-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2013; 2(1): 30-36
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20130201.05
Rethinking Banks Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in Nigeria
Iorpev Luper
Department of Accounting, Benue State University, Makurdi, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Iorpev Luper , Department of Accounting, Benue State University, Makurdi, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The Nigerian economy is faced with a multiplicity of challenges ranging from high unemployment rate, poverty, corruption, youth restiveness, security and political crises which threatens investments, economic growth and the goal of the Nigerian banks to be the financial hub of Africa in the year 2020 as well as the nation’s goal to be one among the top 20 largest economies in the world by the year 2020. Since banks provide linkages to all sectors of the economy, there is need for the Nigerian banks to rethink Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in all the key sectors (such as education, power, health, agriculture, and small and medium-sized enterprises) of the economy. This study examines how socially responsible is the Nigerian banks in addressing these challenges and enhancing the economic growth of Nigeria through Small and Medium Scale Enterprises (SMEs) financing, which is one of the key sector that can drive the economic growth of the nation. Using the data on commercial banks loans to SMEs provided by the CBN statistical bulletin for the period of ten years (from 2001-2010). The results of the descriptive statistics and sample t-test shows that, bank consolidation in Nigeria has led to a decline in SMEs financing to less than one percent on average in the study period, and there is no significant improvement in SMEs financing in Nigeria before and after bank consolidation. This clearly indicates that Nigerian Banks are not committed to their CSR (economic responsibilities) of financing to SMEs which is critical in mitigating these economic challenges and enhancing economic growth. The study recommends among others that, there should be further diversification in SMEs financing. In order to improve the CSR of Nigerian banks, there is also the need for banks to help in the training of SMEs owners as a matter of necessity on the need to maintain proper accounting records in the country.
Keywords: Corporate Social Responsibility, Banking Reforms, Smes Financing, Economic Challenges of Nigeria, Nigerian Economic Growth
Cite this paper: Iorpev Luper , Rethinking Banks Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in Nigeria, International Journal of Finance and Accounting, Vol. 2 No. 1, 2013, pp. 30-36. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20130201.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The financial sector and banks in particular performs pivotal roles toward the sustainability and economic growth of any nation. Banks play these important role of promoting economic growth and development through the process of intermediation, which many economists have acknowledged that the financial system, with banks as its major component, provide linkages for the different sectors of the economy (1,32). According to[46] the effectiveness and efficiency of banks in performing these roles, particularly the intermediation between the surplus and deficit unit of the economy, depends largely on the level of development of the financial system. Thus, to ensure that the banking sector is sound, stable and efficient, the sector has witnessed a number of consolidations globally ( 28,54,46,49).In order to strengthen the banking system and improve the operational efficiency of banks in Nigeria among other Things , at the time, banks in the country were generally weak and inefficient the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) started banking sector reforms. Reference[53] argued that, the bank consolidation reform was designed to ensure a diversified, strong and reliable banking sector, which will ensure the safety of depositors’ money, play active developmental roles in the Nigerian economy, and be competent and competitive players in the African regional and global financial system. CBN on July 6th in 2004 announced the recapitalization of banks capital base from
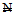 2 billion (US $ 0.0166 billion) to a minimum paid up capital of
2 billion (US $ 0.0166 billion) to a minimum paid up capital of 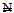 25 billion (US $0.2 billion) with a deadline of 31st December, 2005. To meet the
25 billion (US $0.2 billion) with a deadline of 31st December, 2005. To meet the 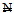 25 billion capitalizations, banks were allowed to merge, consolidate or even acquire other banks[45].This reduced the number of banks from 89 to 25 in 2006 and later 24 through market-induced merger and acquisition[21]. This was the outcome of the first phase of the most extensive and intensive banking reforms in post-independence Nigeria[2]. The reforms undertaken in the banking sector were influenced by the quest for a sounder banking industry, globalization of operations, technological innovations and the adaptation of supervisory and prudential requirements that conform to international standards[28]. This means that, when the banks are strong they will perform the role of facilitating the economic growth of any nation, and Nigeria in particular, more effectively.The banking sector consolidation worldwide and Nigeria in particular, had brought significant changes in the business of banking in terms of efficiency of operation, competition, innovation, technology (20, 39, 50, 54) and increased the awareness and demand of the Nigerian public about social and environmental performance of banks. Hence making corporate social responsibility a thing of continuous quest and that business success does not depend solely on maximizing profits, but on protecting the environment and promoting Banks social responsibility. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a business process that a company adopts beyond its legal obligations in order to create added economic, social and environmental value to society and to minimize potential adverse effects from business activities, which includes interactions with suppliers, employees, consumers and communities in general. Reference[9] argued that the business of banking operates on trust and the Nigerian economy is a stakeholder in the banking system, since it is considered to be the community or environment where banks exist. Thereby making banks CSR an issue to be emphasized. This view is held by[51] that Companies do not function in isolation from the society around them. In fact, their ability to compete, perform their tasks effectively and to be profitable depends heavily on the circumstances of the location where they operate. Since no business can effectively thrive in an environment of chaos.The Nigerian economy today is faced with multiplicity of challenges ranging from high unemployment rate, high poverty (which stood at 69 percent of the 163 million population of Nigeria in 2010,[41] corruption, youth restiveness, political crises, security challenges (which has great effect on investments[3] and economic growth among others). These problems are generally seen as social issues, thus the more social improvements relates to a company’s business, the more it leads to economic benefits as well[51]. Since the role of banks is to enhance economic growth and with all these challenges facing the economy thereby threatening economic growth at this critical time that the Nigerian banks want to be the financial hub of Africa in the year 2020 and the nation is prepared to be one among the top 20 largest economies in the world by the year 2020. Even if the banks are socially responsible to an extent, there is need for the Nigerian banks to rethink both where (that is sector(s) and location) they focus their CSR and how they go about their CSR as no business can thrive in chaos environment. Therefore, Nigerian banks need to rethink CSR in all key sectors (such as education, power, health, agriculture, and small and medium-sized enterprises) of the economy as this will help them to look as being good corporate citizen. Consequently, earn trust, be profitable, assist in reducing poverty and create jobs thereby mitigating the security problem at the same time contributing to the economic growth of the nation. The small and medium-sized enterprise (SMEs) is one key area that can help in curbing these challenges in order to enhance economic growth and sustainability of the nation. According to[21] SMEs are critical to the development of any economy, as they possess great potentials for employment generation, improvement of local technology, output diversification, development of indigenous entrepreneurship and forward integration with large-scale industries. Reference[36] stressed that, SMEs are the engine room for economic growth. According to[9] SMEs may look small or in-consequential but are actually the foundation of any economically stable nation. However, the unfriendly business environment, poor funding, low managerial skills and lack of access to modern technology is affecting SMEs to achieve these objectives in Nigeria; of all the challenges shortage of finance occupies a very central position[21]. SMEs financing is critical in addressing the multiple challenges of the Nigerian economy that are threatening its economic growth today. This paper seeks to answer the question of how socially responsible is the Nigerian banking system to the recurrent problem of SMEs financing in Nigeria. More so, this study is important because it will add to the existing literature of banks CSR in particular on how socially responsible is the Nigerian banks in addressing the challenges and enhancing the economic growth of Nigeria using SMEs financing in Nigeria, which is one of the key sector that can drive the economic growth of any nation. The remainder of this paper is as follows: Section two (2) takes a brief review of related literature; Section three (3) is the methodology; Section four (4) discusses the results of the study; Conclusion and policy recommendations are presented in section five (5).
25 billion capitalizations, banks were allowed to merge, consolidate or even acquire other banks[45].This reduced the number of banks from 89 to 25 in 2006 and later 24 through market-induced merger and acquisition[21]. This was the outcome of the first phase of the most extensive and intensive banking reforms in post-independence Nigeria[2]. The reforms undertaken in the banking sector were influenced by the quest for a sounder banking industry, globalization of operations, technological innovations and the adaptation of supervisory and prudential requirements that conform to international standards[28]. This means that, when the banks are strong they will perform the role of facilitating the economic growth of any nation, and Nigeria in particular, more effectively.The banking sector consolidation worldwide and Nigeria in particular, had brought significant changes in the business of banking in terms of efficiency of operation, competition, innovation, technology (20, 39, 50, 54) and increased the awareness and demand of the Nigerian public about social and environmental performance of banks. Hence making corporate social responsibility a thing of continuous quest and that business success does not depend solely on maximizing profits, but on protecting the environment and promoting Banks social responsibility. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a business process that a company adopts beyond its legal obligations in order to create added economic, social and environmental value to society and to minimize potential adverse effects from business activities, which includes interactions with suppliers, employees, consumers and communities in general. Reference[9] argued that the business of banking operates on trust and the Nigerian economy is a stakeholder in the banking system, since it is considered to be the community or environment where banks exist. Thereby making banks CSR an issue to be emphasized. This view is held by[51] that Companies do not function in isolation from the society around them. In fact, their ability to compete, perform their tasks effectively and to be profitable depends heavily on the circumstances of the location where they operate. Since no business can effectively thrive in an environment of chaos.The Nigerian economy today is faced with multiplicity of challenges ranging from high unemployment rate, high poverty (which stood at 69 percent of the 163 million population of Nigeria in 2010,[41] corruption, youth restiveness, political crises, security challenges (which has great effect on investments[3] and economic growth among others). These problems are generally seen as social issues, thus the more social improvements relates to a company’s business, the more it leads to economic benefits as well[51]. Since the role of banks is to enhance economic growth and with all these challenges facing the economy thereby threatening economic growth at this critical time that the Nigerian banks want to be the financial hub of Africa in the year 2020 and the nation is prepared to be one among the top 20 largest economies in the world by the year 2020. Even if the banks are socially responsible to an extent, there is need for the Nigerian banks to rethink both where (that is sector(s) and location) they focus their CSR and how they go about their CSR as no business can thrive in chaos environment. Therefore, Nigerian banks need to rethink CSR in all key sectors (such as education, power, health, agriculture, and small and medium-sized enterprises) of the economy as this will help them to look as being good corporate citizen. Consequently, earn trust, be profitable, assist in reducing poverty and create jobs thereby mitigating the security problem at the same time contributing to the economic growth of the nation. The small and medium-sized enterprise (SMEs) is one key area that can help in curbing these challenges in order to enhance economic growth and sustainability of the nation. According to[21] SMEs are critical to the development of any economy, as they possess great potentials for employment generation, improvement of local technology, output diversification, development of indigenous entrepreneurship and forward integration with large-scale industries. Reference[36] stressed that, SMEs are the engine room for economic growth. According to[9] SMEs may look small or in-consequential but are actually the foundation of any economically stable nation. However, the unfriendly business environment, poor funding, low managerial skills and lack of access to modern technology is affecting SMEs to achieve these objectives in Nigeria; of all the challenges shortage of finance occupies a very central position[21]. SMEs financing is critical in addressing the multiple challenges of the Nigerian economy that are threatening its economic growth today. This paper seeks to answer the question of how socially responsible is the Nigerian banking system to the recurrent problem of SMEs financing in Nigeria. More so, this study is important because it will add to the existing literature of banks CSR in particular on how socially responsible is the Nigerian banks in addressing the challenges and enhancing the economic growth of Nigeria using SMEs financing in Nigeria, which is one of the key sector that can drive the economic growth of any nation. The remainder of this paper is as follows: Section two (2) takes a brief review of related literature; Section three (3) is the methodology; Section four (4) discusses the results of the study; Conclusion and policy recommendations are presented in section five (5).2. Literature Review
- This section reviews the literature that is relevant to the problem under investigation. The concept of corporate social responsibility (CSR) and Banks CSR to Small and Medium Scale Enterprises (SMEs) in Nigeria will be reviewed.
2.1. Concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- Corporate Social responsibility (CSR) is a genuine commitment by organizations to contribute their quarter to the sustainable development and to improve the quality of life in the work place and in the society at large. According to[37] CSR is about operating in a manner that meets or exceeds the ethical, legal, commercial, and public expectation that the society has of a business. This definition expect business decision to not only focus on profitability but should also be concerned about ethical values, legal requirement as well as respect for people, communities and environment[34]. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is the obligation of the decision makers in corporate organizations to take actions, which protect and improve the welfare of the entire society along with their own interest[10,24,30, 56]. There are several key issues in this definition. One is that social responsibility is an obligation, for which business should be held accountable. Another key issue is the responsibility of the business to protect the society’s welfare in terms of not polluting the environment, not discriminating, not producing harmful products among others. Finally, it must improve the society’s welfare by creating positive benefits for society. These include supporting charitable causes, culture and arts, educational institutions and other community projects and programmes which improve the quality of life in general[8].Reference[18] explain what CSR is by presenting a pyramid of CSR, which shows four stages namely economic responsibilities, legal responsibilities, ethical responsibilities and philanthropic responsibilities. Economic responsibilities mean that businesses have a duty to: produce goods and services which the society requires, goods and services which are sold to the society at a fair price, goods and services which would provide profits adequate to ensure the perpetuation and the growth of the business, and which will adequately reward investors for their risk[19]. The economic responsibilities stage form the foundation or basis of the Carroll’s CSR pyramid. According to[18] Legal responsibilities indicate that the goal of profit maximization by businesses should be approached within the confines of written laws. This entails that the law should be seen as a minimal standards of acceptable conduct in the eye of the society.The third stage of the Carroll’s pyramid reflects the ethical responsibilities of the businesses. According to[34] in the most elementary sense, business ethics represents the set of moral principles or values guiding human behaviour within the economic setting. The ethical beheviour is generally on a level above the law[19]. This implies that the law does not always address all the realms in which ethical questions may be raised. This explained why business owners or managers who excel at meeting their ethical responsibilities are those who embrace emerging social values, even though the law does not yet require it or them to do it. The final stage of Carroll’s pyramid is the Philanthropic responsibilities which expect businesses to be good corporate citizens. This means that business should participate in initiatives or programmes such as contribution to charities, social infrastructure development initiative as well as education and health care programmes among others that promote human welfare or goodwill. Reference[17] asserts that such activities are geared towards external stakeholder group.The arguments offered in favour of business assuming social responsibilities are that: Business is a creation of the society and so it should respond to the demands of the society because if the society does not exist, business will also not exit; CSR programmes create a favourable public image and businesses can retain the needed credibility with the public if it performs its social obligations; the long-term self-interests of the business are best served when business assumes CSR. Also, being social responsible is the moral and right thing to do and business activity does not promote immorality. It is not a moral, and hence the social values cannot be isolated from economic activities; for the avoidance of excessive government regulations and that laws cannot be passed for all circumstances therefore business must resume responsibility to maintain an orderly society[5, 8].According to[8] the arguments against CSR are that the primary responsibility of business is profit maximization and that there is one and only one social responsibility of business; that is, to use its resources and engage in activities designed to increase its profit; CSR will result to conflicting considerations: A business manager will be guided by two considerations, namely private market mechanism and social responsibilities, which are opposite to each other. Also CSR may lead to arbitrary power of business managers if they are given the freedom to use organizational resources for the welfare of the society. They should have no right to interfere with the external environment of the business. More so critics of CSR assert that corporate organizations should have no relationship with welfare schemes because it is the sole responsibility of the government of the land to adopt schemes and measures for the upliftment of the weaker sections of the society. In view of these arguments, it is relevant to observe that it will be beneficial to business organizations to integrate corporate social responsibility into their activities and philosophy[8]. More so, the role of banks is to enhance economic growth among others and being socially responsible to critical sectors of the economy such as SMEs, education, power and so on will help enhance economic growth. Therefore, CSR is the other side of the same coin for banks.
2.2. Banks CSR to Small and Medium Scale Enterprises (SMEs) in Nigeria
- SMEs is any enterprise with a total capital employed of not less than N1.5 million, but not exceeding N 200 million ( including working capital but excluding cost of land ) and with the staff strength of not less than 10 and not more than 300 workers (45,9). SMEs all over the world play important role in the process of industrialization, economic growth, and sustainable development of any economy[6]. According to[21] SMEs are critical to the development of any economy, as they possess great potentials for employment generation, improvement of local technology, output diversification, development of indigenous entrepreneurship and forward integration with large-scale industries. Reference[36] stressed that, SMEs are the engine room for economic growth.In Nigeria, there has been gross under performance of SMEs sub- sector and this has undermined its contribution to economic growth and development. The major challenges of SMEs in the country are namely: unfriendly business environment, poor funding, low managerial skills and lack of access to modern technology. Among these, shortage of finance occupies a very central position[21].The banks, which remain the major source of finance to SMEs world over in most instances are unwilling to grant credit to SMEs. This is due to the perceived risk and uncertainties associated with SMEs. In Nigeria, the poor fragile economic environment and absence of requisite infrastructure has rendered SMEs practice costly and inefficient, thereby worsening their credit competitiveness [21]. This is an indication for the steady decrease in SMEs financing in the country over the years but CSR pyramid shows that business (banks) have an obligations to produce goods and services which the society require and which would produce profits adequate to ensure the perpetuation and growth of business (economic responsibilities) among others. SMEs financing by banks holds all these qualities.The CBN[22] statistics show that, banks loan and advances (which is CSR-Economic responsibilities of banks) to SMEs have been on the decline side over the years. The statistics indicates that, commercial banks loans to SMEs as a percentage of total credit decreased from 48.79 % in 1992 to 32.18% in 1993 and to 22.19% in 1994. The trend slightly increased to 22.94% in 1995 and 25.00% in 1996. There was a sharp decrease from 25.00% to 16.96 % in 1997 and to 15.49% in 1998.The decreased continued until it reached 0.17% in 2009 and 0.15% in 2010. Similarly, merchant banks loans to SMEs as a percentage of total credits reduced from 31.2% in 1992 to 9.0 % in 2000[9]. A careful look at CBN statistics on commercial bank financing to SMEs reveal that, before 1996 total credit to SMEs did not fall below 20 % of their overall total credit. Commercial banks were operating this period under a stipulated guideline that required them to grant credit not less than 20% of their total credit to SMEs wholly owned by Nigerians. This means they were adhering to this guideline as none of their total credit fall below 20% when the policy was operational. However, this was abolished on 1st October, 1996[7]. Since then SMEs, credit has been on the decline[9]. This clearly shows that banks are not committed to its CSR (economic responsibilities - the foundation upon which all other CSR rests) by providing economic services (SMEs financing) which the Nigerian economy require to curb its present challenges and be one of the largest economy in the year 2020. To improve access to finance by SMEs, government and its agencies had established micro credit institution over the years namely: Nigerian Bank for Commerce and Industry (NBCI), and National Economic Reconstruction Fund (Nerfund). The Peoples Bank of Nigeria (PBN), the Community Banks (CB), and the Nigerian Export and Import Bank (NEXIM), and the liberalization of the banking sector, Micro Finance banks, and the Small and medium equity investment Scheme that is the bankers’ initiative, CBN N200 billion refinancing / restructuring of banks loans to Nigerian SMEs among others. At the global level, many economics like Canada and Croatia have acknowledged that SMEs are crucial for industrial restructuring and have formulated national SMEs financing policies, targeted at developing the sector[9]. This is to enable the sub-sector perform effectively and contribute to the economic growth of the nation.
3. Methodology
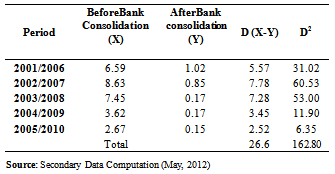
- This study adopts an ex-post facto research, design to examine how socially responsible is the Nigerian banking system to the recurrent problem of SMEs financing in Nigeria. Data from the Central Bank of Nigeria statistical Bulletin on loans and advances of Commercial banks to SMEs spanning for a period of 2001-2010 are collected. The period covered in this study is that of universal banking in Nigeria. The study used simple percentages and paired sample t-test statistics to analyze the data collected. The commercial bank loans to SMEs as percentage of its total credit from 2001-2005 was taken as a separate pair (X), which relates to the period before consolidation of banks in Nigeria. whereas banks loans to SMEs as percentage of its total credits for the period of 2006-2010 was taken as the second pair (Y) which relates to the period after consolidation of banks in Nigeria. Percentages was used to ascertain the extent of the changes to SMEs financing after consolidation; and the paired sample t-test statistics was statistically applied to test if there is a significance difference between SMEs financing by commercial bank before and after consolidation in Nigeria. The hypothesis for this study was stated in a null form thus; Ho1: There is no significant difference between SMEs financing by commercial bank before and after 2005 consolidation in Nigeria.
4. Data Presentation, Analysis and Discussion
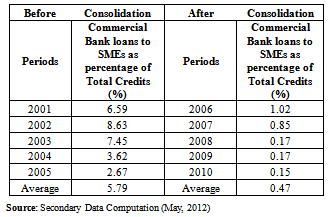
- The results presented below is based on the data collected from CBN statistical bulletin on the ratio of commercial banks loans to SMEs as percentage to total credits in Nigeria between 2001to 2010.Table 1 above indicates percentage of commercial banks loans to SMEs as percentage of total credits before and after consolidation in Nigeria. Table 1 show that the average credits to SMEs before Consolidation was 5.79% and 0.47% after consolidation. Meaning that the difference between before and after consolidation financing to SMEs by commercial bank decrease by 5.31% (i.e 5.78% - 0.47%) See Table 1 above. This represent 91.88% (5.79-0.47/5.79*100) decline in the total credit to SMEs by commercial banks in Nigeria after consolidation. This clearly indicates that Nigerian banks are not committed to their CSR- economic responsibilities ( which is the foundation of upon which all other CSR rest) of providing finance to SMEs, which are critical for mitigating the economic challenge in Nigeria and the engine of economic growth in Nigeria.
|
|
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
- This study seeks to answer the question of how socially responsible is the Nigerian banks. In particular on how socially responsible is the Nigerian banks in addressing the challenges and enhancing the economic growth of Nigeria using SMEs financing in Nigeria, which is one of the key sector that can drives the economic growth of any nation. The study findings indicates that banking sector reforms (consolidation) in Nigeria has led to a decline to SMEs financing to less than one percent (i.e 0.47%) on average, and there is no significant difference between SMEs financing by commercial bank before and after 2005 consolidation in Nigeria. This result challenge previous studies, which show that banks consolidation will not lead to any decrease in SMEs financing and have been supported by empirical findings in some economics. This suggests evidence that banking reforms (Consolidation) will lead to contraction in SMEs financing even in developing economics like Nigeria, and further lends credence to theories that show that consolidation will lead to reduction to SMEs financing. More so the findings clearly indicates that Nigerian banks are not committed to their CSR- economic responsibilities ( which is the foundation of upon which all other CSR rest) of providing finance to SMEs, which are critical for mitigating the economic challenge in Nigeria and the engine of economic growth of the Nation. The study recommends that, despite the relative stability in banking sector, due to Banking Sector Reforms, to improve the CSR of banks in Nigeria, further diversification in SMEs financing is desirable because of the steady decline in SMEs financing. This may be in form of improving the business condition of SMEs by creating more credit bureau supplying information on the solvency of firms. Banks should focus more on SMEs by conducting extensive market research to learn the needs of SMEs, training of entrepreneurs and also look at SMEs financing as providing service that the Nigerian society urgently need now to curb the challenges facing the country and the attainment of its goal of being the top 20 largest economy in the year 2020. The CBN should come up with a guarantee scheme for SMEs financing by banks in Nigeria. This will not only reduce the potential risk banks face by granting credits to SMEs but will in no small measure increase SMEs financing in Nigeria thereby making people to look at Nigerian banks as good corporate citizens.There is need for a code of CSR to be introduce by Central Banks of Nigeria and Federal ministry of Trade and Investment, which will provide guideline on the discharge of bank CSR , monitoring team to ensure compliance by banks and appropriate penalties for discouraging non- compliance. Finally, banks should help in training SMEs owners as a matter of necessity on the need to keep proper accounting records, financial statements or business plans so as to make it easier for banks, creditors and investors to assess the credit-worthiness of their proposals. This will not only reduce the problem of information asymmetry on SMEs but will improve SMEs financing in Nigeria.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- I appreciate all the comments of the delegates at the 2nd African Accounting and Finance Conference, held at NICON Luxury, Abuja-Nigeria were the paper was presented.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML