-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Ecosystem
p-ISSN: 2165-8889 e-ISSN: 2165-8919
2012; 2(5): 140-149
doi: 10.5923/j.ije.20120205.06
Fractional Ecosystem Model and Its Solution by Homotopy Perturbation Method
Piush Kumar Singh , T Som
Department of Applied Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology (Banaras Hindu University), Varanasi – 221005, India
Correspondence to: Piush Kumar Singh , Department of Applied Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology (Banaras Hindu University), Varanasi – 221005, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In the present paper we propose an algorithm based on Homotopy Perturbation Method to solve the fractional Ecosystem model and show the efficiency and accuracy of the algorithm . This Ecosystem model is solved with time fractional derivatives in the sense of Caputo. The nonlinear terms can be easily handled by the using He’s Polynomials. The numerical solutions of the Ecosystem model reveal that only a few iterations are sufficient to obtained accurate approximate analytical solutions. The numerical results obtained are presented graphically. The four different cases are considered and proved that the method is extremely effective due to fractional approach and performance. Comparing the methodology (FHPM) with the some known technique (HPM) shows that the present approach is effective and powerful. The proposed scheme finds the solution with the help of Mathematica and without any restrictive assumptions. We implement it to four different problems.
Keywords: Nonlinear System, Fractional Ecosystem Model, Homotopy Perturbation Method, Fractional Integral Operator
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Ecosystem models play an important role to know the dynamics of the system. Such models are formed by combining known ecological relations with data gathered from field observations ([1]-[8]). These models are then used to make predictions about the dynamics of the real system. However, the study of deficiencies in the model leads to the generation of hypotheses about the possible ecological relations that are not yet known or well understood. Models enable researchers to simulate the conclusions of large-scale experiments that might be too expensive to perform on a real ecosystem. These also enable the simulation of ecological processes over very long period of time (may be some process may take centuries of time in reality), However this can be done in a matter of minutes in a computer model. Ecosystem models have applications in a wide variety of disciplines, in particular, to natural resource management. An important aspect any model evaluation is the validation, that is, the process of confirming that the model behaviour corresponds to reality. The results of the model can be validated by comparison with field data, but this technique limits the validation to a particular set of field conditions. We obtain a sequence of equations in which the solution at any stage is close to the solution at nearby stages. In the present paper we discuss the fractional Ecosystem model and solve it using Homotopy Perturbation Method. We consider the following fractional ecosystem model given by fractional initial value problem of the type:
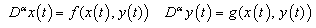 with initial conditions
with initial conditions 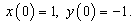 Here f and g are arbitrary functions,
Here f and g are arbitrary functions,  denotes the fractional derivative in the sense of Caputo.
denotes the fractional derivative in the sense of Caputo. 2. Basic Definitions
- In this section, we give the related definitions and properties of the fractional calculus from [9].Definition 2.1. A real function
 is said to be in the space
is said to be in the space 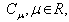 if there exists a real number
if there exists a real number 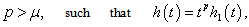 where
where 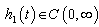 , and it is said to be in the space
, and it is said to be in the space 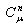 if and only if
if and only if 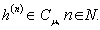 Definition 2.2 The Riemann–Liouville fractional integral operator
Definition 2.2 The Riemann–Liouville fractional integral operator 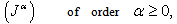 of a function,
of a function, 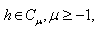 is defined as
is defined as 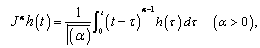
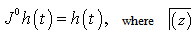 is the well-known Gamma function.Some of the properties of the operator
is the well-known Gamma function.Some of the properties of the operator 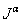 , which we need here, are as follows:For
, which we need here, are as follows:For 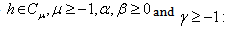 (1)
(1) 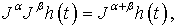 (2)
(2) 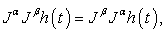 (3)
(3) 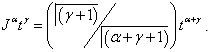 .Definition 2.3. [10] The fractional derivative
.Definition 2.3. [10] The fractional derivative 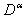 of
of  in the Caputo’s sense is defined as
in the Caputo’s sense is defined as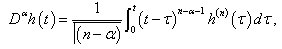 for
for 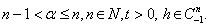 The following are the two basic properties of the Caputo’s fractional derivative [10]:(1) Let
The following are the two basic properties of the Caputo’s fractional derivative [10]:(1) Let 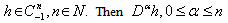 is well defined and
is well defined and 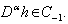 (2) Let
(2) Let 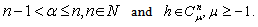 This leads to
This leads to 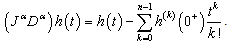 .
.3. Analysis of HPM
- The Homotopy Perturbation Method (HPM), which provides analytically an approximate solution, is applied to various nonlinear problems ([11]-[14]). In this section, we introduce a reliable algorithm to handle the nonlinear ecosystems in a realistic and efficient way. The proposed algorithm will then be used to investigate the system given by:
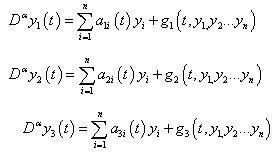 | (1) |
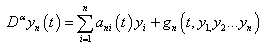 subject to the initial condition,
subject to the initial condition,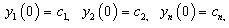 | (2) |
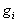 is a nonlinear function for each
is a nonlinear function for each 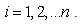 .Using the homotopy perturbation method we can construct the following homotopy for
.Using the homotopy perturbation method we can construct the following homotopy for 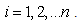 ,
,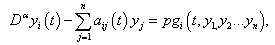 | (3) |
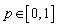 is the homotopy parameter, which takes values from zero to unity. In case
is the homotopy parameter, which takes values from zero to unity. In case 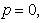 equation (3) becomes a linear equation given by:
equation (3) becomes a linear equation given by: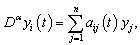 | (4) |
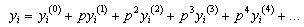 | (5) |
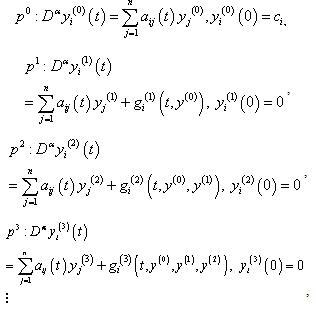 where the function
where the function 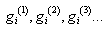 satisfy the following equation:
satisfy the following equation: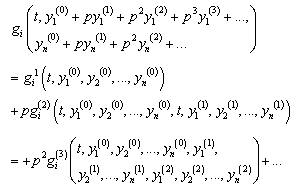 Now taking
Now taking 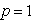 in the equation (5) it gives the solution of the system It is obvious that the above linear equations are easy to solve, and the components
in the equation (5) it gives the solution of the system It is obvious that the above linear equations are easy to solve, and the components 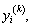
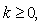 of the homotopy perturbation solution can be completely determined as a series solution, Finally, we approximate the solution
of the homotopy perturbation solution can be completely determined as a series solution, Finally, we approximate the solution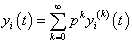 by the truncated series
by the truncated series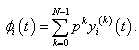 | (6) |
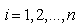
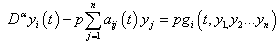 | (7) |
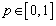 . In this case, the term
. In this case, the term 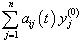 is combined with the component
is combined with the component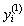 and the term
and the term 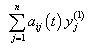 is combined with the component
is combined with the component 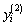 and so on. This variation reduces the number of terms in each component and also minimizes the size of calculations. By substituting equation
and so on. This variation reduces the number of terms in each component and also minimizes the size of calculations. By substituting equation 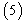 in equation
in equation 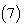 we obtain the following series of linear equations:
we obtain the following series of linear equations: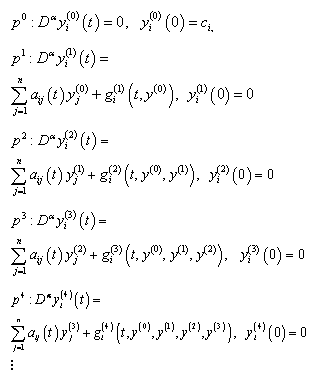
4. Numerical Example
- In this section we show the application of the algorithm based on HPM given above to solve four different linear and non linear fractional Ecosystem model. Example 4.1. Consider the linear system [15]
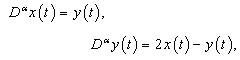 | (8) |
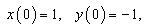 | (9) |
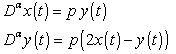 To solve the system given in Eq.
To solve the system given in Eq.  we construct the Homotopy as given in Eq.
we construct the Homotopy as given in Eq.  putting Eq.
putting Eq. 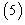 then initial condition
then initial condition 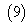 in Eq.
in Eq. 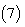 and then comparing the like powers of we get,
and then comparing the like powers of we get, 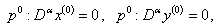 | (10) |
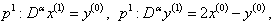 | (11) |
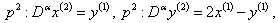 | (12) |
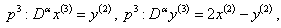 | (13) |
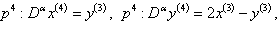 | (14) |
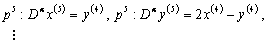 | (15) |
 , the inverse operator of
, the inverse operator of  , on both side of linear equations from
, on both side of linear equations from  with initial conditions
with initial conditions 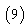 we get
we get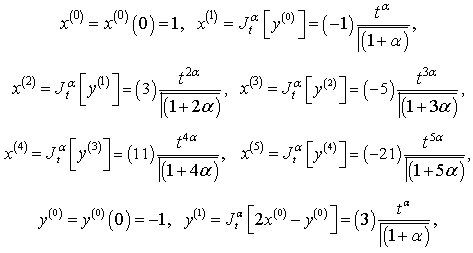
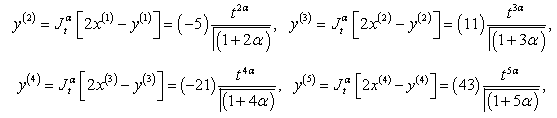 The solution of is given by:
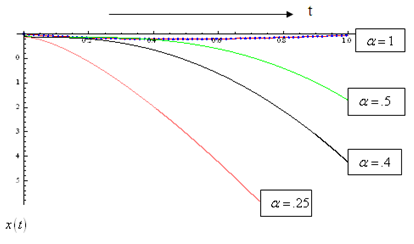
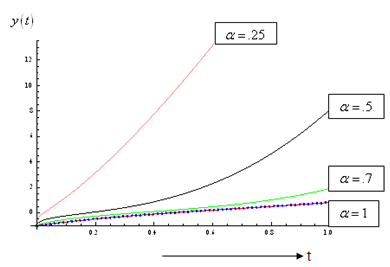
The solution of is given by: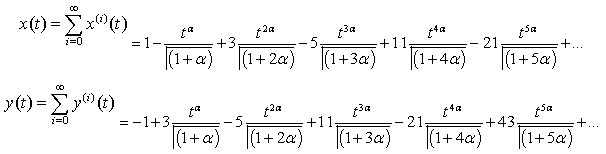 the graph of which is given below:From Fig.1 and Fig.2 we see that the solution obtained by the proposed algorithm for
the graph of which is given below:From Fig.1 and Fig.2 we see that the solution obtained by the proposed algorithm for 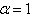 is same as the solution obtained by [16]. Also figures 1 and 2 show the solution for other different values of
is same as the solution obtained by [16]. Also figures 1 and 2 show the solution for other different values of 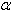 . Fig 1 and 2 show the solutions in red by HPM of the original system and by HPM of the fractional ecosystem model by blue thick dots. Example 4.2. Consider the predator – prey system [15].
. Fig 1 and 2 show the solutions in red by HPM of the original system and by HPM of the fractional ecosystem model by blue thick dots. Example 4.2. Consider the predator – prey system [15]. 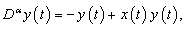 | (16) |
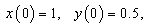 | (17) |
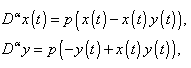
 | Figure 1. Plot of 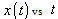 |
 | Figure 2. Plot of 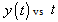 |
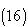 we construct the Homotopy as given in Eq.(7) putting Eq.(5) then intial condition (17) in Eq. (7)and then comparing the like powers of
we construct the Homotopy as given in Eq.(7) putting Eq.(5) then intial condition (17) in Eq. (7)and then comparing the like powers of 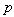 we get,
we get,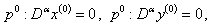 | (18) |
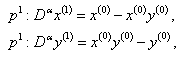 | (19) |
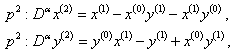 | (20) |
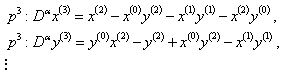 | (21) |
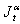 , the inverse operator of
, the inverse operator of 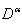 , on both side of linear equations from
, on both side of linear equations from 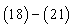 with initial condition
with initial condition 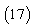 we get,
we get,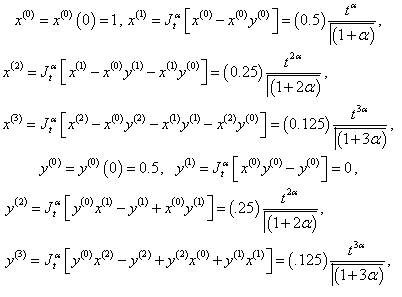 hence the solution of is given by
hence the solution of is given by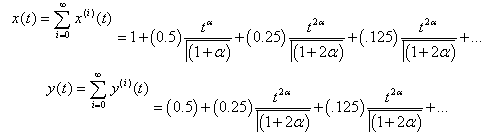 This is the accurate and exact solution of the system
This is the accurate and exact solution of the system 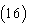 , [7], using Homotopy Perturbation Method.
, [7], using Homotopy Perturbation Method. | Figure 3. Plot of 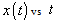 |
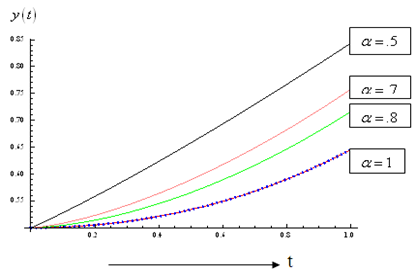 | Figure 4. Plot of  |
 is same as the solution obtained by [16]. Also fig.3 and 4 show the solution for other different values of
is same as the solution obtained by [16]. Also fig.3 and 4 show the solution for other different values of  .Figure 3 and 4 show the solutions of HPM to the ecosystem model by red colour and that of the fractional ecosystem model by blue dots. Example 4.3. Consider the predator – prey system
.Figure 3 and 4 show the solutions of HPM to the ecosystem model by red colour and that of the fractional ecosystem model by blue dots. Example 4.3. Consider the predator – prey system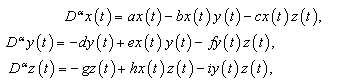 | (22) |
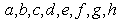 and
and 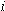 are constants, subject to the initial conditions
are constants, subject to the initial conditions 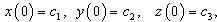 | (23) |
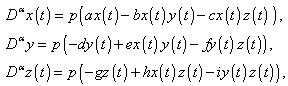 To solve the system given in Eq.
To solve the system given in Eq. 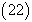 we construct the Homotopy as given in Eq.
we construct the Homotopy as given in Eq. 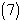 putting Eq.
putting Eq. 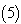 then intial condition
then intial condition 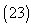 in Eq.
in Eq. 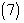 and then comparing the like powers of
and then comparing the like powers of 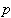 we get,
we get,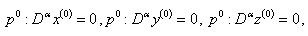 | (24) |
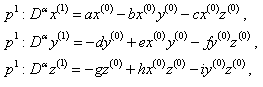 | (25) |
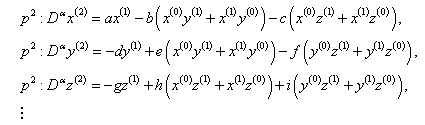 | (26) |
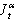 the inverse operator of
the inverse operator of 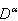 on both side of linear equations from
on both side of linear equations from 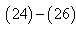 with initial condition
with initial condition 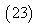 we get,
we get, Hence the solution is given as
Hence the solution is given as
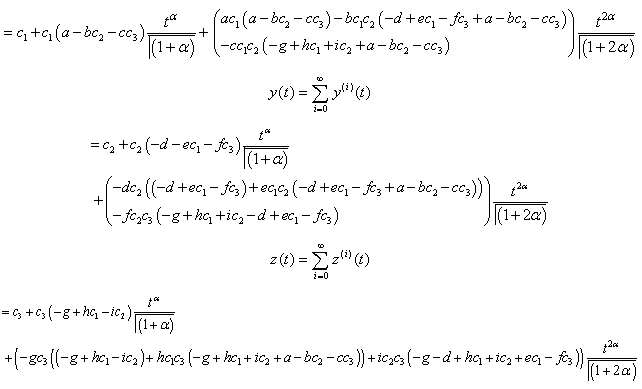 which is the accurate /exact solution of the system
which is the accurate /exact solution of the system 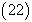 using Homotopy Perturbation Method .Example 4.4. Consider the system [17]
using Homotopy Perturbation Method .Example 4.4. Consider the system [17]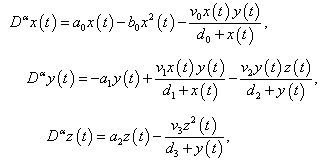 | (27) |
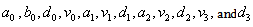 are model parameters assuming only positive values , with the initial conditions
are model parameters assuming only positive values , with the initial conditions 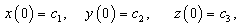 | (28) |
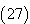 by the factor
by the factor 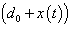 , the second equation of
, the second equation of 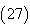 by the factor
by the factor 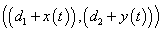 and the third equation
and the third equation 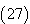 by the factor
by the factor 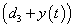 To solve the system given in Eq.
To solve the system given in Eq. 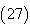 we construct the Homotopy as given in Eq.
we construct the Homotopy as given in Eq. 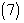 putting Eq.
putting Eq. 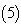 then intial condition
then intial condition 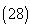 in Eq.
in Eq. 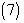 and then comparing the like powers of
and then comparing the like powers of 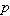 we get,
we get,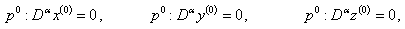 | (29) |
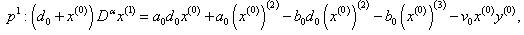
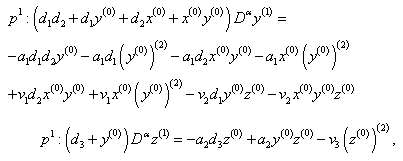 | (30) |
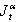 the inverse operator of
the inverse operator of 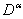 on both side of linear equations from
on both side of linear equations from 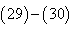 with initial condition
with initial condition 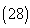 we obtained,
we obtained,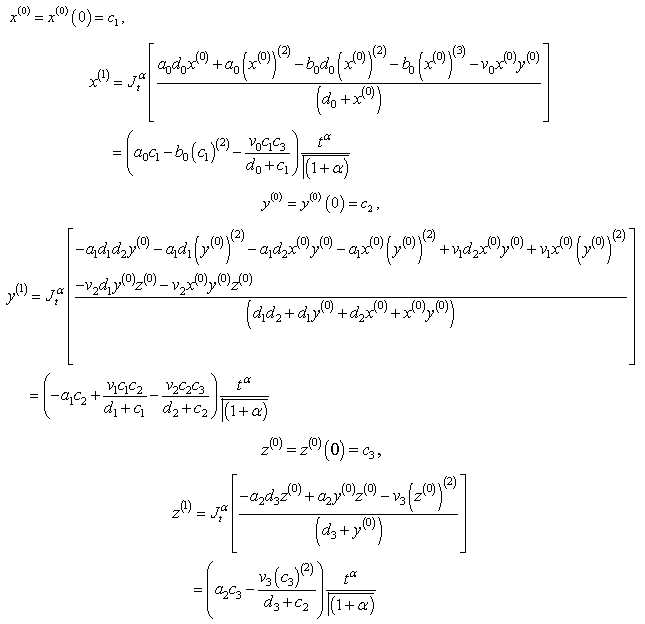 Hence the solution is given by
Hence the solution is given by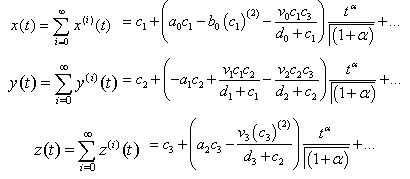 This is closed form of solution of the system
This is closed form of solution of the system 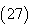 using HPM.
using HPM.4. Conclusions
- In this paper we have introduced an algorithm based Homotopy Perturbation Method to solve the fractional ecosystem model. The method has been applied to get exact and accurate solution for linear and nonlinear systems of fractional Ecosystem model, the solution obtained matches with the solution of the original ecosystem for α=1 and both the variables (populations) increases with time while value of α decreases and the solution converges to the original solution of the linear and nonlinear ecosystem model as the fractional parameter α tends to 1 as found in two examples. This method can also be applied to similar linear and nonlinear models in other systems. Further it is also verified that the FHPM is more efficient than HPM.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The first author expresses thanks to fellow scholars, in particular to Rajneesh Kumar, Vipul Kumar Barnwal and Dr. S Das who helped him in preparation of the present paper.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML