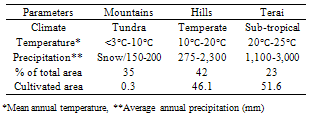
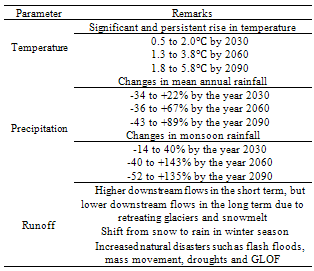
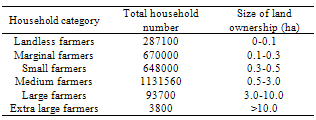
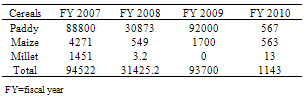
| [1] | Lybbert, T.J., and Sumner, D.A., 2012, Agricultural technologies for climate change in developing countries: Policy options for innovation and technology diffusion. Food Policy, 37(1),114-23. |
| [2] | Aydinalp, C., and Cresser, M.S., 2008, The effects of global climate change on agriculture. Am. Eurasian J. Agr. Envrion. Sci., 3(5),672-6. |
| [3] | Bartlett, R., Bharati, L., Pant, D., Hosterman, H., and McCornick, P., 2010, Climate changeimpacts and adaptation in Nepal. International Water Management Institute (IWMI) Working Paper no 139, Colombo, Sri Lanka; 2010. |
| [4] | Keane, J., Page, S., Kergna, A., and Kennan, J., 2009, Climate change and developing county agriculture: An overview of expected impacts, adaptation and mitigation challenges, and funding requirements. ICTSD-IPC Platform on climate change, agriculture and trade, Issue brief no 2, International Centre for Trade and Sustainable Development, Geneva, Switzerland and International Food & Agricultural Trade Policy Council, Washington DC, USA; 2009. |
| [5] | Khanal, R.C., 2009, Climate change and organic agriculture. J. Agric.Environ., 10(1),100-10. |
| [6] | Barrios, S., Ouattara, B., and Strobl, E., 2008, The impact of climatic change on agricultural production: is it different for Africa? Food Policy, 33(4),287-98. |
| [7] | Dulal, H.B., Brodnig, G., Thakur, H.K., and Green-Onoriose, C., 2010, Do the poor have what they need to adapt to climate change? A case study of Nepal. Local Environ., 15(7),621-35. |
| [8] | Ellis, F., 1996, Agricultural policies in developing countries. CambridgeUniversity Press, Cambridge; 1996. |
| [9] | Pokhrel, D.M., and Thapa, G.B., 2007, Are marketing intermediaries exploiting mountain farmers in Nepal? A study based on market price, marketing margin and income distribution analyses. Agric. Sys., 94(2),151-64. |
| [10] | Lohani, S.N., 2007, Climate change in Nepal-shall we wait until bitter consequences? J. Agric. Environ., 8(1),38-45. |
| [11] | Pokhrel, D.M., and Pandey, B., 2011, Climate change adaptation: strategic vision in agriculture. J. Agric. Environ., 12(1),104-12. |
| [12] | WECS, 2002, Water resources strategy, Nepal. Water and Energy Commission Secretariat, Government of Nepal, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2002. |
| [13] | FAO, 2002, Policy and strategy for poverty alleviation and sustainable housheold security in Nepal. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok; 2002. |
| [14] | CBS, 2002, Population Census 2001:National Report. Central Bureau of Statistics, Government of Nepal, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2002. |
| [15] | MOF, 2011, Economic Survey: fiscal year 2010/11. Government of Nepal, Ministry of Finance, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2011. |
| [16] | Leduc, B., Shrestha, A., and Bhattarai, B., 2008, Case study: gender and climate change in the Hindu Kush Himalayas of Nepal. International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), Gender and Climate Change Worskhop in Dakar, Senegal; 2008. |
| [17] | Malla, G., 2008, Climate change and its impact on Nepalese agriculture. J. Agric. Environ., 9(1),62-71. |
| [18] | Gautam, R., Baral, S., and Herat, S., 2009, Biogas as a sustainable energy source in Nepal: Present status and future challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 13(1),248-52. |
| [19] | NPC, 2010, Three Year Plan Approach Paper 2010/11-2012/13. Government of Nepal, National Planning Commission, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2010. |
| [20] | Bates, B.C., Kundzewicz, Z.W., Wu, S., and Palutikof, J.P., 2008, Climate change and water. Technical paper of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, IPCC Secretariat, Geneva; 2008. |
| [21] | NCVST, 2009, Vulnerability through the eyes of vulnerable: climate change induced uncertainities and Nepal's development predicaments. Institute for Social and Environmental Transition-Nepal (ISET-N, Kathmandu) and Institute for Social and Environmental Transition (ISET, Boulder, Colorado) for Nepal Climate Vulnerability Study Team, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2009. |
| [22] | Erikson, M., Jianchu, X., Shrestha, A.B., Vidya, R.A., Nepal, S., and Sandstrom, K., 2009, The changing Himalayas- impact of climate change on water resources and livelihoods in the Greater Himalayas. International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2009. |
| [23] | McSweeney, C., New, M., and Lizcano, G., 2008, Climate change country profiles: Nepal. United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Kathmandu, Nepal; 2008. |
| [24] | NAPA, 2010, National Adaptation Programme of Action (NAPA). Government of Nepal, Ministry of Environment, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2010. |
| [25] | Regmi, H.R., 2007, Effect of unusual weather on cereal crop production and household food security. J. Agric. Environ., 8(1),20-9. |
| [26] | Burton, I., Huq, S., Lim, B., Pilifosova, O., and Schipper, E.L., 2002, From impacts assessment to adaptation priorities: the shaping of adaptation policy. Climate Policy, 2(2-3),145-59. |
| [27] | Karki, M., Mool, P., and Shrestha, A., 2009, Climate change and its increasing impacts in Nepal. The Initiation, 3(1),30-7. |
| [28] | CBS, 2012, Central Bureau Statistics of Nepal. Government of Nepal, National Planning Commission Secretariat, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2012. |
| [29] | CBS, 2011, National Population and Housing Census-2011. Government of Nepal, National Planning Commission Secretariat, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2011. |
| [30] | NARC, 2010, NARC's strategic vision for agricultural research (2011-2030). Nepal Agricultural Research Council, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2010. |
| [31] | MOEST/UNDP, 2008, National adaptation programme of action on cliamte change. Ministry of Environment, Science and Technology and United Nations Development Programme, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2008. |
| [32] | Samriddhi, 2011, Commercialization of agriculture in Nepal. Samriddhi, The Prosperity Foundation, Discussion Paper, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2011. |
| [33] | HLCSLR, 2010, High Level Commission on Scientific Land Reform 2010. Reports on suggestions to Government of Nepal, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2010. |
| [34] | CBS, 1993, National Sample Census of Agricultural (1991/92). Government of Nepal, Central Bureau of Statistics, Kathmandu, Nepal; 1993. |
| [35] | DFID, 2005, Integrating indigenous and biological knowledge to implement improved dry season feeding strategies on farms in the hils of Nepal. Department of International Development London; 2005. |
| [36] | CBS, 2003, Statistical yearbook. Government of Nepal, Central Bureau of Statistics, National Planning Commission, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2003. |
| [37] | Wily, L.A., Chapagain, D., and Sharma, S., 2008, Land reform in Nepal: where is it coming and where is it going? The findings of a scoping study on Land Reform for DFID Nepal, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2008. |
| [38] | Timsina, N.P., 2011, Climate change phenomenon in Nepal. NGO Federation of Nepal: A national federation of NGOs in Nepal (Presented in South Asian Climate Conference, 1-2 January 2011, organized by ANPFa and SAAPE), (accessed on 2012-01-29); 2011. |
| [39] | Charmakar, S., 2010, Exploring existing local adaptation practices and potential strategic options to address climate change impact on biodiversity and its dependents of Nepal. National Adaptation Programme of Action/ Ministry of Environment, Government of Nepal, Kathmandu, Nepal; 2010. |
| [40] | Manandhar, S., Schmidt, V.D., Perret, S., and Kazama, F., 2011, Adapting cropping systems to climate change in Nepal: a cross-regional study of farmers' perception and practices Reg. Environ. Change, 11(2),335-48 |
| [41] | OXFAM, 2009, Even teh Himalayas have stopped smiling: Climate change, poverty and adaptation in Nepal. Oxfam International, Country Programme Office, Lalitpur, Nepal; 2009. |
| [42] | IPCC, 2007, IPCC Fourth Assessment Report: Climate change 2007. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, UNFCCC, New York; 2007. |
| [43] | IIED, 2011, Costing agriculture's adaptation to climate change. Briefing, The International Institute for Environemnt and Development, London; 2011. |
| [44] | Chapagain, B.K., Subedi, R., and Paudel, N.S., 2009, Exploring local knowledge of climate change: some reflections. J. Agric. Environ., 8(1),106-12. |

 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML