-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2012; 1(5): 120-130
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20120105.06
Anchoring Heuristic and the Estimation of Accounting and Financial Indicators
Marcos Roberto Luppe, Luiz Paulo Lopes Fávero
School of Economics, Business and Accounting, University of São Paulo
Correspondence to: Luiz Paulo Lopes Fávero, School of Economics, Business and Accounting, University of São Paulo.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The literature is unclear about how the perceptions that are involved with accounting judgment occur. The fundamental purpose of this article is to identify the effects of anchoring in the estimation of a balance sheet indicator to represent companies’ net profit. From this perspective, the dynamics of the decision-making process prompt the use of true or false reference points, suggestively called anchors. This study examines how an arbitrary number presented to someone may influence their judgment, regarding a company’s net profit, and the results provide evidence of the existence of anchoring bias in the estimation of this indicator. It’s believed that studies of this nature are fundamental to provide a greater understanding of how heuristics may influence individual judgment and, consequently, how such biases may be avoided.
Keywords: Accounting Judgment, Heuristic, Anchoring, Decision Making
Cite this paper: Marcos Roberto Luppe, Luiz Paulo Lopes Fávero, Anchoring Heuristic and the Estimation of Accounting and Financial Indicators, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 1 No. 5, 2012, pp. 120-130. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20120105.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Much of the work pertaining to positive accounting in Brazil and overseas focuses on aspect related to the impact of a certain set of variables on a specific behavior that provides decision makers with information. The current Brazilian panorama reflects recent international changes, with the search for greater disclosure, accountability and ethical corporate behavior becoming a constant. In this sense, the use of tools meant to monitor the quality of information and decision-making mechanisms has been soaring in important accounting studies seeking to create models that would explain reality and the empirical verification of observed phenomena.Therefore, as outlined by[1], accounting theory seeks to explain and predict the practice of accounting, without a rigorous need for solely approaching future phenomena; in fact, in many cases, it specifically targets existing, if unobserved, behaviors of the decision process.The decision-making process is constantly present in people’s lives. Research indicates that decisions are made based on limited or incomplete information, and individuals frequently fail to realize which information is relevant; this leads them to erroneous reasoning ([2]). In this context, accounting and auditing research concerning information processing in individual decision making has focused on understanding, evaluating and improving decision and judgment as applied to these areas’ contexts[3];[4];[5].Over the years, several approaches to the decision-making process have been developed[6]. Since the 1950s, studies on judgment and decision-making have considered normative models to be important research tools. Behavioral decision theory has occupied itself mainly with the study, explanation and interpretation of the discrepancies between predictions derived from normative models and real judgments and decisions[7].Behavioral finance studies are based on these principles, structured from an interdisciplinary analysis between economics and psychology. The link between these two fields in the decision-making process led to the development of what is called neuroeconomics. Under this denomination, studies have been conducted on financial decisions of several natures (investment choices; purchase, sale and exchange of goods; and others). As behavioral decision theory, neuroeconomics also refuses to accept that decisions are led solely by rational thinking[8]. This approach considers human behavior to be complex, and its understanding should also take psychological aspects such as intuition and emotion into account. Research has shown that individual decision making behavior systematically deviates from normative guidelines based on the presupposition of rationality[9];[10].Rational models assume that individuals have access to complete information in their decisions. This condition permits the attainment of maximum utility in choices, and any limitation in individual processing capacity is ignored or presumably avoided. A more realistic perspective is bounded rationality[11]. Simon argues that decision makers are limited in their ability to process information and, consequently, do not take entirely rational actions. Instead, they attempt to do their best, given the limitations to which they are subject. Due to these limitations, individuals use practical rules, or heuristics, in decision making[12];[13].In the 1960s and 1970s, a series of articles by Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman revolutionized the academic research of human judgment[14];[15];[16];[17];[10]. The core idea behind these studies is that judgments made under uncertainty are frequently based on a limited number of simplifying heuristics, rather than more formal extensive processing. This view offered a cognitive alternative to explain human error, while not assuming irrationality in decisions[18].In 1974, Tversky and Kahneman published a seminal study of judgment under uncertainty, pointing out that people rely on a limited number of heuristics to carry out complex tasks. Such heuristics typically produce correct judgments, but they may also lead to systematic errors. These authors identified three main heuristics used in individual judgment processes: representativeness, availability and anchoring.The results of this study have been applied to several fields other than psychology, with[19] being the first to introduce this line of research into the accounting literature. In that study, the authors analyzed the use of the representativeness heuristic in probabilistic judgments related to accounting decisions.The study related to the reference[3] notes that research of the study of decision making in accounting and auditing basically analyses four activities: (1) the estimation or judgment of current information, (2) the prediction of future results, (3) the evaluation and review of the probabilities of a certain outcome and (4) choices between alternate courses of action. The author in[3] believes these four activities to be potentially susceptible to the effects of cognitive judgment heuristics.[20] also notes that the contributions of studies that analyze the effects of heuristics on the decision process are of great importance to accounting and auditing. The analytical consideration of these heuristics may suggest actions to improve accounting judgment[21].Management decision processes typically rely on value estimates of economic variables, and, according to[22], several studies have questioned people regarding the estimation of mean values in a series of accounting indicators. The results of these studies show that estimates tend to be quite poor, except when indicators are stable (that is, there is no considerable variation in number dimension).Therefore, bearing in mind that all studies analyzing the effects of anchoring in accounting indicator estimates have been carried out either in the United States or in Europe, we seek to investigate the possible occurrence of this phenomenon on estimates made with Brazilian data. In this article, we try to identify the anchoring heuristic in estimation of the net profit of certain companies for fiscal year 2006 (before the beginning of the global crisis), using a few directing parameters to perform estimation: company size, sector and nationality.This article is structured into four sections. The first provides the theoretical basis for our work, and contains a review of the literature necessary to the understanding of our proposal. In the section that follows, we approach topics related to the study itself, namely: our method, the universe of data, definition of the samples used, manner in which data were collected and the analytical resource used in identifying anchoring. We then present the results obtained. Finally, we present our conclusions and point out the main possible extensions of this work.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Judgment and Decision Making
- According to[23], “one of the philosophy’s oldest paradoxes is the apparent contradiction between the great triumphs and the dramatic failures of the human mind. The same organism that routinely solves inferential problems too subtle and complex for the mightiest computers often makes errors in the simplest judgments about everyday events. The errors, moreover, often seem traceable to violations of the same inferential rules that underlie people’s most impressive successes[…]”.Although the authors were referring to the general population, this observation has potentially serious implications to judgment and decision making. Besides the above statement by[23],[24] concludes that there are few dramatic intellectual events in the recent history of the field of judgment and decision making. One such event is the abrupt acceptance of theories that do not follow the axioms of expected utility with labile reference points, separate value functions for gains and losses and nonadditive probability weighting functions, all of which represent characteristics related to prospect theory[9]. The other event is the sudden popularity of cognitive heuristics models for judgment[8] and choice (summarized by[25] apud[24]).The decision making process is a fundamental component of human behavior, and it is in no way surprising that its study would be shared by several fields, from mathematics and statistics, through economics and political science, to sociology and psychology[26].The core of judgment and decision making research is the way in which people combine desires (utilities, personal values, goals, among others) and beliefs (expectations, knowledge) in the choice of a course of action. What is referred to as decision making encompasses the complete process of choosing a course of action. Judgment, in turn, concerns the components of the decision process that deal with the evaluation, estimation and deduction of events and corresponding reactions from the decision maker[24]. In other words, judgment and decision making are cognitive processes whereby a person may evaluate options and select the most adequate among several alternatives[27].The traditional decision making process is based upon the classic rational choice model, which follows a normative structure. Normative theory investigates how choices are made under ideal conditions and establishes that the option that produces the greatest utility must be chosen. According to this model, the rational decision maker chooses an option by evaluating the probabilities of each possible outcome, judging the utility to be obtained from each one, and chooses the one that offers the optimal combination[18].Traditionally, complete information is unavailable, and decisions are made under uncertainty. In 1955 Simon recognized the limited cognitive capacity of the human mind when he introduced the concept of bounded rationality. In his Nobel prize-winning work,[11] suggested that individual judgment is restricted by rationality, and that the concept of bounded rationality provides a structure for questioning the traditional model’s assumptions. He argues that people do not behave in a rational manner, not because they do not wish to, but because they are unable to.The principle of bounded rationality assumes that, in order to deal with the complexities of the real world, a person must build a simplified model for each situation. Simon introduced the concept of rational behavior as being individualized and a function of psychological properties, including perception, thought and learning. This clearly contradicts normative theory and its prescription of approaches that seek a specific ideal or optimal solution for each decision problem.Reference[2] emphasizes, however, that although the concepts presented by Simon are important to show that judgment deviates from rationality, they do not answer the question of how judgment will be subject to specific cognitive biases.In the 1970s, two psychologists, Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman, basing their work on Simon’s notion of bounded rationality and not content with merely observing that we frequently make decisions based on suboptimal strategies, explored how frequently people use mental shortcuts and even biases that limit and eventually distort the capacity for rational decision making[27].The study[10] provided critical information on specific systematic biases that influence individual judgment and anchoring, and their work became a landmark in the study of judgment under uncertainty.
2.2. Anchoring Heuristic
- Numeric judgments are frequently made under uncertainty, and the effect of the anchoring heuristic is apparent in assimilating a numeric estimate toward a previously considered pattern. Anchoring therefore occurs when, in the course of the decision process, a person uses a reference value (an anchor) to choose a given course of action. Adjustments from the “initial anchors” are generally insufficient and lead to biased value estimates[10].A stock that has recently had a substantial price drop may be an example. An investor may be tempted to evaluate the stock’s “worth” from a reference point such as an old trading price range, which would lead to equivocal judgment of the stock’s value, since other important aspects of such an evaluation would not have been taken into account. Another such example could be the purchase of a new car, where the buyer may anchor his or her judgment on a given model’s price list and mentally adjust for discounts which may eventually be granted.Traditionally, in the standard experimental model used to assess the effects of anchoring, participants must carry out two simultaneous tasks: a comparative judgment and an estimative or absolute judgment. Participants are first asked whether the target value to be estimated is greater or lesser than an arbitrary initial value, known as the anchor value. They are then asked to make an absolute estimate of the given quantity[10]. The typical result of this two-stage model is that the absolute estimate is biased toward the initial anchor[10];[28];[29].The authors in[10] provided evidence of the anchoring effect. In what is probably the best-known demonstration of anchoring, participants were asked to estimate the percentage of African nations that are members of the United Nations. The first question asked participants whether the true percentage was greater or lesser than an arbitrary reference point (the anchor). For the subsequent question, participants had to estimate the final percentage. The anchors were found to have a substantial impact on estimates. Several other studies using the same model obtained similar results[30];[31];[32].The study referenced as[33] claim that anchoring may be one of the most remarkable influences in judgment and decision making, as demonstrations of its effects are abundant in several domains of judgment study, including general knowledge questions[30];[32];[34];[35], risk and uncertainty estimates[36], evaluation of property prices[31] and negotiation[37], to name a few.Despite the extensive literature on this theme in several fields and contexts, there is little published work regarding the anchoring heuristic in accounting and auditing. Some worthy of note are[38] on probability evaluations of professional auditors,[39] on the influence of internal anchors on auditing processes,[40] on the influence of anchors on parameters concerning environmental liabilities disclosed in financial statements, and on testing anchoring in the decision making of financial markets participants[41].After presenting the main concepts that guide this study, we will describe the method employed to evaluate the existence and intensity of anchoring bias in decisions relative to the estimation of a balance sheet indicator, which, in this study, is the net profit of certain companies.
3. Method
- We carried out an experiment with students from the graduate programs in Accountancy and Actuarial Sciences of the University of São Paulo. The method employed follows the steps proposed by[34], who describe an innovative approach for quantitative studies of the effects of anchoring on estimation tasks. This experiment design has been used in other anchoring studies, such as those by[35],[42],[43] and[44].Studies of anchoring in estimation tasks have frequently used the traditional two-stage model: participants are asked whether a given anchor is higher or lower than an unknown value, and are then asked to estimate this quantity. The method outlined by[34] differs from this traditional model. The authors present a parameter for measuring the effects of anchoring on estimation tasks and adopt a measurement procedure that requires three groups to be taken from a same population. The calibration group provides estimates for a set of uncertain values, with no mention of the anchor, and gives the degree of confidence on the estimated values on a scale of 1 to 10 points, zero being no confidence whatsoever in the estimate and 10 being complete confidence. Participants in two other groups make their estimates, after judging an anchor. The anchors in these two groups will be selected by their position in the distribution of the calibration group’s estimates; the high and low anchors are respectively fixed in the 15th and 85th percentiles of the distribution of estimates for each question. The two experimental groups make their estimates based on the proposed high or low anchors and then note their degree of confidence in the estimated values, also on a 10-point scale. This method will be presented and exemplified below.In the Brazilian context, a study by[44] uses this method in two experiments. In one experiment, five general knowledge questions were taken from Jacowitz and Kahneman’s original paper and adapted to the Brazilian reality, and the other experiment used six questions on pricing of products and services. The results of these experiments were adequate and similar to those obtained by Jacowitz and Kahneman, which validate the application of their proposed method to our experiment.In the present study, participants were thus asked to estimate the annual net profit of eight companies for fiscal year 2006 (before the beginning of the global crisis), as well as note their confidence in the estimate. The first question, for instance, was formulated as follows:Calibration Group:a) What is your best estimate of Petrobras’s net annual profit in 2006? R$_____________b) Note, on a scale of 0 to 10, your confidence in this price estimate: (0 being no confidence and 10 being complete confidence)
 Experimental Groups:a) In your assessment, was Petrobras’s net annual profit in 2006 higher or lower than X (low anchor value for group 1 and high anchor value for group 2)? R$____________b) What is your best estimate of Petrobras’s net annual profit in 2006 (in Brazilian reais)? R$____________c) Note, on a scale of 0 to 10, your confidence in this price estimate: (0 being no confidence and 10 being complete confidence)
Experimental Groups:a) In your assessment, was Petrobras’s net annual profit in 2006 higher or lower than X (low anchor value for group 1 and high anchor value for group 2)? R$____________b) What is your best estimate of Petrobras’s net annual profit in 2006 (in Brazilian reais)? R$____________c) Note, on a scale of 0 to 10, your confidence in this price estimate: (0 being no confidence and 10 being complete confidence) The choice of companies for this experiment was intentional. It was based on the following criteria: company size, segment and nationality, as well as having their shares publicly traded.Of the selected companies, four are Brazilian and four are US-based. As for market segment, four are retailers, three are industries and one is a service provider. Four may be considered very large corporations, with annual earnings in excess of US$ 5 billion, and four may be considered large enterprises. With these choices, we seek to differentiate between studied companies regarding the adopted criteria.
The choice of companies for this experiment was intentional. It was based on the following criteria: company size, segment and nationality, as well as having their shares publicly traded.Of the selected companies, four are Brazilian and four are US-based. As for market segment, four are retailers, three are industries and one is a service provider. Four may be considered very large corporations, with annual earnings in excess of US$ 5 billion, and four may be considered large enterprises. With these choices, we seek to differentiate between studied companies regarding the adopted criteria.3.1. Sample and Data
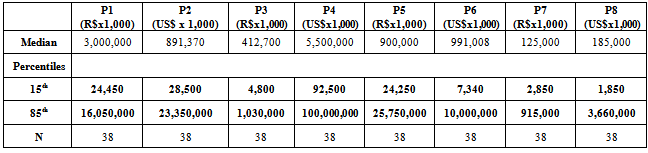
- For the experiment, three classes were selected with approximately 40 to 50 students ranging in age between 20 and 35. The first class responded to calibration questionnaires. Forty-one were collected and 38 were considered valid. The students in this class estimated net annual profit values (2006) for the eight companies mentioned, with no mention of any anchor, and noted their degree of confidence in the estimate on a 10-point scale. The 15th and 85th percentiles of the distribution of each question’s estimate from the calibration group were used, respectively, as low or high anchors for the experimental groups. Table 1 presents median and percentile values of the estimates obtained.
|
3.2. Identification of Anchoring
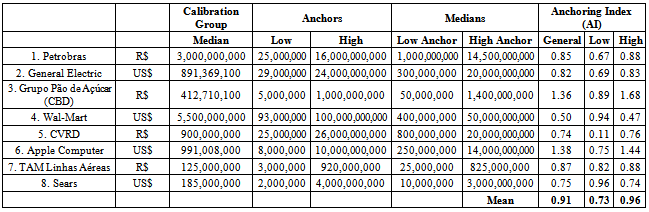
- For descriptive analysis of the effects of anchoring,[34] applied an anchoring index (AI) to measure the movement of “anchored” subjects’ median estimate toward the anchor to which they were exposed. Plausible AI values range from 0 (no anchoring effect) to 1 (subjects’ median estimates coincide with the anchors to which they were exposed). Higher values are also possible. The AI for a given estimation problem is given as follows:
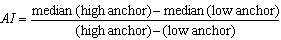 | (1) |
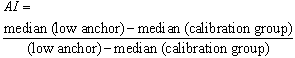 | (2) |
 | (3) |
 | (4) |
4. Results
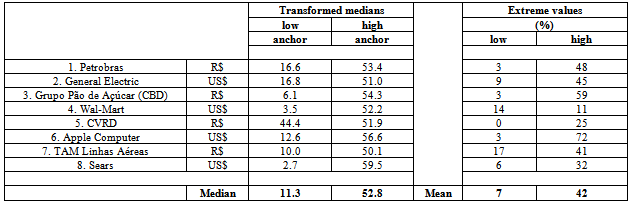
- The experiment’s questions involved estimation of eight companies’ net annual profit in 2006. Table 2 presents each question’s calibration group medians, high and low anchors, “anchored” group estimate medians, the general anchoring index (AI) and the high and low anchors’ AI.The effects of anchoring, as presented in table 2, are noticeably great on estimates of annual net profit (2006) for the eight companies. The mean general AI for the eight questions was 0.91, indicating that the “anchored” groups’ estimate medians moved over 90% toward the anchor when compared to the calibration group’s estimate medians; there was, as noted above, no mention of any anchor in the calibration group.It is interesting to note how, in every question, an arbitrary value may influence a person’s judgment as to the estimated net profit of a company. Petrobras, for instance, had a real net profit of approximately R$ 26 billion in 2006; the estimated profit was R$ 3 billion in the anchorless group, but was R$ 1 billion or R$ 14.5 billion when an arbitrary anchor was presented to respondents, showing a significant difference between values.Anchor influence may be observed in the “anchored” groups’ estimate medians. All high-anchor median values are lower than the high anchors themselves, and all low-anchor medians are lower than the low anchors themselves, except in questions 3 and 6, indicating how these “figures” altered respondents’ judgment and perceptions regarding the subject companies’ net profit.
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5. Conclusions
- The decision making process has been investigated in several fields of science. The subject is evidently treated with a different focus by law, economics, psychology, medicine and in jobs that investigate the accounting operations of organizations. Even more advantageous have been the contributions derived from the interaction between these different fields of science has been even more advantageous. One such promising line of investigation stems from the relationship between economics, psychology and medicine known as neuroeconomics.The author in[11] proposed the idea that the human mind is limited in its ability to process information and make decisions and, therefore, over the course of the decision making process, individuals will avail themselves of heuristics, or “practical rules”, to simplify the complex environment rich in information which influences the formation of their perceptions. Basing themselves on Simon’s notion of bounded rationality, in 1974, Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman presented a program entitled “Heuristics and biases”, which indicated the three cognitive heuristics that affect the decision-making process: representativeness, availability and anchoring. The project herewith has fundamentally used their approaches as guidelines. According to[22], the managerial decision making process is frequently based on subjective human judgment and, consequently, the biases that occur in such judgments can impose significant costs to an organization. Additionally, the author in[48] points out that there are several ways in which anchoring may be manifest in financial decisions.Little of the accounting judgment literature follows the aforementioned principles. Thus, the fundamental objective of this article is to identify the effects of the anchoring heuristic on the evaluation of accounting and financial indicators, specifically when estimating a variable that represents companies’ net profit. The choice of the anchoring heuristic was stimulated by the observations of[39], who highlights that it can influence any decision involving numeric predictions, and the analysis of its effects is paramount for a better understanding of the processing of information by finance, accounting and auditing professionals.In fact, many daily activities require numeric judgment and may thus be prone to the effects of anchoring. The literature has shown how numbers unrelated to a certain purpose can affect the decision making process. Conversely, there is evidence that the assessment of uncertain quantities by people is biased toward an anchor[29]. In this context, with the aim of testing the hypothesis that the anchoring heuristic is manifested in the estimation of an accounting–financial indicator, we employed the method proposed by[34].Taking the results of this experiment as a basis, we conclude that the evidence supports the existence of the anchoring bias in the estimation of the chosen indicator. We were also able to analyze the influence of high and low anchors on individual perception, as well as the relationship between anchoring and confidence in the estimate obtained.Although further experiments are necessary, we were able to identify strong evidence of the presence of anchoring bias in accounting judgment. Additionally, our results corroborate the conclusions of previous studies carried out in other countries, providing indications of how an arbitrary figure may alter individual perception as to a value that may be an important part of assessing a company’s performance. Anchors were presented and results indicated that respondents were influenced by these arbitrary values. Evidently, several sources may elicit anchors, which may result in partially or completely erroneous judgment.In the course of our research, we did not find any studies concerning the analysis of the effects of anchoring on the decision making process of financial and accounting professionals in a Brazilian context. We believe studies of this nature may provide interesting insight toward a greater understanding of how heuristics may influence individual judgment and, consequently, how such biases may be avoided.This study naturally has a limitation that must be mentioned, concerning the use of convenience sampling. Our experiment employed samples comprising graduate Accountancy students at University of São Paulo, meaning that any possible generalizations must be made with certain restrictions. Besides, simplified tasks of the use of heuristics in financial and accounting decisions do not completely capture the complexity of the environment in which such decisions are usually made. However, the use of a simplified task, such as the one we employed, makes it possible to identify potential biases to which professionals in this segment are subject. The manifestation and identification of the bias contribute to a greater understanding of the decision process in accounting.Other studies may examine the effects of anchoring in a real environment, in which accounting and finance professionals use indicators to make decisions. Another possibility for investigation is the analysis of the propensity toward anchoring in corporate auditing processes, where professionals must evaluate a series of accounting and financial indicators in the course of their decisions.Finally, we believe that the positive influence of the analytic models in accounting and finance can be even more used in the context of the emerging economies. In Brazil, specifically, the image of the accountants by the society is hampered by the fact that these are not seen as multidisciplinary and sometimes are recognized as being extremely technical and mechanical. Knowledge of other areas, interdisciplinarity and the use of techniques from economics, psychology or other areas of applied social sciences can make the decision makers in accounting and finance improve their performance and generate new opportunities for behavioral researches.
References
| [1] | Watts, R. L., & Zimmerman, J. L. (1986). Positive accounting theory. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall. |
| [2] | Bazerman, M. H.; & Moore, D. A. (2008) Judgment in Managerial Decision Making, 7th edn. J. Wiley & Sons, NJ, USA. |
| [3] | Ashton, R. H. (1984). Integrating research and teaching in auditing: fifteen cases on judgment and decision making. The Accounting Review, 59 (1), 78-97. |
| [4] | Maines, L. A. (2007). Judgment and decision-making in financial accounting: a review and analysis. In: Judgment and Decision-Making Research in Accounting and Auditing, edited by Ashton, R.H.; & Ashton, A.H. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. |
| [5] | Solomon, I., & Shields, M. D. (2007). Judgment and decision-making research in auditing. In: Judgment and Decision-Making Research in Accounting and Auditing, edited by Ashton, R.H.; & Ashton, A.H. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. |
| [6] | Payne, J. W.; Bettman, J. R., & Johnson, E. J. (1992). Behavioral decision research: a constructive processing perspective. Annual Review of Psychology, 43, 87-131. |
| [7] | Poulton, E.C. (1994). Behavioral Decision Theory: a new approach. New York, NY, Cambridge University Press. |
| [8] | James III, R. N. (2011). Applying neuroscience to financial planning practice: a framework and review. Journal of Personal Finance, 10 (2), 10-65. |
| [9] | Kahneman, D, & Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 47, 263-291. |
| [10] | Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1974). Judgment under uncertainty: heuristics and biases. Science, 185, 1124-1131. |
| [11] | Simon, H. A. (1957). Models of man. New York: John Wiley and Sons. |
| [12] | Hogarth, R. M. (1993). Accounting for decisions and decisions for accounting. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 18 (5), 407-424. |
| [13] | Moisand, D. (2000). Effective financial planning in the presence of judgemental heuristics. Journal of Financial Planning, 13 (4), 130-134. |
| [14] | Kahneman, D, & Tversky, A. (1972). Subjective probability: a judgment of representativeness. Cognitive Psychology, 3, 430-454. |
| [15] | Kahneman, D, & Tversky, A. (1973). On the psychology of prediction. Psychological Review, 80, 237-251. |
| [16] | Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1971). Belief in the law of small numbers. Psychological Bulletin, 76, 105-110. |
| [17] | Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1973). Availability: a heuristic for judging frequency. Cognitive Psychology, 5, 207-232. |
| [18] | Gilovich, T., & Griffin, D. (2002). Heuristics and biases: then and now. In: T. Gilovich, D. Griffin,& D. Kahneman (Eds.), Heuristics and biases (pp.1-18). New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| [19] | Swieringa, R. J.; Gibbins, M.; Larson, L., & Sweeny, J. L. (1976). Experiments in the heuristics of human information processing. Journal of Accounting Research, 14, 159-187. |
| [20] | Shanteau, J. (1989). Cognitive heuristics and biases in behavioral auditing: review, comments and observations. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 14 (2), 165-177. |
| [21] | Shields, M.D. (2009). “What a long, interesting trip it’s been” through the behavioral accounting literature: a personal perspective. Behavioral Research in Accounting, 21 (2), 113-116. |
| [22] | Bylinski, J. H., & Chow, C. W. (1985). Human judgment biases and the teaching of management accounting. Journal of Accounting Education, 3 (1), 167-172. |
| [23] | Nisbett, R. E., & Ross, L. (1980). Human inference: strategies and shortcomings of social judgment. Englewood Cliffs, N. J.: Prentice-Hall. |
| [24] | Hastie, R. (2001). Problems for judgment and decision making. Annual Review of Psychology, 52, 653-683. |
| [25] | Payne, J. W.; Bettman, J. R., & Johnson, E. J. (1993). The adaptative decision maker. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press apud Hastie, R. (2001). Problems for Judgment and Decision Making. Annual Review of Psychology, 52, 653-683. |
| [26] | Kahneman, D, & Tversky, A. (1984). Choices, values and frames. American Psychologist, 39 (4), 341-350. |
| [27] | Sternberg, R. (2000). Psicologia cognitiva. Porto Alegre: Artes Médicas Sul. |
| [28] | Epley, N., & Gilovich, T. (2001). Putting adjustment back in the anchoring and adjustment heuristic: differential processing of self-generated and experimenter-provided anchors. Psychological Science, 12, 391-396. |
| [29] | Epley, N., & Gilovich, T. (2005). When effortful thinking influences judgmental anchoring: differential effects of forewarning and incentives on self-generated and externally provided anchors. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 18, 199-212. |
| [30] | Wilson, T. D.; Houston, C.; Etling, K. M., & Brekke, N. (1996). A new look at anchoring effects: basic anchoring and its antecedents. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 4, 387-402. |
| [31] | Northcraft, G. B., & Neale, M. A. (1997). Experts, amateurs, and real state: an anchoring and adjustment perspective on property pricing decisions. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 39, 84-97. |
| [32] | Chapman, G.,& Johnson, E. (1999). Anchoring, activation and the construction of value. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 79, 115-153. |
| [33] | Mussweiler, T.; & Strack, F. (2001). The semantics of anchoring. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 86, 234-255. |
| [34] | Jacowitz, K. E.,& Kahneman, D. (1995). Measures of anchoring in estimation tasks. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 21, 1161-1166. |
| [35] | Strack, F., & Mussweiler, T. (1997). Explaining the enigmatic anchoring effect: mechanisms of selective accessibility. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 73, 437-446. |
| [36] | Wright, W. F., & Anderson, U. (1989). Effects of situation familiarity and financial incentives on use of the anchoring and adjustment heuristic for probability assessment. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 44, 68-82. |
| [37] | Galinsky, A. D, & Mussweiler, T. (2001). First offers as anchors: the role of perspective-taking and negotiator focus. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 81 (4), 657-669. |
| [38] | Joyce, E. J., & Biddle, G. (1981). Anchoring and adjustment in probabilistic inference in auditing. Journal of Accounting Research, 19, 120-145. |
| [39] | Morris, D. E. (1993). Analysis of auditors’ perceptions and over-reliance on negative information. Managerial Auditing Journal, 8 (6), 14-24. |
| [40] | Kennedy, J.; Mitchell, T., & Sefcik S. E. (1998). Disclosure of contingent environmental liabilities: some unintended consequences. Journal of Accounting Research, 36 (2), 257- 277. |
| [41] | Vitting, A. J. (2010). Detecting anchoring in financial markets. Journal of Behavioral Finance, 11 (2), 129-133. |
| [42] | Green, D.; Jacowitz, K. E.; Kahneman, D., & Mcfadden, D. (1998). Referendum contingent valuation: anchoring and willingness to pay for public goods. Resource and Energy Economics, 20, 85-116. |
| [43] | Mussweiler, T.; & Strack, F. (1999). Hypothesis-consistent testing and semantic priming in the anchoring paradigm: a selective accessibility model. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 35, 136-164. |
| [44] | Luppe, M. R. (2006). A heurística da ancoragem e seus efeitos no julgamento: decisões de consumo. Dissertation (Master Science in Administration) – School of Economics, Business and Accountancy, University of São Paulo, Brazil. |
| [45] | Guilford, J. P., & Fruchter, B. (1978). Fundamental statistics in psychology and education. 6th ed. London: Mc-Graw Hill. |
| [46] | Mussweiler, T.; & Strack, F. (2000). Numeric judgment under uncertainty: the role of knowledge in anchoring. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 36, 495-518. |
| [47] | Mussweiler, T.; & Strack, F. (2000). The use of category and exemplar knowledge in the solution of anchoring tasks. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78, 1038-1052. |
| [48] | Belsky, G. (1999). Seven common mental money mistakes. America’s Community Banker, 8 (10), 22-25. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML