-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications
p-ISSN: 2168-5037 e-ISSN: 2168-5045
2021; 11(1): 1-9
doi:10.5923/j.ijea.20211101.01
Received: Oct. 15, 2021; Accepted: Oct. 29, 2021; Published: Nov. 2, 2021

Impact of Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Produced by Mobile Phones and Networks on Human Health and Eyes
Krishiv Bhatia
Monta Vista High School, Cupertino, CA, USA
Correspondence to: Krishiv Bhatia, Monta Vista High School, Cupertino, CA, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Mobile phones are used everywhere. People in all countries and continents use cell phones and smartphones for whatever they require. 3G and 4G mobile networks have already been deployed in many places in the world. Smartphones, social media, and video streaming are leading to more and more use of mobile networks. Mobile phones emit Radio Frequency Radiation (RFR). Short-term RFR exposure from 3G and 4G mobile phones have no material effects on human health and eyes. Long-term exposure can cause a risk of thermal damage and health problems. The use of 5G mobile phone devices is expanding in the US. 5G networks can connect more devices and provide faster service for smart devices, driverless cars, gaming, social media, industrial robotics, and video streaming. 5G needs to transfer data using millimeter waves (MMWs) to achieve fast transmission speeds to make it possible. Since MMWs are short-range and are obscured by walls, hundreds of thousands of new cell antennas must be installed every 100-200m. This is expected to significantly increase exposure to RFR and MMW radiation. In this article, we review the research carried out on the overall impact of the Electromagnetic Field (EMFs) generated by 3G, 4G, and 5G mobile phones and networks on human health and eyes, in addition to statistics and critical information to take away.
Keywords: Mobile phones, Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR), Millimeter Waves (MMWs), Radio Frequency Radiations (RFR), 3G, 4G, 5G, Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), Exposure, Eye, Health, Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity (EHS)
Cite this paper: Krishiv Bhatia, Impact of Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Produced by Mobile Phones and Networks on Human Health and Eyes, International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications, Vol. 11 No. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.5923/j.ijea.20211101.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Mobile phones are used everywhere in the world. This is evident from the fact that almost 62% of the global population uses mobile phones, while 48.20% own a smartphone (see figures 1 and 2).
 | Figure 1. Percent of the global population owning a mobile phone [1] |
 | Figure 2. Percent of the global population owning a smartphone [1] |
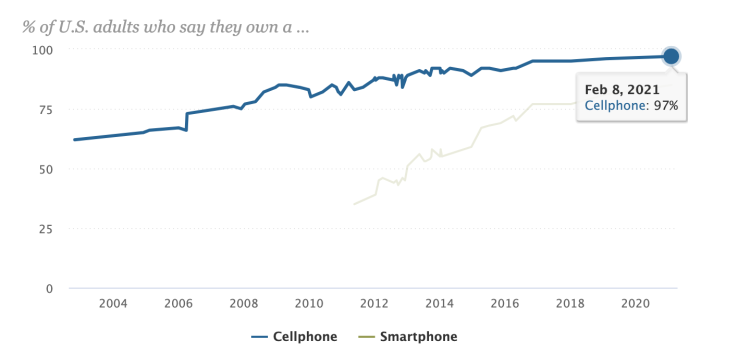 | Figure 3. Percent of US adults owning a cellphone and smartphone [2] |
2. Research
- In this study, recent scientific literature was reviewed to study the possible exposure levels to EM radiations, the 3G, 4G, and 5G mobile network technologies, and their impact on human health and eyes. A summary of the research is provided below.
2.1. The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- The range of frequencies of Electromagnetic Radiations (EMR) is called the electromagnetic spectrum. It ranges from the low frequencies of radio waves to the high frequencies of Gamma Rays [7].
2.2. Ionizing and Non-ionizing Radiations
- As seen in Figure 4, the part to the left of UV radiations is non-ionizing. This includes RF, Microwave, Infrared (IR), and Visible Light. Non-ionizing radiation does not cause damage to the DNA inside cells as their energy is lower than the threshold to cause changes at atomic levels [6,8,9].To the right of visible light in figure 4 are ionizing radiations. These can cause damage to cells and genetic material as they have sufficient energy to break molecular bonds and induce chemical reactions [10].
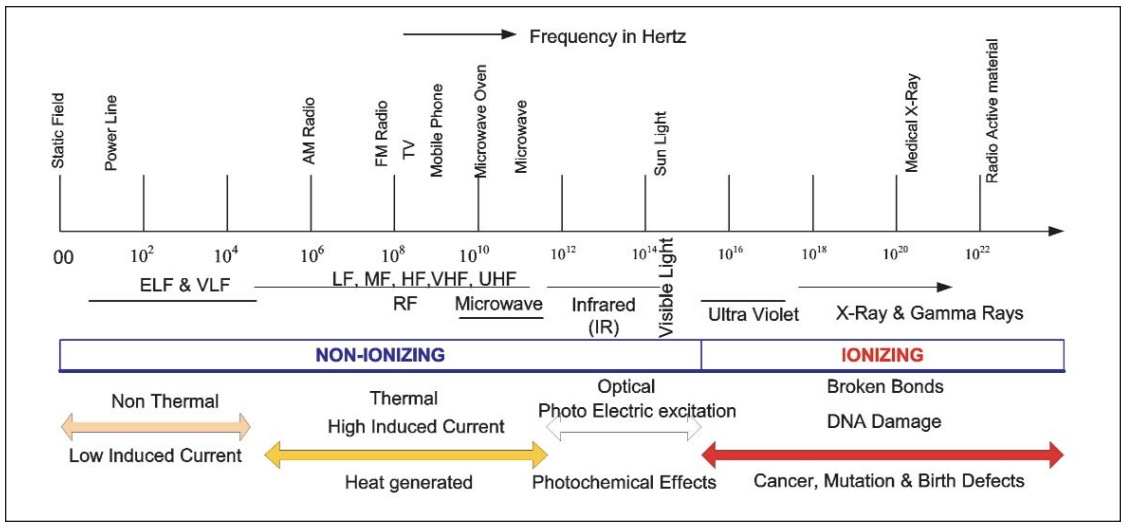 | Figure 4. The Electromagnetic Spectrum [8] |
2.3. Electromagnetic Waves
- Changing electric and magnetic fields produce electromagnetic waves. The electromagnetic waves include X-rays, microwaves, visible light, and radio waves. The electromagnetic waves do not require any medium to exist and can travel through a vacuum, air, and solid materials. All EMR travel at the speed of light c, which in a vacuum is given by the following equation [11]:
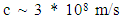 | (1) |
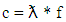 | (2) |
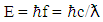 | (3) |
2.4. Mobile Phone Communications with Cell Tower
- Mobile phones both transmit and receive radio frequency signals. When a person talks, his voice is converted into an electric signal. The mobile phone’s circuits convert the electric signal into radio signals which are then transmitted to the nearby cell tower or base station via Radio Frequency (RF) radiations at the speed of light c [12,13].The RF radiations are then received at the cell tower or base station via antennas. The radio signals will be then transmitted through the network to the antenna of the other phone. The phone circuits will then convert the radio signals into electrical signals and then into sound which can be understood by the other party [12,13].A cell phone receives radio waves or signals from the cell tower. The strength of the received signals is shown by the number of “bars” in the mobile phone. When the number of bars is high or maximum, the received signal strength is high since the cell tower is closer. So the mobile phone needs to expend less power in transmitting the radio signals thereby conserving battery life. However, when the number of bars is low, the cell tower is farther away. In this case, mobile phones need to expend more power to transmit stronger signals which drain the battery [12,13].
2.5. EMRs Emitted by Mobile Phones Devices and Networks
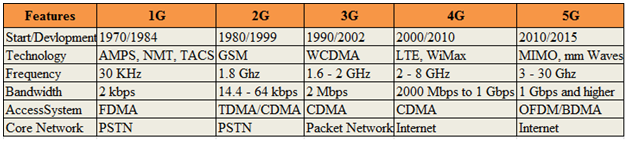
- Mobile phones have antennas that emit radiation in the RF frequency range of the electromagnetic spectrum. RF is a form of non-ionizing radiation that does not damage DNA inside cells, causing cancer [9].Table 1 shows the differences between the features of 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G mobile networks. 3Gs emit RF in the range 1.6-2GHz and 4Gs emit in the range 2-8 GHz [14].
|
2.6. Mobile Phone Devices and Specific Absorption Rate (SAR)
- Exposure to mobile phones and networks depends on multiple factors, including the amount of time a mobile phone is used and the device model. Usage of headsets and hands-free devices reduced exposure compared to holding it close to the head. Proximity to cell phone towers is also important since the farther the person is, the more energy the mobile phone will use to get a good signal increasing the amount of radiation. Hence, exposure is directly proportional to the energy used by a mobile device to get a signal. Being in a high-traffic area is also a factor. The more mobile phones being used in an area, the more energy the device will have to use to get a good signal [19,20].The amount of RF radiation absorbed by the body is called Specific Absorption Rate (SAR). SAR is a metric that measures the RF exposure of devices for safety guidelines. The FCC limit for SAR for RF radiation from mobile phone devices is 1.6 W/Kg [20]. The SAR just shows the limit that should not be exceeded. The specific RF radiation exposures depend on many other factors, including location and operational power [19].Figure 5 provides the head and body SAR values for Samsung mobile phones. Figure 6 provides the same for Apple iPhones. Figures 7 and 8 provide the phones emitting the most and least radiation respectively.
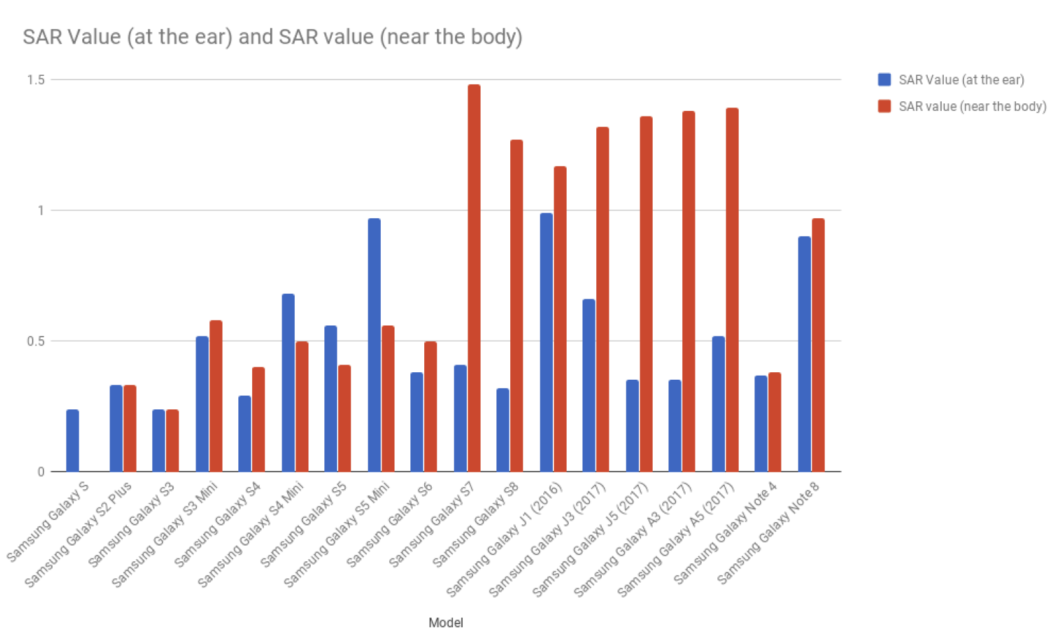 | Figure 5. Samsung mobile phone SAR Values [21] |
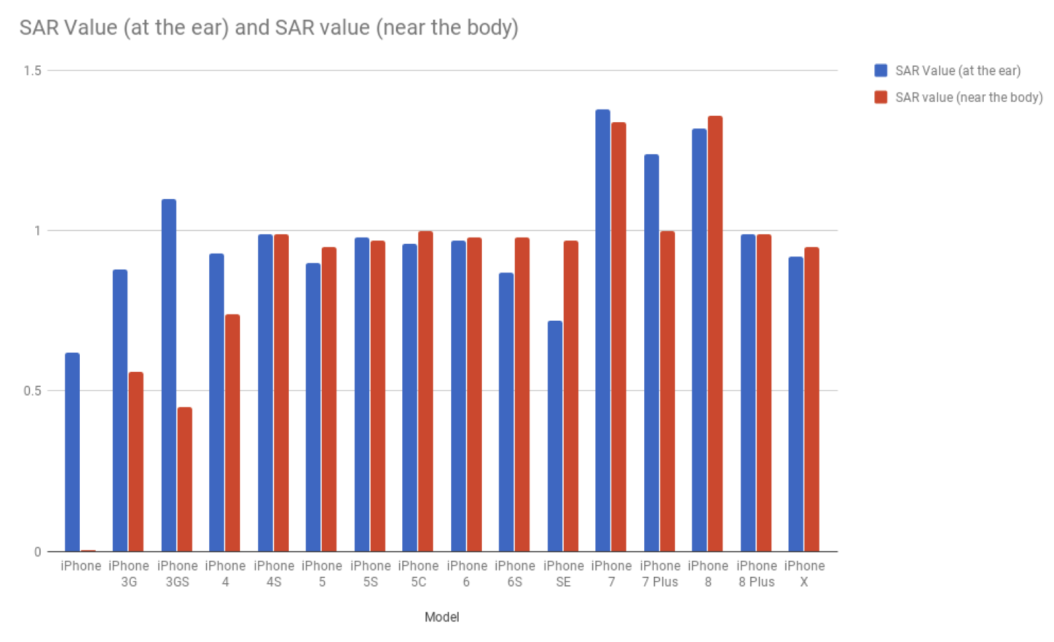 | Figure 6. Apple iPhone SAR Values [21] |
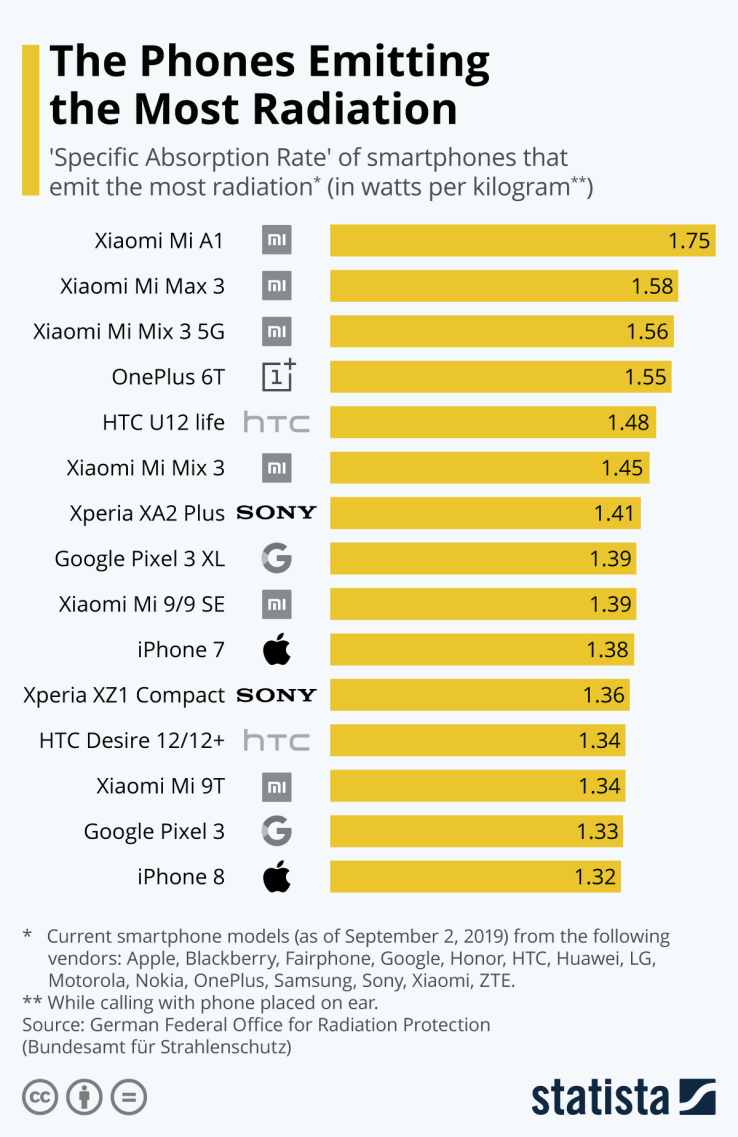 | Figure 7. The phones emitting the most radiation [22] |
 | Figure 8. The phones emitting the least radiation [23] |
2.7. 3G, 4G, and 5G Mobile Network Technologies
- 5G networks provide services that can be 100 times faster than 4G networks. That helps to provide high performance needed for gaming, social networks, IoT, driverless cars, and video streaming. To provide the faster service, they will emit RF in the range 3-30 GHz and go into the MMW (millimeter wave) frequency range from 30-300 GHz [5,14]. This requires the deployment of more base stations and millions of new small antennas on lamp posts and buildings as MMW does not travel through walls [17,18]. Figure 9 below shows the general architecture of 5G mobile networks. 5Gs employ MMWs, which are obscured by walls. Since users spend most of their time indoors and a small amount of time outdoors, the penetration loss of MMWs will be avoided by using Distributed Antenna System (DAS) and massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) antenna arrays. Millions of new short-range antennas called “small cells” will be deployed to increase bandwidth and performance. These will be installed in homes, schools, lamp posts, and other buildings. As such, there will be an increased risk of radiation hazards [17,24].
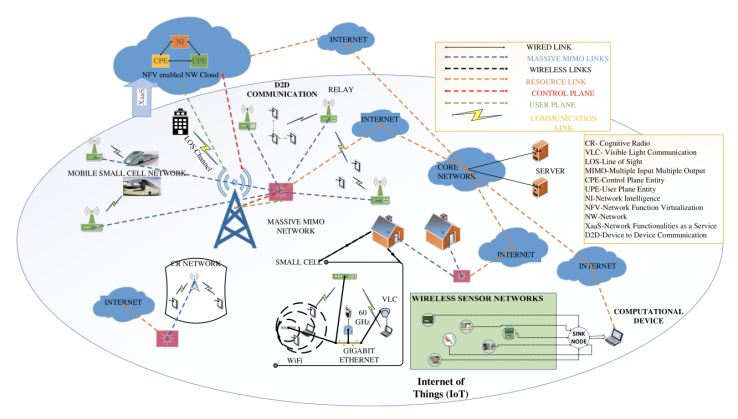 | Figure 9. General 5G mobile network architecture [25] |
2.8. Impact of EMR on Eyes
- Exposure to EMR can cause damage to the retina. Photothermal damage can occur due to long exposures to EMR and a resultant rise in the temperature (> 10°C) of the retina. Photochemical damage causes retinal cell damage and even cell death due to exposure to visible light. Photomechanical injuries are caused by high irradiance exposures, for example, to lasers leading to damaged tissues [26,27,28].Both low-power and high-power microwave radiation are carcinogenic, which can damage lens tissues due to non-thermal effects [29]. RF causes effects on the retina and cornea, including both animals and humans [20,30]. But no effects were observed in the eyes of monkeys, animals that are very similar to humans, which is interesting, but it easily could be because of our different eye structures or inaccurate testing [31].
2.9. Impact of EMR on Human Health
- Although non-ionizing radiation does not cause damage to DNA in cells or tissues, it does produce thermal or heating effects. As such, long-term exposure from high-power non-ionizing radiation (e.g. broadcast transmitters) could have health effects including tumors, cancers, and neurobehavioral disorders [8,32].In addition, the residents living near high-power lines have an increased risk of leukemia due to exposure to magnetic fields. The risk of leukemia decreases with increasing distance from the power lines [8,32].Exposure to microwave radiation causes thermal effects and heating. This concept is used in microwave ovens to heat food. Long exposure to microwave radiation has been linked to Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity (EHS) which are common symptoms like irritability, headaches, depression, fatigue, memory loss, and sleep issues [8,32].Exposure to high levels of RF radiation can lead to EHS, chronic headaches, and drowsiness due to the long-term impact of tissue heating [32]. Studies have shown it been linked to environmental intolerances and hypersensitivity to chemical agents [33]. It has also been linked to neurobehavioral dysfunctions and neurobiological effects. However, further studies are needed to clarify and confirm the effects [34]. Studies confirm that RF-EMF exposure does not lead to mitochondrial dysfunctions [35].Exposure to visible light, Infrared (IR), and Ultraviolet (UV) radiations can cause injury to the retina and heating of the skin. Long exposures can even lead to cataracts, eye damage, and skin burns. In addition, long exposure to UV radiations can also lead to premature aging, skin damage (including wrinkles, keratosis, and solar elastosis), inflammation of the cornea, and even skin cancer (melanoma, basal cell, and squamous cell cancers) [8,29,32,36].Long exposure to X-Rays and Gamma Rays (which are ionizing radiations) can cause leukemia, bone cancer, lung cancer, and other genetic mutations leading to cancers [8].
2.10. Effects of 3G and 4G Mobile Phones on Eyes
- Cell phone usage has been linked to refraction defects due to the thermal effects of RF radiation. This is irrespective of which side of the head the cell phone is held. However, marginal vision defects were noted in the study [6,9].
2.11. Effects of 3G and 4G Mobile Networks and Phones on Human Health
- Studies have not confirmed small or short-term EMR exposure from 3G and 4G mobile networks and phones to lead to harmful effects, including Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity (EHS). However, long-term exposure leads to cellular stress, an impact on the general well-being of humans, and cancer risk [6]. Since the RF radiation from cell phones is non-ionizing, a little exposure to it does not damage DNA in any way. In addition, although long exposures to non-ionizing radiation can cause thermal damage and health problems like sunburn and melanoma, it is not a significant risk [6]. Studies of EMRs emitted from 3G mobile phones found no significant impact in the blood and eye tissues of rats [6]. Studies have also not been shown to link brain tumor, glioma, or meningioma to RF-EMF, but studies should be carried out on long-term impacts of more than 15 years. RF-EMF has been classified as possibly carcinogenic by the International Agency for Research on Cancer [4].
2.12. Possible Health Effects of 5G Mobile Networks and Mobile Phones
- 5Gs will emit MMW range frequencies in the range of 30-300 GHz. For RF frequencies higher than 6 Hz, a public concern arises [5,18,24]. Some experiments have reported increases in indicators of DNA damage, DNA double-strand breaks, a decrease in the levels of Protein kinase C, chromosomal changes, asynchronous centromere replications, enhanced and inhibited rates of cell proliferation, increase in cell diameter, inhibition of cell growth, reduction in viable cancer cells and changes in structural cell morphology. But many of those experiments were either done with low animal numbers, had inadequate dosimetry and temperature control, or had a specific absorption rate (SAR) above the limit [16].No confirmed evidence of DNA damage has been found in the skin cells due to MMWs. Additionally, no confirmed evidence of biological effects relevant to human health as well as genotoxic damage in epithelial and skin cells can be attributed to MMWs [16]. However, there is a high risk of EHS in the long term due to 5G [17].
2.13. Protection from Mobile Phone and Network Radiations
- Since cell phones have become a big part of our life, we probably can’t stop using them. The exposure can be minimized by taking many steps. Time spent on cell phone usage can be limited. Speakers, earbuds, headsets, or other hands-free accessories can be used to keep the phone far away from the body. Texting instead of talking can be done (if applicable) to keep the cell phone at a distance from the body. The phone can be used in an area with good reception, transmitting signals at a lower frequency. Avoid talking when the cell phone signal is weak as the cell phone increases the transmission frequency [37,38,39].
3. Results
- Exposure to light or EMR can cause photothermal, photomechanical, or photochemical damage to the eyes. While photothermal eye damage is caused by longer wavelengths (near IR), photochemical damage is caused by shorter wavelengths (near UV) having high energy [24].Cell phones emit RF radiation in the EMR spectrum. RF radiation from mobile phones is non-ionizing and can cause thermal damage. 3Gs and 4Gs emit radiation in the range 1.6-8 GHz. The thermal effects of RF radiation from cell phones have been linked to refraction defects in human eyes [6,9].While small RF-EMF radiation from mobile devices does not damage health and does not cause much harm, long exposures can cause thermal damage, cellular stress, headaches, fatigue, cancer risk, and health problems [6,9].But the situation with 5G networks is different. They emit RF in the range of 3-30 GHz and go into the MMW range from 30-300 GHz. They also provide faster service for driverless cars, gaming, and IoT. Although no confirmed impacts of MMWs have been found on health and skin cells, studies are still being carried out to ascertain the impact. Some possible risks are DNA damage, chromosomal changes, inhibited cell growth, and changes in cell structural morphology [16].It is essential to choose suitable quality mobile phone devices with low SAR as they reduce the impact of RF radiations. It is also recommended to minimize talking time and use a headset or hands-free devices [37,38,39].
4. Conclusions
- Short-term exposure to the non-ionizing RF radiations from 3G and 4G mobile phones and networks has been confirmed to have no significant impact on human health [9]. But cell phone usage has been linked to refraction defects in human eyes. Although risks are present of long-term exposure like EHS and brain tumors, studies have not been able to provide a confirmation [6,9].The risk of radiation exposure from mobile phones can be reduced by minimizing talking time on the phone, using hands-free technologies, using models with low SAR and consuming less energy to get a good signal, and using it outside closed buildings [37,38,39].However, the exposures from the 5G mobile phones and network frequencies are a concern and overall do damage health a little bit, even if not damaging as much as one would expect [16]. Since the technologies are new, further studies are still being carried out to ascertain the risks. The 5G Appeal, endorsed by 400+ scientists and doctors, requests that all 5G networks be suspended until further research is done, and this logically does make a lot of sense [16].
5. Future Research Direction
- Future research should focus on learning the bioeffects at the specific frequencies of 5G networks in the range of 3–30 GHz and across the MMW band (frequencies higher than 30 GHz). Temperature controls could be researched to avoid the heating effects of electromagnetic radiation [15].Studies should be done to ascertain the long-term impact of RF-EMF on brain tumors for more than 15 years. Further, studies of the long-term impact of RF-EMF on children and adolescents should also be done [4].Additionally, further research should be done to gauge the impact of RF-EMR on the human brain and the neurobiological effects [34].
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML