-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Ecosystem
p-ISSN: 2165-8889 e-ISSN: 2165-8919
2014; 4(3): 150-158
doi:10.5923/j.ije.20140403.07
Drought in Northern Bangladesh: Social, Agroecological Impact and Local Perception
Abu Reza Md. Towfiqul Islam1, Anjum Tasnuva1, Subaran Chandra Sarker2, Md. Masudar Rahman3, Md. Sanaul Haque Mondal4, Md. Mujahid Ul Islam1
1Department of Disaster Management, Begum Rokeya University, Rangpur, 5400, Bangladesh
2Department of Geography and Environmental Science, Begum Rokeya University, Rangpur, 5400, Bangladesh
3Department of Geography and Environmental studies, University of Rajshahi, Rajshahi, 6205, Bangladesh
4International Rice Research Institute, Dhaka, 1207, Bangladesh
Correspondence to: Abu Reza Md. Towfiqul Islam, Department of Disaster Management, Begum Rokeya University, Rangpur, 5400, Bangladesh.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The 1994, 2000 and 2006 drought appeared to bad memories in the northern region of Rangpur division, Bangladesh. The objective of this research was to explore social and agro-ecological impact of drought and local perception in the study area. A semi-structural questionnaire was employed from February to March, 2014 where 120 respondents were chosen stratified sampling to acquire information at drought prone area. Both quantitative and qualitative techniques were used as a main tool for purpose of the study. The results revealed that drought were adversely impacted on social and agro-ecology in the study area. Local perception depicted that drought is as a curse of God and the outcome of sin while some perceive are evaluated as human negligence and shortage of water. The study was also revealed that higher knowledge variability were belonging to group 3 and group 4 people. The descriptive and inferential statistics indicated that there was a significant correlation between literacy and occupation type with social and agro-ecological impact of drought. But, there were no significant relationship between age, household size and land ownership with social and agro-ecological impact of drought. It is suggested that if awareness and literacy level increases to diminish social and agro-ecological impact of drought in the study area.
Keywords: Northern bangladesh, Local perception, Knowledge variability, Agro-ecological impact and literacy level
Cite this paper: Abu Reza Md. Towfiqul Islam, Anjum Tasnuva, Subaran Chandra Sarker, Md. Masudar Rahman, Md. Sanaul Haque Mondal, Md. Mujahid Ul Islam, Drought in Northern Bangladesh: Social, Agroecological Impact and Local Perception, International Journal of Ecosystem, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2014, pp. 150-158. doi: 10.5923/j.ije.20140403.07.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Drought can occur in any climate of the world and cause harmful impacts on human beings and natural ecosystems [1-2]. Drought may be meteorological (problematic weather patterns), hydrological (lack of rain), agricultural (low commodity production) and socio-economic (low incomes and social consequences) explanations; that it is drought's impact on people and their activities [3]. Wangai et al. [4] assesses the actual losses of both livestock and wildlife species at Kuku of southern Kenya during the 2009 drought and the subsequently socio-economic initiatives undertaken to adapt to the drought. Northern region of Rangpur is one the most severe drought prone area in Bangladesh with an average rainfall of about 1430 mm per year. Irregular characteristics of rainfall and global climate changes are the main causes of drought. In recent decades, agriculture production and livestock production are significantly reduced in the northern region of Rangpur division, Bangladesh. The impact of drought not only leads to the shortage of water and food but also have a long-term environmental, socio-economic and health impact on the population [5].Wilhite [6] studied that drought has priority to other natural disasters in the frequency of occurrence, duration and extent, loss of life, economic and social impacts and severe effects in the long run. Rezayi et al. [7] surveyed economic, social, environmental and ecological impacts of drought in Zanjan province of Iran and concluded that these negative impacts were economic, environmental, social, and ecological. Drought is a chief environmental concern which hampering photosynthesis of plant and adversely affecting the herbivorous animals. Drought is one of the major abiotic stresses which adversely affect crop growth and yield and thus a constraint for plant productivity worldwide [8].Furthermore, coping mechanism to drought that fails to meet the new challenges of drought re-occurrences, socio-economic and long term climate changes impacts [9]. Bimal [10] studied the coping mechanism practiced by drought victims (1994-95) in North Bengal, Bangladesh. The results of his study indicated that drought is a reversible phenomenon in Bangladesh, affecting plant growth and leading to loss of crop production, food shortage for many people’s starvation. Drought led to a decrease in rice and wheat production of 3.5 × 106 ton in 1994–95 [11]. The 2006 drought indicated a reduction of aman crop production of about 25–30% in the northwestern part of Bangladesh [12]. Drought causes abnormal increases in prices due to loss of agriculture, increases the unavailability of jobs, and reduces access to food for rural people, especially small and landless laborers’ [13]. However, drought not only causes the agriculture losses which enhances seasonal food crisis but also reduces livestock and biodiversity losses, migration tendency seen in drought prone area. The northern part of Bangladesh is differentiated by its monotones landscape and desertification climate. The region is characterized by persistent below-average rainfall and thus depleting of groundwater levels in aquifers leading to water scarcity for family unit, industry and agricultural purpose. Many researchers focus their research on the impact of droughts on agricultural, environmental, social and economy [14-20]. But no research has done in the northern part of Bangladesh on agro-ecological problems due to drought that make threats both human and livestock. Most of the people relied on agriculture and domestic animal for their livelihoods in this region. In this regard, this research work has an attempt to explore the agriculture and biodiversity impact due to drought in the study area. The main objective of this research is to examine the impact of drought on social and agro-ecology and local perception in the northern Bangladesh.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
- The study area is situated in the north-western region of Bangladesh which covers 2 % of the total area of Bangladesh. The study area comprises of 3 Upazilla in two drought-prone districts namely Rangpur and Nilphamary. It is located at 25° 77′ N latitude to 89° 41′ E longitude (Fig.1). Climate of the study area has a tropical wet and dry. Annual rainfall is about 1430 mm and average temperature is 25℃ [21].
 | Figure 1. Location map showing severe drought prone area in the northern region of Rangpur Division, Bangladesh |
2.2. Study Design
- The study was mainly based on primary data. Data were collected through long session of interview from February to March 2014. Both quantitative and qualitative research methods were employed to collect primary data for the study. A detailed field survey was conducted through in depth interview using both open and closed-ended questionnaire. By adopting quantitative research method, the study attempts to explore the local perception about drought and direct impact of drought on drought prone area. For qualitative research, this study was employed field observation and focus group discussion to get socio-demographic characteristics, livestock loss and biodiversity, stability distribution in the study. The interview session was carried out into Bangla language. Because most of the respondents are illiterate and they expressed their experience about 1994, 2000 and 2006 drought by Bangla language which translated into English. The semi-structure questionnaires were prepared and approved by the panel of experts including the faculty member of Disaster Management of Begum Rokeya University and agriculture researcher in the study area. The questionnaire reliability was 80% by using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient method. The focus group discussion were including 6-8 people per group, and key informant interview such as union chairman’s (local representative of union parishad) and school teacher were held for achieving aim of this study. The mail purpose of this group discussion that motivates the drought affected people to delivering information willingly. The focus group discussions through interview were able to get vital information on changing attitude, knowledge variability and behavior of local people in the study area. Northern Bangladesh were selected purposively due to severe drought affect region where Rangpur and Nilphamary district of Badarganj, Taraganj and Kisharganj upazila (local administrative area) were chosen three unions name Radhanagar, Ecorchali and Putimari as a drought prone area. Here proportional stratified sampling technique was used for the selection of three unions of severe drought affected people. A total of 140 questionnaires were distributed; 120 questionnaires were finished and back owing to time and other logistical constraint a contribution rate of 85 percent in the study area. Finally, the questionnaire was pre-tested before data collection. A semi-structured questionnaire comprised of five portions. The first portion consists of the socio-demographic characteristics of the respondents. The second portion focuses on people perception and perceptive knowledge about drought over the last 10 to 20 years. The third portion consists of social impact adapted by drought affected people. The fourth portion contains agricultural impact which depleted agriculture production. The last portion contains ecological impact of drought owing to loss of flora and fauna in the study area. The scale was used for the construction of perception basis of 30 statements/items [22]. A five point Likert scale of rating was employed as follows: strongly disagree, disagree, do not know, agree and strongly agree. It was rating of 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 for positive response and the rating was reversed for negative response with respondent statement dealing with drought perception and biodiversity impact. Drought impact was assessed by knowledge variability based on box plot model. Pearson correlation coefficient study was done at the same time and pursued by the same statistical technique. The research work deal with mainly two questions: (1) what is the local perception of drought especially drought prone area? (2) What are the impacts of drought on social, agro-ecology in Northern Bangladesh?
2.3. Software Package
- The data obtained from the questionnaire were coded, processed and analyzed through SPSS (16 versions), Box plot model (7 version) and MS excel (7 versions). Both descriptive and inferential statistical techniques were used to explore the social and agro-ecological impact of drought in the study. Location map was prepared by Arc View GIS (3.3 versions). Statistical analysis revealed that a stratified sampling of 120 questionnaire will result in a mean sampling error (e) of 3% at 95% significance level of .05 and a standard deviation (s) of 0.5 [23-24].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Socio-demographic Characteristics
- Socio-demographic characteristics of respondents in the study area are summarized in the table 1. Socio-demographic status is needed for knowing slow onset disaster condition like drought with its future impact assessment. Ages of the respondents were divided into four groups. About 55% of total respondents were above 50 years of age. In the study area, about 69 % respondents were male whereas rests of the respondents were female. About 56 % of total respondents were illiterate which show that lower level of literacy among the respondents and about 22% had completed primary education while only 7 % was completed tertiary education in the study area. So, the education levels of most respondents were fall within G-1, G-2 and G-3 respectively. About 49 % land were own among the respondents whereas 31 % and 20 % land were hire and joint venture. The average household size was 4 members belong to 45 % of total respondents. Among the respondent about 75 % respondents were employed in agricultural activity while rest of the respondents were engaged in business, jobs and others. Most of the respondents were below the poverty level according to socio-demographic information. Income levels of respondents were belonging to G-1 and G-2 in the study area people (Table 1).
|
3.2. Perceived Evaluation of Drought
- People perception and its social aspects are interlinked to scientific view on any occurrence in a society [25]. People have different view on drought in the study area. According to people perception about drought, 58 %, 55 %, 56 %, 57 %, 50 % and 45 % respondents were agreed to think that drought was a curse of God, water shortage, dry weather condition, human intervention, dry red soil and outcome of sin respectively (Fig. 2). On the other hand, 22 %, 35 %, 40 %, 42 %, 40 % and 30 % respondents were disagreed to believe that drought was a curse of God, water shortage, dry weather condition, human intervention, dry red soil and outcome of sin respectively while rest of the respondents 20 %, 10 %, 4 %, 1 %, 10 % and 25 % were don’t know what is drought (Fig. 2). Result revealed that most of the respondents were found to be lower literacy and income level. In the last decade, this region experiences drought once in every year [26]. Study area people were less aware about social and agro-ecological impact of drought.
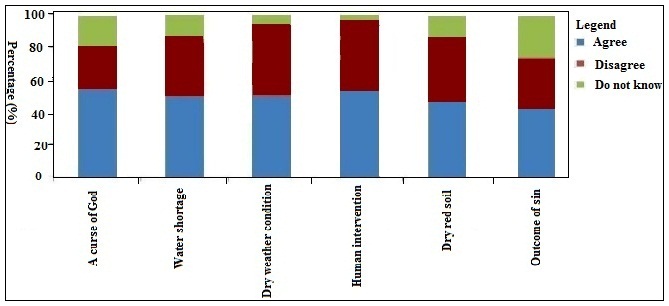 | Figure 2. People perceive evaluation about drought in the study area |
3.3. Social Impact
- Livelihood pattern becomes change in the drought prone area. It was noticed that the probability of migration rate will increases more significantly during drought period than the normal period. Social impact of drought and it mainly show up the probability of migration from drought prone area. The result was shown that about 84 % drought victims migrated from drought prone area for better livelihoods and the government assistance during 1994 severe drought while 65% of other household migrated for different incidents except drought. About 59 % drought victims leaved the area in 2006 drought whereas only 40 % victims migrated from drought affected area in recent years. About 26% past drought victims migrated from the area with no drought period while 18 % of other household migrated for different unpleasant incident of the area (Fig. 3). The IPCC assessment narrates that droughts will affect 8 million people by 2050 [27]. However, their migration decision did not change even after they have received cash assistance and information assistance about how to cope with the droughts [28]. The result is reliable with the finding of [7, 29] who stated that drought has social impact.
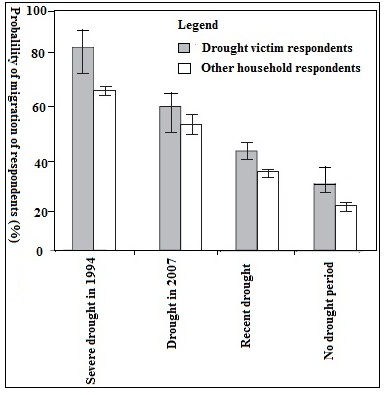 | Figure 3. Social impact of drought according to probability of migration of respondents (%) |
3.4. Agricultural Impact
- Agriculture is the spinal column of Bangladesh and is equivalent to the food safety of the country. Agriculture sector is the contributor of income and employment generation in Bangladesh. Apart from this, inadequate pre-monsoon rainfall, a delay in the onset of the rainy season or an early departure of the monsoon may create droughts in Bangladesh [30]. Drought creates a credible threat on the agriculture. It has a huge influence on production loss. It was calculated that the paddy faces the highest loss due to drought. Production of paddy is very much dependent on water availability. During drought period paddy does not get enough water which causes production loss. The result indicated that mainly paddy is much affected due to drought in the study area. About 53.33% production of paddy was reduced significantly whereas the production of potato, jute, onion and bean were decreased 13.33%, 26.66%, 6.66% and 4% respectively due to drought in the area (Fig. 4). Droughts adversely affect the crop production causes annual damages of 2.32 million hectares crop production [18]. Scarcity of water is limited crop production while irrigation coverage is only 56% [31]. Three drought affected union people in Rangpur division of Northern Bangladesh commented at a focus group discussion that:
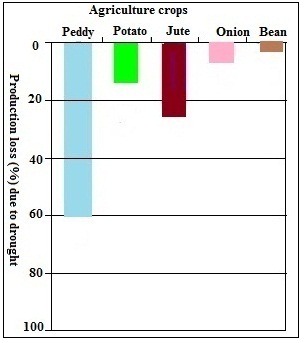 | Figure 4. Agriculture impact of drought according to production loss of agriculture crops (%) |
3.5. Ecological Impact
- Drought has adverse impact on ecology that analysis by using the Likret scale. A total 57 % people were agreed that drought has an impact on cattle while 30 % people were strongly disagreed that cattle was not in such danger during drought period and rest of the respondents had no idea about this. About 65% people were strongly agreed that goat dies during drought while 25 % people were disagreed strongly on this opinion. Drought can be the cause of death for sheep and boar too. 30% people were agreed with this while 70% were strongly disagreed in this statement (Fig.5). Ngaka [34] depict that the most significant impact of drought was livestock losses in South Africa. Grass dies during drought. In the study area about 37 % people agreed with it. On the contrary, about 60% people disagreed with it and rest of the people did not know. Banyan tree is unable to survive during drought- about 43% people agreed with it where 45% people disagreed. Almost 45% people agreed that jackfruit trees die during drought while 30% disagreed and 25% people had no idea on it. Mango tree also dies during drought. About 40% people agreed that mango tree is affected by drought. On the other hand, 45% disagreed while 15% could not answer (Fig.5). Drought affects both animals and plants species. Among animal species cow, goat, sheep, boar are highly affected by drought. Grass, banyan tree, jackfruit tree and mango tree are the notable plant species which may die during drought. Death rates in times of drought are usually particularly high among certain species of sheep and cow being in general less resistant than boar and cattle. Lack of water, food, and habitat protection may also cause decreased reproductive success and survivorship. Drought is certainly a widely underestimated ecological stress and selection force [35]. In the time of drought, the study area people face the scarcity of food and habitat destruction. Infrequently the damage is merely momentary and their habitat and food supply return to normal when the drought is over. Wangai et al. [4] show that actual losses for cattle, goats and sheep were significantly high during 2009 drought in Kenya. Young animals, elderly stock and pregnant females are the most vulnerable within any particular species. Death rates increase as the period of drought continues, as the period of nutritional stress lengthens and as the degree of stress intensifies. Plants grown in arid and semi-arid environments are exposed to long periods of water deficit and reduction in photosynthetic rate is commonly observed in plants grown under drought conditions [36]. A union chairman (local representative) from Ecorchali, Taraganj upazila of Rangpur district was given a statement that: “We face a problem for our livestock production especially affect the animal and plant species when water shortage was prevailing in the area. We had to wait for long time for domestic animals food and water. They suffer a lot during drought time and reduce noteworthy livestock production”.
 | Figure 5. Ecological impact of drought according to respondent’s perception (%) in the study area |
3.6. Drought Knowledge Variability
- Knowledge variability plays a significant role in a community [37]. Results indicated that more than 40 % respondents were knowledgeable about droughts for belong to G-3 and G-4 of people respectively. This is because of well educated and higher income people belong to G-3 and G-4. On the other hand, less than 40 % respondents were less knowledgeable about drought for G-1 and G-2 of people. Education could be performing a lead role to ensure knowledge variability about drought (Fig. 6). Result was also shown that most of the male respondents were well informed about drought occurrence than female respondents in the study area (Fig. 6). Female respondents were identified lower literacy level compared to male respondent.
 | Figure 6. Knowledge variability and knowledge of gender about drought in the study |
3.7. Correlation Analysis
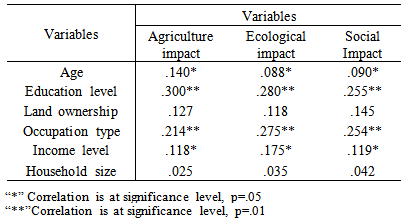
- Correlation analysis is a technique that describes the degree of relationship between two variables. The Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to assess the relationship between them in the study area. Simply, Pearson correlation coefficient tells how much one variable tends to change when other one does. The results was shown that there was a positive weak relationship between age of respondents and agriculture impact of drought (r= 0.14, p=.05). On the other hand, no significant relationship were existed between ecological and social impact of drought (r= .088; r= .09, p=0.05) for G-1 and G-2 of people.
|
4. Conclusions
- Drought is a slow onset natural disaster which creates a threat to social and agro-ecological balance in the northern region of Bangladesh. In the study area, there was always irregular rainfall and the cultivation period requires more water which hampered by upstream dam of Teesta river as well as makes a problem in the drought affected area. The result was shown that the social and agro-ecological impacts of drought are decreased with the increase of literacy level as well as awareness and knowledge variability and the use of new innovative technology. Education plays a crucial role in order to raise the respondent’s knowledge and awareness building about drought. Local perceived analysis about drought depicted a negative opinion belong to group 1 and group 2 people. Knowledge variability indicated that highest knowledge variability was identified in group 3 and group 4 due to higher education level. Correlation analysis revealed that significant strong positive correlation was existed between education and occupation type with social, agro-ecological impact of drought for group 3 and group 4 of people in the study area. From the discussion, it can be concluded that the social impact of drought led to migration tendency in the study area. Agriculture impact of drought included decrease in food production. Ecological impact of drought brought about loss of livestock including goat, sheep and boar, increase in mortality rate of fish in ponds and decrease of biodiversity of plant species. Therefore, it is suggested that if awareness build up and literacy level increase to reduce these adverse impact of drought in the northern Bangladesh. This study has recommended that Government should take initiatives with different training program, implementation of strategic plan, job opportunity and relief during drought season. Future research is needed to in-depth assessment of culture, health and biodiversity impact of drought in the study area.
ACKMOWLEDGEMENTS
- Authors would like to sincerely thank to the participants who gave valuable information for research purpose. Thanks are due to faculty member of Disaster Management of Begum Rokeya University for validating data and facilities of this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML