-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Energy Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1891 e-ISSN: 2163-1905
2012; 2(4): 145-150
doi: 10.5923/j.ijee.20120204.06
Power Quality Improvements in Wind Diesel Hybrid Systems Using Bacteria Foraging Optimization Technique for Controller Parameter Optimization
K. S. Sandhu 1, Sudhir Sharma 2
1Department of Electrical Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Kurukshetra, India
2Department of Electrical Engineering,DAV Institute of Engineering and Technology, Jalandhar, India
Correspondence to: Sudhir Sharma , Department of Electrical Engineering,DAV Institute of Engineering and Technology, Jalandhar, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The wind energy conversion systems when operate in weak grid or in isolated mode may cause power quality problems due to variation in wind speed and other circuit conditions. To improve the power quality of wind generation system a wind-diesel hybrid system is proposed in this paper. The power quality of the system is improved by controlling the excitation and input power of the synchronous generator. The PID controller is used in input power controller. A new optimization technique i.e. bacteria foraging optimization to optimize the PID controller gains is used to improve the power quality of the proposed system.
Keywords: Wind- Diesel Hybrid System, Induction Generator, Power Quality, Optimization
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Wind power generation is increasing rapidly as the concern over environmental issues is gaining importance. Wind being the clean green energy is preferred by many countries over the other forms of energy. Induction generator is used for energy conversion in wind generation due to its advantage over the other types of generators. When the wind energy conversion systems are used in grid connected mode with strong grids they pose less power quality problems as compared to their operation in weak grid and isolated mode. Hence in order to control the power quality of wind generation system operating in isolated modes a wind diesel hybrid system is proposed in this paper. As the active and reactive power controls are not possible with induction generator the diesel engine coupled with synchronous generator is used for power quality improvement. Major power quality problems which appear are voltage related, frequency variations, harmonics and flicker etc. Wind diesel hybrid systems are developed and discussed by many researchers[1-15] In this paper the active and reactive power of the system is controlled by controlling the excitation and speed of the synchronous generator. PID controller is used for governor control which control the input power to diesel engine hence the speed of the engine is varied. Speed (input power) control with appropriate values of controller gains is found to be effective to improve the power quality of wind generation. Tuning of PID controller is difficult as many researchers used different optimization techniques[17]. But we have tried a new optimization technique i.e. Bacteria foraging optimization technique is proposed to optimize the controller gains. Advantages of Bacteria foraging and optimization of PID controller using bacteria foraging is discussed in[18-20]. In this paper power quality parameters are compared in three cases i.e. without controller, with controller (controller gains randomly selected) and third with optimized controller gains. Simulated results using optimized controller gains show the improvement in power quality of wind generation in contrast to other randomly selected values of controller gains.
2. Bacteria Foraging
- Natural selection tends to eliminate animals with poor foraging strategies and favor propagation of genes of those animals that have successful foraging strategies. This activity of foraging led the researchers to use it as optimization process. E. Coli bacteria that are present in our intestine also undergo foraging strategies. Based on the research of foraging behavior of E. coli bacteria many reserchers[18-20] exploit a variety of bacterial swarming and social foraging behavior, discussing how to connect social foraging process with distributed non-gradient optimization. In the bacterial foraging process, four motile behaviors are mimicked. They are described as chemotaxis, swarming, reproduction and elimination and dispersal. Chemotaxis: A chemotactic step can be represented by a tumble followed by a tumble or a tumble followed by a run. A tumble which is represented by a unit length random direction, ϕ(j), is generated; it is used to define the direction of movement after a tumble.
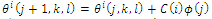 where θi(j,k,l) represents the ith bacterium at jth chemotactic, kth reproductive and lth elimination and dispersal step. C(i) is the size of the step taken in the random direction specified by the tumble (run length unit).Swarming: E. coli bacteria cells provide an attraction signal to each other so they swarm together. The swarming can be represented by mathematical equations:
where θi(j,k,l) represents the ith bacterium at jth chemotactic, kth reproductive and lth elimination and dispersal step. C(i) is the size of the step taken in the random direction specified by the tumble (run length unit).Swarming: E. coli bacteria cells provide an attraction signal to each other so they swarm together. The swarming can be represented by mathematical equations: 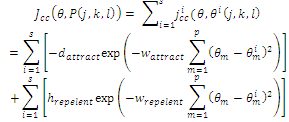 Where Jcc (θ,P(j,k,l) is the cost function value to be added to the actual cost function to be minimized to present a time varying cost function, S is the total number of bacteria, p is the number of parameters to be optimized which are present in each bacterium, and dattract , Wattract hrepelent , Wrepelent are different coefficients that should be chosen properly.Reproduction: The least healthy bacteria die and the other healthier bacteria each split into two new bacteria, which are placed in the same location. This makes the population of the bacteria constant.Elimination and Dispersal: It is possible that in the local environment, the lives of a population of bacteria changes either gradually (e.g., via consumption of nutrients) or suddenly due to some other influence. Events can occur such that all the bacteria in a region are killed or a group is dispersed into a new part of the environment. They have the effect of possibly destroying the chemotactic progress, but they also have the effect of assisting in chemotaxis, since dispersal may place bacteria near good food sources. From a broad perspective, elimination and dispersal are parts of the population-level long-distance motile behavior. This section is based on the work in[18-20]. A more detailed description of BF can be found in[19].
Where Jcc (θ,P(j,k,l) is the cost function value to be added to the actual cost function to be minimized to present a time varying cost function, S is the total number of bacteria, p is the number of parameters to be optimized which are present in each bacterium, and dattract , Wattract hrepelent , Wrepelent are different coefficients that should be chosen properly.Reproduction: The least healthy bacteria die and the other healthier bacteria each split into two new bacteria, which are placed in the same location. This makes the population of the bacteria constant.Elimination and Dispersal: It is possible that in the local environment, the lives of a population of bacteria changes either gradually (e.g., via consumption of nutrients) or suddenly due to some other influence. Events can occur such that all the bacteria in a region are killed or a group is dispersed into a new part of the environment. They have the effect of possibly destroying the chemotactic progress, but they also have the effect of assisting in chemotaxis, since dispersal may place bacteria near good food sources. From a broad perspective, elimination and dispersal are parts of the population-level long-distance motile behavior. This section is based on the work in[18-20]. A more detailed description of BF can be found in[19].3. Simulink Model
- The developed simulink model of wind diesel hybrid system is shown in figure 1. This system consists of induction generator of 330 kVA, 480 V, 60 Hz operating in parallel with a synchronous generator of 330kVA, 480 V, 50 Hz driven by a diesal generator[detailed parameters of IG and synchronous generator are annexue as – I]. The active and reactive power of the system is controlled by controlling the governer opening of diesal engine and excition control of the synchronous generator. A capacitor bank of 70 kVAR is for suplly of reactive power to SEIG. A fixed resistive load of 100 kW is taken for this study. The simulink model of diesal engine and governer is shown in figure 2. With the increase in wind speed the speed of the induction generator is also incresed hence the out put power of induction generator is also increases. Intially the load is shared by synchronous generator and induction generator but now this is supplied by the induction generator and hence the speed of synchronous generator is increased.The rotor speed is used as feedback for this controller. The Voltage variations are due to the recative power variations in the system. The variations are compansated by controling the reactive power output from synchronous generator by controlling its excitation. Simulink model of excitation system avaliable in library of simpower system is used as controller.The Excitation System block is a Simulink system implementing a DC exciter without the exciter's saturation function. The basic elements that form the Excitation System block are the voltage regulator and the exciter. The exciter is represented by the following transfer function between the exciter voltage Vfd and the regulator's output ef.
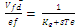 | (1) |
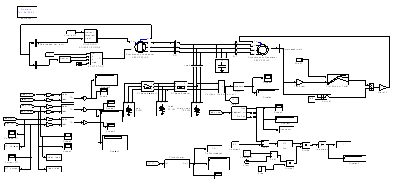 | Figure 1. SIMULINK model of wind diesel hybrid system with controllers |
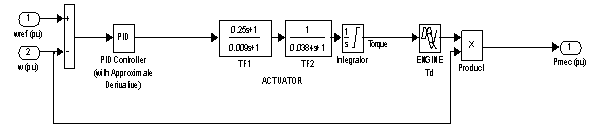 | Figure 2. Simulink model of diedel engine and governor |
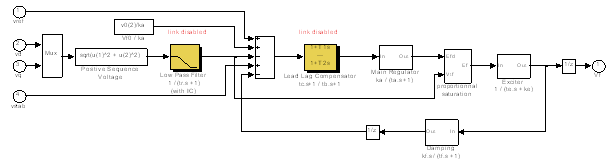 | Figure 3. (SIMULINK model of exciter system taken from Simulink library) |
4. Generation Of Error Signal
- The PID controller used in generator governor control for controlling the frequency of the system. Controller parameters are fine tuned using bacteria foraging optimization technique. Figure 4 shows the Simulink model for getting the error signal using Integral Time Square Error (ITSE) method. Here the reference frequency is 60 Hz. The measured frequency is compared with the reference frequency. Time delay of 4 sec is given so that an initial transient dies. This model is linked with MATLAB code for error minimization using bacteria foraging technique. Voltage is controlled by controlling the reactive power in the system. The reactive power is controlled by controlling the excitation of synchronous condenser.
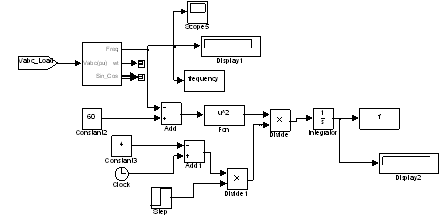 | Figure 4. SIMULINK model of ITSE method for error signal generation |
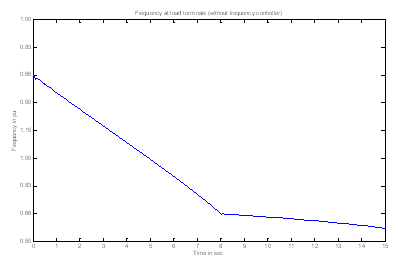 | Figure 5. Frequency at Load terminals (System operating without frequency controller) |
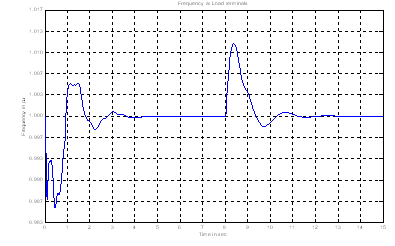 | Figure 6. Frequency at Load terminals (Randomly selected PID controller parameters) |
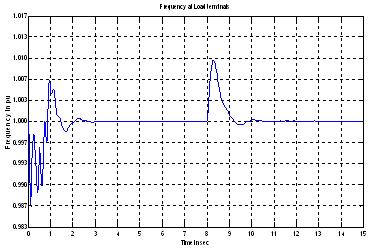 | Figure 7. Frequency at load terminals (optimized controller parameters) |
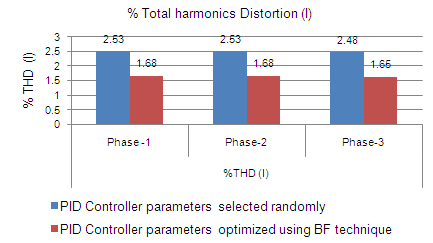 | Figure 8. % Total harmonics distortion in current |
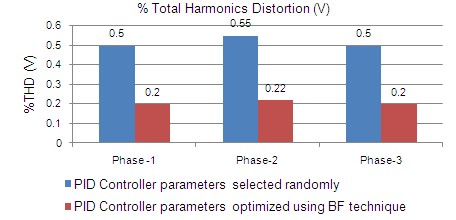 | Figure 9. % Total harmonics distortion in voltage |
5. Results & Discussions
- The error signal is generated as mensioned in section and linked with the MATLAB programe written for bacteria foraging optimization. The optimisied parameters i.e. Ki, Kp, Kd are taken and are used in PID controller. Three different sets of reading are thaken to investigate the effect on power quality of the system.In the first set no frequency controller (governor control of diesel generator) is in the circuit and the wind variations are incorporated and their effect on %THD (I) and and frequency is recorded. No variations are observed in the volatge as reactive power of the system is almost constant. Figure 5 the variation in frequency w.r.t to simulation time. It is observed that the system is not statable as the frequency is dropped to very low value which is beyond the permitted limits.The effect on the other power qualty parameters is almost negligible as only distubance incorporated is wind variations. The second set of readings is taken with governer controller and exciation controller in the system. The parameters i.e. Ki, Kp, Kd for PID controller used in governer control are randomly chosen as ki=75, kp = 0.03 and kd = 85. Figure 6 shows the variations in frequency when wind speed changes from 6 m/s to 8 m/s at the instant of 8 sec. In third case the optimized controller parameters (obtained using bacteria foraging optimization technique) are used in PID controller. Using these optimized PID gains i.e. kp = 162.82, ki = 0.008528 and kd = 155.72 the variation in frequency is shown in figure 7. The change in frequency at 8 sec (instant of disturbance) is recorded and it is observed that the maximum variations recorded in the frequency at load terminals are 1.009 pu to 0.999 pu after the disturbance which is less than the variations as obtained with randomly selected gains. The settling time of the disturbance is also reduced to 2 sec from 4 sec. Fig 8 and 9 shows the improvement in total harmonics distortion as the %THD (I) is reduced to 1.68 from 2.53 in phase A & B and from 2.48 to 1.65 in phase C. The %THD (V) is also reduced from 0.50 to 0.20 in phase A & C and from 0.55 to 0.22 in phase B.The comparision of %THD(I) is also given in table -1.
6. Conclusions
- The system proposed wind diesel hybrid system is investigated for various power quality parameters at varying wind speed. The major effect is seen in frequency and harmonics emissions. Steady state realization of frequency after the disturbance is seen fast when the PID controller used in governor control is using controller parameters obtained trough BF optimization as compared to randomly selected parameters. Since only frequency controller is focused in this chapter the effect of this controller on frequency as well as on power quality is clearly seen. Large variations in frequency are seen when there is no frequency controller in the system and the frequency variations are goes beyond the limits. This scheme is found very useful as all the power quality parameters are controlled with this scheme such as active and reactive power requirements, load terminal voltage, frequency and harmonics.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML