-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2013; 2(5): 292-296
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20130205.03
Investigating Customer Satisfaction Driven Values in the Retail Banking Industry
Ibok Nkanikpo Ibok1, Akpan Sunday John2
1Department of Marketing, University of Uyo, Uyo, PMB 1017, Nigeria
2Department of Marketing, Federal Polytechnic Ado Ekit, Ado Ekiti, PMB 5351, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Ibok Nkanikpo Ibok, Department of Marketing, University of Uyo, Uyo, PMB 1017, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study is an attempt to investigate those factors that drive customer’s satisfaction in the retail banking industry using a sample of 45 MBA students of the University of Uyo. The data was collected from the 45 students because they have at least an account with one bank or the other in Akwa Ibom State. The data collected were then analyzed using multiple regression. From the analysis, the study revealed that customer’s satisfaction was positively correlated with all the variables except queuing time which had a negative correlation, suggesting that bank customers would want prompt service delivery irrespective of how tight the situation might be. This is in essence, a way of meeting their expectations, if their satisfaction must be guaranteed. Based on this, some recommendations were made for future research.
Keywords: Customers’ Satisfaction, Value Drivers, Retail Banking
Cite this paper: Ibok Nkanikpo Ibok, Akpan Sunday John, Investigating Customer Satisfaction Driven Values in the Retail Banking Industry, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 2 No. 5, 2013, pp. 292-296. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20130205.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Understanding what drives customers satisfaction has been one of the notable areas in many marketing literature ([6],[7], and[13]). In theory, factors associated with customer’s satisfaction are different across cultures and across industries that cannot be generalized. In Nigeria, despite the importance of customer’s satisfaction and the growing interest in the banking sector development, there has remained low empirical research to investigate what determines customer’s satisfaction in this important industry. Indeed extant literature indicate that despite such growing interest in the banking sector, no significant studies had been observed to have focused on consumers satisfaction especially in the Nigerian context of retail banking operations ([15]).Customer’s satisfaction holds significant importance in the banking sector development, but the inability of some banks to determine what drives their customers banking behaviour may result in serious customers’ defection which may also affect the banks ability to increase future business growth. This therefore suggests that dissatisfaction drives customers away and is a key factor in customers switching behaviour. ([15],[2], and[16]). However, in the banking industry, a fundamental determinant of long term customer relationship is customer satisfaction. Previous researches have identified several factors to have affected customer’s satisfaction but none of these studies have been undertaken in the retail banking industry of the Nigerian society. For instance; ([2]) confines his study to only corporate customers. A study by ([1]) compares the service performance between the commercial bank and the microfinance banks, and made no attempt to examine those factors that determine customers’ continued loyalty to the banks. Some other studies on bank performance in Nigeria were also carried out, but their focus has not been on customer’s satisfaction in the retail banking context. Thus it is timely for this study to investigate customer’s satisfaction determinants within the context of retail banking, with a view to identifying those factors that most likely predict customer’s satisfaction in the retail banking industry.
2. Determinants of Customer Satisfaction
- Determinants of customers satisfaction are diverse in the literature and there is no generally accepted list of factors that can explain what satisfies the customer or not, because customers satisfaction differ across culture and across industry ([4] and[3]). ([12]) asserted that the higher the level of customer satisfaction in any given company, the higher the profitability would be and vice versa. In the banking industry, many factors have been found to relate with customer satisfaction. For example, fast and efficient service, confidentiality of bank, speed of transaction, friendliness of bank staff, accuracy and timeliness of billing system, competitive pricing and service quality have been found to have significantly influence customer satisfaction ([14],[20], and[9]). ([10]) In their study on banking characteristics employed service quality, staff quality, corporate architecture, Bank atmosphere and overall service delivery as independent variables.Recent studies in the strategic marketing of bank services ([15]) argued that bank specific characteristics are more important than any other factor in determining customers’ satisfaction in the service industry. Thus, ([25]) in their examination of the relationship between service quality, customer satisfaction and store loyalty reveals that firms which give a higher priority to meeting their customer expectation achieve higher performance. These firms are known for their use of annual and long term strategic marketing plan, performing marketing research about the needs and wants of their customers, and they are proactive in their planning approach as well as employing many other marketing efforts that will give them performance advantage in the market. ([27]). ([16]) and ([17]) also stressed that customer satisfaction is important for business success and performance. ([7]) examined the causal relationship between customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in the North American banking industry and concluded that there is a positive relationship between customer satisfaction and loyalty. Accordingly, ([23]) maintained that a high level of customer satisfaction will decrease customer perceived need to switch service provider. This implies that customer dissatisfaction leads to low level of loyalty ([18],[9] and[20]). Further suggesting that customer satisfaction and customer loyalty are inextricably related and that dissatisfaction can foster a customer intention to switch ([8]).
3. Customer Satisfaction and Service Quality
- ([26]) defined customer satisfaction as a collection of outcomes of perception, evaluation and psychological reactions to the consumption experience with a product / service. ([3]) contend that the currently relevant factors determining customer satisfaction in the retail banking industry include: fast and effective service delivery, competitive pricing, service quality, staff competence and ability of the bank to maintain confidentiality. These factors are of course moderated by the bank reputation in terms of credibility, trustworthiness, reliability, service delivery, speed and accuracy. ([14]) noted that poor service quality is a critical factor in causing customer not to be satisfied and ([24]) obvious observation that the most important factors discouraging customers banking behaviour are delay in transaction, staff incompetency, unreliable transaction, poor service delivery, unfriendly staff attitude among other factors.([22]) stated that service is an intangible good which appeal differently to different customers and that certain level of service should be achieved in order to satisfy the customers. Thus the quality of customer service and overall service quality are expected to be positively correlated with customers satisfaction based on the arguments of ([19]), ([21]), ([28]) and ([16]). The number of customers is always taken as a proxy to marketing performance measure on the part of service providers because it is believed that intensive marketing effort would enable service firms to better understand their customers’ needs, wants and preferences and invariably satisfy their yearnings and expectations. Therefore, drawing from the literature and research model as shown in figure 1, it is hypothesized that customers satisfaction in the retail banking industry is significantly related to service efficiency, security, confidentiality, speed, transaction accuracy, staff quality and queuing time among others.
4. Research Objective
- The main objective of this study was to determine the factor(s) that most likely influence customer satisfaction in the retail banking industry.
5. Research Question
- Based on the above objective, the study sought answers to the following research questions:(i) Does speed of transaction positively relate with customer satisfaction?(ii) Is staff quality or competence positively related with customer satisfaction?(iii) Do security and bank confidentiality significantly influence customer satisfaction?(iv) Does competitive pricing significantly affect customer satisfaction(v) Does queuing time relate positively with customer satisfaction?
6. Hypotheses
- Based on the literature and research model shown in figure 1, five hypotheses were formulated for this study as follows:H1: Transaction and accuracy relates positively with customer satisfaction.H2: Staff quality and competence relates positively to customer satisfaction.H3: Banks security and confidentiality relates positively to customer satisfaction.H4: utilization of competitive pricing relates positively to customer satisfaction.H5: Customer queing time is positively related with satisfaction.Therefore transaction speed and accuracy, staff competence, bank security/confidentiality, competitive Pricing and queuing time are independent variables while customer satisfaction is measured in terms of commitment, loyalty, retention, referrals or recommendation of service as the dependent variable. Detailed operationalization of the proposed conceptual framework is as presented in figure 1 below:SERVICE VARIABLES
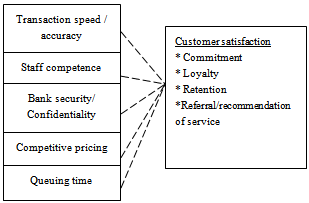 | Figure 1. Schematic framework of the proposed model |
7. Methodology
- The target respondents for this study were University Of Uyo MBA students who are regular patrons of bank services, A questionnaire was developed and delivered personally by the researcher but there was subsequent contact by telephone in order to encourage participation. The survey began by asking respondents to choose from a list of 5 items, one thing that appealed to them when choosing the bank(s). Out of the 45 copies of questionnaire issued out, 27 valid responses were received. The questionnaire items were derived from the literature review and examined five aspects of bank services and quality characteristics as outlined in figure 1 which represents construct and serve as independent variables in the analysis, while satisfaction is the dependent variable, allowing the relative importance of each dimension to be assessed. Nominal scale measurements were used in the survey, mainly using a 5 point liket scale. The SSPS software was used in the study analysis, which made use of regression tools to examine the relationship between the study variables.
|
8. Data Analysis and Results
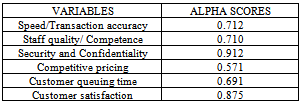
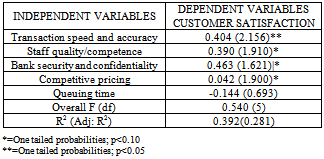
- The hypotheses were tested using multiple linear regression and the results are as presented in table 2. The first hypothesis tested the relationship between transaction speed and accuracy with customer satisfaction. The results showed that customer satisfaction is positively related to speed and accuracy of transaction. (B=0.404; P< 0.05) thus H1 is accepted.The second hypothesis was related to staff quality and competence in influencing customer satisfaction. The results revealed that there is a positive relationship between staff quality and competence with customer satisfaction. (B= 0.390; P< 0.010) thus H2 is accepted.The third hypothesis tested the relationship between bank security/ confidentiality and customer satisfaction. The result of the analysis revealed that customer satisfaction is significantly related to bank security and confidentiality of transactions. (B= 0.463; P<0.05) thus hypothesis three is accepted.The fourth hypothesis relates with the utilization of competitive pricing –(interest rates and commissions) with customer satisfaction. It was found that no relationship exist between the two variables. Thus H4 is not supported. The fifth hypothesis relates with customers waiting time and its effect on customer satisfaction. The result revealed a significant negative relationship between queuing time and customer satisfaction. (B=` -0.144; P >0.05). Thus hypothesis five was rejected. The results of the hypothesis tests are presented in table 2 below
|
9. Discussion
- The result of the multiple regression analysis revealed that all the hypotheses were supported except one. The results showed that transaction speed and accuracy, staff quality and competence, bank security/ confidentiality and customer queuing time are seen as crucial elements in achieving customer satisfaction. Table 2 further shows that some of the factors were very significant than others. These findings do agree with some of the factors revealed in the findings of ([11]) that the relevant factors determining customer continued patronage of a bank include speed and accuracy of business, reliability in service transaction, staff knowledge in handling customer problems, convenience and privacy in transaction. The results further indicate that there is a strong and positive relationship between the independent variables and customer satisfaction. Thus indicating that if all these variables are significantly improved, then customers satisfaction will be maximized which is the prime object of every marketing firm ([15],[3],[14],[20], and[23]). Also that queuing time is negatively related to customer satisfaction suggest that a good service will increase customer satisfaction and decrease waiting time by customer and this agrees with the view of ([12]) and ([1]) whose respective studies observed that customers satisfaction will lead to customer’s affective commitment and consequently loyalty to the brand.These results highlight the extent to which the predictors that is the independent variables do explain the level of customer satisfaction in the retail banking industry. These results highlight that the predictors can explain up to 39 percent of the variance in customer satisfaction (adjusted r2 = 0.392). The findings further revealed that transaction speed, bank security and confidentiality were the most robust predictors of customer satisfaction (Beta = 0.463, Sig. 1.621) and this was closely followed by transaction speed and accuracy (Beta=0.404; Sig .2.156)Overall, the regression model was significant (Sig. F change=0.000) as shown by the ability of the independent variables to predict up to 54 percent of customer satisfaction. In all, the results are consistent with previous studies.
10. Conclusions and Recommendations
- This study attempts to find value drivers in customer’s satisfaction within the retail banking context. For satisfaction to be achieved, the banks have to improve on the speed and quality of service delivery, train their staff on customer relationship, guarantee security and confidentiality of transaction, provide competitive commission and interest rate and reduce customer waiting time at any given transaction. However, the banks should know that satisfaction is a necessary but not a sufficient condition for loyalty and so everything done or supposed to be done must be geared towards having loyalty from the customer, this is because customers can be satisfied without necessarily being loyal.Therefore, based on these views from many scholars and this current research, it can be concluded that service characteristics are strong determinants of customer satisfaction with a bank. Thus, cultivating a customer focus, strategic flexibility in the marketplace can guarantee sustainable competitive advantage through customer satisfaction. This is an important part in ensuring customer loyalty and retention. Further research should identify other factors that are responsible for customer’s satisfaction in the retail banking industry. Further research can proceed in several directions. The most obvious is for future research to examine the relationship between service perceptions and other variables such as corporate architecture,, parking space, atmospherics etc. Secondly, measures of customers’ satisfaction are notably lacking, particularly in the banking sector, future research should develop and design comprehensive satisfaction measures. Thirdly, managers can enhance their understanding of customer satisfaction by improving their ability to monitor customer perception of their service; researchers should therefore explore and capture service perception as experienced by customers. Finally our sample data were obtained from MBA students of University of Uyo. We cannot assume that the perceptions of Nigerian retail customers may not be different from others elsewhere, this is worthy of future investigation.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML