Economic Growth in Fiji”, Economics Department, Reserve Bank of Fiji, WP 03. |
| [126] | World Bank (2005). World Development Report. "A Better Investment Climate For Everyone", The World Bank, Washington D. C., 2005. |
| [127] | Yartey, C. A. (2008). “Well Developed Financial Intermediary Sector Promotes Stock Market Development: Evidence from Africa,” Journal of Emerging Market Finance. |
| [128] | Yartey, C. A. and Adjasi, C. K. (2007). Stock Market Development in Sub-Saharan Africa: Critical Issues and Challenges, IMF Working Paper, WP/07/209. |
| [129] | Zaghdoudi, T., Ochi, A. and Soltani, H. (2013). Banking Intermediation and Economic Growth: Some Evidence from MENA Countries. Advances in Management & Applied Economics, 3(4) 51-57. |
| [130] | Zellner, A. (1979). Statistical Analysis of Econometric Models, Journal of the American Statistical Association, (367):628-643. |
| [131] | Zhang, K. H. (2001). “How Does Foreign Direct Investment Affect Economic Growth?”, Economics of Transition, 9(3), 679-693. |
| [132] | Zhang, J., Wang, L. and Wang, S. (2012). Financial development and economic growth: Recent evidence from China, Journal of Comparative Economics, 40, 393–412. |
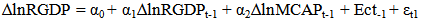
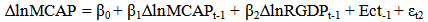
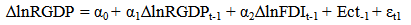
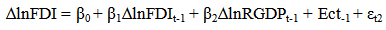
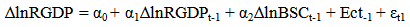
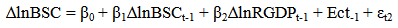
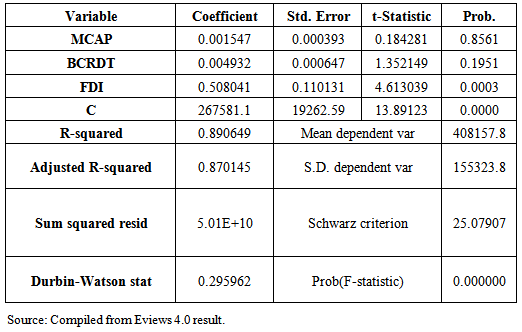
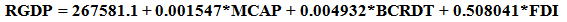 The equation shows α =267581.1 which is the intercept. This is the base level of prediction when the MCAP, BCRDT and FDI are equal to zero. The coefficient of MCAP, BCRDT and FDI measures how a unit change in independent variable affects the dependent variable. From the results, a unit change in total market capitalization leads to about 0.15% increase in Real GDP. While a unit change in banking sector credit leads to 0.49% increase in Real GDP and accordingly a unit change in FDI leads to 50.80% increase in Real GDP. This shows that there is a positive relationship between total market capitalization, banking sector credit, foreign direct investment and the Real GDP. R – Squared (R2) is the fraction of the variance of the dependent variable explained by the independent variable. In this result the R2 is about 89%, meaning that about 89% of Real GDP is explained by the MCAP, BCRDT and FDI.Sum squared residual is a measure of error in using the estimated regression equation to estimate the values of the Real GDP. The mean and standard deviation of Real GDP is N408157.8 and 155323.8 million respectively.
The equation shows α =267581.1 which is the intercept. This is the base level of prediction when the MCAP, BCRDT and FDI are equal to zero. The coefficient of MCAP, BCRDT and FDI measures how a unit change in independent variable affects the dependent variable. From the results, a unit change in total market capitalization leads to about 0.15% increase in Real GDP. While a unit change in banking sector credit leads to 0.49% increase in Real GDP and accordingly a unit change in FDI leads to 50.80% increase in Real GDP. This shows that there is a positive relationship between total market capitalization, banking sector credit, foreign direct investment and the Real GDP. R – Squared (R2) is the fraction of the variance of the dependent variable explained by the independent variable. In this result the R2 is about 89%, meaning that about 89% of Real GDP is explained by the MCAP, BCRDT and FDI.Sum squared residual is a measure of error in using the estimated regression equation to estimate the values of the Real GDP. The mean and standard deviation of Real GDP is N408157.8 and 155323.8 million respectively. Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML