-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2013; 2(3): 174-183
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20130203.05
Determinants of Corporate Governance Disclosure: The Case of Tunisian Firms Listed on the Tunis Stock Exchange
Souhir Neifar1, Khamoussi Halioui2
1Department of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Management University of Sfax, 3018, Tunisia
2Department of Management, College of Economics, Management and Information Systems, University of Nizwa, 616, Oman
Correspondence to: Khamoussi Halioui, Department of Management, College of Economics, Management and Information Systems, University of Nizwa, 616, Oman.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This research aims to examine the factors influencing the extent of disclosure on corporate governance in Tunisian context. In this study, we focus on a sample of 23 companies listed on the Tunis stock exchange for a period of three years (2007-2009). Our results show that companies which disclose more about corporate governance are those characterized by the high growth potential, dispersed ownership structure, whose leaders do not stack as the chairman of the board of administration and general director, the more successful and the less indebted. We also tested the effect of the variable «foreign participation» in the same relationship; however, the results show no significant effect of this variable.
Keywords: Corporate Governance Disclosure, Corporate Governance, Disclosure, Transparency, Foreign Participation
Cite this paper: Souhir Neifar, Khamoussi Halioui, Determinants of Corporate Governance Disclosure: The Case of Tunisian Firms Listed on the Tunis Stock Exchange, International Journal of Finance and Accounting, Vol. 2 No. 3, 2013, pp. 174-183. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20130203.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction and Motivations
- Increasing scandals, financial and economic crises have affected confidence in capital markets and mainly to business leaders and their policies. So shareholders have become increasingly interested in terms "risk" and "no surprise". Thus, the research on disclosure has regained importance. Previous research has focused essentially on disclosure of financial information as a solution to the problem of information asymmetry between managers, shareholders and other outsiders. However, recently, disclosure of non-financial information has turned crucial for both the company and its environment. As a result, "new regulations, new requirements and ever-increasing demands for transparency determine companies to follow the recent trends in corporate reporting (or disclosure) in order to comply with ‘best practice’ regulations: e.g., narrative reporting, balance in the structure of reports, inclusion of management report, reporting corporate governance and social responsibility, balancing financial and non-financial information, comparability over time, etc"[1].The importance of corporate governance disclosure has increased for many reasons. First, this type of disclosure protects the rights of minority shareholders, creditors and other stakeholders, who have no knowledge about the conduct of the business activity resulting in asymmetric information[2]. Thus, disclosure is important to mitigate asymmetric information and agency problems[3]. Indeed, asymmetric information causes inefficient investment, which explains the existence of many disclosure regulations that attempt to reduce information asymmetry by making the private information public[4]. As a result, shareholders and prospective investors can evaluate the management leadership and make decisions on the evaluation of shares. This can increase investor’s awareness and enable them to reduce the decline in the value of the firm[2, 5]. Corporate governance disclosure allows analysts to evaluate the policies of corporate governance of a company and their risks because corporate governance is an important indicator of future profitability[6]. In addition, the accuracy of analyst earnings forecast is higher for companies that disclose more about their corporate governance[6]. Moreover, the performance of a company is not solely based on its profitability and growth prospects embedded in its business model, but also on the effectiveness of its governance arrangements, which ensures that investors' funds are not expropriated or wasted on inappropriate projects[7]. The disclosure can even achieve the political cost of non-compliance and therefore, reduce litigation[8]. Despite the importance of corporate governance disclosure is not limited to a micro scale of the company, but it widens to a macro scale that can affect the economies.The objective of this study is to examine the determinants of disclosure on corporate governance in the Tunisian context. The central questions of this study are: What are the levels of corporate governance disclosure in Tunisian companies? What are the factors that influence disclosure practices of corporate governance in the Tunisian context? Does foreign ownership have a significant effect on the level of corporate governance disclosure?Using a hypothetical-deductive approach, we proceed as follows: section 2 describes the literature review and research hypotheses, section 3 describes the research methodology, section 4 is dedicated for the presentation and discussion of results and section 5 serves as a conclusion.
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
- More than the traditional determinants of any type of disclosure related to the characteristics of the company (size, leverage and firm performance) other determinants may be advanced: economic determinants and those related to governance systems.
2.1. Economic Determinants
- According to[9], studies belonging to the positive accounting theory are generally based on the economic assumption of utility maximization. Those studies favor economic determinants in their attempts to explain the choice of accounting methods by managers.
2.1.1. Foreign Participation
- Asymmetric information causes inefficient investment, that’s why many disclosure regulations attempt to reduce the asymmetric information by publicizing private information[4].Although the previous performance of the company and other factors may encourage foreign investors to invest in the company, the investors provide funding to companies that are more likely to be protected against managers’ expropriation[10, 11]. To avoid this, shareholders are generally concerned about disclosure and corporate governance. Recent studies have shown that there is a positive relationship between the foreign ownership and the extent of voluntary disclosure. For example, reference[12] found a positive relationship between foreign ownership and the extent of voluntary disclosure in Chinese companies. This finding suggests that foreign shareholders play a positive role in the monitoring management. Several studies have highlighted the importance of the governance structure in the investment decision. In fact, reference[13] show that firms with better governance practices are more profitable, more valuable, less risky, less volatile, and pay more dividends. Reference[14] add that, the best shareholder protection is empirically associated with the increased value of the assets of the company. For all these reasons, foreign investors pay more attention to corporate governance than domestic investors[15]. According to[11], the interest of foreign investors depends on the quality of corporate governance. Reference[6] confirms this idea by pointing out the importance of corporate governance in making investment decisions. This motivates the stock exchange and regulators to introduce regulations requiring information related to corporate governance. Foreign investors are usually minority shareholders[16,17] and are facing risk of expropriation by corporate executives and/or majority shareholders. This problem is also aggravated by distance[18]. If the domestic minority shareholders are able to monitor managers easily, monitoring costs for foreign investors could be very high[10, 19, 20]. In addition, This type of shareholder has an informational disadvantage compared to local investors and incur more monitoring costs when they make investments in companies with poor corporate governance[21, 22]. Reference[23] proved that American investors consider the cost of collecting information as an important determinant of their decision to invest in foreign stocks. For these reasons, transparency and full disclosure of information is essential for companies that have foreign shareholders. According to[24], transparency and full disclosure of information are the basic attributes of the mechanism of corporate governance and are considered an extremely important factor in the quality of corporate governance. These inter-firm differences in the quality of disclosure and transparency of information are important issues for investors to evaluate a business[25]. Reference[7] show that companies which improve the practices of transparency and disclosure obtain higher returns. The score of transparency and disclosure is often used to measure the level of corporate governance disclosure(e.g., as in[26];[25];[6]; etc…).The above discussion supports the literature on disclosure and corporate governance and suggests that disclosure and good quality of corporate governance help to reduce agency conflicts by reducing the lack of information existing between managers and shareholders[27], delimiting the powers and influencing the decisions of managers[28]. Although this variable has not been examined for such a disclosure, we claim only a positive relationship between the level of corporate governance disclosure and the proportion of foreign investors.Then, the first hypothesis is formulated as follows:H1)Proportion of foreign investors in the company has a positive impact on the level of corporate governance disclosure.
2.1.2. Growth opportunities
- The existence of growth opportunities is usually associated with asymmetric information and higher agency costs[29, 30]. Different are the results of previous studies analyzing this determinant. By reviewing the annual reports and websites of the 52 largest and most liquid Turkish companies (based on the volume of trade) listed in ISE (Istanbul Stock Exchange) in 2003, reference[2]showed the existence of a positive relationship between growth opportunities and the level of disclosure and transparency. Reference[5] also showed that companies that publish more information are those that have higher price-to-book value ratio. However, reference[31] found that there is no relationship between corporate governance disclosure and growth opportunity. We finally note the possibility of a negative relationship between growth opportunities and corporate governance disclosure. If the increase in equity value is generated by the issue of shares, this can result in a low price-to-book value ratio. Nonetheless, several researchers have found that companies disclose more when they have recently issued capital[32]. This has been argued by[2].Given previous results, we formulate our second hypothesis as follows:H2)Growth opportunities of the company have a positive impact on the level of corporate governance disclosure.
2.2. Determinants Related to Governance Systems
2.2.1. CEO Duality
- Previous researches in accounting that study the relationship between CEO duality, i.e. the role of Chief executive officer(CEO) is combined with that of the chairman of the board, and the level of corporate governance disclosure have led to conflicting conclusions. Although reference[33] has found a positive and insignificant relation between CEO duality and corporate governance disclosure, yet, reference[31] and.[34] reported a negative relationship. This confirms the previous studies that have examined the relationship between this governance mechanism and other types of disclosure. For example, reference[35] found that CEO duality is associated with a low-level of voluntary disclosure in Hong Kong, while, reference[36] reported no significant association between this variable (CEO duality)and the level of voluntary disclosure in Singapore.Based on the agency theory, we formulate our third hypothesis as follows:H3)CEO duality has a negative impact on the level of corporate governance disclosure.
2.2.2. Ownership Concentration
- The agency theory suggests that the dispersed ownership will generate monitoring costs and additional information requests[37]. In order to increase confidence between shareholders and managers and to reduce monitoring cost generated by the separation of ownership, the company must focus on disclosure. Previous studies have shown a negative association between ownership concentration and the level of corporate governance[31, 34,38]. These results confirm some of the other studies that have analyzed the relationship between governance mechanism and other types of disclosure[20, 39].Based on the agency theory, we formulate our fourth hypothesis as follows:H4)Ownership concentration has a negative impact on the level of corporate governance disclosure.
|
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Sample and Data
- Our initial sample consists of firms listed on the Tunis Stock Exchange. We eliminated financial companies (banks, insurance companies, leasing companies and investment companies) not to bias our results because of their specific regulations regarding financial statements and disclosure. We analyzed the annual reports of 23 non-financial companies listed on the Tunis Stock Exchange for three years (2007, 2008 and 2009). The total number of observation was 68. The choice of this period is motivated by the availability of those reports in the Council Financial Market (CFM) during the collection period. These reports are collected directly by consulting CFM which gave us the annual reports. We also consulted the Tunis Stock Exchange (TSE) which provided us a magnetic media that contains information’s about companies. Note also, that financial statements and other financial information of each company are collected from the web site of TSE.
3.2. Model Specification and Variable Measurement
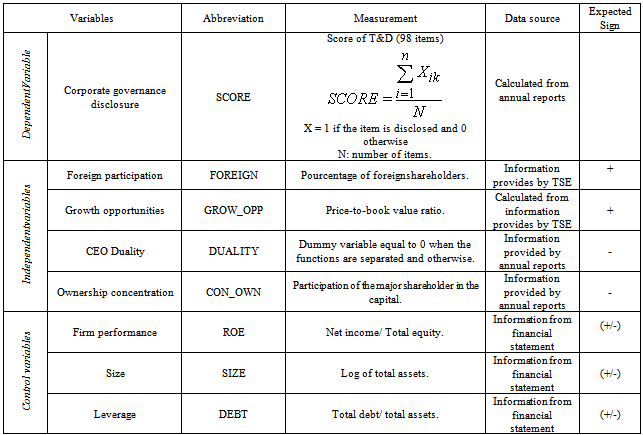
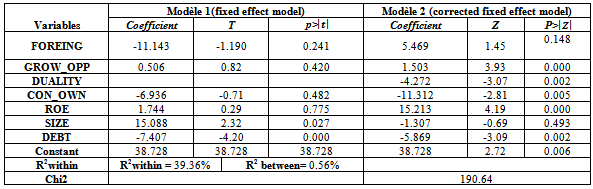
- The variables of this study can be classified into three types: dependent variable, independent variables and control variables.The econometric model is written as follows:
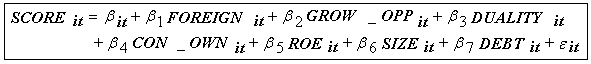 With βietβit: coefficients;:error term.The indices I and t correspond to the company and the period of the study.
With βietβit: coefficients;:error term.The indices I and t correspond to the company and the period of the study.4. Presentation and Discussion of Results
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
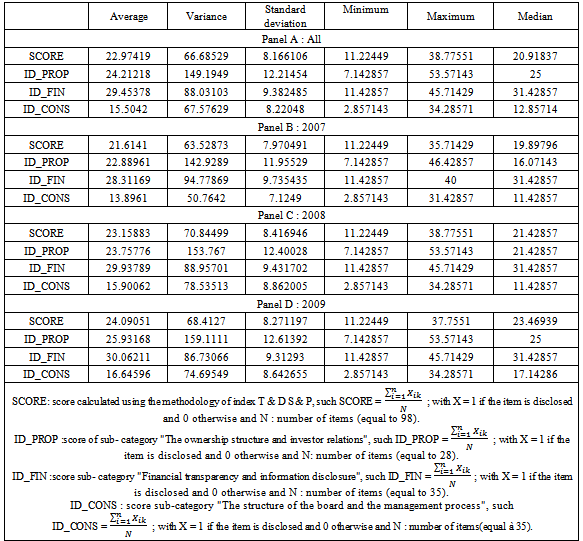
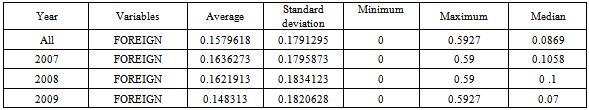
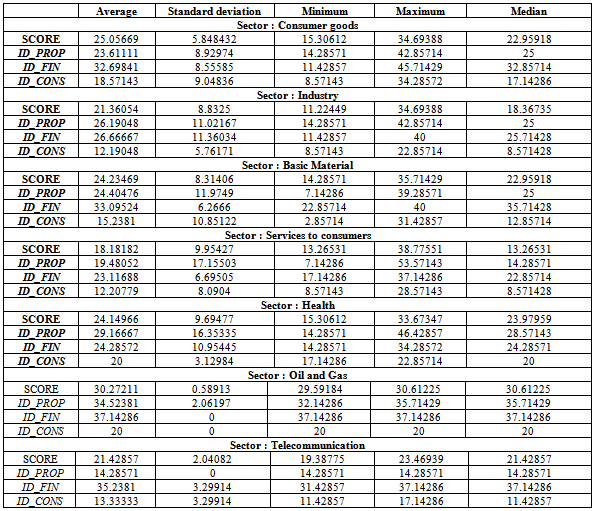
- Table 2 provides a description of the level of disclosure on corporate governance in Tunisian firms per year and per industry.According to table 2, we find that the score of corporate governance disclosure "SCORE" varied from a minimum of 11.22449 to a maximum of 38.77551. The variability of the level of disclosure is important, that show the existence of a considerable dispersion with a standard deviation of 8.166106. We find the half of our sample has a score of disclosure more than 20.91837. We also note that firms with a minimal global score have no sub-minimum score in all subcategories. Indeed, the minimum sub-score on the "ownership structure and investor relations" is 7.142857; the minimum sub-score on information on "board structure and management process " is equalto 2.857143, while the minimum sub-score on the "financial transparency and disclosure" is 11.42857 (total equal 21.42857≠ 11.22449).The average overall score "SCORE" (22.97419%) is proportionately low. Similarly, the sub- scores are relatively despicable, especially in terms of board structure and management process (mean score =15.5042).The highest scores are obtained in the sub-category "financial transparency and disclosure of information" and information about "the ownership structure and investor relations" with an average score of 24, 21218 and 29.45378 respectively.As a result, firms listed on the Tunis Stock Exchange give much importance to information about financial transparency, ownership structure and relationship with investors. However, information on the structure of the board and the management process proved to be the least disclosed in annual reports with an average score of 15.5042.Finally, despite its importance for both analysts and potential investors, Tunisian companies are not so transparent in terms of disclosure on corporate governance in general and in terms of information about "structure of the board of directors and the management process" in particular. The examination of the annual level of disclosure on corporate governance shows that the yearly level of each sub-category score has improved between 2007 and 2009. The average for this type of disclosure was 21.6141 in 2007; it increased to 23.158 in 2008 and to 24.09 in 2009. The improvement in the overall score was not a result of an improvement of a sub-score and the stability of the other. Indeed, from Table 2, all sub-scores were increased during the period from 2007 to 2009. These results can be explained by the response of Tunisian companies to the need for more transparency and disclosure, especially after the economic and financial crisis 2008.This increase may be as to restrict the departure of foreign investors during the period 2007 to 2009. In addition, in 2007, foreign shareholders held 28% of market capitalization of the Tunisian market, while in 2008, they held only 24.74% and 21.15% in 2009 (Annual Report of the Tunis Stock Exchange 2010).Table 3proves these analyses.The average of foreign participation in Tunisian firms listed on Tunis Stock Exchange in our sample is equal to 0.1579618, its minimum is 0 and the maximum value is 0.5927. Half of our sample foreign participation is more than 0.0869. Foreign participation in Tunisian companies fell from an average of 16.36273% in 2007 to an average of 16.2191% in 2008 to reach 14.8313% in 2009. This can be explained by the release of a significant proportion of foreign capital in emerging markets following the economic and financial crisis 2008. To make a more thorough analysis ofthe level of disclosure on the governance of Tunisian firms listed on the Tunis Stock Exchange, we examine the level of such disclosure by industry. Figure 1 provides an analysis of area of the sample examined.
|
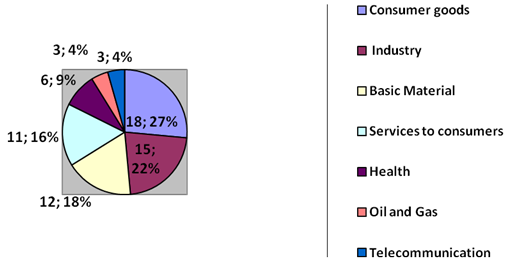 | Figure 1. Industries of the sample |
|
|
4.2. Multivariable Analysis
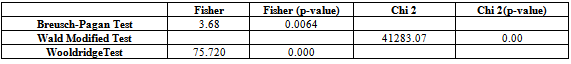
- The objective of this study is to determine the factors that influence the level of disclosure on corporate governance in annual reports of Tunisian companies listed on the Tunis Stock Exchange. However, before using the regression on panel data, we should check necessary conditions such as the normality of residuals, multi-collinearity problem between independent variables, heteroscedasticity and auto- correlation problems.We use the test of Breusch-Pagan and Wald to test the existence of heteroscedasticity problem, and the test of Wald modified to test the auto-correlation problem (Table II).
|
|
5. Conclusions
- The economic environment suffers from multiple constraints. The scandals and bankruptcies have reduced the area of business. Implementing and using an effective corporate governance system was one of the recommended solutions to overcome these situations. A recent study has demonstrated the importance of an effective governance system. A good system of governance can help to stabilize the share price even during a period of political crisis [43]. This explains the need for more information on corporate governance by shareholders and stakeholders. Our study shows that the level of corporate governance disclosure in the Tunisian context remains lower than the level reported by other contexts such as Malaysia 65.3%, Bahrain 45.2%, 40.3% Egypt, and Turkey 51.9%[44]. Note that despite the existence of a good practice guide on corporate governance in Tunisia, this guide is not applicable to a large proportion of these firms. Indeed, this guide provides only recommendations that have a voluntary aspect. In this study, we examined the determinants affecting the level of corporate governance disclosure in the Tunisian context. Our results based on regression on panel data show that firms which disclose more about corporate governance are those characterized by a high growth potential, dispersed capital structure, whose leaders do not stack as the chairman of the board of directors and general director, the more successful and the less indebted.Multiples are the contributions of our study. First, this research contributes to the literature of governance by examining another aspect of governance based on transparency governance. Second, it contributes to the literature of the disclosure by focusing on the disclosure of corporate governance. Moreover, this study examines the relationship between foreign ownership and disclosure on corporate governance. A relationship that has been highlighted by several studies without empirical testing.Nonetheless, our study is limited by the unavailability of all the annual reports, which has limited our sample. Then, the small number of observations may reduce the generalization of results. Besides, there are other statistical limitations. In addition, the traditional statistical techniques suffer from certain limitations such as inability to model the non-linear relationship between the inputs and outputs and the need to check the distributional assumptions such as normality[45].Finally, we can explain the differences that exist between this study and other studies analyzing the same subject in other contexts by focusing on economic, political and cultural factors that specify each country. Even in the Tunisian context, which is undergoing political change, the results of this type of analysis may differ in the future. Actually, terms of transparency and good governance are frequently used in a national context as well as the international one. Indeed, the 2008 economic crisis has not fully recovered, then, the world might face a new crisis caused by the debts of some European countries. As a result, future research can focus on the analysis of the effects of cultural and political determinants on corporate governance around the world. Awareness of the impact of corporate governance on financial stability in times of crises, even those policies [43], and the effect of corporate governance in attracting foreign capital, regulators in emerging countries in general must try to improve the governance and transparency in the companies.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML