-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Energy Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1891 e-ISSN: 2163-1905
2014; 4(1): 16-20
doi:10.5923/j.ijee.20140401.04
Performance and Emissions Analysis of Intercooled Direct Injection Diesel Engines Used for Power Generation during Day and Night Times Operation – A Case Study
N. S. Senanayake1, T. S. S. Jatunarachchi1, G. A. Kahandagamage2
1Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Open University of Sri Lanka, Nawala, Sri Lanka
2Lanka Transformers (Pvt) Limited, Colombo, Sri Lanka
Correspondence to: N. S. Senanayake, Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Open University of Sri Lanka, Nawala, Sri Lanka.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This paper presents the results of a study carried out to analyze the exhaust gas composition and the plant performance in terms combustion efficiency and Specific Fuel Consumption (SFC) of a diesel engine used for electrical power generation, when operated in day time and night time. For the study, 17MW turbocharged, intercooled direct injection diesel engine consisting of 18 cylinders was used. The results showed a reduction (2.34%) in SFC in the night time operation in which the charge air temperature was lower and relative humidity was higher than those of the day time. The combustion efficiency as well as overall efficiency was found to be increased by 1% in the night time. The CO in the exhaust showed a reduction (13%) in the night time, indicating efficient combustion. The O2 showed a slight increase (1.8%) in the night time. However, NOx in the exhaust was found to be increased almost four fold despite the reduction in the exhaust gas temperature and increased moisture in the charge air compared to the day time. The reason for the increase in NOx was attributed to the increase in excess air. The lower combustion temperature was not sufficient to suppress the NOx formation.
Keywords: Exhaust gases, Combustion efficiency, Specific fuel consumption, Diesel engines
Cite this paper: N. S. Senanayake, T. S. S. Jatunarachchi, G. A. Kahandagamage, Performance and Emissions Analysis of Intercooled Direct Injection Diesel Engines Used for Power Generation during Day and Night Times Operation – A Case Study, International Journal of Energy Engineering, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 16-20. doi: 10.5923/j.ijee.20140401.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Diesel engine exhaust is composed of a mixture of many different toxic chemicals that are harmful to human being and to the environment. These emissions have relationship to the charge air parameters that controls the combustion inside the cylinder. On the other hand charge air parameters also have an effect on the engine performance. The toxic chemicals of most concern in diesel exhaust are the oxides of nitrogen (nitric oxide, nitrogen dioxide), carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, aldehydes, primarily formaldehyde, acetaldehyde and acrolein, and various hydrocarbons particles. The higher average temperature of combustion of diesel engines generates more oxides of nitrogen than gasoline engines. NO and NO2 are the most important oxides of nitrogen and these kind of nitrogen oxides are generally called NOx emissions. NO is a toxic gas which is formed during combustion at high temperature zones in the combustion chamber (i.e. the automobile engines, power plants and furnaces). Many research carried out in the area of exhaust gas analysis in relation to the fuel types and other operating parameters are for small engines, primarily used in automobiles. However, the effect of toxic exhaust gas produced in large capacity diesel engines is significant as the fuel burnt in a comparatively small period is very large. Therefore, it is very important that these engines are operated under conditions that reduce NOx emissions without sacrificing the engine performance. According to preliminary investigations carried out at the Heladhanavi Thermal Power Plant in Puttalum District in Sri Lanka, it has been observed that Specific Fuel Consumption (SFC) has shown a considerable variation in day time and night time operations owing to the fact that significant changes in the ambient temperature and the relative humidity in the area, the plant is situated. Heladhanavi Power Plant is a 100MW thermal power plant, consisting of six Watseka 18V46 turbocharged, intercooled direct injection diesel engines, each with a capacity of 17MW. The present study was carried out to analyze the exhaust gas composition and the plant performance in terms combustion efficiency and SFC of this intercooled direct injection diesel engine used for electrical power generation.
2. Literature Review
- Many studies have been carried out to determine the effects of fuel composition on the exhaust gasses. They were more on the use of fuel mixtures such as Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG) and bio fuels. The effect of them on the cylinder pressure development and the characteristic of exhaust gasses have been studied[1, 2]. Several studies have been reported on the effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) on emissions[3, 4], main focus being to control NOx emissions. In these studies reductions in NOx have been reported to a different degrees depending upon other variables such as charge air temperature and percentage of EGR. In a recent study, the combined effect of EGR and Cetane improver has been found to reduce the NOx emissions by 25% with a slight increase in carbon monoxide (CO), hydro carbon (HC) and smoke opacity[5]. Especially biodiesel increases NOx in the exhaust of diesel engines which are predominant when the temperature in the combustion chamber is high as reported by many authors[6 – 8]. Several factors affects for the decrease in NOx emissions with the increase of EGR. The introduction of CO2 and H2O that have higher specific heat capacities results in a lower exhaust temperature during the combustion which gives less NOx production. Water vapor and CO2 are also dissociated during combustion and modifies the combustion process and results in a decrease in flame temperature giving less NOx[9, 10]. The effects of intake air humidity on the performance of a turbo-charged 4-cylinder diesel engine have been investigated by Asad etal, 2012. In this study, the relative humidity of the intake charge was varied from 31 to 80% at a fixed ambient air temperature of 26°C. The results indicated that increasing the intake air moisture leads to a reduction of NOX emissions by 3-14% under the test conditions. The CO and HC emissions were found to be largely insensitive to the humidity levels and were otherwise extremely low[11]. The effect of charge air properties on the efficiency and SFC has also been reported by several researehers[12 -18]. These studies focussed on the effect from the moisture in the charge air or in the fuel on the diesel engine performance[19]. Lin and Jeng (1996) reported findings of a study on the effect of humidity and temperature of intake air on the performance and the emission characteristics of diesel engines. According to this study air consumption rate, brake torque, and nitrogen oxide in the exhaust were found to be decreased, while specific fuel consumption, carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide increased with the temperature and the humidity of charge air[20]. Inlet air temperature and the air-to-fuel ratio also have a significant effect on the maximum in-cylinder pressures and its position relative to the cylinder top dead center, the shape of the pressure rise curve, and the heat relese rates[21]. In a study carried out by Maiboom (2008) the charge air temperature in a diesel engine was varied from 20°C to 38°C and found that increase in charge air temperature at constant boost pressure resulted in a slight decrease in rate of heat release. The increase of inlet temperature with exhaust gas recirculation has contrary effects on combustion and emissions, for example, the reduction of NOx emissions with increased inlet temperature [10].
3. Method
- A Watseka 18V46 turbocharged, intercooled engine that consists of 18 cylinders was used for the experiments. This was a recently 48,000 running hour maintenance completed engine at 54,890h. All the injector pumps and injector nozzles were in good condition. Cylinder head, piston and liner maintenances have been done recently. The load of the engine was set at 17MW. The measurements were taken during the day time and the night time in order to change the ambient conditions. Time of running during which all measurements were taken was four hours in each of day time and night time. During the running periods, flue gas composition, fuel consumption, charge air temperature and relative humidity, and the pressure development in the cylinders were measured.To analyze the exhaust gas composition, the gas analyzer Test 350 XL/M instrument was used. The measurement probe was inserted into the stack through an opening provided on the stack pipe and three measurements were obtained. The measurements on fuel consumption were carried out during the same time periods. The readings of the individual fuel racks of the engine were recorded with a marking on the rack to see the amount of fuel injected in to the engine. The electrical energy exported during four-hour period was also obtained by the energy meters installed in the plant during the same time periods.Also during the four hour periods in day time and night time experiments, the ambient and charged air properties (temperature and humidity) were measured in one hour intervals. The pressure developments inside the cylinders were analyzed using the “Leman Permit XL analyzer”. The analyzer was connected to the combustion chamber through the indicator cock on the cylinder head and pressure inside was recorded for four cycles. Then the recorded values were fed into the computer. The pressure (p) curves and the rate of change of pressure with respect to crank angle (a), (dip/da) curves were plotted by using Premet software v 4.12.
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Exhaust Gas Composition
- Table 1 shows the average values of the ambient pressure, temperature and relative humidity (RH) measured in day time and night time. Also listed in the table are the charge air conditions before after and cooler in day time and night time operations.Table 2 shows the average compositions of the exhaust gasses recorded in day time and night time operations. Also given in the table are the ambient and charge air temperatures, and the exhaust gas temperatures.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 For day time;
For day time;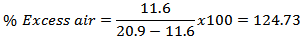 For night time;
For night time;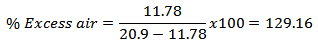 According to Table 2 the average exhaust gas temperature of the engine reduces by 24℃ in the night time. Also the moisture in the air during night is higher than that of the day time as recorded in Table 1. The higher specific capacity of water compared to oxygen and nitrogen results in lower flame temperature hence the exhaust gas temperature[9, 10]. Because of low temperature and the presence of moisture in the charge air, the density of air increases and the amount of CO generated is also reduced as per the improvement in the combustion. CO2% of the flue gas had reduced as the amount of fuel burnt is reduced due to improvement of fuel consumption. Although the forrmation of NOx is inhibited by the reduction in flame temperature[9], in this study the NOx formation was found to incraese in the night time, despite the reduction in flame temperature. This could be due to more excess air in the night time as well as increased moisture that provides nessessary O2 for the formation of NOx. The reduced flame temperature in the night seemed to be insignifcant to prevent or drastically reduce the formation of NOx. On the other hand increase in excess air supply in the night could have contributed to increase the nitrogen in the charge air, hence the formation of NOx.The CO was found to be reduced by about 13% in the night time indicating a complete combustion and the higher combustion efficiency. At the same time, CO2 was reduced slightly (about 2%) in the exhaust. This indicated that in the total exhaust, the other components especially the NOx has increased as shown in the Table 2. The increase of NOx in the night was almost four fold.
According to Table 2 the average exhaust gas temperature of the engine reduces by 24℃ in the night time. Also the moisture in the air during night is higher than that of the day time as recorded in Table 1. The higher specific capacity of water compared to oxygen and nitrogen results in lower flame temperature hence the exhaust gas temperature[9, 10]. Because of low temperature and the presence of moisture in the charge air, the density of air increases and the amount of CO generated is also reduced as per the improvement in the combustion. CO2% of the flue gas had reduced as the amount of fuel burnt is reduced due to improvement of fuel consumption. Although the forrmation of NOx is inhibited by the reduction in flame temperature[9], in this study the NOx formation was found to incraese in the night time, despite the reduction in flame temperature. This could be due to more excess air in the night time as well as increased moisture that provides nessessary O2 for the formation of NOx. The reduced flame temperature in the night seemed to be insignifcant to prevent or drastically reduce the formation of NOx. On the other hand increase in excess air supply in the night could have contributed to increase the nitrogen in the charge air, hence the formation of NOx.The CO was found to be reduced by about 13% in the night time indicating a complete combustion and the higher combustion efficiency. At the same time, CO2 was reduced slightly (about 2%) in the exhaust. This indicated that in the total exhaust, the other components especially the NOx has increased as shown in the Table 2. The increase of NOx in the night was almost four fold.4.2. Combustion Efficiency
- The combustion efficiency was calculated using Seigert formula[22].
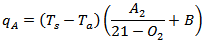
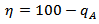 Where,
Where,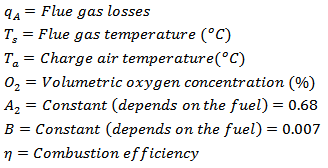 For day time;
For day time;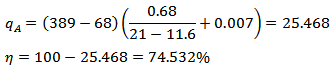 For night time;
For night time;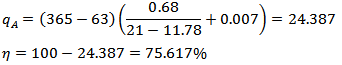 According to the calculations using Seigert formula, only a small improvement (by 1%) in combustion efficiency can be obtained in the night time operation.
According to the calculations using Seigert formula, only a small improvement (by 1%) in combustion efficiency can be obtained in the night time operation.4.3. Overall Efficiency and SFC
- Table 3 gives the actual fuel consumption and the energy exported in the same period. The overall efficiency of the engine was calculated by using the following equation with the Lower Heating value (LHV) of fuel used as 40.54MJ/kg.
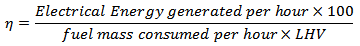
|
4.4. Pressure Development
- The pressure (p) and (dip/da) curves versus the crank angle (a) after Top Dead Center (TDC) were plotted by using Premet software v 4.12 and a sample of which is shown in Figure 1. The right shifted curve is for the night time. In all the cylinders, the maximum pressure development was found to be delayed in night time compared to day time value, the maximum and minimum values being 3o and 0.75o after TDC.
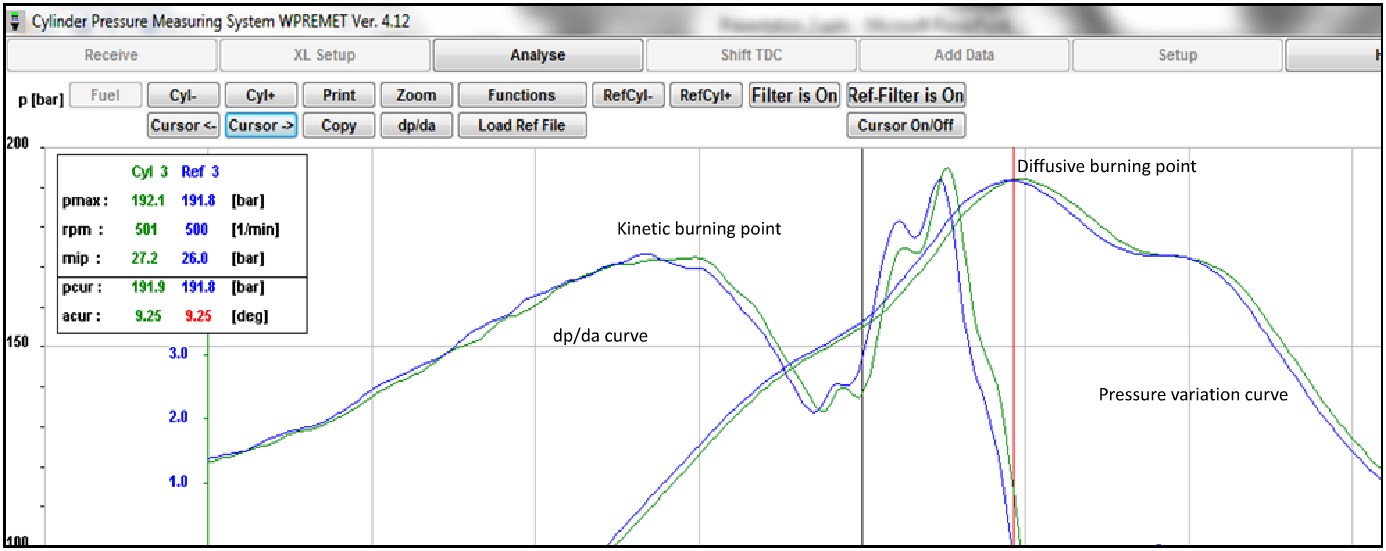 | Figure 1. Pressure and pressure derivative with respect to crank angle for day time and night time operation |
5. Conclusions
- In conclusion, the performance of the diesel engines used for power generation was found to be improved when operated in the night time with lower charge air temperature and higher humidity compared to the day time, giving fuel savings. Based on the study the following conclusions were made.● The combustion and the overall efficiency in the night time were both improved by 1%. Though this is a small amount, the savings in fuel is very much significant, the value being 71kg/h in this occasion. Also the SFC was reduced by 2.34% in the night time compared to the day time.● The emission of CO was found to reduce indicating improved combustion in the night time. ● On the other hand, emissions of NOx were found to be increased significantly due to the increased excess air. The lower flame temperature expected in the night time owing to the presence of high content of moisture and low charge air temperature was not sufficient to reduce the NOx emissions.
References
| [1] | V. Ayhan, A. Parlak, I. Cesur, B. Boru and A. Kolip, Performance and exhaust emission characteristics of a diesel engine running with LPG, International Journal of the Physical Sciences, Vol. 6(8), pp. 1905 – 1914, April, 2011. |
| [2] | R.S. Kumar, R. Manimaran and V. Gopalakrishnan, Performance and emission analysis using Pongamia oil biodiesel fuel with an artificial neural network, Advanced Engineering and Applied Sciences, 2013, 3(1), pp. 17 – 20. |
| [3] | A. Mohebbi, S. Jafarmadar and J. Pashae, Performance evaluation and emissions improving of turbocharged DI Diesel Engine with Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR), International Journal of Automotive Engineering, Vol. 2, No. 2, April 2012. |
| [4] | A. Tsolakis, A. Megaritis, M. L. Wyszynski and K. Theinnoi, Engine performance and emissions of a diesel engine operating on diesel – RME (rapeseed methyl ester) blends with EGR (exhaust gas recirculation), Energy, Vol. 32, Issue 11, November 2007, pp. 2072 – 2080. |
| [5] | K. Venkateswarlu, B. S. Rama, C. Murthy and V. V. Subbarao, The Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation and Di-Tertiary Butyl Peroxide on Diesel-Biodiesel Blends for Performance and Emission Studies, International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology Vol. 54, May, 2013, pp. 49 – 60. |
| [6] | S. Oberweis and T.T. Al-Shemmer, Effect of biodiesel blending on emissions and efficiency in a stationary diesel engine. In International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality, (ICREPQ’10). Granada, Spain, 23-25 March, 2010. |
| [7] | Y. X. Li, N.B. McLaughlin, B.S. Patterson and S.D. Burtt, Fuel efficiency and exhaust emissions for biodiesel blends in an agricultural tractor. In CSAE/SCGR 2005 Meeting, Winnipeg, Manitoba, 26-29 June 2005, Paper No. 05-067. |
| [8] | R. M. Alagu and E.G. Sundaram, Nitrogen oxide emission in biodiesel fuelled CI engines - A review. Proceedings of Frontiers in Automobile and Mechanical Engineering (FAME) 25-27 Nov. 2010: 156-163. |
| [9] | N. Ladommatos, S.M. Abdelhalim, H. Zhao, Z. Hu, Effects of EGR on heat release in diesel combustion, SAE paper No. 980184, Society of Automotive Engineers Inc, Warrendale, PA, 1998. |
| [10] | A. Maiboom, X. Tauzia, J.F. Hetet, Experimental study of various effects of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) on combustion and emissions of an automotive direct injection diesel engine, energy, 33, pp. 22 – 34, 2008 |
| [11] | U. Asad, C. Kelly, M. Wang, and J. Tjong, Effects of Intake Air Humidity on the NOx Emissions and Performance of a Light-Duty Diesel Engine, ASME 2012 Internal Combustion Engine Division Fall Technical Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, September 23-26, 2012. |
| [12] | R. Mamat, N. R. Abdullah, H. Xu, M. L. Wyszynski and A. Tsolakis, Effect of boost temperature on the performance and emissions of a common rail diesel engine operating with rapeseed methyl ester (RME), Proc. World Congress on Engineering, June 30 – July 2, 2010, London, UK. |
| [13] | H. A. Saber, R. R. Ibraheem Al-Barwari and Z. J. Talabany, Effect of ambient air temperature on specific fuel consumption of naturally aspirated diesel engine, Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 1, No.1, pp. 1 -7, 2013. |
| [14] | S. Swami Nathan, J. M. Mallikarjuna and A. Ramesh, Effects of charge air temperature and exhaust gas re-circulation on combustion and emission characteristics of an acetylene fuelled HCCI engine, Fuel, Vol. 89, 2010, pp. 515 – 521. |
| [15] | C. Jayakumar, Z. Zheng, U. M. Joshi, W. Bryzik, N. A. Henein and E. Scattler, Effect of inlet air temperature on auto-ignition of fuels with different Cetane number and volatility, Proc. ASME International Combustion Engineering Division Fall Technical Conference (ICEF 2010), October 2 -5, 2011, Morgan Town, West Virginia, USA. |
| [16] | R. G. Papagiannakis, T. C. Zannis, E. A. Yfantis and D. T. Hountalas, Comparative evaluation of the effect of intake charge temperature, pilot fuel quantity and injection advance on dual fuel compression ignition engine performance characteristics and emitted pollutants, Proc. ASME 2009 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Vol. 3: Combustion Science and Engineering, Nov. 13 – 19, 2009, Florida, USA. |
| [17] | K. Chithamparam Asary, N.V. Mahalakshmi, and K. Jeyachandran, Reduction of NOx Emission from Diesel Engine using Urea Injection with SCR Technique with Different Catalyst Connected in Series, International Review of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 161 – 165, January 2012. |
| [18] | L. Karikalan, M. Chandrasekaran, K. Sudhagar, Comparative Studies on Vegetable Oil Usage in C.I Engines as an Alternative to Diesel Fuel, International Review of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 7, No. 4, pp. 705 – 715, May 2013. |
| [19] | Abdulaziz H. E l- Sinwai, K. Takrouri, O. Ostar and N. Haimour, The effect of high water content of fuel on diesel engine emission, Global Journal of Researches in Engineering (C), Vol. XII, Issue III, Version 1.0, 2012. |
| [20] | C. Y. Lin and Y.L Jeng, Influences of charge air humidity and temperature on the performance and emission characteristics of diesel engines, Journal Ship Research, Vol. 40, No. 2, pp. 172-177, June 1996. |
| [21] | R. K. Maurya and A. K. Agarwal, Experimental investigation of the effect of the intake air temperature and mixture quality on the combustion of a methanol – and gasoline – fuelled homogeneous charge compression ignition engine, Proc. The Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, Vol. 223, No. 11, pp. 1445 – 1458, November 1, 2009. |
| [22] | TSI, Combustion Analysis Basics, An Overview of Measurements, Methods and Calculations Used in Combustion Analysis, TSI Incorporated, 2004. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML