-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2013; 2(8): 472-477
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20130208.11
The Mediating Impact of Ethical Orientation on the Religiosity and Undergraduate Auditing Students’ Ethical Sensitivity Relationship
Ahmed Mohamed Alteer1, Sofri Bin Yahya2, Md Harashid Haron3
1Faculty of Economics and Political Sciences, Misurata University
2Graduate School of Business, Universiti Sains Malaysia
3School of Management, Universiti Sains Malaysia
Correspondence to: Ahmed Mohamed Alteer, Faculty of Economics and Political Sciences, Misurata University.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The purpose of this paper is come up with theoretical model through understanding the causes and motives behind the auditors' sensitive to ethical dilemma through Auditing Students. This study considers the possibility of auditing students’ ethical sensitivity being affected by two individual factors, namely ethical orientation and religiosity. The finding of this study that there are several ethical theories a models provide a significant understanding of ethical issues and supported that ethical orientation and religiosity may affect ethical sensitivity decision among student. The suggestion model proposes that ethical sensitivity is influenced by religiosity via ethical orientation. Nonetheless, the influence of religiosity on ethical sensitivity is expected to be via ethical orientation.
Keywords: Auditing, Students, Ethical sensitivity, Religiosity and ethical orientation
Cite this paper: Ahmed Mohamed Alteer, Sofri Bin Yahya, Md Harashid Haron, The Mediating Impact of Ethical Orientation on the Religiosity and Undergraduate Auditing Students’ Ethical Sensitivity Relationship, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 2 No. 8, 2013, pp. 472-477. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20130208.11.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Libya, an Arabic country, shares a similar culture, language, religion and other values with surrounding countries in this region. In Libya, the language is Arabic, and the main religion is Islam (Abubaker, 2007). In the Libyan culture, Islam is considered a comprehensive religion covering social and political aspects in life, as well as piety of the soul and the moral principles of an individual’s behaviour (Twati, 2006). So far as the economy of Libya is concerned, Libyan auditors are working in a developing economy context, and the Libyan people have a strong relationship between individuals each others (Agnaia, 1996). It has noted that the educational accounting curriculum in the local environment did not meet with the economic and social developmental needs in Libya context (Al-kilani, 2000). This result is confirmed by a previous study that an accounting-related education currently falls short of the rehabilitation of graduates who are able to do accounting work properly (Dalli, 2003). As well, the Aldrogi (2004) study in relation to the quality of performance of public accountants in Libya, indicated that the audit services were not of a high degree of quality for validating financial statements. In addition, Ashour’s (2004) study of accounting and auditing profession in the Libyan situation, identified a clear shortcoming of the practicing of ethics in the accounting profession in Libya.In addition, the target of Al-Shaikhi’s (2006) study identified the causes of the low level of trust of auditors in Libya. Respondents in this study confirmed that auditors in the Libyan environment had accepted their client without being sure of his/her integrity, or to accept some clients without being sure of its impact on their professional conduct, and they confirmed the absence of an adequate awareness to external ethics of their professions, as well as shortcomings in the laws governing this profession. Furthermore, accounting and auditing are very important not only for the market systems, but also for other economic systems (American Accounting Association, 1978). The importance of accounting is related to be an ethical accounting. Ethics is currently widely recognized by the public, regulators as well as the professionals. The audit decision exercise by professional has been recognized as an essential part of preparing auditing financial reports. Accordingly, the basic assumptions underlying the audit function, and then to rule that requires professional accountants to act ethically, especially with regard to independence (Jones & Ponemon, 1993; Thorne, 1998).Auditing is a public service that intends to provide investors verification of management and economic allegations. Thus, auditors should have moral obligation with public and investors to conduct an audit with professional independence and objectivity. However, the management hires and pays fees to the Auditor. Therefore, the auditor has a contractual obligation to conduct audit and provide his client with the audit opinion about the financial statements. Consequently, the auditor has complex responsibilities with full conflicting interest, which stem from the Auditor obligation to management's as well as to public (Chan & Leung, 2006; Shaub, 1989). Thus, the nature of the auditing task is characterised by a complex relationships that govern the ethical framework in audit.Furthermore, Various individual variables including demographic characteristics, personality traits, beliefs, values and attitudinal measures have been proposed in the literature of business ethics to have an impact upon ethical decision making process (Mosbah, 2010). However, the potential influence of individual factors on ethical sensitivity has been recognized in both the psychology and organizational behavior literature (Hunt & Vitell, 1986; Roy, 2009; Street, Douglas, Geiger, & Martinko, 2001). Individual variables such as religiosity and ethical orientation play a central role in ethical sensitivity because the evidences show that individuals have evaluate their decision according to theses variables in order to religion provides rules and obligations to individuals, as well as moral ideology (Ferrell & Gresham, 1985). Additionally, many studies that examine ethical decision-making have investigated ethical judgement (e.g., Abdomohammadi & Baker, 2005; Au & Fan, Ying Han 2009; Ho & Lin, 2008; Fritzsche & Oz, 2007; Karacaer, Gohar, Aygun and Sayin, 2009; Shafer, Morris & Ketchand 2001; Steenhaut, Kenhove, 2006). However, study ethical judgement is important but people can not judge ethical unless be sensitive to moral dilemma. Yet, few studies have examined religiosity and ethical orientation together that are associated with auditors' ethical sensitivity. Therefore, this study is going to contribute and fill up the gap in the ethical decision literature by introducing the linking between religiosity and ethical sensitivity via ethical orientation.
2. Literature Review
- Many sources have provided theoretical foundations for research into the ethical behaviour area. Some researchers have examined frameworks to understand the determinants of ethical decision making using psychology theory or models. In the business ethics literature the majority of them have been focusing on the formulation and testing of ethical decision-making models (Dubinsky & Loken, 1989; Ferrell & Gresham, 1985; Ferrell et al., 1989; Hunt & Vitell, 1986; Rest, 1986; McShane & Glinow, 2007;street et al., 2001; Trevino, 1986). However, these models are not normative models that describe what people should do or whether their current moral behaviour is reasonable. Nevertheless, they are descriptive models which describe how people act or think. Since the results of these models can be either ethical or unethical behaviour, using these categories as ethical decision making models might be considered wrong. Nevertheless, the term is being used here to indicate that these are models of the decision making process in which one engages when faced with an ethical dilemma (McMahon, 2002). Ethical decision research in auditing area is a part of a larger area of psychological research called behaviour decision section which is concerned about individuals and small group judgments and decision making to understand how judgments are made, how they can be improved and what are the reasons behind those judgements (Trotman, 1998). Several researchers have examined frameworks to understand the determinants of ethical decision making using psychology theory or models such Ferrell et al. (1989), Hunt and Vitell (1986) and Rest (1986).
2.1. Ethical Sensitivity
- Ethical sensitivity is “the empathic interpretation of a situation in determining who is involved, what actions to take, and what possible reactions and outcomes might ensue” (Endicott, 2001, p7). The Ethics Education Framework (EEF) presented by International Accounting Education Standards Board (2006) describe individual ethical sensitivity as the ability to recognize an ethical threat or issue when it occurs and being aware of alternative courses of action which can lead to an ethical solution. It also includes an understanding of how each alternative course of action affects the parties concerned. Numerous independent variables have been examined to determine their influence on ethical sensitivity. These variables include personal characteristics such as (i.e. ethical orientation, religiosity).
2.2. Religiosity
- Religiosity is “the extent to which an individual’s committed to the religion he or she professes and its teachings, such as the individual attitudes and behaviours reflect this commitment” (Johnson, Jang, Larson & Li, 1995, p. 25). Hence the impact of religion on an individual's beliefs and behaviour depends on the individual level in religion and one important places on religion itself (Sood & Nasu, 1995). Given the instrumental role of religion and religiosity in business ethics were the subject of considerable attention in an effort to develop an understanding of human behaviour and attitudes. Previous studies and try using religion to explain human behaviour to that of key personal characteristics. For example, according to Magill (1992) personal religiosity can be used to rationalize nature of ethical behaviour. Also, Giorgi and Marsh (1990) mention that religion and the level of religiosity positively influenced an individual’s ethical stance or position.
2.3. Ethical Orientation
- Forsyth (1980) defines moral idealism as “the degree to which an individual focuses upon the inherent rightness or wrongness of actions regardless of the results of those actions”. It portrays an ideology based on altruism and optimism and embraces the welfare of others (Singhapakdi et al., 1999). In making ethical decisions, moral idealists use idealistic rather than practical criteria; individuals who have high idealism believe that desirable outcomes can be acquired, and harming others is universally and always bad and should be avoided (Swaidan, Rawwas, & Al-Khatib, 2004). In addition most ethical sensitivity studies have investigated an ethical orientation association. However, the results of these studies are inconsistent, and it is unclear whether an ethical orientation influences ethical sensitivity or otherwise. For example, Chan and Leung, (2006), and Shaub, (1989) found no statistical relationship between an ethical sensitivity and an ethical orientation. In contrast, Shaub et al., (1993); Cohen et al. (1995) found an association between an ethical orientation and an ethical sensitivity.
3. Theoretical Framework
- Ferrell and Gresham (1985) state that “It is impossible to develop a framework of ethical decision making without evaluating normative ethical standards derived from moral philosophy”. Hunt-Vitell developed a general ethical theory that provides a formal model to make ethical decisions explicit. They proposed a model to explain the decision-making process in situations involving an ethical problem. Their model follows Rest’s (1986) four components model for ethical decision making. the model posits that before starting an ethical decision, individual must perceive some ethical issue in an ethical problem situation and speculate about the various possible alternatives and consequences. Moreover, Hunt and Vitell (1986) included moral philosophies, deontology and teleology, as the core of their model of ethical decision making. Social psychologists have also considered moral philosophies to be a significant variable affecting an individual’s ethical decisions (Singhapakdi, Salyachivin, Virakul, & Veerayangkur, 2000). At this point, the individual evaluates the outcomes of each behavioural alternative via a deontological and/or a teleological philosophical lens. Furthermore, Forsyth (1980; 1992) claims that the concepts explaining moral philosophies are relativism and idealism. This moral philosophy model suggests that individuals who demonstrate different perspectives in relation to relativism and idealism diverged when making moral judgments (see Forsyth 1978; 1981; 1984; 1985). Forsyth’s (1980) ethical ideology theory was derived from teleological and deontological theories. He suggests that an individual varies his/her moral beliefs and attitudes, that is either he/she makes judgments based on universal moral rules or rejects universal moral principles in favour of some relativistic position. Thus Forsyth classified an individual’s ethical ideologies along two dimensions: either idealism or relativism. Idealism is concerned with securing the welfare of others and avoiding negative consequences which may harm others (Forsyth 1992) whereas relativism feels that moral actions depend upon given situations. Thus an idealist person makes an ethical judgment based on universal moral rules and the principle of no harm to others, whereas a relativist person makes an ethical judgment based on personal feelings and situations (Forsyth 1980). Moreover, Hunt and Vitell (1986, 1993) claimed that religiousness could affect an individual’s perception of an ethical situation and other components of ethical decisions. This model discovered that people who practiced their religion tended to consider themselves more ethically minded than those who did not. Hence, the strength of religiousness might lead to differences in one’s ethical decision-making process. However, according to Baron and Kenny (1986), a mediation effect exists when a previously significant relationship between two variables is no longer significant when all other paths are controlled. Based on Baron and Kenny’s (1986) approach, three conditions are required to establish the mediation association. Firstly, the independent variable must be related to the mediator; secondly, the independent variable must be related to the dependent variable; and thirdly, the mediator must be related to the dependent variable. Taking these three conditions into account, and according to the Hunt and Vitell (1986) theory, this study expects that ethical orientation will mediate the relationship between the religiosity and ethical sensitivity. There is also an Islamic ethical behaviour overview which could used to explain individual ethical decision making behaviour. Islamic ethics model was presented by(Ajmi, 2007) which had mentioned that Islamic ethical behaviour approach was introduced by Asfhani in 1108 which explained that behaviour is effected by individual characteristics sach as religiosity and the model suggested that this factor impact the level of individual ability to evaluate moral act and to be more sensitive about moral issues (Hilmi, 2005). Consequently, the proposed theoretical framework of this study is as shown in following figure.
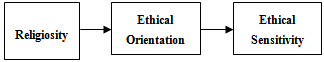 | Figure 1. Research Framework |
4. Religiosity, Ethical Orientation and Ethical Sensitivity Link
- Hunt and Vitell (1986, 1993) claimed that religiousness could affect an individual’s perception of an ethical situation and other components of ethical decisions. This model discovered that people who practiced their religion tend to consider themselves more ethically minded than those who did not. Hence the strength of religiousness might lead to differences in one’s ethical decision making process. Furthermore, Weaver and Agle (2002) affirm that individuals formed a religious belief based on the teachings of religion which will in turn shape their behaviour and attitudes. In the latest study on ethical students’ attitudes in US, Albaum and Peterson (2006) indicated that students who claimed to be highly religious tended to display more morality than others who were less religious. Singhapakdi, Marta,Rallapalli, and Rao (2000), using a sample of 453 marketers found that religiosity was a significant predictor of ethical problem recognition. Angelidis and Ibrahim (2004) in their sample of 473 Christian business students, found that high religiosity corresponded to greater concern about the ethical component of corporate social responsibility. On the other hand, some previous empirical studies presented non significant effect of religiosity on ethical behaviour such as Knotts, Lopez, and Mesak (2000). In Malaysia, Saat et al. (2009), using a sample of 378 respondents, revealed that the level of religiosity affect accounting students’ ethical sensitivity at the first stage of ethical decision making. Similar to Singhapakdi et al.’s (2000) view, Ibrahim et al. (2008) found that the ethical dimension of corporate social responsibility has affected the level of religiosity among managers and students.The role that religiosity plays in affecting ethical behaviour is well documented ( Allmon et al., 2000; Conroy & Emerson, 2004; Saat et al. 2009) . For example, the degree of religiosity is generally associated with higher ethical attitudes (Conroy & Emerson, 2004). Some researchers indicated that, higher religiosity people may be inclined to view unethical situations more negatively than less religious people (Albaum & Peterson, 2006; Singhapakdi et al., 2000; Woodbine & Yuningsih, 2004). Furthermore, Hunt and Vitell (1986) in their theory suggested that, individuals who are more religious will tend to be more perceptive of ethical problems than others who are lower religiousness. Forsyth (1980; 1992) argues that the key concepts which explain individuals’ moral philosophies are relativism and idealism. His ethical ideologies were derived from deontological and teleological moral theories and consist of a personal value system which describes an individual’s beliefs about ethical principles (Douglas & Schwartz 1999). He also supports the descriptive approach to ethics, by assuming that changing circumstances can alter one’s frame of reference and the ethicality of a given situation or judgment (hence justifying the use of relativism). Accordingly, this study expects that highly religious auditors will tend to aware the existence moral via ethical orientation. In particular, the following proposition were formulated: Ethical orientation will mediate the relationship between audit student religiosity and their ethical sensitivity
5. Conclusions
- Fortunate enough, there are several ethical theories that provide a significant understanding of ethical issues. The theories are underpinned by ethical principles that lead to the successful decisions and good decision. Actually, during the 1980s, researchers began to develop several ethical decision making models. In general thesis models were developed by experts in psychology based on disciplines such as organizational behaviour and marketing. Those studies had proposed the general ethical decision-making models (Rest, 1986; Trevino, 1986). Others, such as Ferrell and Gresham (1985); Hunt and Vitell (1986); Ferrell et al. (1989); Dubinsky and Loken (1989) focused their target on ethics of marketing areas. Jones (1991) added a new concept called moral intensity to supplementation models in accounting area researchers endeavoured to develop a model of ethical /unethical decision-making. However, no empirical research to date supports the superiority of one model over the others. For this reason, it is a better approach to identify the aggregate knowledge these models provide. On the whole among individuals who regarded religious interests as being will show a high level of the ethical sensitivity when they face a moral dilemma if ethical orientation is high. Otherwise high religiosity does not always mean high ethical behaviour (Rashid & Ibrahim, 2008), for example, while the misfit between a level of religiosity and ethical orientation is expecting to give the opposite effect or reduction the level of ethical sensitivity to moral dilemma. Based on the above, there is a possible effect of religiosity on ethical sensitivity via ethical orientation.
References
| [1] | Abdolmohammadi, M. J., & Baker, C. R. (2006). Accountants’ value preferences and moral reasoning. Journal of Business Ethics, 69(1), 11-25. |
| [2] | Abdualhadi, A. (1997). Abouhayan Al-Tawhidi :philosopher writers and Artist of philosophers cairo: House of Culture for publication. |
| [3] | Abubaker, A. (2007). Influence of core cultural values on the communication. behaviour of staff in libyan organisation. Retrieved 12/11/2010, from Newcastle University research at: http://research.ncl.ac.uk/ARECLS/vol4_documents/ABUBAKER.pdf. |
| [4] | Agnaia, A. A. (1996). Assessment of management training needs and selection for training: the case of Libyan companies. International Journal of Manpower, 17(3), 31-51. |
| [5] | Ajmi, A. Z. A. (2007 ). Pretext to Sharia Abu Qassem ibn Muhammad Al-Makarim Al-Isfahani. Cairo: Dar Asslam. |
| [6] | Albaum, G., & Peterson, R. A. (2006). Ethical attitudes of future business leaders. Business & Society, 45(3), 300-321. |
| [7] | Allmon, D. E., Page, D., & Rpberts, R. (2000). Determinants of perceptions of cheating: Ethical orientation, personality and demographics. Journal of Business Ethics, 23(4), 411-422. |
| [8] | Al-shaikhi, A.-M. t. R. (2006). Causes of The Low Level of Auditors Confidence by The IRS in Libya. MA, Garyounes University, Benghazi. |
| [9] | Angelidis, J., & Ibrahim, N. (2004). An exploratory study of the impact of degree of religiousness upon an individual's corporate social responsiveness orientation. Journal of Business Ethics, 51(2), 119-128. |
| [10] | Barnett, T., & Vaicys, C. (2000). The moderating effect of individuals' perceptions of ethical work climate on ethical judgments and behavioral intentions. Journal of Business Ethics, 27(4), 351-362. |
| [11] | Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator – mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of personality and social psychology, 51(6), 1173-1182. |
| [12] | Barrick, M. R., & Mount, M. K. (1993). Autonomy as a moderator of the relationships between the Big Five personality dimensions and job performance. Journal of applied Psychology, 78(1), 111-118. |
| [13] | Beaty, J. C., Cleveland, J. N., & Murphy, K. R. (2001). The relation between personality and contextual performance in" strong" versus" weak" situations. Human Performance, 14(2), 125-148. |
| [14] | Brass, D. J., Butterfield, K. D., & Skaggs, B. C. (1998). Relationships and unethical behavior: A social network perspective. Academy of Management Review, 14-31. |
| [15] | Chan, C. F. (2007). Predicting Organization Citizenship Behavior of Financial Institute Employees with Big Five Personality Factor and Organizational Values. |
| [16] | Chan, S. Y. S., & Leung, P. (2006). The effects of accounting students' ethical reasoning and personal factors on their ethical sensitivity. Managerial Auditing Journal, 21(4), 436-457. |
| [17] | Conroy, S. J., & Emerson, T. L. N. (2004). Business ethics and religion: religiosity as a predictor of ethical awareness among students. Journal of Business Ethics, 50(4), 383-396. |
| [18] | Dubinsky, A. J., & Loken, B. (1989). Analyzing ethical decision making in marketing. Journal of Business Research, 19(2), 83-107. |
| [19] | Endicott, L. (2001). Ethical Sensitivity Activity Booklet: University of Minnesota Design Team Authors. |
| [20] | Aldrogi, M. O. (2004). Useing the expectations gap to measure the quality of external audit services. MA, Academy of Graduate Studies, Tripoli. |
| [21] | Al-Kilani, A.-A. (2000). Accounting Education and its Relationship with Economic and Social Development in Libya. Journal of Economic Research, 1+2, 7-22. |
| [22] | Ashour, B. M. (2004). How extent accounting and auditing profession keep abreast in Libya to the requirements of economic restructuring. Paper presented at the Privatization in Libyan economy Conference, Benghazi. |
| [23] | Fan, Y. H. (2009 ). The Impact of Chinese Auditors’ Values on their Ethical Decision-making at http://www.researchgate.net/publication/45844253. from ResearchGate |
| [24] | Ferrell, O., Gresham, L. G., & Fraedrich, J. (1989). A synthesis of ethical decision models for marketing. Journal of Macromarketing, 9(2), 55-64. |
| [25] | Ferrell, O. C., & Gresham, L. G. (1985). A contingency framework for understanding ethical decision making in marketing. The Journal of Marketing, 49(3), 87-96. |
| [26] | Fritzsche, D., & Oz, E. (2007). Personal values’ influence on the ethical dimension of decision making. Journal of Business Ethics, 75(4), 335-343. |
| [27] | Gaa, J. C. (1992). Discussion of A Model of Auditors' Ethical Decision Processes. A Journal of Practice & Theory, 11, 60-66. |
| [28] | Giorgi, L., & Marsh, C. (1990). The Protestant work ethic as a cultural phenomenon. European Journal of Social Psychology, 20(6), 499-517. |
| [29] | Hilmi, M. (2005 ). Methods of research in Humanities between Muslim Scholars and western philosophers (1 ed.). Lebanon Dar Al-kotob Al-llmiyah. |
| [30] | Ho, Y. H., & Lin, C. Y. (2008). Cultural values and cognitive moral development of accounting ethics: A cross-cultural study. Social Behavior and Personality: an international journal, 36(7), 883-892. |
| [31] | Hunt, S. D., & Vasquez-Parraga, A. Z. (1993). Organizational consequences, marketing ethics, and salesforce supervision. Journal of Marketing Research, 78–90. |
| [32] | Hunt, S. D., & Vitell, S. (1986). A general theory of marketing ethics. Journal of macromarketing, 6(1), 5-16. |
| [33] | Ibrahim, N. A., Howard, D. P., & Angelidis, J. P. (2008). The relationship between religiousness and corporate social responsibility orientation: Are there differences between business managers and students? Journal of Business Ethics, 78(1), 165-174. |
| [34] | Jones, S. K., & Ponemon, L. A. (1993). A Comment on" A Multidimensional Analysis of Selected Ethical Issues in Accounting". The Accounting Review, 68(2), 411-416. |
| [35] | Karacaer, S., Gohar, R., Aygün, M., & Sayin, C. (2009). Effects of Personal Values on Auditor’s Ethical Decisions: A Comparison of Pakistani and Turkish Professional Auditors. Journal of Business Ethics, 88(1), 53-64. |
| [36] | Karajeh, A. A.-A. H. (2004). How Far External Auditors are Committed to Code of Conduct in Jordan, and the Ways which Encourage them to Follow Professional Behavior. Ph.D, Amman Arab University Amman. |
| [37] | Keim, M. T., & Grant, C. T. (2003). To tell or not to tell: an auditing case in ethical decision making and conflict resolution. Issues in Accounting Education, 18(4), 397-407. |
| [38] | Knotts, T. L., Lopez, T. B., & Mesak, H. I. (2000). Ethical judgments of college students: An empirical analysis. The Journal of Education for Business, 75(3), 158-163. |
| [39] | Magill, G. (1992). Theology in business ethics: Appealing to the religious imagination. Journal of Business Ethics, 11(2), 129-135. |
| [40] | McMahon, J. M. (2002). An analysis of the factor structure of the multidimensional ethics scale and a perceived moral intensity scale, and the effects of moral intensity on ethical judgment. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University. |
| [41] | Mcshane, S. L., & Glinow, V. (2007). Organizational Behavior (4 ed.). australia: Higher Education. |
| [42] | Mokhlis, S. (2009). Relevancy and measurement of religiosity in consumer behavior research. International Business Research, 2(3), 75-84. |
| [43] | Nughaimshi, A. M. (1994). Psychology case. Riyadh: Muslim House for publishing and distribution. |
| [44] | Rashid, M. Z., & Ibrahim, S. (2008). The effect of culture and religiosity on business ethics: A cross-cultural comparison. Journal of Business Ethics, 82(4), 907-917. |
| [45] | Rest, J. R. (1986). Moral development: Advances in research and theory: Praeger New York. |
| [46] | Roxas, M. L., & Stoneback, J. Y. (1997). An investigation of the ethical decision-making process across varying cultures. The International Journal of Accounting, 32(4), 503-535. |
| [47] | Roy, C. (2009). The impact of moral intensity and ethical climate on the decision-making of finance and accounting professionals in government. Walden University. |
| [48] | Saat, M. M., Porter, S., & Woodbine, G. (2009). Does religiosity influence ethical sensitivity? An investigation on Malaysian future accountants. Malaysian Accounting Review, 8(2), 17-41. |
| [49] | Shafer, W. E., Morris, R. E., & Ketchand, A. A. (2001). Effects of personal values on auditors’ ethical decisions. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 14(3), 254-277. |
| [50] | Shaub, K. M. (1989). An empirical examination of the determinants of auditors' ethical sensitivity. Ph.D, Texas Tech University, Texas. |
| [51] | Singhapakdi, A., Marta, J. K., Rallapalli, K. C., & Rao, C. (2000). Toward an understanding of religiousness and marketing ethics: An empirical study. Journal of Business Ethics, 27(4), 305-319. |
| [52] | Sood, J., & Nasu, Y. (1995). Religiosity and nationality: An exploratory study of their effect on consumer behavior in Japan and the United States. Journal of Business Research, 34(1), 1-9. |
| [53] | Steenhaut, S., & Kenhove, P. v. (2006). ‘An Empirical Investigation of the Relationships among a Consumer’s Personal Values, Ethical Ideology and Ethical Beliefs’. Journal of Business Ethics, 64(2), 137-155. |
| [54] | Street, M. D., Douglas, S. C., Geiger, S. W., & Martinko, M. J. (2001). The impact of cognitive expenditure on the ethical decision-making process: The cognitive elaboration model. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 86(2), 256-277. |
| [55] | Thorne, L. (2000). The Development of Two Measures to Assess Accountants. Prescriptive and Deliberative Moral Reasoning’, Behavioral Research in Accounting, 12(1), 139–169. |
| [56] | Trevino, L. K. (1986). Ethical decision making in organizations: A person-situation interactionist model. The Academy of Management Review, 11(3), 601-617. |
| [57] | Twati, J. M. (2006). Societal and organisational culture and the adoption of management information systems in Arab countries. PhD Griffith University, Faculity of Griffith Business School, Brisbane, Australia. |
| [58] | Victor, B., & Cullen, J. B. (1988). The organizational bases of ethical work climates. Administrative Science Quarterly, 33(1), 101-125. |
| [59] | Weaver, G. R., & Agle, B. R. (2002). Religiosity and ethical behavior in organizations: A symbolic interactionist perspective. The Academy of Management Review, 27(1), 77-97. |
| [60] | Wennerholm, C. L., M. (2006). Ethics in the auditing profession: A comparison between auditors and students. MA, Internationella Handelshögskolan. |
| [61] | Woodbine, G. Yuningsih (2004). Cognitive Moral Development Within A Chinese Business Context: Testing the Theory. Jurnal Akuntansi dan Keuangan (Balance), 2, 281-302. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML