-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2014; 3(2): 60-67
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20140302.02
Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities as Non Accounting Information to Predict MSMEs Credit Risk in Trincomalee District of Sri Lanka
HM. Nijam
Department of Accountancy and Finance, Faculty of Management and Commerce, South Eastern University of Sri Lanka, Oluvil, #32360, Sri Lanka
Correspondence to: HM. Nijam, Department of Accountancy and Finance, Faculty of Management and Commerce, South Eastern University of Sri Lanka, Oluvil, #32360, Sri Lanka.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The nature of Micro Small and Medium sized Enterprises (MSMEs) often creates obstacles in giving proper financial statement information for estimating credit risk. Alternative models for SME loan default prediction being suggested in literature employ non-accounting information as supplements to financial statement information-based models thereby enabling more practical and accurate prediction of loan default. Using the data collected from randomly selected 62 MSME borrowers from Trincomalee District of Sri Lanka, this study has found that Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities, an important supporting factor driven by the external environment which is mostly beyond the control of the organization, is also significantly correlating with nature of repayment of commercial loan extended to MSMEs. Rural/Urban Characteristics, Distance from the lender, Accessibility to Market, Accessibility to Communication and Accessibility to Public Institutions and Utilities are the proxies employed for Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities and are found to have statistically significant relationship with MSME credit risk. Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities is therefore significant non accounting information signaling MSME credit risk. This finding derives an overall evidence for the fact that the environmental factors will also assist to predict MSME credit risk.
Keywords: SME, Credit Risk, Default Prediction
Cite this paper: HM. Nijam, Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities as Non Accounting Information to Predict MSMEs Credit Risk in Trincomalee District of Sri Lanka, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 3 No. 2, 2014, pp. 60-67. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20140302.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The Small and Medium Sized Enterprises (SMEs) all over the world have been playing an important role in the spheres of industrialization, commerce and overall economic growth. Besides increasing per capita income and output, SMEs also contribute to local resource utilization, generate employment opportunities and reduce regional development disparities thereby promoting economic development and growth. In Sri Lanka, Micro Small and Medium sized Enterprises (MSMEs) (the acronyms SMEs and MSMEs are interchangeably used in this study) are scattered in agriculture, plantation, construction, manufacturing, trade and other service sectors and contributed to 40 percent of the total Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in 2010 and 52% in 2011. Moreover, cottage industries have been identified as one of the key tools to promote self-employment and small enterprise backyard economy. Within the manufacturing sector SMEs account for 96% of the industrial units, 36% of the industrial employment and 20% of the value addition [28].In these backdrops, within the commercial client segment, small business lending is gradually becoming asa major target for many banks [1]. Though lending is a most important business function for commercial banks, for various reasons, banks do not expand its loan portfolio on MSMEs, principal of which are poor credit worthiness (credit risk), lack of collateral security and the constraint imposed on banks’ capital by regulations [21]. Poor credit worthiness leads to higher credit risk causing increased non-performance of loan which ultimately results in loan delinquency and loan impairment. For most of the bank failure, the large numbers of non-performing loans have been the main cause [31]. According to Financial System Stability Review 2012 of the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, the asset quality of commercial banks deteriorated in 2012 by the increased non-performing loan (NPL), volumes and NPL ratios. The NPLs increased from Rs. 106 billion in end September 2011 and Rs. 99 billion in end 2011 to Rs. 121 billion by end September 2012. Further, gross NPLs as a percentage of total loans and advances (NPL ratio) indicated a marginal increase from 3.8% in end 2011 to 4% by end September 2012. The increase in NPLs since September 2011 was mainly due to the increase in NPLs in three sectors. These sectors are tourism (23%), trading (19%) and consumption related pawning advances (38%). Further, tourism (12%), construction and manufacturing (7%) and trading (4%) sectors also recorded high NPL ratios. Banks should continue to operate with proper credit risk assessment and monitoring and recognizing any potential risks in advance to mitigate any adverse impact due to build-up of credit risks [8]. According to the Sri Lanka Banking sector special report of Fitch rating in 2012, over half of Sri Lankan bank loans comprise lending to corporates which includes SMEs and lending to SMEs is likely to increase in search of higher net interest margins to counter the effects of increasing competition and rising deposit costs. Fitch also expects the SMEs to be a growth segment in the current economic environment, although this could present challenges in the form of a further upgrade of risk management processes and systems.Lending entities are therefore much concerned on the prediction of credit risk associated with the borrowing firms in order to avoid credit delinquency and better plan and perform their lending function. There are seminal accounting, finance and econometric researches that focused on prediction of financial distress of organizations. Most of such default prediction models have traditionally employed accounting and finance information available in the financial statements of listed corporates. These modalities can not be equally applied in the contexts of SMEs as there are practical constrains in gathering accounting and financial data and information required to the traditional corporate risk prediction models. It is widely agreed that the SMEs inherit their own features and characteristic which create different signaling of their potential success and failures. The accuracy of prediction of distress/insolvency of SME borrowers is said to be improved with the inclusion of relevant non-accounting and qualitative information into the model. Altman.E.I at el, 2008 confirms that using qualitative variables as predictors of company failure significantly improves the prediction model’s accuracy for SMEs as what has been found in other studies for large corporations (e.g. [14]). However, there is no conclusive list of such non-accounting variables nor there exists an agreed framework of classification thereof. Altman.E.I at el, 2008 has identified ‘event data as a potentially powerful addition to annual financial data available on SMEs. Occurrence of certain events (e.g company default on credit agreements) can be thus considered as proxies for non-accounting variables. Non accounting variables that can be used as credit risk predictor can be broadly classified into Borrower’ Driven Factors and Environment Driven Factors. Though there are literatures being progressively added on Borrower’ Driven Factors (e.g. event data introduced by Altman. E.I at el, [1]), the environment driven factors that are directly or indirectly impacting on the business performance also need to be studied in relation to the credit risk of SMEs. This research thus studies the impacts of accessibility to auxiliary amenities; a set of crucial environmental factors in which SMEs depend, in relation to SMEs’ behaviors on credit repayment.
2. Research Problem
- Increasing trend of MSME lending and recent deterioration in assets quality of commercial banks by an increase in Non-Performance Loan, Commercial Banks need to pay paramount attention on credit risk management, especially in the contexts of MSMEs. Prudent management of the risk on SME lending requires prediction of financial distress of borrowers from SMEs which in turn requires published financial statements under applicable accounting standards which are difficult to be obtained in the contexts of the MSMEs in Sri Lanka. Developing risk prediction models for SMEs therefore necessarily need to incorporatenon- accounting and qualitative information for practical and effective assessment of MSME credit risk.It is common that most of the MSMEs are highly depended on local resources and services in the course of their businesses. The performance of MSMEs in the island is not even and appears to scale depending on inter alia the mixture of favorable and unfavorable situations they encounter on access to various local resources and services fundamental for their business. It can therefore be presumed that when an MSME is located in an environment in which such resources and services are accessible at least ‘cost’, it may be in an advantageous position in generating income thereby impacting on the ability to repay the loan. Do MSMEs differ in credit repayment pattern depending on their accessibility to auxiliary amenities? Is ‘accessibility to auxiliary amenities’ a useful predictor of MSMEs credit risk?
3. Research Objective
- The main objective of this paper is to investigate the relationship between the SMEs’ accessibility to auxiliary amenities and their tendency on credit repayment or default. That is, to examine whether the information about accessibility to auxiliary amenities can be used to predict the credit risk for MSMEs. Information about accessibility to auxiliary amenities as described previously can be treated as “environmental factors” under non accounting information used to predict credit default and this study thus seeks to search for the possibility of inclusion of information about accessibility to auxiliary amenities as non-accounting information under default prediction of MSMEs in Sri Lanka.
4. Review of Literature
- There is no globally accepted definition for SMEs. Different institutions and countries tend to define the SME based on different parameters related to objectives, purpose and characteristics of their jurisdiction. Number of employees, capital employed annual turnover and nature and characteristics and the business are some of the most commonly used parameters to distinguish SMEs from large corporate and other establishments. As Gamage, [13] recognized, there are different terms used in different documents to identify this sector. In Sri Lanka SME is defined differently by different institutions. Department of Small Industry (DSI) defines SMEs as enterprise with fewer than 50 people and capital investment less than Rs.5 million. [26]. ForSri Lanka Export Development Board (SLEDB) it is an enterprise of less than Rs8 million investment excluding land and buildings and less than Rs. 50 million annual export turnover [16]. Industrial Development Board (IDP) defines a small industry as an establishment whose capital investment in plant and machinery does not exceed Rs.4 million and the total number of regular employees does not exceed 50 persons [9]. According to the recent guidelines issued by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL), SMEs are defined as enterprises that have an annual turnover less than Rs 600 million and its borrowings below Rs 200 million [30].Banks are realizing that small and medium sized companies are a distinct kind of client with specific needs and peculiarities that require risk management tools and methodologies specifically developed for them (Altman and Sabato [2]. It is now commonly believed that small and medium sized firms differently signal the existence of its financial distress and thus requires tailored model to predict the credit risk and potential distress. SME failure ratesare very difficult to obtain as such organizations are not very often listed as large corporate firms. However, in the past few years, considerable numbers of researches have been conducted to determine the rates and causation of such failures. Some of the seminal works in this respect include that of Phillips and Kirchhoff [25], Watson and Everett [29], Everett and Watson [11], Headd [15].The prevalence of literature on credit risk modeling for large, listed companies is extensive. In 1967 William Beaver performed a distress prediction test with application of t-test by evaluating the predictability of certain accounting ratios within similar pair- matched sample (Beaver, W., [4]. The approaches of seminal works in this field command, as Altman. E.I at el, [1] captured, between two approaches; one the z-score model which use historical accounting data to predict insolvency (e.g. 3) and the other models constructed based on securities market information [20]. Literature on the credit risk of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) is relatively limited as compared to the magnitude of literature existing on credit risk modeling for large publicly-listed corporates for which researchers could use information on publicly and periodically released financial statements. This owes mainly to the fact that these smaller, unlisted firms do not publicly release accounts, nor do they have stock prices, making modeling of the probability of default impossible unless access to data from sources such as credit registers can be accessed. (Martina Lawless and Fergal McCann, 2012).The issue of SME credit risk is however of particular interest to policy makers, given both their importance on banks’ balance sheets and their contribution to real economic activity. This is in spite of the finding that in times of recession or crisis, SMEs are particularly vulnerable as their limited diversification and dependence on short-term credit give them much less of a buffer against demand falls than are available to larger firms [22].Altman and Sabato [2] is of the view that credit risk models developed for large firms fall a short in predicting SME’sloan default. However, a small number of financial ratios tailored to SME specificities produce relatively better results. Papers such as Fidrmuc and Hainz [12], Behr, Guttler and Plattner [4], Dyrberg-Rommer [10] and McCann and McIndoe-Calder [19] are among a small group of researches to model SME credit risk. These papers use financial parameters in similar spirit to those used in Altman’s [3] seminal Z-score model for corporate defaults prediction. These models generally find that indebtedness, liquidity, profitability and sector-specific effects are important borrower-level determinants of SME default. In the contexts of SMEs’ credit risk analysis, it is not always feasible to depend only on accounting and financial data in financial statements which are not published as listed corporate companies. This thus arises a need of other non-financial information to supplement the process of default prediction.Altman.E.I at el, [1] confirms that using qualitative variables as predictors of company failure significantly improves the prediction model’s accuracy for SMEs what has been found in other studies for large corporations (e.g. Grunet et al. [14]) and further claims that this result is even more significant for SMEs on the ground that a large part of financial information of SMEs is oftentimes quite limited. Moreover, certain qualitative information can be systematically obtained and regularly updated enabling the financial institutions to take timely lending decisions and effective credit management. Altman.E.I at el, [1] claims that for the first time, they are able to explore the value added by qualitative information specifically for SMEs and found that this information, when available, is likely to significantly improve the prediction accuracy of the model by up to 13%. Yet, there exists only few studies that have modeled loan impairment for SMEs focused on the role of non-financialvariables that may signal SME’s credit risk or creditworthiness. Yet there are researches that proved that certain crucial non-financial variables can also be used in the contexts of SMEs to predict the nature of performance of or ability to repay loans extended. As small businesses typically do not have detailed public financial statements, lenders need necessarily to look for such other non-financial information to determine a borrower’s creditworthiness and to monitor existing loans. As Altman.E.I at el, [1] claims that the occurrence of ‘event’ data are potentially powerful addition to annual financial data available on SMEs in prediction of default risk. Such event data includes the evidence of company default on credit agreements and/or trade credit payments or whether the firm is late to file its financial statements etc. They established that risk prediction model can supplement them to adjust risk scores more frequently than is possible with just annual accounting data. Hudson [17] applied qualitative information about the age, industrial, and regional structure of liquidated companies using a sample of 1,830 liquidated companies between 1978 and 1981 in the UK and found that young companies form the majority of the liquidated companies and also found that a company needs at least around 9 years to be regarded as established (i.e. lower the default risk of a start-up) and that a newly formed company is most likely to have a “honeymoon period” of around 2 years before being in real risk. Berger, Klapper, and Udell [6] argue that small banks have a comparative advantage over large banks in making “relationship” loans, that is, loans that use “soft” information. Soft information is more qualitative and subjective than “hard” information and may be relatively difficult to communicate. Among the types of local information already mentioned, information regarding the character of the business owner, a key element in many small business lending decisions, seems particularly open to interpretation. In theory, both large local banks and small local banks can obtain character information rather easily, for example, through repeated contacts between the loan officer and the borrower in either informal social settings or face-to-face business meetings. However, loan officers at small banks may be able to use that information more easily than those at large banks, because they are likely to be able to convey their impressions through fewer layers of management. Historically, much of that information was most efficiently gathered locally, and it might include knowledge of the local economy and community, knowledge of the borrower’s industry (since some industries are concentrated locally or regionally), knowledge of the borrower’s particular firm, and knowledge of the “character” and skills of the small business owner or owners. Brevoort and Hannan [7] find direct empirical evidence that lender and borrower location do matter in small business lending, even within local areas. Using data for local banks and local businesses, these authors find that banks lend more to nearby borrowers than to distant borrowers, other factors held equal.Pandy and Muralidharan [24] found that the percentage of total income derived from sources other than crop production, the amount of loan, the purpose of loan, per capita consumption expenditure, and the ratio of cash expenditure to total expenditure were the major characteristics that classified borrowers into defaulter and non-defaulters. According to Oni O.A et al., [23] found that ‘flock size’, ‘age’ and ‘educational level and Income’ of the farmers significantly influence the loan repayment at alpha value of 0.10, 0.01 and 0.05 respectively. At the same time, sex, marital status, age, educational level, town were not significant in loan repayment [27].
5. Design and Methodology
- The dependent variable of this this research is SME Credit Risk and the independent variable is Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities (AAA). SME credit risk is here defined into three discrete categories which are as follows.
 Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities was analyzed by five discrete parameters of Rural/Urban Characteristics, Distance from the lender, Accessibility to market, Accessibility to Communication and Business Linkages and Accessibility to Public Institutions and Utilities. All these parameters of Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities are driven by external environment but significantly affecting MSMEs existence, performance and growth. Chi-Square Test was performed to examine the relationship between these discrete variables of the research. Data was collected from randomly selected 62 MSME borrowers from Trincomalee District of Sri Lanka. The sample of 62 MSMEs constituted to 10% of total MSME borrowers from the Banks sampled and the MSME samples were drawn proportional to the size of each loan category of Type-01, Type-02 and Type-03 above defined, in the banks under study during the period of 10 years from the year 2000.
Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities was analyzed by five discrete parameters of Rural/Urban Characteristics, Distance from the lender, Accessibility to market, Accessibility to Communication and Business Linkages and Accessibility to Public Institutions and Utilities. All these parameters of Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities are driven by external environment but significantly affecting MSMEs existence, performance and growth. Chi-Square Test was performed to examine the relationship between these discrete variables of the research. Data was collected from randomly selected 62 MSME borrowers from Trincomalee District of Sri Lanka. The sample of 62 MSMEs constituted to 10% of total MSME borrowers from the Banks sampled and the MSME samples were drawn proportional to the size of each loan category of Type-01, Type-02 and Type-03 above defined, in the banks under study during the period of 10 years from the year 2000. 6. Discussion of Findings
- Rural/Urban CharacteristicsThe fact whether a MSME is situated in urban or rural area determines their tendency on loaner payment. For this analysis, the nature of business location was categorized into rural and urban while the credit risk was analyzed into three discrete categories above mentioned (that is, Type-01, Type-02 and Type-03). The following Chi-Square Tests results were obtained.
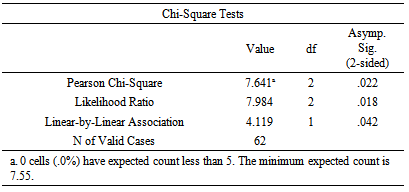 The above table provides that Rural/Urban Characteristics significantly correlates with nature of loan repaymentat Pearson Chi-Square of 7.641 and P-value of 0.022 which is below the Alpha value of 0.05. The cross tabulation for the above variables are shown in the following table.
The above table provides that Rural/Urban Characteristics significantly correlates with nature of loan repaymentat Pearson Chi-Square of 7.641 and P-value of 0.022 which is below the Alpha value of 0.05. The cross tabulation for the above variables are shown in the following table.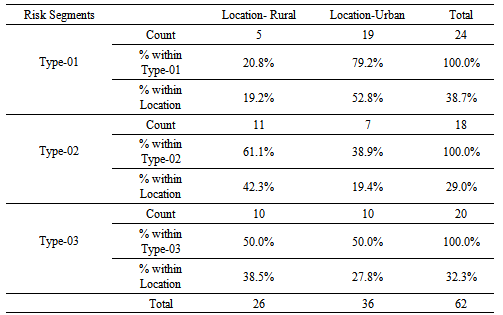 It is found that 52.8% of the urban MSME customers fall within Type 01- Risk Segment where 19.4% and 27.8% are under Type-02 and Type-03 segments respectively. At the same time 80.8% of MSME customers of their business at rural localities fall within the Type 02 and Type 03 categories. The findings thus indicate that Type -02 and Type-03 segments of risk are mostly likely to occur with those MSME customers from rural areas whereas majority of urban customers tend to fall under Type -01 segment which is the risk free segment. Distance from the Lender
It is found that 52.8% of the urban MSME customers fall within Type 01- Risk Segment where 19.4% and 27.8% are under Type-02 and Type-03 segments respectively. At the same time 80.8% of MSME customers of their business at rural localities fall within the Type 02 and Type 03 categories. The findings thus indicate that Type -02 and Type-03 segments of risk are mostly likely to occur with those MSME customers from rural areas whereas majority of urban customers tend to fall under Type -01 segment which is the risk free segment. Distance from the Lender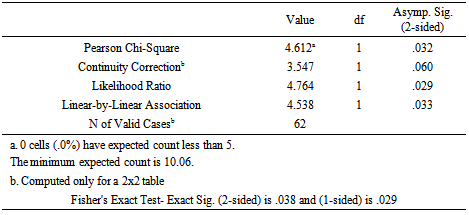 Distance of MSME customers from their primary business location to the bank (bank from which they borrowed) significantly correlates with the risk of repayment of loans when customers were analyzed into two distance segments of 0-50 Km and more than 51 Km and the default risk was observed into two categories of ‘Type-01 andType-02&03 combined. Accordingly, following Chi-Square Tests results were obtained. The above Chi-Square Test table indicates that correlation is significant with Pearson Chi-Square of 4.612 and P-value of 0.032 which is below the Alpha value of 0.05. The observed frequencies plotted in cross tabulation for segments defined for distance parameter and the risk types are shown in the following table.
Distance of MSME customers from their primary business location to the bank (bank from which they borrowed) significantly correlates with the risk of repayment of loans when customers were analyzed into two distance segments of 0-50 Km and more than 51 Km and the default risk was observed into two categories of ‘Type-01 andType-02&03 combined. Accordingly, following Chi-Square Tests results were obtained. The above Chi-Square Test table indicates that correlation is significant with Pearson Chi-Square of 4.612 and P-value of 0.032 which is below the Alpha value of 0.05. The observed frequencies plotted in cross tabulation for segments defined for distance parameter and the risk types are shown in the following table. 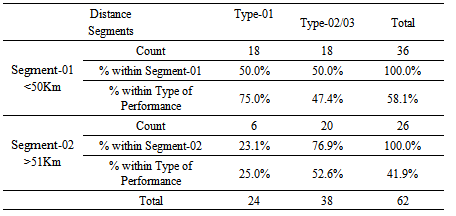 It reveals that 76.9% MSME customers with their business location more than 50 Km away from the lender fall within either non-performance (Type-02) or impaired loans (Type-03) whereas 75% of the customers who settled their loan on time (Type -01) tend to have their primary business location within 50 Km from the lending bank. This indicates that the more the MSME customers are far from the Bank, the more they tend to be non-performing or of written off loan and vice versa.Accessibility to Public Market
It reveals that 76.9% MSME customers with their business location more than 50 Km away from the lender fall within either non-performance (Type-02) or impaired loans (Type-03) whereas 75% of the customers who settled their loan on time (Type -01) tend to have their primary business location within 50 Km from the lending bank. This indicates that the more the MSME customers are far from the Bank, the more they tend to be non-performing or of written off loan and vice versa.Accessibility to Public Market 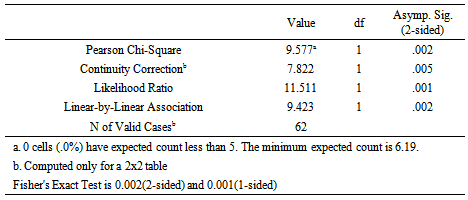 The accessibility of the customers to the nearest public market significantly correlates with nature of repayment of MSME loan when the accessibility to nearest public market falls within two relative score categories of “Higher” and “Average or Low” and the default risk was again analyzed into two categories of ‘Timely settlement’ (Type-01) and ‘Non-performance or impaired loans’ (Type-02/03 combined). Accordingly, following Chi-Square Tests results were obtained. The above Chi-Square Test table reveals that correlation between accessibility to the nearest public market and the nature of repayment of loan is significant at Pearson Chi-Square of 9.577 and P-value of 0.002 which is far below the Alpha value of 0.05. Cross tabulation on the above parameters is presented in the table below.
The accessibility of the customers to the nearest public market significantly correlates with nature of repayment of MSME loan when the accessibility to nearest public market falls within two relative score categories of “Higher” and “Average or Low” and the default risk was again analyzed into two categories of ‘Timely settlement’ (Type-01) and ‘Non-performance or impaired loans’ (Type-02/03 combined). Accordingly, following Chi-Square Tests results were obtained. The above Chi-Square Test table reveals that correlation between accessibility to the nearest public market and the nature of repayment of loan is significant at Pearson Chi-Square of 9.577 and P-value of 0.002 which is far below the Alpha value of 0.05. Cross tabulation on the above parameters is presented in the table below. 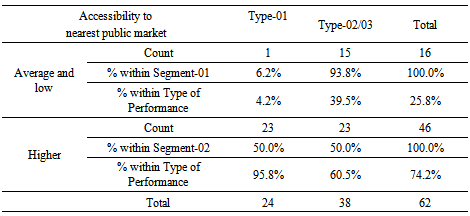 It is thus revealed that 93.8% MSME customers having an ‘average and low’ level of accessibility to public market fall within either non-performance or written off loan categories (Type -02/03 combined) whereas95.8% of the customers who settled their loan on time (Type -01) tend to have their business location in a place with higher accessibility to a public market. Accessibility to Communication and Business LinkagesAccessibility to communication facilities and Business Linkages at the location of the business is found to significantly correlate with nature of repayment of MSME loan when the independent variable was observed within two relative score categories of “Higher” and “Average or Low” and the nature of default risk, dependent variable was analyzed into two categories of ‘Timely settlement’ (Type-01) and ‘Non-performance or impaired loans (Type-02/03 combined)’. Accordingly, following Chi-Square Tests results were obtained.
It is thus revealed that 93.8% MSME customers having an ‘average and low’ level of accessibility to public market fall within either non-performance or written off loan categories (Type -02/03 combined) whereas95.8% of the customers who settled their loan on time (Type -01) tend to have their business location in a place with higher accessibility to a public market. Accessibility to Communication and Business LinkagesAccessibility to communication facilities and Business Linkages at the location of the business is found to significantly correlate with nature of repayment of MSME loan when the independent variable was observed within two relative score categories of “Higher” and “Average or Low” and the nature of default risk, dependent variable was analyzed into two categories of ‘Timely settlement’ (Type-01) and ‘Non-performance or impaired loans (Type-02/03 combined)’. Accordingly, following Chi-Square Tests results were obtained. 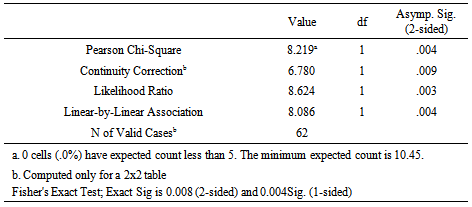 The above Chi-Square Test table reveals that correlation between Accessibility to communication facilities and Business Linkages at the location of the business and the nature of performance of loan is significant at Pearson Chi-Square of 8.219 and P-value of 0.004 which is below the Alpha value of 0.05. Cross tabulation on the above parameters is presented in the table below.
The above Chi-Square Test table reveals that correlation between Accessibility to communication facilities and Business Linkages at the location of the business and the nature of performance of loan is significant at Pearson Chi-Square of 8.219 and P-value of 0.004 which is below the Alpha value of 0.05. Cross tabulation on the above parameters is presented in the table below. 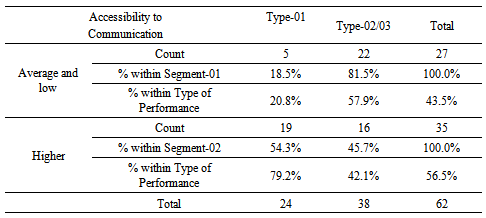 Cross tabulation indicated that 81.5% MSME customers having an ‘average or low’ level of accessibility to communication facilities and Business Linkages at the location of the business fall within either non-performance or impaired loans categories (Type -02/03 combined) whereas 79.2% of the customers who settled their loan on time (Type -01) tend to have their business location in a place with higher accessibility to communication facilities and business networks. Accessibility to public institutions and utilities Accessibility to public institutions and utilities at the location of the business is also found to significantly correlate with nature of repayment of MSME loan when it falls within two relative score categories of “Higher” and “Average or Low” and the nature of loan repayment/default risk was analyzed into two categories of ‘Timely settlement’ (Type-01) and ‘Non-performance or impaired loans’ (Type-02/03 combined). Accordingly, following Chi-Square Tests results were obtained.
Cross tabulation indicated that 81.5% MSME customers having an ‘average or low’ level of accessibility to communication facilities and Business Linkages at the location of the business fall within either non-performance or impaired loans categories (Type -02/03 combined) whereas 79.2% of the customers who settled their loan on time (Type -01) tend to have their business location in a place with higher accessibility to communication facilities and business networks. Accessibility to public institutions and utilities Accessibility to public institutions and utilities at the location of the business is also found to significantly correlate with nature of repayment of MSME loan when it falls within two relative score categories of “Higher” and “Average or Low” and the nature of loan repayment/default risk was analyzed into two categories of ‘Timely settlement’ (Type-01) and ‘Non-performance or impaired loans’ (Type-02/03 combined). Accordingly, following Chi-Square Tests results were obtained. 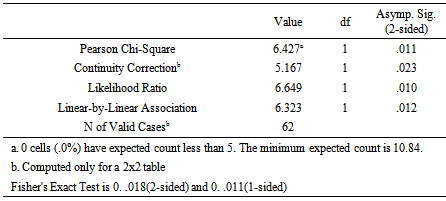 Chi-Square Test reveals that correlation between Accessibility to public institutions and utilities at the location of the business and the nature of performance of loan is significant at Pearson Chi-Square of 6.427 and P-value of 0.011 which is below the Alpha value of 0.05. Cross tabulation on these variables is provided below.
Chi-Square Test reveals that correlation between Accessibility to public institutions and utilities at the location of the business and the nature of performance of loan is significant at Pearson Chi-Square of 6.427 and P-value of 0.011 which is below the Alpha value of 0.05. Cross tabulation on these variables is provided below.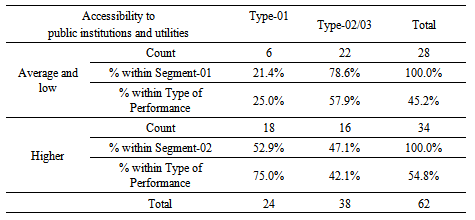 Cross tabulation indicated that 78.6% SME customers having an ‘average or low’ level of accessibility to public institutions and utilities at the location of the business tend to fall within either non-performance or impaired loan categories (Type -02/03 combined) whereas 75% of the customers who settled their loan on time (Type -01) are found to have their business location in a place with higher accessibility to public institutions and utilities.
Cross tabulation indicated that 78.6% SME customers having an ‘average or low’ level of accessibility to public institutions and utilities at the location of the business tend to fall within either non-performance or impaired loan categories (Type -02/03 combined) whereas 75% of the customers who settled their loan on time (Type -01) are found to have their business location in a place with higher accessibility to public institutions and utilities.7. Conclusions
- The relationship identified in this study contributes to MSMEs credit risk or loan default prediction where the nature of MSMEs often creates obstacles in giving proper financial statement information for estimating credit risk and alternative models being employed require incorporation of non-accounting information for effectively predicting loan default of SMEs.This work has proved that Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities which are some important supporting factors driven by the external environment which is mostly beyond the control of individual organizations are also significantly correlating with nature of repayment of commercial loan extended to MSMEs. Rural/Urban Characteristics, Distance from the lender, Accessibility to Market, Accessibility to Communication and Business Linkages and Accessibility to Public Institutions and Utilities are the proxies employed for Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities and are found to have statistically significant relationship with the nature of repayment of commercial loan extended to MSMEs. Accessibility to Auxiliary Amenities therefore can be treated as significant non-accounting information signaling MSME credit risk. This finding derives an overall evidence for the fact that the environmental factors will also assist to predict MSME credit risk.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML