-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
2012; 1(4): 53-58
doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20120104.01
Investigation on Information Content of Conservative and Non-Conservative Accounting Earnings
Younes Badavar Nahandi 1, Morteza Khanlari 2
1Economic, Management and Accounting Department, Islamic Azad University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran
2Economic, Management and Accounting Department, Islamic Azad University of Tabriz, Supreme Audit Court, Tabriz, Iran
Correspondence to: Morteza Khanlari , Economic, Management and Accounting Department, Islamic Azad University of Tabriz, Supreme Audit Court, Tabriz, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The present research examines the relationship between conservatism in financial reporting and information content of accounting earnings. In this study, conservatism and information content is measured by Basu (1997) Easton and Harris (1991) models, respectively. This study is applied research and its method is ex post facto (casual-comparative). Statistic population is firms listed in Tehran Stock Exchange (TSE). By using the firm-year method during the period of 1380 to 1387, 764 observations from 145 firms listed in TSE have been selected. The multiple regression test has been used to test research hypothesis. The results show a non-linear relationship between information content of accounting earnings and conservatism. In addition, the results suggest a non-linear relationship between conservatism and cost of capital.
Keywords: Information Content, Accounting Earnings, Unconditional Conservatism, Conditional Conservatism, Financial statements, Cost of Capital
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Financial statements are a major component of financial reporting. The main aim of financial statements is to report condensed and classified information about financial position, flexibility, and performance, which is useful for the wide range of financial statements users in sound economic decision-making[1]. Financial reporting and accounting concepts requires that information have certain characteristics. One of these characteristics is conservatism, which implies prudence in financial reporting. Conservatism is a dominant characteristic of financial reporting that have captured attentions in the world of accounting and financial reporting since early 20th century[2]. Whether conservatism enhances the quality of financial statements or not is an old issue in accounting literature. In the other hand, financial information has information content when the financial statements users utilize them in decision-making[3]. In traditional accounting, conservatism is defined as an uncertainty phenomenon[4]. Givoly & Hayn define conservatism as the accounting choices in uncertainties, which lead to understatement of assets and revenues and overstatement of expenses[5]. Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in SFAC No. 2 defines conservatism as "a prudent reaction to uncertainty to try to ensure that uncertainties and risks inherent in business situations are adequately considered. Thus, if two estimates of amounts to be received or paid in the future are about equally likely, conservatism dictates using not for redistribution the less optimistic estimate; however, if two amounts are not equally likely, conservatism does not necessarily dictate using the more pessimistic amount rather than the more likely one. Conservatism no longer requires deferring recognition of income beyond the time that adequate evidence of its existence becomes available or justifies recognizing losses before there is adequate evidence that they have been incurred"[6]. However, in Iran conceptual framework conservatism is defined as a component of reliability as "applying some degrees of prudence in forecasting uncertainties as if neither revenue or assets be overstated nor debt or expenses be understated[1].There are two different views regarding accounting conservatism. Some researchers argue that conservatism is useful for financial statements users and analysts and attach information content for it. In contrast, others argue that it is unfavourable for accounting users and providers. Proponents of the first view highlight that conservatism drives in enhancing the quality of financial reporting and mitigates information asymmetry between providers and users of financial reporting which, in its turn, decreases agency cost. In addition, they point out that conservatism is a procedure in uncertainties that step up firms' value. In contrast, opponents of conservatism document that it drives in mitigating the quality of financial reporting and this may face investors and other users of financial reporting with a big loss. In this view, the higher conservatism and the demand for revenues` underestimation have positive relationship. Paek & et al. view conservatism as a factor in misleading revenue recognition process. However, they assert that it is against the benefits of investors and lenders and also the role of financial reporting. Another reason of conservatism opponents is its negative effect on firms financial reporting. They argue that conservatism cause propensity to early disclosure of financial information. This propensity to early disclosure may be an obstacle on discretionary disclosure[7]. However, with respect to aforementioned views on conservatism, these questions arise: Does conservative financial information have information content for all the users? Is there a difference between information content of conservative andnon-conservative accounting income?
2. Literature Review
- Iatridis provided evidence that firms that use high standards of accounting quality in their financial reporting practices adopt a conservative approach in reporting losses and profits, which would further reinforce the credibility of their financial statement[8].Balachandran & Mohanram investigated the relationship between conservatism and information content. They measured conservatism as understatement of book values and asymmetric timeliness of earnings applying developed procedure of Panmen & Zhang (2002) and Basu (1997). They did not find evidence showing that increasing conservatism (conditional and unconditional) leads to a decrease in information content. In fact, they observed that increasing unconditional conservatism related to information content of book values. In overall, their findings indicate that increasing conservatism does not result in increasing information content[9].Brown et al. using a firm sample of 20 country studied that whether conditional conservatism affects information content of accounting earnings. They found that the relationship between conditional conservatism and information content of accounting earnings is related to the level of accrual accounting application in the given country. In the countries with high level of accrual accounting, conditional conservatism and information content have a positive relationship. Their results are consistent with the notion that conditional conservatism has a conventional role in mitigating management opportunistic behavior in applying accrual accounting. However, they highlight that conditional conservatism advantages are related to the environment and there is no advantage in the countries with low accrual accounting[10].Roychowdhury & Watts investigated the relationship between asymmetric timeliness of earnings and market to book ratio as the unconditional and conditional conservatism measures. They documented that there is a negative significant relationship between these two measures of conservatism. In addition, they showed that the longer asymmetric timeliness of earnings causes to decrease this negative relationship. Moreover, their results indicate that the high level of conservatism and incurring special items` loss have relationship[11].Beatty et al. and Zhang found evidence that explains conservatism has a great role on debt contracts and it brings co-benefits for both lenders and borrowers[12,13].Chen et al. demonstrated that conditional conservatism, which relates to difficult-to-verify accounting disclosures, and also higher quality of accounting information and lower cost of capital have relationships and unconditional conservatism, which relates to opportunistic managerial efforts, and lower quality of accounting information and higher cost of capital have relationships[14].Kousenidis et al. investigated the earnings information content. Their findings point out that there is a non-liner relationship between conservatism and the level of earnings relevance. More specifically, they indicated that relevance level increases by moving from low conservative firms toward the semi conservative firms and it reduces by moving toward high conservative firms[15].Kim & Pevzner studied the benefits of conditional conservatism for shareholders. They illustrated that higher conditional conservatism and the lower likelihoods of bad news have relationships. Also, they found a weak relationship between stronger (weaker) stock market reaction for bad (good) news about firms' earnings and conditional conservatism[16]. Hassas-yeganeh & Shariyri examined the relationship between central ownership and conservatism. They end up with the result that central ownership and conservatism have negative relationships. These result supports self-interest hypothesis and strategic congruency and it is against active monitoring hypothesis[1].Rezazadeh & Azad studied the relationship between information asymmetry among investors and the level of conservatism in financial reporting using companies listed in TSE during the period of 2002 and 2006. They applied differences between stocks sale and buy offering price to measure information asymmetry and conservatism, respectively. Their results show a positive significant relationship between information asymmetry and practiced conservatism in financial statements. Moreover, they observed that information asymmetry among investors drives in changing in conservatism level[17].Ebrahimi Kordlar & Shahriyari highlighted that there is a negative relationship between size, investment and central ownership and positive relationship between competitive level and governmental ownership with conservatism. However, they did not find a significant relationship between effective rate of tax and conservatism[18]. Bahramfar & Hassani investigated the effect of board of director characteristics on conservatism. They pointed out that there is a positive significant relationship between members of director`s ownership and conservatism and negative relationship between outside directors and conservatism[19].Mehrani et al. studied conservatism in accounting income and its relationship with accrual items. Their results demonstrate that accounting income is more sensitive, about 3.66 times, to stock negative return than stock`s positive return. In addition, accrual items determine 78 percent of asymmetric timeliness of earnings[20].Mashayekhi et al. explored the relationship between conservatism and dividend level and earnings persistency. They found that increasing conservatism leads to decreasing dividend. Moreover, they indicated that decreasing earnings persistency does not result in increasing conservatism[21].Nan & Wen illustrate that conservatism mitigates financing inefficiency in industries with generally low profit prospects, but aggravates the inefficiency in industries with generally high profit prospects. They assert that when a firm can improve information quality by a costly effort, a good firm’s effort level to improve the information quality is lower than the social optimal level, and a more conservative system motivates good firms to exert more effort to improve the information quality. Further, they found that distorted financing decisions may induce distorted investment decisions, and conservatism has a more pronounced effect to improve overall efficiency by discouraging investment distortions through its impact on financing decisions[22].
3. Hypothesis Development
- Before FASB (Financial Accounting Standard Board) statement No.8 which issued by co-operating with IASB (international accounting standard board), including conservatism in standards was for increasing the reliability of reported information. However, in statement No. 8, these boards argue that including conservatism leads to bias in financial reporting and also it is not consistent with neutrality. Therefore, we explore that if FASB and IASB decision about excluding conservatism is a sound decision and whether Iran Accounting Standard Committee (IASC) should do so. To achieve this goal we set forth this question: Does conservatism increase the information content of accounting earnings? If the answer is yes, so we propose IASC not to follow FASB and IASB. Anyway, our hypothesis is as following:
3.1. Models and Variables Definition
- Basu defines conservatism as applying the high degree of reliability in recognizing and recording good news (capital increasing) and in contrast applying the low degree of reliability in recognizing and recording bad news (capital decreasing)[23].In this study, we use Basu model to measure conservatism level and break down firms to the firms with high conservatism (HC), median conservatism (MC) and low conservatism (LC) as following:
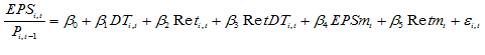 Where:EPSi,t is earnings per share of firm i in year t;Pi,t-1 is stock price of firm i at the beginning of year t,DTi,t is censured variable that if returns of firm i in year t is negative is 1 otherwise 0,Reti,t is annual combined return of firm i in year t,RetDTi,t is stock return multiple relative censured DT, (if return is negative RetDTi,t = Reti,t and otherwise 0).Since using of more firms and fewer years cause cross-sectional association in data, EPSmt and Retmt are used as a control variable that are mean of cross-sectional earnings per share and mean of stock return, respectively.In Basu`s model it is assumed that bad news (capital decreasing) affect on earnings faster than good news (capital increasing) and, in the model, β3 is extra determination power of bad news than good news for earnings measurement. Therefore, it is applied as a conservatism measure.According to Basu, more conservatism leads to more asymmetric in recognizing bad news rather than good news. Then, more conservatism leads to more β3 coefficient. Consequently, according to Pope & Walker evidence as in[24], β0 intercept indicates mean of the firms cost of capital during the period of study.The fundamental qualitative characteristics are relevance and faithful representation[6]. Francis & Schipper define information content of accounting earnings as its ability in determining market returns[25].Easton & Harris (1991) model is used to estimate information content of accounting earnings as following:
Where:EPSi,t is earnings per share of firm i in year t;Pi,t-1 is stock price of firm i at the beginning of year t,DTi,t is censured variable that if returns of firm i in year t is negative is 1 otherwise 0,Reti,t is annual combined return of firm i in year t,RetDTi,t is stock return multiple relative censured DT, (if return is negative RetDTi,t = Reti,t and otherwise 0).Since using of more firms and fewer years cause cross-sectional association in data, EPSmt and Retmt are used as a control variable that are mean of cross-sectional earnings per share and mean of stock return, respectively.In Basu`s model it is assumed that bad news (capital decreasing) affect on earnings faster than good news (capital increasing) and, in the model, β3 is extra determination power of bad news than good news for earnings measurement. Therefore, it is applied as a conservatism measure.According to Basu, more conservatism leads to more asymmetric in recognizing bad news rather than good news. Then, more conservatism leads to more β3 coefficient. Consequently, according to Pope & Walker evidence as in[24], β0 intercept indicates mean of the firms cost of capital during the period of study.The fundamental qualitative characteristics are relevance and faithful representation[6]. Francis & Schipper define information content of accounting earnings as its ability in determining market returns[25].Easton & Harris (1991) model is used to estimate information content of accounting earnings as following: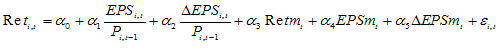 Where:ΔEPSi,t is earnings changes per share of firm i in t and t-1 years and ΔEPSmt is mean cross-sectional earnings per share. Other variable as defined before. Easton & Harris (1991) model is estimated for each conservatism portfolio separately. α1 coefficient in Easton & Harris (1991) model indicates information content of all observations and each portfolio.Fransis & Schipper document that information content of accounting earnings is estimated utilizing significance level of correlation between earnings and return that is measured by t-statistic of earnings and changes in earnings variables and adjusted R2[25].First, research hypothesis is regressed using Basu model for each firm-year. Then, using obtained coefficients, sample firms with respect to β3 value, a conservatism measure, is broken down firms to the firms with high conservatism (HC), median conservatism (MC) and low conservatism (LC). Then, information content of accounting earnings is calculated for each portfolio using Easton & Harris (1991) model and thereafter regression tests is developed for investigation of conservatism effect on information content of accounting earnings.
Where:ΔEPSi,t is earnings changes per share of firm i in t and t-1 years and ΔEPSmt is mean cross-sectional earnings per share. Other variable as defined before. Easton & Harris (1991) model is estimated for each conservatism portfolio separately. α1 coefficient in Easton & Harris (1991) model indicates information content of all observations and each portfolio.Fransis & Schipper document that information content of accounting earnings is estimated utilizing significance level of correlation between earnings and return that is measured by t-statistic of earnings and changes in earnings variables and adjusted R2[25].First, research hypothesis is regressed using Basu model for each firm-year. Then, using obtained coefficients, sample firms with respect to β3 value, a conservatism measure, is broken down firms to the firms with high conservatism (HC), median conservatism (MC) and low conservatism (LC). Then, information content of accounting earnings is calculated for each portfolio using Easton & Harris (1991) model and thereafter regression tests is developed for investigation of conservatism effect on information content of accounting earnings.4. Methodology and Data Collection
- Present study is casual-comparative research since it investigates conservatism effect on information content of accounting earnings. Data sample consists of all firms listed in TSE, sampling method is systematic-elimination, and sample firms must have following conditions:1. Fiscal year must be ended at the end of year and must have not changed their fiscal year during the period of study.2. Transaction intervals must not be more than 3 month.3. Must not be investment or banks for its special nature.4. Data must be available for testing hypothesis for the period of study (2003-2010).5. Must have at least four observations for achieving reliable level of conservatism.As a result of these conditions a sample of 145 firms with 764 year-firm observations was obtained. Literature and conceptual framework were gathered by documental method. Financial statement and notes issued by TSE were used as a research tool. In addition, Rahavarde Novin software was applied to extract the research data.
4.1. Empirical Results
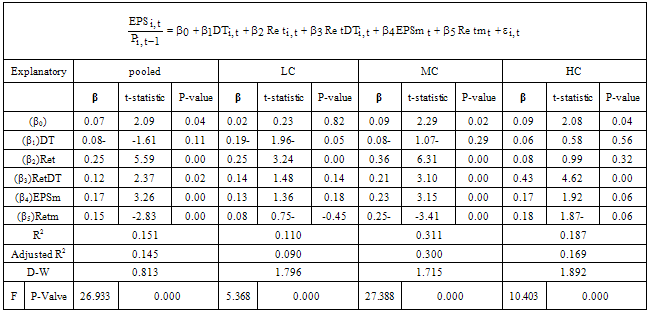
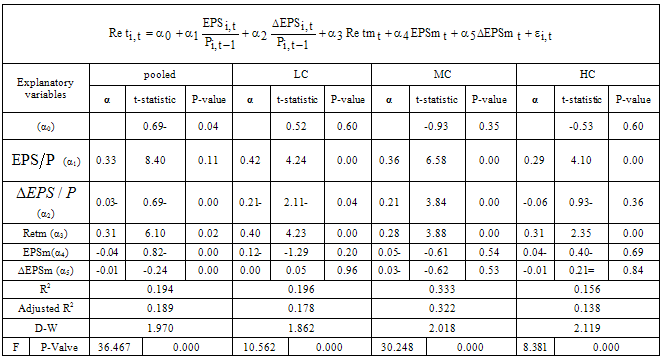
- Descriptive statistic explains the population`s parameters so in Table 1 descriptive statistic is presented based on the models.
|
|
|
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
- The aim of this study was to investigate conservatism effect on information content of accounting earnings in financial reporting of firms listed in TSE during the period of 2003-2010. Conservatism was measured through Basu model (1997) and information content of accounting earnings through Easton & Harris (1991) model. The results of testing research hypothesis present existence of nonlinear relationship that means information content of accounting earnings increases by moving from low conservatism portfolios toward median conservatism portfolios and reduces by moving toward high conservatism portfolio. This result is consistent with the results of Balachandran & Mohanram (2006), Kousendidis et al. (2009). Moreover, the findings show that misleading the relationship between earnings and return stem from practicing low and high conservatism. However, misleading the relationship between earnings and return by practicing high conservatism is more than low conservatism. In addition, the results demonstrate the nonlinear relationship between conservatism and cost of capital.Considering the results of the study, we suggest IASC not to follow IASB and FASB.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML