-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Energy Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1891 e-ISSN: 2163-1905
2012; 2(6): 285-292
doi: 10.5923/j.ijee.20120206.03
Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) on Performance and Emission of a Compression Ignition Engine with Staged Combustion (Insertion of Unburned Hydrocarbon)
Hussain. J 1, Palaniradja. K 2, Alagumurthi. N 2, Manimaran. R 1
1Pondicherry Engineering College, Puducheery, India
2Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Pondicherry Engineering College, Puducheery, India
Correspondence to: Hussain. J , Pondicherry Engineering College, Puducheery, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The usage of EGR adopted diesel engine increasing day by day worldwide to reduce the NOx emissions. The EGR adopted engines can reduce NOx Considerably but it adversely improves the emissions of UHC nearly 40 to 50 %. We can avoid this effect by Reutilization of UHC. In this paper the experimental investigation has been carried out on EGR adopted direct injection compression ignition engine with insertion of unburned hydro carbon rich exhaust. The results were presented and compared with all EGR levels. The result were evidenced that can reduce 20 to 25 % of UHC by this method.
Keywords: EGR, Engine Performance, Staged Combustion, Nox
Cite this paper: Hussain. J , Palaniradja. K , Alagumurthi. N , Manimaran. R , "Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) on Performance and Emission of a Compression Ignition Engine with Staged Combustion (Insertion of Unburned Hydrocarbon)", International Journal of Energy Engineering, Vol. 2 No. 6, 2012, pp. 285-292. doi: 10.5923/j.ijee.20120206.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Better fuel economy and higher power with lower maintenance cost has increased the popularity of diesel engine vehicles. Diesel engines are used for bulk movement of goods, powering stationary/ mobile equipment, and to generate electricity more economically than any other device in this size range. In most of the global car markets, record diesel car sales have been observed in recent years[1]. The exhorting anticipation of additional improvements in diesel fuel and diesel vehicle sales in future have forced diesel engine manufacturers to upgrade the technology in terms of power, fuel economy and emissions. Diesel emissions are categorized as carcinogenic[2]. The stringent emission legislations are compelling engine manufacturers to develop technologies to combat exhaust emissions. To meet these emission regulations with competitive fuel economy, exhaust gas after-treatment and optimized combustion are necessary. However, it is still unresolved which concept will succeed considering production and economic feasibility[3]. Diesel engines are very popular power plants for decentralized power production in rural areas all over the world as well as for powering the farm equipment due to their fuel economy, ease of maintenance and robustness. Diesel engines are assumed as a good alternative to gasoline engines because they produce lower amount of emissions[4]. On the other hand, higher emissions of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) have been noticed as major problems. Although, major constituents of diesel exhaust include carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O), nitrogen (N2), and oxygen (O2); carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), oxides of nitrogen (NOx), and particulate matter (PM) are present in smaller but environmentally significant quantities. In modern diesel engines, first four species normally consist of more than 99% exhaust, while last four (the harmful pollutants) account for less than 1% exhaust[5]. NOx comprise of nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and both are considered to be deleterious to humans as well as environmental health. NO2 is considered to be more toxic than NO. It affects human health directly and is precursor to ozone formation, which is mainly responsible for smog formation. The ratio of NO2 and NO in diesel engine exhaust is quitesmall, but NO gets quickly oxidized in the environment, forming NO2[6]. Since diesel engine mainly emits NO hence attention has been given to reduce the NO formation[7].
1.1. Nox Formation Mechanism
- NO is formed inside the combustion chamber in post-flame combustion process in the high temperature region. The NO formation and decomposition inside the combustion chamber can be described by extended Zeldovich Mechanism[8]. The principal reactions at near stoichiometric fuel–air mixture governing the formation of NO from molecular nitrogen are
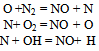 The initial rate controlled NO formation (i.e. when[NO]/[NO2]e_1) can be described by the Eq. (1). In the expression[NO] denotes the molar concentration of the species and[O2]e and[N2]e denotes the equilibrium concentration[7].
The initial rate controlled NO formation (i.e. when[NO]/[NO2]e_1) can be described by the Eq. (1). In the expression[NO] denotes the molar concentration of the species and[O2]e and[N2]e denotes the equilibrium concentration[7].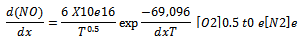 mol s/cm3 The sensitivity of NO formation rate to temperature and oxygen concentration is evident from this equation. Hence in order to reduce the NOx formation inside the combustion chamber, the temperature and oxygen concentration in the combustion chamber need to be reduced. Even though, certain cetane improving additives are capable of reducing NOx, the amount of reduction is reported to be inadequate. Moreover, most of these additives are expensive. Retarded injection is an effective method employed in diesel engines for NOx control. However, this method leads to increased fuel consumption, reduced power, increased HC emissions and smoke. Water injection is another method for NOx control however this method enhances corrosion of vital engine components.In addition, it adds to the weight of the engine system because of requirement of a water storage tank. It is also difficult to retain water at a desired temperature during cold climate[9].
mol s/cm3 The sensitivity of NO formation rate to temperature and oxygen concentration is evident from this equation. Hence in order to reduce the NOx formation inside the combustion chamber, the temperature and oxygen concentration in the combustion chamber need to be reduced. Even though, certain cetane improving additives are capable of reducing NOx, the amount of reduction is reported to be inadequate. Moreover, most of these additives are expensive. Retarded injection is an effective method employed in diesel engines for NOx control. However, this method leads to increased fuel consumption, reduced power, increased HC emissions and smoke. Water injection is another method for NOx control however this method enhances corrosion of vital engine components.In addition, it adds to the weight of the engine system because of requirement of a water storage tank. It is also difficult to retain water at a desired temperature during cold climate[9].1.2. Exhaust Gas Recirculation
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation is an effective method for NOx control. The exhaust gases mainly consist of carbon dioxide, nitrogen etc. and the mixture has higher specific heat compared to atmospheric air. Re-circulated exhaust gas displaces fresh air entering the combustion chamber with carbon dioxide and water vapor present in engine exhaust. As a consequence of this air displacement, lower amount of oxygen in the intake mixture is available for combustion. Reduced oxygen available for combustion lowers the effective air–fuel ratio. This effective reduction in air–fuel ratio affects exhaust emissions substantially. In addition, mixing of exhaust gases with intake air increases specific heat of intake mixture, which results in the reduction of flame temperature. Thus combination of lower oxygen quantity in the intake air and reduced flame temperature reduces rate of NOx formation reactions[10,11]. The EGR (%) is defined as the mass percent of the recirculated exhaust (MEGR) in the total intake mixture (Mi).
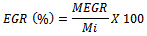 Desantes et al. used NDIR-based CO2 concentration measurement at the intake ([CO2]int) and exhaust manifold ([CO2]exh) for the determination of EGR rate[12].
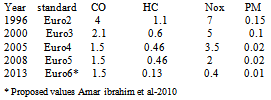
Desantes et al. used NDIR-based CO2 concentration measurement at the intake ([CO2]int) and exhaust manifold ([CO2]exh) for the determination of EGR rate[12].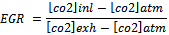 The engines using EGR emit lower quantity of exhaust gases compared to non-EGR engines because part of the exhaust gas is re-circulated[13]. Thus even if the concentration of toxic substances in the exhaust gas remains unchanged, the total quantity of emission of toxic substances reduce for the same volumetric concentration. Diesel engines operating at low loads and generally tolerate a higher EGR ratio because re-circulating exhaust gases contain high concentration of oxygen and low concentration of carbon dioxide and water vapors. However at higher loads, the oxygen in exhaust gas becomes scarce and the inert constituents start dominating along with increased exhaust temperature. Thus, as load increases, diesel engines tend to generate more smoke because of reduced availability of oxygen[5]. Wagner et al. tried to achieve lower emission of NOx and soot using highly diluted intake mixture. At very high EGR rate (around 44%), PM emission decreased sharply with a continuous drop in NOx emission but this high EGR rate significantly affect the fuel economy[14]. Sasaki et al. conducted experiments using EGR on direct injection gasoline engine and reported that an appropriate volume of EGR improves fuel economy and HC emissions. This phenomenon was presumably due to the intake temperature increase by EGR, which improved the flame propagation in the relatively lean region of the air–fuel mixture, which is non-uniformly distributed[15]. Kusaka et al. also found that at low loads, EGR combined with intake heating can favorably reduce THC emission with improvement in thermal efficiency[16]. EGR was also used in a direct injection spark ignition engine as an effective way for improving fuel economy[17,18]. Das et al. used EGR to reduce NOx emissions in hydrogen – supplemented SI engine without any undesirable combustion phenomena[19]. Sato et al. performed experiments using methanol in direct injection compression ignition engine and found that combustion performance becomes inferior under light load conditions because temperature in combustion chamber fell due to very high latent heat of methanol, thus hampering formation of combustible air–fuel mixture[20]. Selim et al. operated the diesel engine in dual fuel mode with natural gas and found inferior performance and emissions at low loads because lean mixtures formed at low loads were hard to ignite and had slow burning characteristics. EGR was found to be a method of improving engine performance and emissions of such engines[21]. However, application of EGR also leads to penalties. In case of diesel engines, these penalties include higher specific fuel consumption and particulate matter emissions. Effectively, a trade-off between NOx and soot is observed with the use of EGR[22–27]. The reduction in flame temperature reduces the rate of soot oxidation/re-burning. As a result, in EGR system, more soot is formed during combustion and it remains un-oxidized and eventually appears in the exhaust[10]. The rise in smoke (soot) level of engine exhaust due to EGR affects the engine performance in various ways. Increased soot level causes considerable increase in the carbon deposits and wear of the various vital engine parts such as cylinder liner, piston rings, valve train and bearings. Wear of the materials also increase due to chemical reactions taking place on the surface (adsorption, corrosion) or due to abrasion of material or rupture of anti-wear film by soot. The application of EGR also adversely affects the lubricating oil quality and engine durability[28–33]. Gautam et al. experimentally proved that soot interacts with oil additives reducing its anti-wear properties possibly by abrasive wear mechanism. Increased wear due to EGR is because of presence of soot in lubricating oil[29]. Studies on valve-train wear in presence of soot were performed by Nagai et al. As the EGR rate was varied from 0 to 17% to 25%, the wear of cam noses and rocker arm tips was found to increase significantly[30]. If the exhaust gas is re-circulated directly to the intake, it results in increased intake charge temperature i.e. hot EGR. An increase in inlet charge temperature always results in shorter ignition delay and may improve thermal efficiency[34]. If the exhaust gas is cooled before recirculation to combustion chamber, then it is called cooled EGR. Cooling of EGR increases the charge density therefore improves volumetric efficiency of the engine. Also, it provides additional benefits by lowering NOx emissions to a greater extent. However, condensation of moisture present in the exhaust increases corrosion in combustion chamber. Plee et al. reported that major influence on NOx emission is due to change in temperature rather than oxygen availability[35]. In the present study, EGR was implemented to see the effect of EGR on wear of piston rings. The piston rings are most vital parts between piston and cylinder. The engine was operated for 96 hin normal running conditions and the wear of the piston rings and deposits on vital engine parts were assessed. The engine was again operated for 96 h with EGR and similar observations were made for piston ring wear and deposits. Since, EGR results in more soot formation, which in-turn affects the lubricating oil by thickening the oil and increases the wear debris in lubricating oil. Increased soot level and wear debris in lubricating oil may adversely affect the piston rings because piston rings are used to scrap off the excess lubricating oil from the cylinder liner and return it to oil sump. Engine performance and carbon deposits on injector tip, cylinder head and piston crown were also investigated. Various emission legislations were tabulated in Table 1
The engines using EGR emit lower quantity of exhaust gases compared to non-EGR engines because part of the exhaust gas is re-circulated[13]. Thus even if the concentration of toxic substances in the exhaust gas remains unchanged, the total quantity of emission of toxic substances reduce for the same volumetric concentration. Diesel engines operating at low loads and generally tolerate a higher EGR ratio because re-circulating exhaust gases contain high concentration of oxygen and low concentration of carbon dioxide and water vapors. However at higher loads, the oxygen in exhaust gas becomes scarce and the inert constituents start dominating along with increased exhaust temperature. Thus, as load increases, diesel engines tend to generate more smoke because of reduced availability of oxygen[5]. Wagner et al. tried to achieve lower emission of NOx and soot using highly diluted intake mixture. At very high EGR rate (around 44%), PM emission decreased sharply with a continuous drop in NOx emission but this high EGR rate significantly affect the fuel economy[14]. Sasaki et al. conducted experiments using EGR on direct injection gasoline engine and reported that an appropriate volume of EGR improves fuel economy and HC emissions. This phenomenon was presumably due to the intake temperature increase by EGR, which improved the flame propagation in the relatively lean region of the air–fuel mixture, which is non-uniformly distributed[15]. Kusaka et al. also found that at low loads, EGR combined with intake heating can favorably reduce THC emission with improvement in thermal efficiency[16]. EGR was also used in a direct injection spark ignition engine as an effective way for improving fuel economy[17,18]. Das et al. used EGR to reduce NOx emissions in hydrogen – supplemented SI engine without any undesirable combustion phenomena[19]. Sato et al. performed experiments using methanol in direct injection compression ignition engine and found that combustion performance becomes inferior under light load conditions because temperature in combustion chamber fell due to very high latent heat of methanol, thus hampering formation of combustible air–fuel mixture[20]. Selim et al. operated the diesel engine in dual fuel mode with natural gas and found inferior performance and emissions at low loads because lean mixtures formed at low loads were hard to ignite and had slow burning characteristics. EGR was found to be a method of improving engine performance and emissions of such engines[21]. However, application of EGR also leads to penalties. In case of diesel engines, these penalties include higher specific fuel consumption and particulate matter emissions. Effectively, a trade-off between NOx and soot is observed with the use of EGR[22–27]. The reduction in flame temperature reduces the rate of soot oxidation/re-burning. As a result, in EGR system, more soot is formed during combustion and it remains un-oxidized and eventually appears in the exhaust[10]. The rise in smoke (soot) level of engine exhaust due to EGR affects the engine performance in various ways. Increased soot level causes considerable increase in the carbon deposits and wear of the various vital engine parts such as cylinder liner, piston rings, valve train and bearings. Wear of the materials also increase due to chemical reactions taking place on the surface (adsorption, corrosion) or due to abrasion of material or rupture of anti-wear film by soot. The application of EGR also adversely affects the lubricating oil quality and engine durability[28–33]. Gautam et al. experimentally proved that soot interacts with oil additives reducing its anti-wear properties possibly by abrasive wear mechanism. Increased wear due to EGR is because of presence of soot in lubricating oil[29]. Studies on valve-train wear in presence of soot were performed by Nagai et al. As the EGR rate was varied from 0 to 17% to 25%, the wear of cam noses and rocker arm tips was found to increase significantly[30]. If the exhaust gas is re-circulated directly to the intake, it results in increased intake charge temperature i.e. hot EGR. An increase in inlet charge temperature always results in shorter ignition delay and may improve thermal efficiency[34]. If the exhaust gas is cooled before recirculation to combustion chamber, then it is called cooled EGR. Cooling of EGR increases the charge density therefore improves volumetric efficiency of the engine. Also, it provides additional benefits by lowering NOx emissions to a greater extent. However, condensation of moisture present in the exhaust increases corrosion in combustion chamber. Plee et al. reported that major influence on NOx emission is due to change in temperature rather than oxygen availability[35]. In the present study, EGR was implemented to see the effect of EGR on wear of piston rings. The piston rings are most vital parts between piston and cylinder. The engine was operated for 96 hin normal running conditions and the wear of the piston rings and deposits on vital engine parts were assessed. The engine was again operated for 96 h with EGR and similar observations were made for piston ring wear and deposits. Since, EGR results in more soot formation, which in-turn affects the lubricating oil by thickening the oil and increases the wear debris in lubricating oil. Increased soot level and wear debris in lubricating oil may adversely affect the piston rings because piston rings are used to scrap off the excess lubricating oil from the cylinder liner and return it to oil sump. Engine performance and carbon deposits on injector tip, cylinder head and piston crown were also investigated. Various emission legislations were tabulated in Table 1
|
1.3. Specification of the Engine

2. Experimental Setup and Methodology
- A two-cylinder constant speed diesel engine generator set was chosen to study the effect of EGR on the performance and emissions, carbon deposits, and wear of diesel engine components. The specifications of engine are given in section 2.1. The engine is coupled with an AC generator and the current generated is used by a resistive load bank, thus in-turn loading the engine. The generator is calibrated and all losses in the generator such as copper losses, armature current losses and friction and windage losses (unaccounted losses) are accounted for and taken into consideration while analysing the data. For recirculation of the exhaust gas, appropriate plumbing was done. No insulation on the pipe line was provided therefore allowing the re-circulated exhaust gases to partially cool down. the Exhaust gas drawn from the 1st and 3rd cylinder were partially allowed inside the 2nd cylinder with the help of separate EGR control valve and the fuel supplied to the 2nd cylinder was controlled by separate flow valve and corresponding fuel rate also considered for calculation The schematic diagram of the engine setup is shown in Fig. 1.
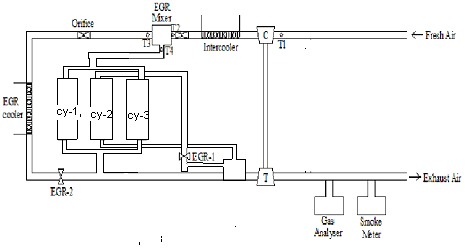 | Figure 1. The schematic diagram of the engine setup |
|
3. Results and Discussion
- The engine was run on different loads at 1500 rpm with different EGR rates (from 0% to 25%) to investigate the effect of EGR on engine performance and emissions. The performance and emission data was analysed and presented graphically for thermal efficiency, BSFC, exhaust gas temperature, HC, CO, NOx emission, and smoke opacity.
3.1. Engine Performance Analysis
- The trends of thermal efficiency are shown in Fig. 2. Thermal efficiency is found to have slightly increased with EGR at lower engine loads. The possible reason may be re-burning of hydrocarbons that enter the combustion chamber with the re-circulated exhaust gas. At part loads, exhaust gas has less CO2 and fairly high amount of O2. Also, partly-cooled EGR acts like a pre-heater of the intake mixture. When this exhaust gas is re-circulated in the cylinder, the unburned HC in exhaust gas burns because of sufficient O2 available in combustion chamber and reasonably high intake temperatures. In staged combustion excess of unburned hydrocarbons utilized with reduced fuelling rates at higher engine loads, the thermal efficiency remains unaffected by EGR. At higher loads, exhaust gas has higher amount of CO2, which reduces maximum temperature in combustion chamber along with oxygen availability therefore re-burning of HC is not significant.
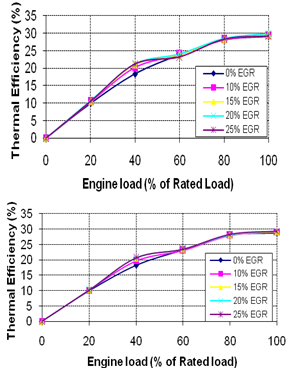 | Figure 2. Thermal Efficiency for Different EGR Rates ,a).EGR Without Staged Combustion, b) EGR With Staged Combustion |
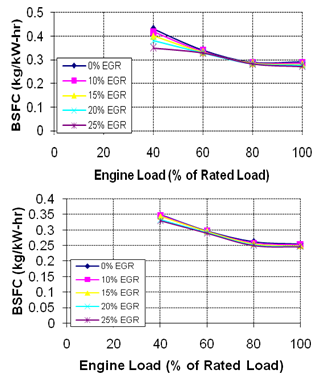 | Figure 3. Brake Specific Fuel Consumption for different EGR Rates,a).EGR Without Staged Combustion b) EGR With Staged Combustion |
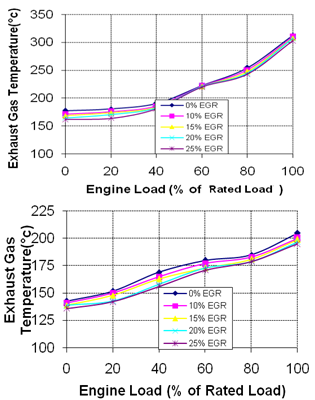 | Figure 4. Exhaust Gas Temperatures for various EGR rates, a).EGR Without Staged Combustion b) EGR With Staged Combustion |
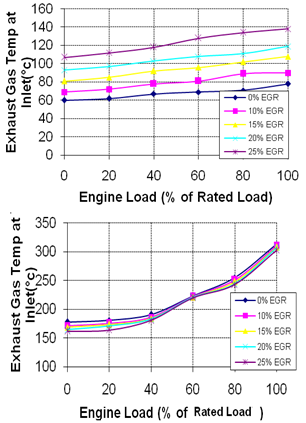 | Figure 5. Exhaust Gas Temperature at the entry of inlet manifold for various EGR Rates, a).EGR Without Staged Combustion b) EGR With Staged Combustion |
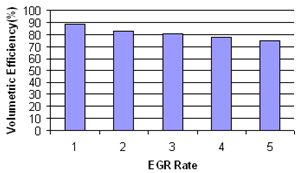 | Figure 6. Volumetric Efficiency for different EGR Rates |
3.2. Engine Emission Analysis
- Effect of EGR on unburned hydrocarbon (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) are shown in Figs. 7 and 8, respectively. These graphs show that HC and CO emissions increase with increasing EGR. Lower excess oxygen concentration results in rich air–fuel mixtures at different locations inside the combustion chamber. This heterogeneous mixture does not combust completely and results in higher hydrocarbons, and carbon monoxide emissions. At part loads, lean mixtures are harder to ignite because of heterogeneous mixture and produce higher amount of HC and CO. Fig. 9 shows the main benefit of EGR in reducing NOx emissions from diesel engine. The degree of reduction in NOx at higher loads is higher. The reasons for reduction in NOx emissions using EGR in diesel engines are reduced oxygen concentration and decreased flame temperatures in the combustible mixture. At the part load, O2 is available in sufficient quantity but at high loads, O2 reduces drastically, therefore NOx is reduced more at higher loads compared to part loads.
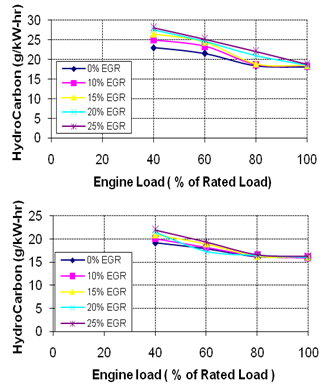 | Figure 7. Hydro Carbons for different EGR Rates, a).EGR Without Staged Combustion, b) EGR With Staged Combustion |
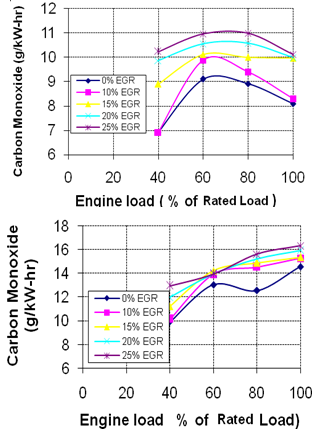 | Figure 8. Carbon Monoxide for different EGR Rates, a).EGR Without Staged Combustion , b) EGR With Staged Combustion |
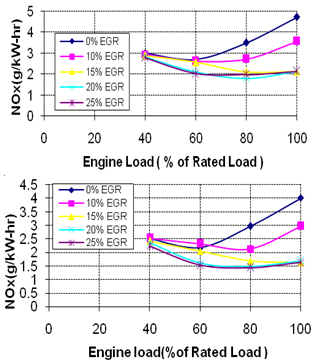 | Figure 9. NOx for different EGR Rates, a).EGR Without Staged Combustion , b) EGR With Staged Combustion |
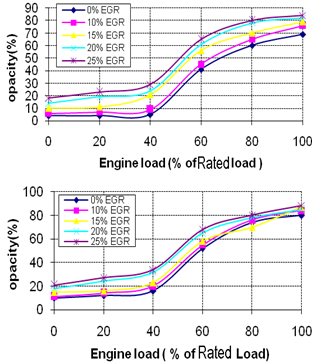 | Figure 10. Smoke Opacity for different EGR rates, a).EGR Without Staged Combustion , b) EGR With Staged Combustion |
4. Conclusions
- In the present research, experimental investigations were conducted to study the effect of EGR with and without staged combustion on performance and emissions of a diesel engine. EGR displaces oxygen in the intake air by exhaust gas re-circulated to the combustion chamber. Reduced oxygen and lower flame temperatures affect performance and emissions of diesel engine in different ways. Thermal efficiency is slightly increased and BSFC is decreased at lower loads with EGR compared to without EGR. But at higher loads, thermal efficiency and BSFC are almost similar with EGR than without EGR. Exhaust gas temperature is decreased with EGR. Hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and smoke opacity are increased with EGR, but NOx emission decreases significantly. It can be observed that 15% EGR rate is found to be effective to reduce NOx emission substantially without deteriorating engine performance in terms of thermal efficiency, SFC, and emissions. At lower loads, EGR reducesNOx without deteriorating performance and emissions at higher levels. At higher loads, increased rate of EGR reduces NOx to a great extent but deteriorates performance and emissions. Thus, it can be concluded that higher rate of EGR can be applied at lower loads. EGR can be applied to diesel engine without sacrificing its efficiency and fuel economy and NOx reduction can thus be achieved.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We wish to express our appreciation to Pondicherry Engineering College for supporting the project under which the current investigation has been conducted. Also we wish to express our gratitude to our guide for providing experimental data for this investigation and the guidelines during the coordination of the experiment
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML