-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Clinical Psychiatry
p-ISSN: 2332-8355 e-ISSN: 2332-8371
2019; 7(1): 1-7
doi:10.5923/j.ijcp.20190701.01

Parkinson’s Disease with Impulse Control Disorders: Higher Prevalence (Frequency) of Symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Salerno L.1, Ramat S.1, 2, Solari G.1, Grassi G.1, 2, Pallanti S.1, 3, 4
1INS, Institute of Neuroscience, Florence, Italy
2Department of NEUROFARBA, University of Florence, Florence, Italy
3Stanford Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Stanford, CA, USA
4Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, NY, USA
Correspondence to: Salerno L., INS, Institute of Neuroscience, Florence, Italy.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

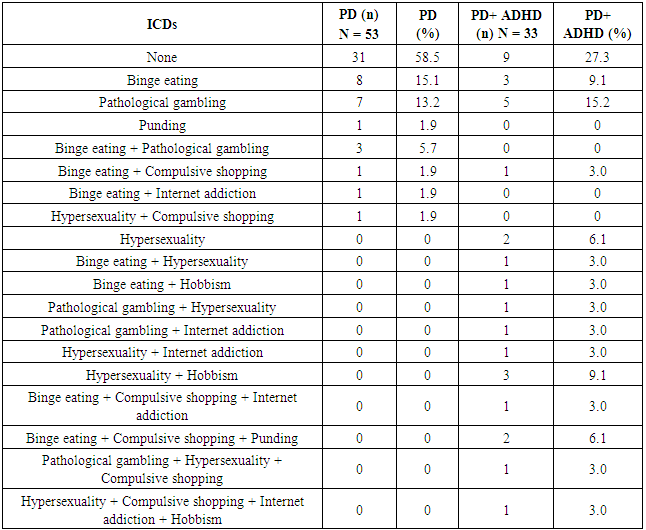
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are both characterized by dysexecutive symptoms and attentional difficulties related to basal ganglia networks’ dysfunction. Moreover, a small proportion of patients with PD suffer from Impulse Control Disorders (ICDs), which share motor and impulsivity symptoms with ADHD. Recent studies reported a link between ADHD and neurodegenerative disorders such as Lewy Bodies dementia. Thus, the aim of our study was to explore the prevalence of ADHD and ADHD symptoms in PD patients and to compare ADHD prevalence in PD patients with and without comorbid ICDs. Methods: We administered the Diagnostic Interview for ADHD in Adults (DIVA 2.0) to 86 PD patients with and without comorbid ICDs. The PD diagnosis was based on Gelb’s criteria while the presence of ICDs was defined according the Questionnaire for Impulsive-Compulsive Disorders in Parkinson's Disease-Rating Scale scores. Results: We found adult ADHD in thirty three out of 86 patients (38.37%). Importantly, the frequency of adult ADHD and ADHD symptoms was higher in the PD+ICDs group respect to the PD group (52.17% of PD+ICDs versus 22.5% of PD patients). Inattentive symptoms resulted higher in people with PD+ICDs in respect to those with PD only, in both childhood and adulthood (14% versus 2.5% for adult inattention and 23.8% versus 10% for childhood inattention, respectively). Conclusion: The unexpected high rate of adult ADHD in PD patients and especially in those with PD+ICDs points out the importance to consider the screening for ADHD in the PD population. To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first investigating the occurrence of ADHD in patients with PD+ICDs. Further studies using validated diagnostic tools for assessing ADHD in this population are warranted to replicate our findings.
Keywords: Attention deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, ADHD, Impulse control disorders, Parkinson's disease, Comorbidity
Cite this paper: Salerno L., Ramat S., Solari G., Grassi G., Pallanti S., Parkinson’s Disease with Impulse Control Disorders: Higher Prevalence (Frequency) of Symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, International Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2019, pp. 1-7. doi: 10.5923/j.ijcp.20190701.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurological condition characterized by both motor and non-motor symptoms. Motor symptoms include tremors at rest, bradykinesia, postural instability and rigidity. Non-motor symptoms are equally disabling and include executive dysfunctions, attentional problems, cognitive decline, sleep disorders, autonomic failures and fatigue. Among non-motor symptoms affecting PD individuals, impulsive behaviour - intended as the failure to resist an impulse or a temptation to act without think beforehand - has received greater attention in the last years. Such interest started from the discovery that a subpopulation of people with PD also suffered from Impulse Control Disorders (ICDs), a group of repeated behaviours linked to immediate rewards [1]. ICDs typically reported in PD patients include gambling disorder, hypersexuality, binge eating, compulsive shopping, punding and dopamine dysregulation syndrome (DDS) [2]. Several studies showed a higher prevalence of ICDs in patients with PD in comparison to the general population across different countries [3, 4]. Although the prevalence of ICDs in PD patients seems to be higher in those treated with dopamine agonists, it does not seem to be solely related to pharmacological treatments [3, 4]. Moreover, ICDs tend to be more prevalent in patients with an earlier age of PD onset, and in those with premorbid traits of novelty seeking personality (e.g. exploratory activity for new and exciting stimulation, impulsiveness, avoidance of frustration) or a history of substance use disorders (SUDs) [5]. While the identification of ICDs made the impulsivity dimension of central importance for patients with PD [1], impaired attentional processes have been also documented, with evidence supporting the hypothesis of an attentional network dysfunction in the emergence of visual hallucinations in PD [6].Attentional problems, impulsivity and high level of motor activity represent the core symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). ADHD is one of the most commonly neurobiological disorder with a childhood onset, affecting approximately 5% of population worldwide [7]. ADHD tends to persist throughout life, with some changes in the clinical presentation over the course of development [8]. Also, recent studies showed that a proportion of adult ADHD patients do not show a childhood onset [9-11], but present the same functional impairment and the same number of psychiatric comorbidities than those with an ADHD with a childhood-onset [12].Interestingly, recent findings showed a high prevalence of ADHD in a clinical population affected by dementia with Lewy Body (DLB) [13]. Thus, ADHD might be equally present in other forms of age-related degenerative conditions such as PD. Moreover, ADHD is a lifelong condition characterized by a constellation of symptoms that – if not recognized in developmental age or in first adulthood – may be interpreted as a sign of aging or can be obscured by the emergence of a neurocognitive disorder. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the presence of ADHD symptoms in patients with PD with and without ICDs and without cognitive impairment due to a neurocognitive disorder, by using a validated instrument for the retrospective recall of ADHD symptoms [14].
2. Study Design, Methods and Sample Characteristics
- In this cross-sectional study we enrolled 86 outpatients with an idiopathic PD with and without ICDs comorbidities. Patients were recruited from the Careggi Hospital, Florence (Italy), from December 2015 to March 2017. PD diagnosis was made using published criteria [15] and the presence of an impulse control disorder was assessed using a specifically developed rating scale, the Questionnaire for Impulsive-Compulsive Disorders in Parkinson's Disease-Rating Scale (QUIP-RS). The QUIP-RS is composed by 4 questions investigating the presence of compulsive gambling, buying, eating and sexual behaviour, and 3 related disorders (excessive PD medications use, punding and hobbysm) [16]. According to QUIP-RS scores, patients have been divided into two samples: 40 patients with PD only (PD) and 46 patients with both PD and ICDs (PD+ICDs).We excluded patients with a cognitive impairment established by a score below the cut-off at the Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly (IQCODE) [17] administered to the collateral informant, and by a Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) score of less than 24 [18].Pharmacological treatment different from levodopa has been converted using the conversion factors published by University of Birmingham to express different doses of anti-parkinsonian medications on a single scale [19]. Socio-demographic information, such as individual’s age at PD onset and antiparkinsonian therapies have been recorded by assessors who were not aware of the study hypothesis.In order to explore the rate of adult ADHD in the study population, we administered the Italian version of the clinical interview DIVA 2.0 (Diagnostic Interview for ADHD in Adults 2.0) to those who scored ≥ 4 (representing the screening cut-off for the presence of ADHD) to the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS-v1.1) Symptom Checklist [20, 21]. The DIVA 2.0 is a semi-structured interview that investigates the presence of childhood and adult ADHD according to the DSM-IV criteria, providing a list of examples for the symptoms presentation in both life periods. It also contains five areas of functioning where symptoms can cause impairments: work and education; relationships and family life; social contacts; free time and hobbies; self-confidence and self-image. The DIVA 2.0 was administered by clinicians with expertise in ADHD diagnosis and in presence of collateral informants (siblings), in order to obtain reliable data for the symptoms presentation in both the life periods investigated.The presence of anxiety and depression symptoms was assessed through the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) [22] and the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D-17 items) [23] respectively. We also assessed impulsivity traits with the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale, version 11 (BIS-11) [24, 25].Our primary outcome was the rate of patients presenting a number of current and childhood ADHD symptoms exceeding the recommended cut-off of DSM-5 and meeting the impairment criterion.Our study complied with the Declaration of Helsinky. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant or legal surrogate. All participants could withdraw at any point if they chose to.
2.1. Statistical Analyses
- We tested for normality using Shapiro-Wilk Test, as it is more appropriate for small sample sizes (<50 individuals). The assumption of normality was violated for the majority of variables and for both groups (p > .05), consequently we used nonparametric tests to determine if there were differences between the two groups on continuous or ordinal dependent variables. Differences in categorical variables were analysed with the Fisher’s exact test if cells had an expected count less than five. Continuous variables were examined with the Mann-Whitney U test. SPSS Statistic 21 was used for analysis. Statistical significance was set at a p-value of <0.05, two sided.
3. Results
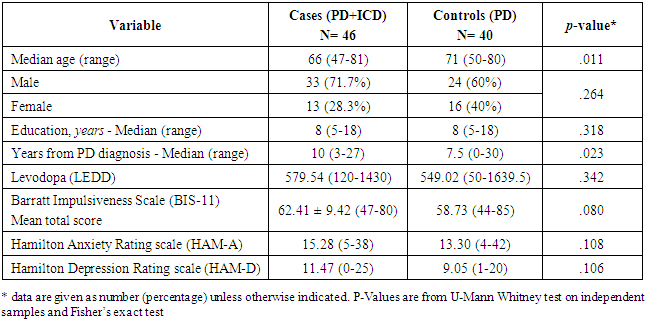
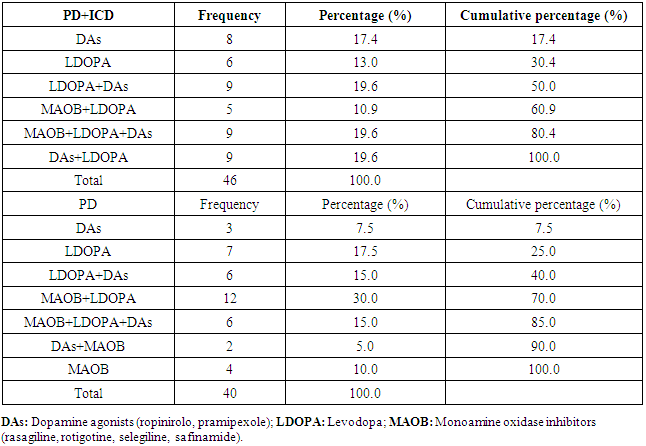
- The PD+ICDs group was composed by 33 males (71.7%) and 13 females (28.3%), with a median age of 66 years old (range 47-81). The PD group was composed by 24 males (60%) and 16 females (40%) with a median age of 71 (range 50-80). The two groups did not significantly differ for sex, while they differed for age (PD patients were older than PD+ICDs patients, U=1.214, z = 2.548, p = .011). Also, the two groups differed for years from the diagnosis (the PD+ICDs group passed more years from the diagnosis than the PD group, U=658, z = -2.274, p = .023). On the other hand, the two groups did not differ for anxiety and depressive symptom scores assessed through the HAM-A and the HAM-D. Surprisingly, the two samples did not differ on impulsivity symptoms assessed through the self-report scale BIS-11. Finally, the levodopa-equivalent daily dose (LEDD) did not differ between the two groups. Clinical and demographic characteristics of the study population are summarized in Table 1, while Table 2 shows pharmacological treatments at the time of the study.
|
|
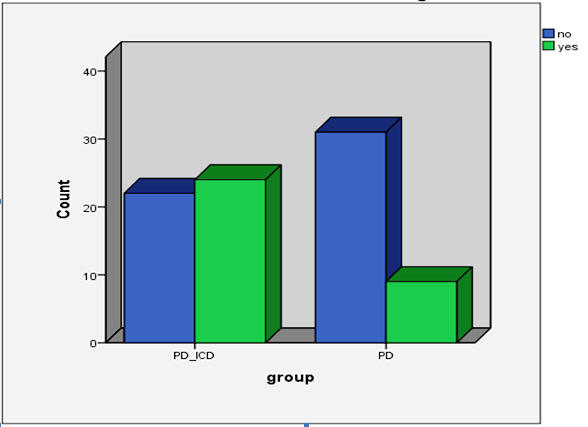 | Figure 1. Frequency of ADHD in the PD+ICDs group versus the PD group according to DIVA 2.0 |
|
4. Discussion
- In this study, we found a surprisingly high rate of adult ADHD in a sample of PD patients. Indeed, 38.37% of the whole PD sample had showed a clinical picture of adult ADHD according to the DIVA 2.0. Specifically, the presence of an adult ADHD was significantly higher in PD patients with comorbid Impulse Control Disorders in comparison to patients with only PD (52.17% vs 22.5% respectively). Also, PD+ICDs patients reported higher rates of both inattentive and hyperactivity/impulsivity symptoms in adulthood than PD patients without ICDs. Moreover, for most of patients, collateral information supported the presence of ADHD even in the developmental age, with associated impairment. Interestingly, according to DIVA 2.0, higher inattentive symptoms appeared to characterize patients with PD+ICDs in respect to those with PD only. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study investigating the presence of ADHD in this such a clinical populations.Several hypotheses could account for our results. First of all, neuroimaging studies showed some commonalities in basal ganglia alterations between PD and ADHD patients. Indeed, recent findings indicated an enlarged echogenic substantia nigra area in children with ADHD in respect to matched controls, which has been also found in people with PD [26, 27]. This feature has been considered as a marker of a dysfunctional nigrostriatal dopaminergic system [26]. Also, volumetric reductions in basal ganglia in ADHD have been linked to symptoms typically reported in PD patients such as deficits in motivation, reward processing, goal-directed behavior and motor control [28, 29, 30]. Consistently with the hypotheses of a dopaminergic striatal dysfunction, methylphenidate, which is one of the most effective treatment of ADHD, targets the striatal dopamine transporters, and works by blocking about 70% of them [31]. Interestingly, recent data showed that methylphenidate seems to improve mobility and gait stability in elderly, reducing falls in older adults [32] and that high doses of methylphenidate are helpful in improving gait and motor symptoms in older patients with PD undergoing subthalamic nucleus (STN) stimulation [33].Moreover, there is some evidence about a genetic link between PD and ADHD. In fact, data from Jarick et al. [34] suggested a contribution by copy number variants at the PARK2 locus to the genetic susceptibility of ADHD, that is of interest considering that PD has been associated to mutations and copy number variations (CNVs) in PARK2. However, a recent study found no genetic association between ADHD and PD in nine ADHD candidate single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) [35].Finally, the two disorders share several phenomenological similarities. First, teens with ADHD often show the presence of neurological soft signs, principally related to motor coordination and motor overflow movements that appear to be connected with functional deficits in the cerebellum and the basal ganglia [36]. Secondly, both ADHD and PD patients show impaired decision-making processes and tend to develop addictive disorders [37, 38, 1]. Indeed, ADHD patients tend to develop addictions through drugs enhancing dopaminergic transmissions (such as amphetamines and cocaine) and PD patients with ICDs often develop the so-called Dopamine Dysregulation Syndrome (DDS), characterized by excessive assumption of dopaminergic medications [39, 40]. Although several studies suggested a role of dopamine-replacement therapies (DTRs) in the onset of ICDs such as DDS in PD patients, increased impulsivity has been found also in drug-naïve patients. Indeed, there is evidence showing the involvement of other factors than the only dopaminergic agents in the ICDs development such as the younger age, a family history of alcoholism and gambling problems, and a higher LEDD [41, 1]. Thus, some authors suggested that a disrupted connectivity in brain networks including cerebellum, basal ganglia, cortex and spinal projections could underlie the vulnerability for ICDs for some PD patients [42]. Consistent with these studies, our patients in the PD+ICDs group were significantly younger than those in the group of patients with only PD, but they did not differ in the LEDD. Finally, as recent research has suggested an association between ADHD psychostimulants use and the risk of developing basal ganglia and cerebellum diseases [43], it is important to underline that our sample of patients did not receive any specific treatment for ADHD in their past. Therefore, it is likely that ADHD constitutes an independent risk factor for developing PD or ICDs in people with PD. However, longitudinal studies are needed in order to confirm such hypotheses. Several limitations are worth of mentioning. First, even though the clinical interview DIVA 2.0 is considered the gold standard for diagnosing ADHD in adulthood, its use in PD population is questionable since it has not been validated in this population. Also, the validity of an ADHD diagnosis in the elderly population is still controversial and little is known about its phenomenology in this population. Indeed, DSM-5 criteria for adult ADHD were not developed on old people. However, a large epidemiological study in The Netherlands found a prevalence of full syndromic ADHD of 2.8% and of 4.2% for symptomatic ADHD in men and women aged 55-85 years [43]. Thus, the adaptation and validation of the DIVA 2.0 in elderly people and neurological populations such as PD population is crucial to confirm or refute our preliminary findings. Another limitation related to the assessment tools used in this study is the putative effect of a recall bias for the presence of ADHD symptoms before 12 years old. Although in our study we included only patients who had a relative (a sibling) informing for the childhood period, we cannot exclude a bias in the collateral report. Future research should consider inclusion of school report cards or the presence of more than one collateral informant for reducing the possibility of a misdiagnosis.Secondly, we used two instruments for assessing cognitive performances (the MMSE and the IQCODE) that are probably not sensitive enough to relieve attentional problems that could overlap with ADHD symptoms. Thus, further studies using cognitive tests specifically recommended for PD are needed [44].Finally, despite we found a higher rate of adult ADHD in people with PD than expected on the basis of prevalence found in the general population [43], the lack of a healthy controls group suggests caution in interpreting our results.Notwithstanding all the difficulties in disentangling the brain mechanisms underlying the attentional difficulties affecting people with PD and those with ADHD, we believe that the investigation of the presence of attention deficits with a developmental onset in people with PD can be of value in delineating the boundaries between the two disorders. Moreover, the characterization of attentional difficulties through more sensitive assessment tools, in such populations, could be of help in identifying those subjects who are more at risk for developing DDS.
5. Conclusions
- This is the first study investigating the occurrence of adult ADHD in a population of patients with PD. Our results showed a high rate of adult ADHD in PD patients, especially in PD patients with comorbid ICDs. This finding pointed out that, after that impulsivity has been recognized as an important aspect to be evaluated in PD, it is time to investigate the attentional domain and its networks in patients with PD with a cognitive impairment not-related to a neurocognitive disorder. Consequently, it would be important to consider also the screening for ADHD in such clinical populations. The diagnosis of ADHD in elderly is challenging and it is far more in older people affected by other mental health conditions such as PD. ADHD is a lifelong condition that can modify its clinical presentation thorough time, therefore a deep knowledge of the disorder by neurologists and gerontologists is essential to carefully consider it in their clinical practice with their elderly patients. For helping them, adaptation and validation of the available diagnostic instruments or the development of new ones are fundamental.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This project received a financial support from The CNS Onlus, a not-for-profit association and from the INS, Istituto di Neuroscienze, via Alfonso Lamarmora 24, 50121 Firenze.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML