-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Energy Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1891 e-ISSN: 2163-1905
2014; 4(1): 10-15
doi:10.5923/j.ijee.20140401.03
Enhanced Photo-thermal Response of a Cement-based Composite Containing Carbon Nanotubes
Gérrard Eddy Jai Poinern, Jurek Marin Malarecki, Derek Fawcett
Murdoch Applied Nanotechnology Research Group. Department of Physics, Energy Studies and Nanotechnology, School of Engineering and Energy, Murdoch University, Murdoch, Western Australia 6150, Australia
Correspondence to: Gérrard Eddy Jai Poinern, Murdoch Applied Nanotechnology Research Group. Department of Physics, Energy Studies and Nanotechnology, School of Engineering and Energy, Murdoch University, Murdoch, Western Australia 6150, Australia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Direct absorption solar thermal collectors have the potential to offer an unlimited source of renewable energy with minimal environmental impact. The results of laboratory based testing and outdoor testing using a 1 m diameter parabolic dish solar oven have shown that a modified cement mortar containing small quantities of carbon nanotubes can improve its photo-thermal response compared to the plain mortar. Laboratory based testing under visible light recorded a temperature difference of up to 8.1ºC between the plain cement mortar and the optimized carbon nanotube based cement mortar. Solar oven studies recorded a temperature difference of up to 132ºC between the optimized carbon nanotube based cement mortar (293ºC) and the plain cement mortar (161ºC). These studies have revealed that modifying a cement mortar with 5 mg of carbon nanotubes can effectively improve its photo-thermal response and its ability to perform as an effective thermal absorber.
Keywords: Photo-thermal response, Renewable energy, Carbon nanotubes
Cite this paper: Gérrard Eddy Jai Poinern, Jurek Marin Malarecki, Derek Fawcett, Enhanced Photo-thermal Response of a Cement-based Composite Containing Carbon Nanotubes, International Journal of Energy Engineering, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 10-15. doi: 10.5923/j.ijee.20140401.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Solar energy is the largest source of renewable energy available on Earth. The hourly solar flux incident on the Earth’s surface is greater than the annual human consumption of energy in a year[1]. Despite this large amount of renewable solar energy being available, approximately 80% of energy used worldwide still predominantly comes from fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas[2]. Unfortunately, problems such as global warming and carbon dioxide emissions are normally associated with conventional fossil fuel based power generation technologies. Thus, there is a need to develop new and efficient renewable energy based technologies capable of delivering economically sustainable sources of energy in an environmentally friendly manner. Solar energy is the largest source of renewable energy that has been collected, concentrated and converted into a variety of usable forms of energy. Nevertheless, there are still problems associated with efficiently collecting and converting solar energy into other useful forms of energy. One of the most common methods of collection is through solar thermal collectors such as solar water heaters[3, 4], solar cookers[5, 6] and solar ponds[7, 8]. The design of solar thermal collectors for collecting solar radiation and efficiently converting the energy is varied[2]. A typical solar thermal collector consists of an absorber, generally in the form of plates and tubes which are coated with a spectrally selective material that improves the absorption of solar energy. The absorber then transfers heat to a circulating fluid contained within the tubes of the absorber [9]. The significant advantages of using this type of solar energy collecting system consist of: 1) it is potentially 100% renewable; 2) it produces no emissions, and 3) it greatly reduces the cost of heating the circulating fluid. However, the efficiency of a solar thermal collector is heavily dependent on how effective the absorber can capture solar energy. It is therefore not surprising that there is considerable interest in improving the performance of the current absorber material, which will in turn produce greater heating efficiencies. Hence, developing new absorber materials with improved thermal properties compared to their conventional counterparts has the potential to significantly improve the solar collector performance. The discovery of new forms of carbon nano-structured materials from the Cn family consisting of nano-tubes (CNTs)[10-12], nano-filaments[13], nano- capsules[14] and carbon nano-spheres (CNS)[15] revealed that these materials had significantly enhanced properties compared to conventional carbonaceous materials. Studies of CNTs have shown that besides being the blackest material discovered to date[16], and it also has both excellent thermal and electrical conductivities[17, 18]. However, it is their thermal conductivities that make them attractive for potential solar thermal absorbers. And depending on their structure and composition, the thermal conductivity of CNTs varies as a function of temperature and peak before 300 K and decrease for greater temperatures[19]. Interestingly, room temperature measurements of thermal conductivity for bulk samples of single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) gave values greater than 200 Wm-1K-1, while individual multi-walled nanotubes (MWCNTs) were found to have values greater than 3000 Wm-1K-1[19]. In comparison, the thermal conductivity of copper at room temperature is around 401 Wm-1K-1[20]. In addition, CNTs remain stable at elevated temperatures up to 2800°C in a vacuum and around 750°C in air[16]. Furthermore, when comparatively small amounts of CNTs are added to bulk materials there is a significant enhancement of material properties. Improvement in material properties include increased strength[21], thermal and electrical conductivities[22, 23, 24]. For example, the inclusion of 1% by mass of CNTs to an insulator mass such as epoxy resin was found to increase in the thermal conductivity of the resin twofold[19].Unfortunately, CNTs are virtually insoluble in most aqueous and organic solvents since they tend to agglomerate due to strong van der Waals interactions[25, 26]. Consequently, CNTs disperse poorly and adhere to intended composite materials weakly, which prevent effective load transfer taking place within the composite. The lack of effective bonding between CNTs and the bulk material can result in the in unsatisfactory mechanical properties[25]. Therefore, it is important to resolve the issues of dispersion and adhesion of CNTs within a bulk material in order to optimise the full benefits of improved mechanical and thermal properties of the composite[21]. Since CNTs are particularly good adsorbents, aqueous solutions containing a natural emulsifier have been shown to promote the dissolution of individual CNTs by physically adsorbing onto the CNT bundle surfaces and causing the CNTs to separate. The emulsifier molecules attach to the surface of the individual CNTs, which disrupts the interactions between the CNTs and stabilises the isolated CNTs in solution[27]. For example, the formation of aqueous CNT solutions was made possible through the use of starch-iodine complexes and amylose-iodine complexes [28].In this preliminary study, a novel solar thermal absorber material composed of CNTs and commercially available high temperature resistant calcium aluminate based refractory cement is synthesised and tested. The poor solubility of CNTs was addressed by using Gum Arabic (GA) as the dispersant in the aqueous solutions. The photo-thermal response of a series of 50 g CNTs/Cement mortar composites, containing varying amounts of CNTs ranging from 1 mg to 5 mg of CNTs was studied under both visible and ultraviolet light. The influence of higher concentrations of CNTs was also investigated before the optimized 5 mg CNTs absorber was placed in a parabolic dish solar oven and the photo-thermal response measured. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) was used to characterize and examine the distribution of CNTs within the cement mortar absorbers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- The multi-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were supplied by Advanced Nanotechnology Limited, Australia, (now Antaria, Australia), while the Gum Arabic (GA) derived from the acacia tree was supplied by Sigma-Aldrich, USA and was used without further purification. All aqueous solutions used throughout this study were made using Milli-Q® water (18.3 MΩ cm-1) produced by an ultrapure water system (Barnstead Ultrapure Water System D11931; Thermo Scientific, Dubuque, IA). The ultrasound processor used to prepare the dispersed CNTs samples was an UP50H (50 W, 30 kHz, MS7 Sonotrode (7 mm diameter, 80 mm length)) supplied by Hielscher Ultrasound Technology. The high temperature resistant cement was used to manufacture the CNTs/cement pellets that would become the solar absorber material, was supplied by Ciment Fondu®
2.2. Preparation of CNTs/Cement Mortar Absorber
- Each respective mass of CNTs ranging from 1 mg to 6 mg and 10 mg (measured using an analytical balance AND ER-180A: ± 0.00005g) were added to their respective glass sample beakers each containing 11 mL of Milli-Q® water and 2 g of GA which acted as the dispersing agent. The solution is then subjected to 10 minutes of ultrasound irradiation using the UP50H ultrasound processor set to 20% amplitude. The solution was then allowed to cool for 15 minutes before being mixed with a cement/sand blend with a ratio of 2/3 respectively for each CNTs mass sample. The water/cement ratio of 0.4 recommended by the cement manufacturer was maintained during the mixing process[29]. The respective CNTs/cement mortar slurries were then poured into 25 mL Terumo plastic syringes pre-treated with a light coating of cooking oil (olive), which served as moulds for forming the mortar pellets. The light coating of oil was sprayed on to the inner surfaces of the syringes to prevent mortar sticking and assisted in the removal of the mortar pellet. In addition to the CNTs/cement mortar pellets was a set of control pellets, which consisted of only cement mortar. All the pellets were given three days to cure and dry before being removed for the moulds. The syringe-based moulds were able to produce sturdy pellets with a diameter of 20 mm and a length of 70 mm.
2.3. Photo-thermal Response
- The photo-thermal response of the control pellets and the various CNTs/cement mortar pellets were investigated under 3 difference light exposure regimes. In the first regime, a control and a series of CNTs/cement absorbers were exposed to visible light from a conventional 100 W light globe placed at a distance of 10 cm from the respective samples in turn. The samples were exposed to visible light from the light globe for 2100 s (35 min), during this time the temperature rise was measured using a Digitech QM-1600 digital thermometer. During the second light exposure regime, a 300 W Sanolux Radium ultraviolet (UV) lamp was used. The lamp was positioned 10 cm from the sample and the temperature rise was recorded over the 2100 s test period. In the final investigation, each CNTs/cement absorber was placed into a parabolic dish solar oven (1 m in diameter) for 900 s (15 min) and the increase in temperature was recorded. In all photo-thermal response measurements, the temperature sensor was centrally located in the bulk of the sample via a pre-drilled 2 mm diameter hole, which was filled with Dow Corning® 340 heat sink compound.
2.4. CNTs Distribution in Cement Absorber
- Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) was used to investigate the distribution of CNTs throughout the CNTs/cement pellets, which formed the solar absorber. All samples prepared for FESEM were first sputter coated with a 3 nm layer of gold to ensure conductivity. All micrographs were taken using a high resolution FESEM [Zeiss 1555 VP-FESEM] at 3 kV with a 30 µm aperture operating under a pressure of 110-10 Torr.
3. Results and Discussions
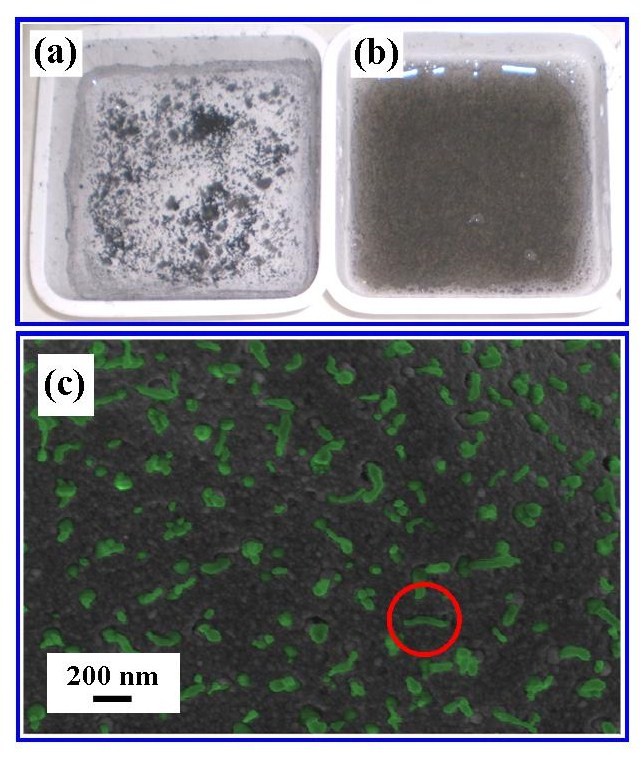
- The insolubility of CNTs in Milli-Q® water was address by using a natural dispersant. In this case the dispersant used was Gum Arabic (GA) which is derived directly from the acacia tree. In this case 2 g of GA was added a solution of 11 mL of water before the CNTs were added and ultrasound treatment applied. After 10 minutes of ultrasound irradiation the CNTs with GA were thoroughly dispersed throughout the solution as shown in Figure 1(b). This was not the case for the solution without GA, in this case the CNTs tended to agglomerate on the surface of the solution as shown in Figure 1(a). The subsequent mixing of CNTs/GA solution with cement and mineral sand also proved to be effective in dispersing the CNTs throughout the cement mortar pellets, which formed the solar absorber. Figure 1(c) presents a micrograph of a typical cross-section taken of a cement mortar pellet using FESEM microscopy.
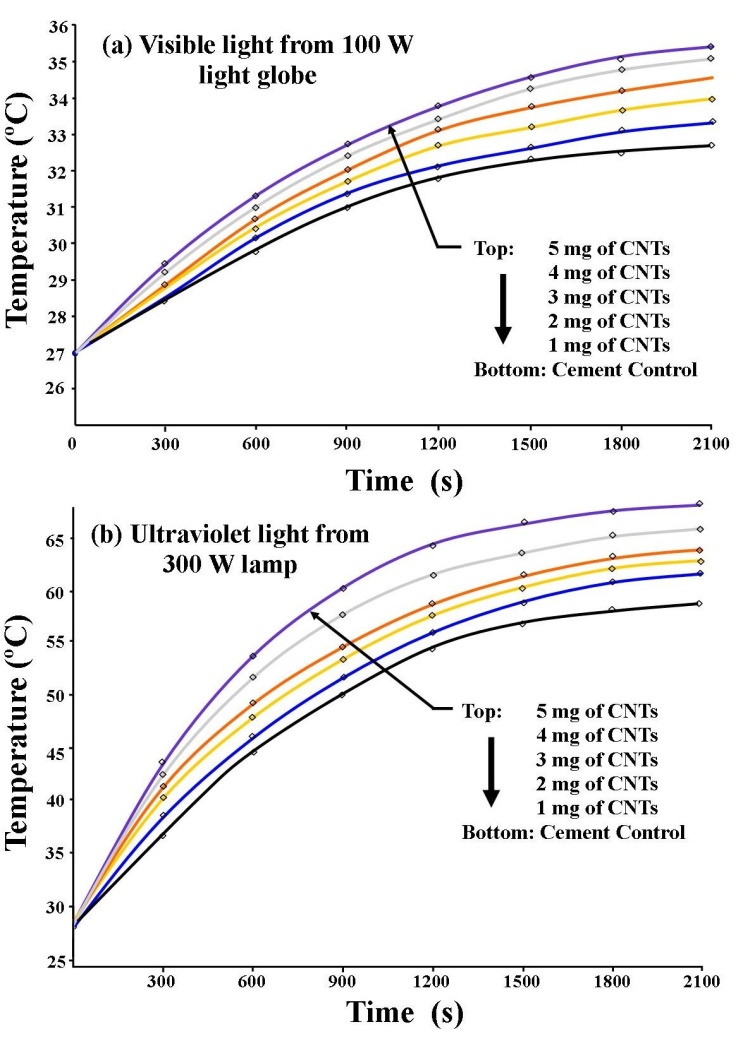 | Figure 2. Photo-thermal responses of various CNTs mass based CNTs/cement mortar absorbers to visible light (a) and ultraviolet light (b) |
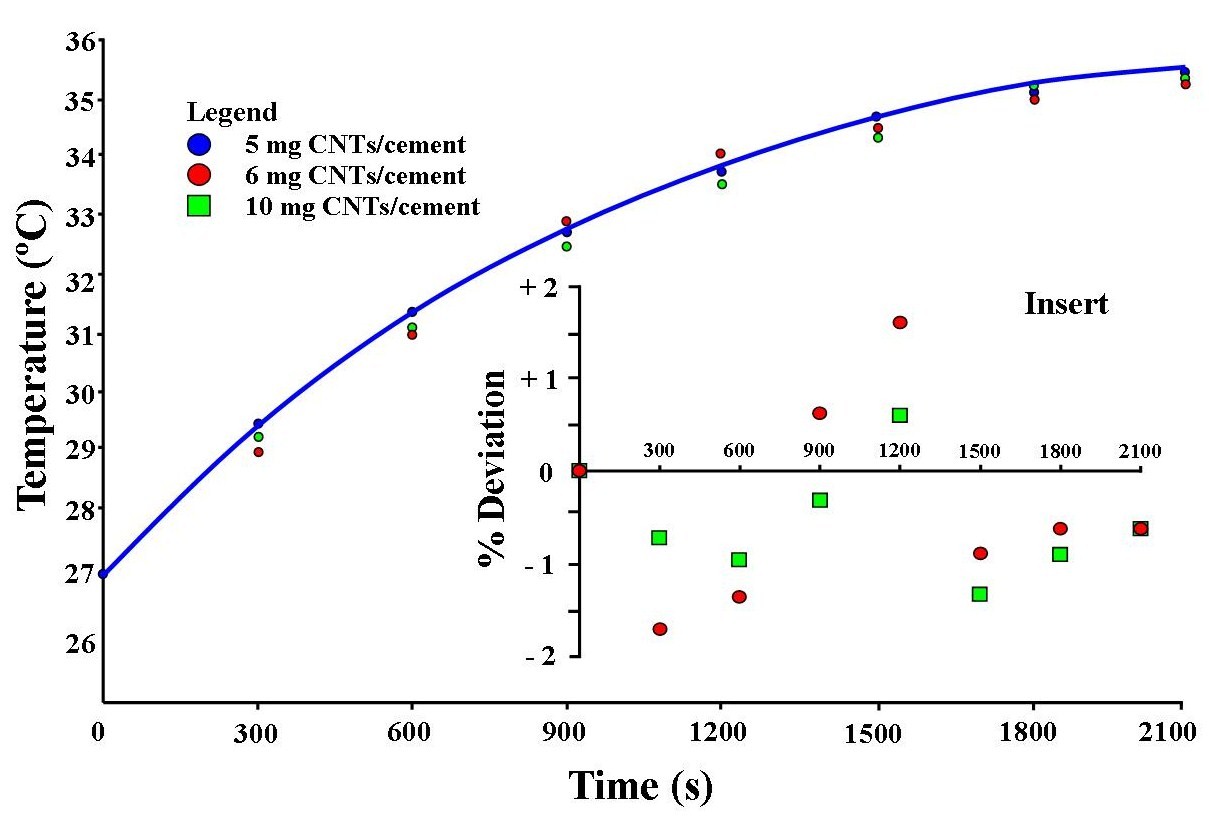 | Figure 3. Photo-thermal response of optimized 5 mg CNTs/cement mortar compared to higher fractions of CNTs when illuminated by a 100 W visible light globe |
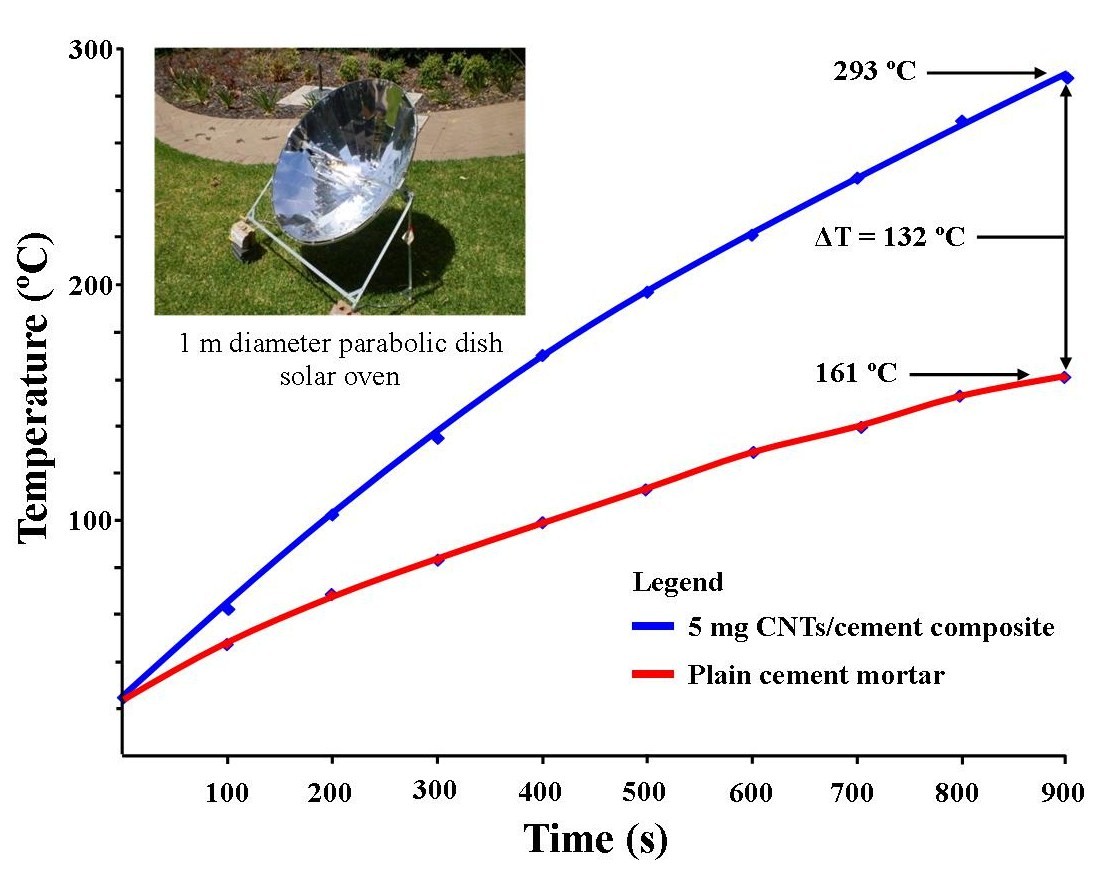 | Figure 4. Photo-thermal response of 5 mg CNTs/cement mortar pellet compared to a plain cement mortar pellet when mounted in a 1m diameter parabolic dish solar oven |
4. Conclusions
- The result of this preliminary investigation into the photo-thermal response of CNTs/cement mortar based ceramics has highlighted the significance of incorporating small quantities of CNTs into a conventional building cement mortar. In all cases, adding small quantities of CNTs has produced a noticeable increase in the photo-thermal of the mortars. The optimal value of 5 mg of CNTs (0.01% by mass of mortar pellet) produced the most profound effect in both laboratory-based studies and in the field study, which used a 1 m diameter parabolic dish solar oven. The solar oven was able to produce at temperature of 293ºC in 900 seconds for the 5 mg CNTs composite mortar and clearly indicate the positive photo-thermal enhancement by the addition of the small quantity of carbon nanotubes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to thank both the Western Australian Nanochemistry Research Institute (WANRI) and Burrup Fertilizers Pty Ltd for supporting this study.
Disclosure
- The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML