-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2013; 2(5): 287-291
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20130205.02
BUILD REAL*: A Case Study on Risk Analysis Using Simulation in a Rent or Buy Decision
Santi Swarup Kandikonda
Incharge Business Advisory Clinic, Associate Professor, Department of Management, Faculty of Social Sciences, Dayalbagh Educational Institute, Dayalbagh, Agra, 282 005, India
Correspondence to: Santi Swarup Kandikonda, Incharge Business Advisory Clinic, Associate Professor, Department of Management, Faculty of Social Sciences, Dayalbagh Educational Institute, Dayalbagh, Agra, 282 005, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Anchoring affects our investment decisions. Anchoring involves comparing only one piece of information heavily over others. Raj is in transport business. Raj wants to buy a truck which otherwise he rents for transporting building material. He initially compares only fuel costs with truck rentals and feels that it is definitely cheaper and more convenient to purchase truck than to go for a rental truck. Through counselling, author made him reflect on his decision by gathering more information about the expenses and benefits involved in the purchase decision. Also the impact of variables like number of working days, fuel costs and miscellaneous expenses on the decision were studied. When we use static and optimistic values of variables the decision looks good. But business environment is not static. Using spread sheet simulation we can clearly identify the risks associated with such decisions. This case study can also be used to create risk awareness in students by presenting the impact of variables on the final rent or buy decision using Excel and simulation add ins.
Keywords: Risk Analysis, Rent or Buy Decision, Simulation, Anchoring, Decision Making
Cite this paper: Santi Swarup Kandikonda, BUILD REAL*: A Case Study on Risk Analysis Using Simulation in a Rent or Buy Decision, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 2 No. 5, 2013, pp. 287-291. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20130205.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Investment decisions by big firms are sometimes influenced by biases. Reducing these biases increases returns[1]. There are many such biases which affect decisions[2]. These are Confirmation bias, where evidence which contradicts preconceived notion is neglected; Anchoring, where people give more weightage to one information over other for decision making; Loss aversion, which results in being too cautious in our decisions. In the course of giving advise to a Small and Medium Business (SMB) owner, the author came across a situation where 'Anchoring'[3] was found to influence the investment decision. Is it possible to increase the risk awareness and make the entrepreneur reflect on his decision was the motivation for this study. Reflection involves slow, effortful and deliberate decision making which helps us to understand bias and also eliminate them from decision making[4]. Author has taken help of excel simulation add-in for making entrepreneur realize the risks involved in the decision making. It is important for entrepreneurs to first think about their decision[5] before taking the decision.
2. Review of Literature
- The consumer buying vs. renting an asset decision depends on the perceived value of the asset. If the perceived value or fundamental value is higher than the asset price, buying takes place otherwise consumer rents the asset. Beracha and Johnson (2012) have indicated that crowding towards homeownership raises fundamental value of homes and renting proves to be a superior strategy for the potential homeowners[6]. Knox and Eliashberg (2009) developed a measure to identify the tendency of the consumer to buy a video at a full price than buying at a lower price or renting[7]. Reed and Greenhalgh (2002) indicated that renting results in freeing cash flows for other services and also keeps consumer debt free[8]. So consumers have to weigh the fundamental value of an asset and also the lost opportunity of having free cash flows while making a rent vs. buy decision. According to Massingham (2013), the decision of whether to buy or make necessary knowledge is an important cognitive ability[9]. Fiol and O'Connor (2003) identified two mind sets in information processing. Simple mindsets, oversimplify their environment and make cognitive mistakes i.e. overlook important information. Complex mind sets on the other hand allow firms to notice and understand the stimuli resulting in better decisions[10]. The discounted cash flow (DCF) techniques (Brealey & Myers, 2009) are the standard methodology used for assessing the rent buy decision[11]. If the present value of incremental cash inflows is more than the cash outflow (from buying) then it is worth buying the asset. Otherwise, it is better to rent the asset. While assessing these incremental cash flows there is a need to incorporate both forecast of revenues and costs and do a sensitivity analysis to identify their impact on cash flows[12]. Using simple mindset one can conclude straightaway that buying is a better option. But using a complex mindset, if one does sensitivity and simulation analysis, one can identify the most important variable affecting the decision as well as the impact of changes in these variables on the net cash flows. So through counseling it is possible to make client reflect on the decision using the sensitivity and simulation analysis. Cash flow estimation is the first step in this process.Cash flows are estimated as revenues minus expenses minus depreciation and then taxes are deducted. Depreciation is a non cash item so it is added back again. We have used this method[13] where we have subtracted depreciation first and then taxes from EBITDA (Earnings before taxes, interest, depreciation and amortization) and then added back depreciation to this value to get cash flows.
3. Data Collection & Justification for the Case
- Gerring (2004) indicated that a case is a spatially bounded phenomenon .. observed at a single point in time or over some definite period of time. A case study is an intensive study of a single unit for the purpose of understanding a larger class of (similar) units'[14]. Case selection is the process of choosing cases for case study research. The best practice of case selection depends on the purpose for which cases are selected[15]. In this research paper, the selection process used was theoretical, which replicates theory[16]. The purpose is to educate the client about the risk in buy vs. rent decision and also to illustrate the application of financial management principles in decision making for management students. Author is Incharge of Business Advisory Clinic, which offers free advice to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). The data was collected in three phases and revision and application were done in last two phases. In the phase I, the entrepreneur was interviewed to initially understand the decision faced by him. In phase II, more data was collected for formulating the case study. In the phase III, the sensitivity and simulation analysis were shared with the client to enhance his risk awareness. Phase IV is the revision phase and Phase V is the application of the case study in the MBA class room. This case study showed potential for application of financial principles and class room learning. So author developed the case, revised and discussed the case study in the classroom before submitting for publication.
4. Case Overview
- Mr. Raj Kumar (Raj) is in the building material business (Buildreal) for past 4 years. His business is doing well. He feels that just like all other business there are swings in his business also but they are not significant. Over the last three years, he was able to save some cash. He wants to invest this cash in the purchase of a truck. He wants to know whether he should go ahead with this decision or not.The material (which is basically the basement material) is transported from Delhi to Noida for grinding. After grinding it was sent to Ghaziabad for washing at Raj's plant. Raj has a washing plant at Ghaziabad. Then the washed material was sold to various suppliers in Ghaziabad. Sometime Raj even sends this material to the customer's premises by trucks. Presently he is using the transport services of a Ghaziabad transporter. Looking at the fuel costs involved, he thinks it is more profitable to own his truck. He feels that purchase of his own truck will result in improved margins.
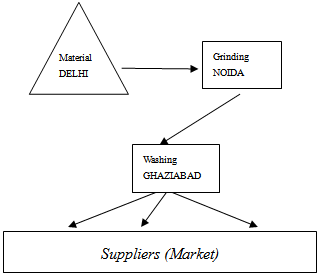 | Figure 1. Process Flow |
5. Objectives & Methodology
- The objectives of this case study analysis are to a. Identify incremental cash flows and consider static values for variables (optimistic) and analyse the impact on the decision.b. Using a range of values analyse the impact of variables on decision making using simulation analysis.This case study can be analysed in small teams of 5 to 6 students of Graduate management students. Here students may be formed in to teams. Each team may first discuss and brainstorm for cash flow identification and do a cost benefit analysis. Care should be taken to ensure that the team comprises of both analytical and average students. Some teams may otherwise decide buying truck without any data analysis (bounded rationality). Each team will have a representative who may present group calculations and other team representatives may join the discussion. Faculty can ask questions and lead the student interactions. Focus can be on calculation of incremental cash flows and also simulation analysis.
6. Data Analysis
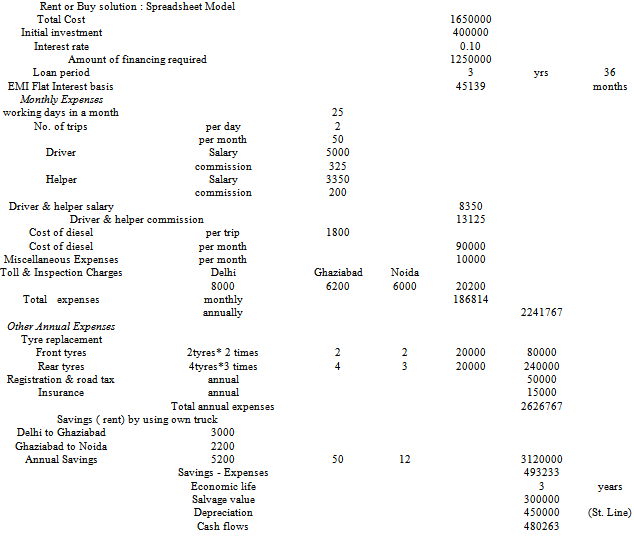
- i) Calculate Equated Monthly Instalment (EMIs) for Rs. 1,250,000 amount at 10% flat rate and for a 3 years period.ii) Calculate monthly expenses based on 25 working days. these are driver & helper salary and commission, cost of fuel (per trip * 50 trips per month). Consider Rs. 10,000 as miscellaneous expenses per month. Also add sum of all toll and inspection charges per month. Convert this monthly expenses to annual expenses by multiplying by 12 (months in a year).iii) Calculate tyre replacement expenses (front and rear separately) add registration and road tax to the same. Annual insurance charges are also added. iv) Add all the annual expenses.v) Calculate annual savings by not using a transporters truck. vi) Annual savings are total savings minus total expenses.Vii) Calculate depreciation based on economic life of 3 years and salvage value of Rs. 300,000.viii) Cash flows are calculated by first subtracting depreciation from the difference between annual savings and expenses and then applying taxes and adding back the depreciation.iX) When we use static values of 25 working days, fuel cost of Rs. 1800/- and miscellaneous expenses of Rs. 10,000 we get cash flows as Rs. 480,263/-. X) Simulation analysis indicates that the probability of getting positive cash flows (>0) is only about 57%.
7. Sensitivity and Simulation Analysis
- The following variables were considered for the calculation of possible cash flows. Working days in a month, Cost of diesel and Miscellaneous expenses.The sensitivity analysis is carried out to identify the most important variable with maximum impact on cash flows. The results are as given below:
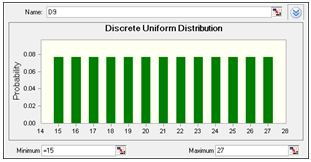 | Figure 2. prob. Distribution of No. of working days (15 to 27) |
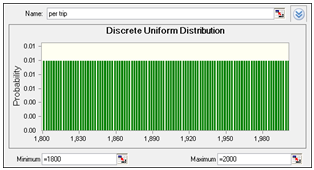 | Figure 3. Probability Distribution of Cost of fuel per trip (Rs. 1800 to Rs. 2,000) |
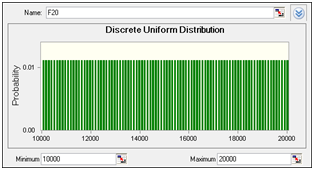 | Figure 4. Probability Distribution of Miscellaneous Expenses (Rs. 10,000 to 20,000) |
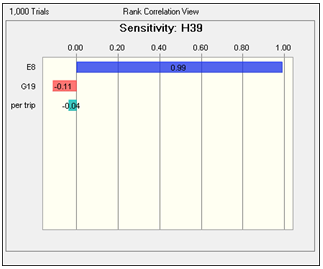 | Figure 5. Sensitivity Chart |
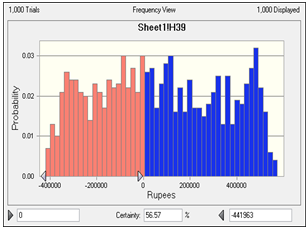 | Figure 6. Simulation Chart |
8. Conclusions
- This case study has two objectives viz., first to enhance the awareness of risk in the entrepreneur and secondly, to make management students aware of the importance of dynamic business environment and the role of risk analysis in buy or rent decisions. The results of the simulation indicate that the chance of positive cash flows happening is not very high. The chance of success is only slightly above the classical coin tossing probability (H: 0.5 & T: 0.5). This indicates that the purchase decision is very risky. So, Mr. Raj Kumar should not be in a hurry to purchase the truck. He needs to understand the dynamics behind this business first.Using this case study for calss room teaching also enhances the ability of students to understand the nature of risk and its impact on cash flows in buy or rent decisions. This case study analysis is supported by the findings of Lovallo et al.[1] that the process of analysing decisions is equally important while taking decisions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The author wishes to acknowledge the continuous support and guidance received from Prof. P.S. Satsangi, Chairman, Advisory Committee on Education, Dayalbagh (ACE), Agra, India and also the anonymous reviewers for their kind comments in improving the quality of the study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML