-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2013; 2(2): 82-88
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20130202.05
Antecedents of Internal Audit Effectiveness: A Moderating Effect of Effective Audit Committee at Local Government Level in Nigeria
Mu’azu Saidu Badara 1, Siti Zabedah Saidin 2
1Student in Accounting, Universiti Utara Malaysia
2Senior Lecturer Universiti Utara Malaysia School of Accountancy, College of Business Universiti Utara Malaysia
Correspondence to: Mu’azu Saidu Badara , Student in Accounting, Universiti Utara Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Research on internal audit effectiveness is an important avenue that will improve the existing conditions of internal audit at different organization particularly at local government level and thereby assist toward objective achievement of such organization. Therefore, the aim of this paper is to examine the antecedents of internal audit effectiveness: a moderating effect of effective audit committee at local government in Nigeria. The paper is a literature review paper and it is ongoing PhD thesis of the researcher.
Keywords: Antecedent of Internal Audit Effectiveness, Effective Audit Committee, Local Government in Nigeria
Cite this paper: Mu’azu Saidu Badara , Siti Zabedah Saidin , Antecedents of Internal Audit Effectiveness: A Moderating Effect of Effective Audit Committee at Local Government Level in Nigeria, International Journal of Finance and Accounting, Vol. 2 No. 2, 2013, pp. 82-88. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20130202.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Internal audit has become an unavoidable control mechanism in both public and private sectors (Cohen & Sayag, 2010). Therefore it is the right time to seriously consider the issue of internal audit (Sumritsakun & Ussahawanitchakit, 2009), particularly at local government in order to contribute toward their improvement. Internal audit effectiveness is the ability of the internal auditors to achieve established objective within the organization. In effect, such objective should be stated in clear terms and the means for achieving such objectives should also be provided (Dittenhoper, 2001)Organizations with effective and efficient internal audit function are more than those that have not such a function to detect fraud within their organizations (Corama, et al 2006; Omar & Abu Bakar, 2012; Radu, 2012). Therefore, there is need for the internal audit to be effective so as to create improvement in the government parastatals (Unegbu & Kida, 2011). Hence, internal audit needs to be effective particularly at local government in order to assist in meeting local government objectives particularly in Nigeria.In Nigeria, research has showed that the internal audit at local government level are not effective (Adeyemi, et al, 2012; Ebimobowei & Kereotu, 2011; Kuta, 2008; Kwambo, 2009; Musa, 2012). In line with this, Arena and Azzone (2010), Cohen and Sayag (2010), Chaveerug (2011) and Mihret et al, (2010) emphasize the need for future studies to empirically examine the factors that influence internal audit effectiveness and the possible interactions among them. Consequently, literature has also showed that antecedents of internal audit effectiveness and their possible interactions have not been fully examined (Mihret et al, 2010). Similarly, it is also interesting to focus on the model that will lead to the strength of internal audit effectiveness (Aguolu, 2009), likewise, Johnsen and Vakkuri (2001) noted that local government auditing has been less studied and reported in the literature. In addition, Arena and Azzone (2010), Cohen and Sayag (2010), Mihret et al (2010) and Theofanis et al (2011) recommend that different variables, standard and construct can be used toward determining the internal audit effectiveness. In view of the above issues, the researcher intends to carry out research on the antecedents of internal audit effectiveness: A moderating effect of effective audit committee at local government level in Nigeria. Section two of the paper present the literature review, section three provide research framework and conclusion.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Internal Audit Effectiveness
- The issues of internal audit effectiveness are indispensable because it creates improvement in the government ministries (Unegbu & Kida, 2011). A program can be seen as effective if its outcome goes along with its objectives (Ahmad et al, 2009; Ussahawanitchakit & Intakhan, 2011). IIA (2010) defined internal audit effectiveness “as the degree (including quality) to which established objectives are achieved. The objectives of an internal audit for every organization are depend upon the goals set out by the management of the organization (Pungas, 2003) as such, the objective of internal audit in local government should also goes a long with the set up goals by the management of the particular councils, additionally, the degree of internal audit effectiveness tends to vary within organizational level as well as country (Al-Twaijry et al., 2003). This mean the internal audit effectiveness can also vary within the local levels. Several studies have been conducted on internal audit effectiveness, (Aguolu, 2009; Ahmad, et al 2009; Arena & Azzone 2010; Cohen & Sayag, 2010; Chaveerug , 2011; Dominic & Nonna, 2011; Feizizadeh, 2012; Intakhan & Ussahawanitchakit, 2010; Kuta, 2008; Mihret & Yismaw, 2007; Mihret et al 2010; Omar & Abu Bakar, 2012; Theofanis, et al 2011; Unegbu & Kida, 2011; Ussahawanitchakit & Intakhan, 2011). None of these studies consider the propose antecedent in determining the internal audit effectiveness at local government particularly in Nigeria. This research work extends the prior research by examining the antecedent of internal audit effectiveness: A moderating effect of effective audit committee at local government level in Nigeria.
2.2. Effective Internal Control System
- Glance (2006) provided that internal control system refers to “the systems, processes and procedures that local government council establishes in order to ensure that it’s established objectives are met”. In the same vein, internal control system serves as a process that guides an organization towards achieving its established objectives (Jokipii 2010; Vijayakumar & Nagaraja, 2012). Therefore, all government ministries and agencies should improve the effectiveness of internal control system, internal audit function and organization commitment because they improve good governance (Eko & Hariyanto, 2011). Baltaci and Yilmaz (2006) observed that establishing internal control system and audit practices at the local government level has received little or no attention. And without such establishment, detection and control of misconduct in the local government would not be possible. Therefore, it is good for local government to improve the effectiveness of their internal control system in order to enhance the effectiveness of internal audit particularly in Nigeria. Similarly, Baltaci and Yilmaz (2006) discovered some of the world countries that has weak internal control system at their local government level which include; Argentina, Bosnia, China, Columbia, India-Karnataka State, Indonesia and Philippines. This is similar to the study of (Adeyime, 2012; Kuta, 2008; Kwambo 2009; Musa, 2012) which also found that local government in Nigeria has weak internal control system, which needed to be improve. Some of the studies that have been conducted on internal control system are (Aikins 2011; Baltaci & Yilmaz, 2006; Eko & Hariyanto, 2011; Kwanbo, 2009; Nilniyom & Chanthinok, 2011). The studies did not examine the relationship between effective internal control systems with internal audit effectiveness particularly at local government in Nigeria. In this vein, Fond and You (2010), Jokipii (2010) recommend that more research in the area of effective internal control system is required. Therefore, this research extends the previous research by examining the relationship between effective internal control system and internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.
2.3. Risk Management
- In recent years risk management has become an agenda in both public and private sectors (Anuntaakalakul 2010; Wood, 2009). This is because organization that experience high level of risk, is possible for them to lose the achievement of their organizational objective (Sumritsakun & Ussahawanitchakit, 2009). Therefore, local government particularly in Nigeria should improve the effectiveness of their risk management, because effective risk management enables the achievement of organizational objective (Gordon et al, 2009). Risk management is the identification of risks associated with activities and establishing means to respond to the risk by putting into practice all the necessary controls that will reduce the possibility of the occurrences or the consequences of such risk (Vasile, Croitoru & Mitran, 2012). Risk management serves as a powerful tool for local government management and local authorities are required to make an annual assessment of their risk management in order to determine their effectiveness in practice (Crawford, & Stein, 2004).Most of the previous research that has been conducted on risk management focuses attention on the role of internal audit in risk management for example (Coetzee & Fourie, 2009; Sobel, 2011; Schneider, Sheikh& Simione, 2011; Vasile, CroitoruI & Mitran, 2012). Only few consider the impact of enterprise risk management on the internal audit function for example (Beasley, et al, 2006). They ignore to examine such relationship with internal audit effectiveness at local government level. Some few studies measured risk management with other variables (Anuntaakalakul, 2010; Wood, 2009). Despite the above studies, Beasley et al, (2006) recommend that research should examine the relationship between of enterprise risk management and internal audit. Also, Wood (2009) observed that there is still need for a lot of research to be done on risk management. Therefore, this study extends the previous by considering the relationship between risk management and internal audit effectiveness at local government in Nigeria.
2.4. Audit Experience
- Recently, research in the area of professional experience in accounting and auditing are increasing (Gaballa & Ning, 2011). Audit experience refers to different kind of knowledge and skills which the auditors obtain as a result length of tenure of the job practice in the auditing professions. Auditors are required to utilize their experience toward achieving effectiveness (Intakhan & Ussahawanitchakit, 2010). Some of the recent studies that have been conducted on audit experience some (Asare et al, 2009; Chi et al, 2010; Gaballa & Ning, 2011; Intakhan & Ussahawanitchakit 2010; Ussahawanitchakit, 2012; Ussahawanitchakit & Intakhan, 2011; Wang et al, 2012). However, despite the above studies, none of the studies examine the relationship between audit experiences and the internal audit effectiveness particularly at local government level. Consequently, Intakhan and Ussahawanitchakit (2010) and Ussahawanitchakit (2012) recommend that future research is needed to conduct research on audit experience. This research extends the previous research by examining the relationship between audit experience and internal audit effectiveness at local government in Nigeria.
2.5. Cooperation Between Internal and External Auditors
- Research in cooperation between internal and external auditors are increased in last few decades (Fowzia, 2010; Mihret & Admassu 2011), effective and efficient integration between the two auditors lead to a higher quality of auditing (Munro & Stewart, 2011). Therefore, such cooperation should play an important role in the aspect of internal audit effectiveness at local level. English dictionary defined cooperation as the act of working or acting together in order to achieve common goals. In this context, internal and external auditors may have several common objectives which serve a basis for their cooperation (Al-Twaijry, Brierley & Gwilliam, 2004). Advantages of the cooperation relationship between the two auditors include; fee reduction, improved client-relationship and better understanding by the external auditor of the organization operations. Also, internal audit department can benefit from the knowledge of the external audit concerning other similar issues in term of knowledge and other auditing activities (Fowzia, 2010). Some of the recent studies that examine cooperation between internal and external audit (Desai et al, 2010; Fowzia, 2010; Mihret & Admassu, 2011; Munro & Stewart, 2011). Despite the above studies, future research should look at the impact of cooperation between internal and external audit in developing countries because most of the previous researches on this topic were based on the developed world (Mihret & Admassu, 2011; Munro & Stewart, 2011). Therefore, this study extend the previous studies by examining such relationship at local government in Nigeria.
2.6. Performance Measurement
- Performance measurements in internal audit are undoubtedly a crucial topic for practitioners (Ziegenfuss 2000). In this regard, recently performance measurement received reasonable attention in internal auditing because it constitutes one of the most essential managerial functions (Rupsys & Boguslauskas, 2007). Therefore, consideration has to be given in measuring the performance of internal audit, particularly at local government level in order to improve their effectiveness. In Nigeria, performance of public service whether at Federal, State or Local government is measured with the objective of ensuring efficiency in the government activities (Dogarawa, 2011). And well structured performance measurement system could be use toward improving organizations strategic goals effectively (Kaplan, & Norton, 1996). Performance measurement refers to the process of determining the extent level of achievement of establish objective by internal auditors. It’s important to consider performance measurement of internal auditors in order to determine their effectiveness (Feizizadeh, 2012). However, Amirkhanyan (2011) emphasize that some performance measures are more effective than others. This indicates that performance measurement varies even in term of effectiveness. Some of the recent studies that have been conducted on performance measurement are; (Amirkhanyan, 2011; Odhiambo et al, 2012; Dogarawa, 2011; Rupsys & Boguslauskas, 2007).Therefore, it would be importance to conduct a research on performance measurement in the public sector (Buhovac & Groff, 2012). In view of this, this study extends previous studies by examining the relationship between performance measurement and internal audit effectiveness particularly at local government in Nigeria.
2.7. Effective Audit Committee
- One of the essential elements in determining the effectiveness of internal audit is the reporting structure which requires direct reporting to the audit committee (Krishnamoorthy, 2008; Owolabi & Dada, 2011). Recently, concerned over the audit committees as one of the component of corporate governance has received tremendous attention especially when considering that the member constitute people with high caliber that have some degree of independence, qualification, experience and knowledge (Alkdai & Hanefah, 2012; Nimer et al, 2012; Owolabi & Dada, 2011; Quigley 2012). Owolabi and Dada (2011) emphasize that effective audit committee will definitely enhance reliable, dependable, effective and efficient corporate governance, this is because it establishment in the corporate governance in Nigeria dated 1990 has lead to reduction of corporate ineffectiveness. Effective audit committee refers to the ability of the audit committee to achieve established objective. Therefore, audit committee is effective when they meet the goals for which they were established (David, 2009). Similarly, audit Committees have the responsibilities of measuring performance of the internal audit function, appointment and dismissal of the heads of internal audit, recommending the appointment and dismissal of external auditors, support and promote the audit function within various organizations such as independence and objectivity (Davies, 2009). Therefore, audit committee at local level particularly in Nigeria should ensure that their effectiveness has improved internal audit effectiveness. Some of the recent studies that has been conducted on the direct relationship of effective audit committee focusing on the impact of the audit committee on financial reporting of companies and audit fees, (Akarak & Ussahawanitchakit; 2010; Alkdai & Hanefah, 2012; Nimer et al, 2012).
2.7.1. Effective Audit Committee as Moderating Variable
- Moderating variables are variables that affect the connection between independent variable and dependent variable (Bennett, 2000). However, research has showed that moderating variables perform the function of independent variable by strengthen other independent variables toward achieving the dependent variables (Bennett, 2000; Baron & Kenny 1986). For introducing moderating variable, Baron and Kenny (1986) noted that moderator variables are mostly introduced when there is an unexpectedly weak or inconsistent relation between independent and dependent variable. While Russ and McNeilly (1995) affirmed that research on individual moderating variable it appears to be of great important from managerial point of view. Nevertheless, Bennett (2000) emphasized that decision about whether a variable should serve as moderating variable or not should be based on theory and the conceptual framework that guides the research. In line with this, the theory that guides the research framework is contingency theory. Hence, effective audit committee is proposed as the moderating variables of the antecedent of internal audit effectiveness. Because it is important to empirically examine the moderating effects of effective audit committee (Sharma, et al, 2011). Some of the recent studies that have been conducted on the moderating effect of effective audit committee, gives concerned at company’s level, ignore such effect on public sectors particularly local level in Nigeria (Kamarudin et al, 2012; Krishnamoorthy 2008; Sharma et al, 2011). This study extends the previous studies by examining the antecedents of internal audit effectiveness: A moderating effect of effective audit committee at local government level in Nigeria.
2.8. Theoretical Framework
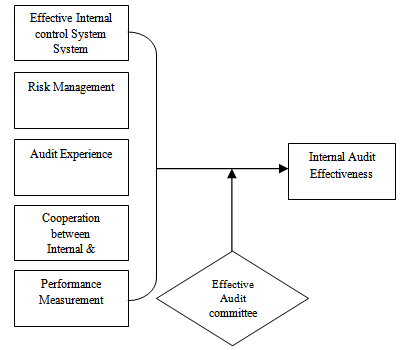 Proposition P1 Effective internal control system seems to have a positive relationship with internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.P2 Risk management has positive relationship with internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.P3 Audit experience has a positive relationship with internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.P4 Cooperation between internal and external auditors seem to have impact on the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in NigeriaP5 Performance measurement has positive relationship on internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.P6 Effective audit committee seem to moderate the relationship between effective internal control system and the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria. P7 Effective audit committee seem to moderate the relationship between risk management and the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria. P8 Effective audit committee seem to moderate the relationship between audit experience and the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria. P9 Effective audit committee seem to moderate the relationship between cooperation between internal and external auditors and the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria. P10 Effective audit committee seem to moderate the relationship between performance measurement and the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.Underpinning TheoryContingency theory is known as one of those theory that are usually been used recently in management accounting and auditing research (Abushaiba & Zainuddin, 2012; Valanciene & Gimzauskiene, 2009) though use of theory may have different effect, and equally it effectiveness depend upon the stage/or field that is been proposed (Drazin & Van de Ven, 1985). Contingency theory enables a researcher to systematically introduce factors to explain or predict expected phenomena (Umanath, 2003). The theory hypothesize a conditional relationship between two or more independent variables with a dependent variable and subject it to an empirical test (Drazin & Van de Ven, 1985) it’s also contributes in the identification of relationship that is complex among variables i.e. examining moderating or mediating effect of variables (Heo & Han, 2003). In line with the above, this theory is applied in the context of internal audit effectiveness which depend upon the contingent variables such as effective audit committee, effective internal control system, risk management, audit experience, cooperation between internal and external auditors and performance measurement.
Proposition P1 Effective internal control system seems to have a positive relationship with internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.P2 Risk management has positive relationship with internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.P3 Audit experience has a positive relationship with internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.P4 Cooperation between internal and external auditors seem to have impact on the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in NigeriaP5 Performance measurement has positive relationship on internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.P6 Effective audit committee seem to moderate the relationship between effective internal control system and the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria. P7 Effective audit committee seem to moderate the relationship between risk management and the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria. P8 Effective audit committee seem to moderate the relationship between audit experience and the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria. P9 Effective audit committee seem to moderate the relationship between cooperation between internal and external auditors and the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria. P10 Effective audit committee seem to moderate the relationship between performance measurement and the internal audit effectiveness at local government level in Nigeria.Underpinning TheoryContingency theory is known as one of those theory that are usually been used recently in management accounting and auditing research (Abushaiba & Zainuddin, 2012; Valanciene & Gimzauskiene, 2009) though use of theory may have different effect, and equally it effectiveness depend upon the stage/or field that is been proposed (Drazin & Van de Ven, 1985). Contingency theory enables a researcher to systematically introduce factors to explain or predict expected phenomena (Umanath, 2003). The theory hypothesize a conditional relationship between two or more independent variables with a dependent variable and subject it to an empirical test (Drazin & Van de Ven, 1985) it’s also contributes in the identification of relationship that is complex among variables i.e. examining moderating or mediating effect of variables (Heo & Han, 2003). In line with the above, this theory is applied in the context of internal audit effectiveness which depend upon the contingent variables such as effective audit committee, effective internal control system, risk management, audit experience, cooperation between internal and external auditors and performance measurement.3. Conclusions
- This research examines antecedents of internal audit effectiveness: a moderating effect of effective audit committee in local government in Nigeria. The research is constraint to those variables identified in literature review and it is at local government level. However, despite the limitation of the paper, the study is the first study to be conducted on the antecedents of internal audit effectiveness; a moderating effect of effective audit committee at local government in Nigeria, the research contribute to the existing literature on internal audit at local government as noted that local government auditing has been less studied and reported in the literature (Johnsen & Vakkuri, 2001), it’s contribute to body of knowledge by extending the existing literature on the internal audit effectiveness through determining the effectiveness of internal audit at local level using the variables identified in literature review and also contribute toward improving the internal audit effectiveness at local government particularly in Nigeria. Similarly, it’s contribute on the internal audit effectiveness at local level since most of the previous studies fail to develop a model showing the relation between risk management and internal audit effectiveness at local level. Finally, this paper is ongoing PhD thesis of the researcher.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML