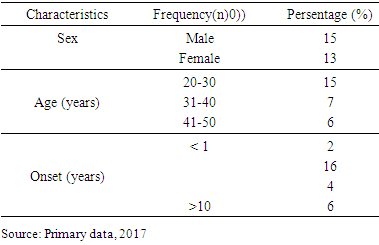-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Clinical Psychiatry
p-ISSN: 2332-8355 e-ISSN: 2332-8371
2018; 6(2): 40-46
doi:10.5923/j.ijcp.20180602.03

Changes of Body Weight and Triglyceride Level in Schizophrenia Patients Treated with Atypical Antipsychotics
Saidah Syamsuddin1, Agustine Mahardika2, Hawaidah1, Sony T. Lisal1
1Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, Makassar, Indonesia
2Postgraduate, Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, Makassar, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Agustine Mahardika, Postgraduate, Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, Makassar, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Schizophrenia is a syndrome that could cause a serious functional decline and an extensive health problems. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality among Schizophrenis patients has been linked to high prevalence of metabolic syndrome. The objective of this study is to determine changes in body weight and triglyceride levels in schizophrenic patients who had received atypical antipsychotics. This study conducted in observasional analytic design with prospectif cohort approach. Sampel were 28 schizophrenic patients. Their body weight and triglyceride level were examined at base line, at the first and second month after therapy with atypical antipsychotics. The results showed that after one month therapy there was a significant weight gain of 1.39 kg and an increase in triglycerides of 10.04 mg / dl. In the second month of therapy there was a weight gain of 2.26 kg and an increase in triglycerides of 16.39 mg / dl. There was a significant increase of body weight and triglycerides in the first and second months with a value of p <0.05. The presentage of elevated triglyceride levels is higher when compared to weight gain percentage. It is necessary to have adequate dietary regulation and physical activity for schizophrenic patients receiving atypical antipsychotics to prevent undesired metabolic side effects.
Keywords: Atypical antipsychotics, Schizophrenia, Body weight, Triglyceride
Cite this paper: Saidah Syamsuddin, Agustine Mahardika, Hawaidah, Sony T. Lisal, Changes of Body Weight and Triglyceride Level in Schizophrenia Patients Treated with Atypical Antipsychotics, International Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2018, pp. 40-46. doi: 10.5923/j.ijcp.20180602.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Schizophrenia is a syndrome which could cause a serious functional impairment and extensive health problems. The prevalence of schizophrenia is 1%, with onset mostly in young adults, and could cause excessive morbidity and mortality [1, 2]. Patients with schizophrenia have 10-25-year reduction in life expectancy [3], whereas mortality in schizophrenic patients is 2-3 times greater than general population [4].One of the causes of increased mortality in schizophrenics is cardiovascular disease [5]. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality among Schizophrenic patients had been linked to high prevalence of metabolic syndrome [6]. Atypical antipsychotics are second-generation antipsychotics which currently the first-line treatment of schizophrenia because they also have less extrapyramidal effects than first-generation antipsychotics, but atypical antipsychotics can cause serious metabolic-related side-effects, including weight gain and central obesity [7]. According to one of the studies a study, patients receiving atypical antipsychotic therapy had an average weight gain of 0.6 kg per week and occurred since the first week of therapy [8]. Elevation of weight and obesity may decrease patient compliance to continue treatment and lowering functional outcome [9, 10].There was a significant correlation between weight gain and elevated triglyceride levels and fasting cholesterol in patients receiving atypical antipsychotic therapy [11]. There were also studies suggesting that psychotic patients using second-generation antipsychotics showed a significant increase in triglycerides and had a 4-fold increased risk of hypertriglyceridemia compared with the control group, which found no different results among the atypical antipsychotics used [12]. Studies conducted in Indonesia suggested an increase in total cholesterol and triglycerides in patients who have been receiving olanzapine for 4 weeks [13].Epidemiological evidence indicates that plasma triglycerides levels predict CVD [14]. Hokanson and Austin already showed in 1996 in a meta analysis that triglycerides is an independent risk factor for CVD [15]. Presence of elevated concentrations of atherogenic TG-rich remnant lipoproteins is the principle abnormality responsible for this association. When triglycerides are elevated, lipoprotein metabolism is altered, which increases CVD risk [16].The presence of metabolic side effects including increased triglycerides in the use of antipsychotics, especially atypical antipsychotics requires serious attention, but studies on the impact of lipid abnormalities on atypical antipsychotic use in Indonesia are limited. Based on this background, this study aimed to determine changes in body weight and triglyceride levels in schizophrenic patients who have received atypical antipsychotics.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
- Subjects were recruited at psychiatric ward in Special Hospital of South Sulawesi Province. Subjects were all patients who met the diagnosed criterian of Schizophrenia based on ICD-10. All subjects were 20-50 years old. Patients suffering from chronic metabolic and chronic disease were excluded. All subjects were provided with complete written and oral descriptions of the study, written informed consent was also obtained. The protocol was approved by the local ethics committee. Samples were taken by Consecutive Sampling. All schizophrenia patients who met the study criteria were taken until the required samples were met.
2.2. Design and Procedure
- This was an observational analytic study with prospective cohort design. All schizophrenic patient who met the inclusion criteria were included in the study group and personal data were recorded including name, sex, age, last education, occupation and history of the disease first.
2.3. Blodd Sampling and Measurement
- All the subject were measured for weight, height, waist circumference. Blood sampling were taken at the beginning of therapy, 1 month and 2 month after therapy with atypical antipsychotics. 4 ml blood was taken after 1 hours of fasting and was analysed at the beginning of therapy, 1 month and 2 month after therapy with atypical antipsychotics.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- Data was analyzed using (SPSS) and presented as tables and graphs. Paired t test was used for the significancy of weight changes and triglycerides levels changes.
3. Result
3.1. Sample Characteristic
- The consecutive resulted in one group consist of twenty eight subject.
|
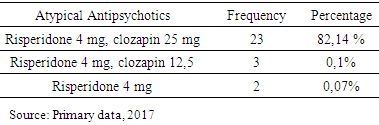
3.2. Atypical Antipsychotics
|
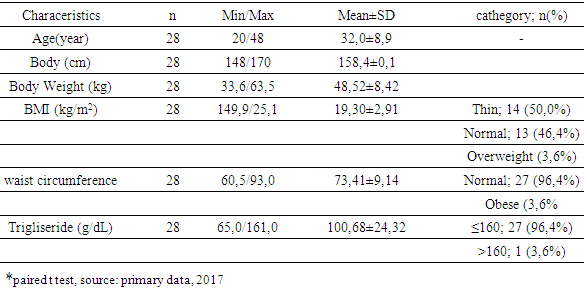
3.3. Baseline Measurement
- Characteristics of the initial measurements of the subjects showed that age between 20 - 48 years with mean: 32.0 years. Height between 148-170 cm with mean: 158.4 cm. Weight between 33.6 - 63.5 kg with mean: 48.52 kg. Some were relatively thin (50.0%), only 3.6% overweight based on IMT category and only 3.6% obese central based on waist circumference. There was 3,6% subjects had high triglycerides level.
|
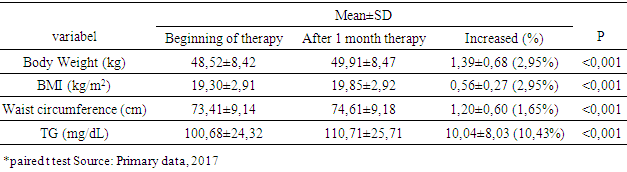
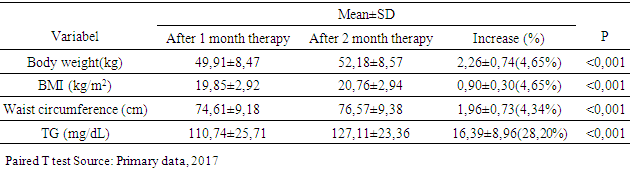
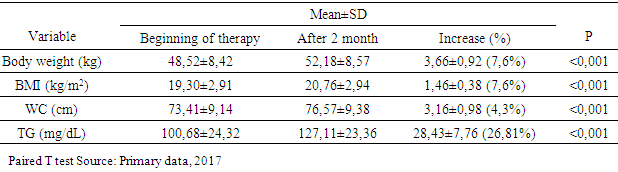
3.4. Changes in Body Weight, BMI, Waist Circumference and Serum Triglyceride
|
|
|
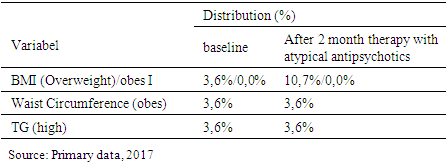
3.5. Overweight Distribution, Obesity and High Triglyceride Levels
|
4. Discussion
- Characteristics of age-based samples showed that the largest number of samples was in the 20-30 year age range (53%). Symptoms of schizophrenia usually appear in late adolescence or young adulthood. Onset in men is usually between 15-35 years and in women between 25-35 years old [17]. By the onset of disorder, onset of 1-6 years occupies the highest number (57.1%). An intensive study found that the onset of negative symptoms tended to occurred for 5 years, before a positive symptom emerged, and when the positive symptoms appeared the patient would be immediately taken to the hospital [19]. Data from this study showed that BMI and waist circumference at baseline were obtained from the subjects with the lowest BMI category (50.0%), followed by normal BMI category (46.4%) and overweight category (3.6%). Lack of weight could be caused by a lack of food intake in schizophrenic patients who had not received treatment. Negative and positive symptoms experienced by schizophrenic patients could cause it. Negative symptoms are poor speech, lack of motivation, lack of self-care, social withdrawal, and anhedonia [2]. These symptoms could affect food intake in schizophrenic patients. Patients with chronic schizophrenia tend to neglect personal appearance, tidiness and neglected personal hygiene and tend to withdraw socially [18]. In this study the atypical antipsychotics used by subjects were risperidone and clozapine. Risperidone was used in therapeutic doses, while clozapine just used for sedatives. In this study weight gain occured in the first month and continued until the second month. After 1 month of atypical antipsychotic treatment, there was a change of 1.39 ± 0.68 kg (2.95%). The increase in body weight after 2 months was 2.26 ± 0.74 kg (4.65%). While total weight gain was 3.66 ± 0.92 kg. It appeared that weight gain was greater in the second month. This may be due to the effect of antipsychotic therapy that has reached its maximum at weeks 4 to 6 [2], followed by its effects on weight gain and metabolism. Receptors associated with weight gain are H1 receptors H1 and serotonin 5 HT2C, when blockade occured in both of the receptors, at the same time the subjects may experience weight gain. Weight gain was the result of increased appetite in the hypothalamus feeding center, but unrelated peripheral-related factors were also involved in weight gain due to antipsychotics [19].Another study of schizophrenic patients who had been treated for 14 weeks with antipsychotics, found that the mean weight gain in olanzapine use was 5.4 kg, clozapine was 4.3 kg and risperidone was 2.3 kg [20]. While the study in patients with risperidone and clozapine therapy showed weight gain of 0.4 kg per week (risperidon) and an increase of 0.5 kg per week (clozapine) [21]. The magnitude of weight gain varies among atypical antipsychotics. Clozapine and olanzapine have the greatest effect of weight gain in long-term or short-term use. Risperidon has a moderate effect in weight gain. Quetiapine provides minimal to moderate effects, depending on the length of therapy whereas ziprasidone has the lowest weight gain effect. All antipsychotics have an effect in increasing weight in different degrees due to different actions to serotonergic receptors, dopaminergic, cholinergic, histamergic and other neurotransmitter systems [22]. The serotonin system has long been known as a neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of food intake. The 5HT1A agonist increases the food intake and 5 HT2C lowers it while the 5HT2C antagonist increases the food intake. Studies show the regulation of serotonin on NPY regulation. The 5HT2C antagonist causes an increase in food intake through increased NPY levels in the paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is an important area of the brain involved in food intake and weight regulation and it is rich in 5 HT2C. Administration of clozapine led to an increase in the density of immunoreactive NPY cells in the tasty food nucleus of rat rats due to the 5HT2C antagonist work that led to disinhibition of neuron NPY [23]. There is evidence to suggest dopamine involvement in eating behavior. Dorsal striatum and ventral striatum are inhibited by dopamine, where both areas are associated with calorie regulation and food reward effects. The release of dopamine in a number of areas such as nucleus accumbens is increased by sweetness. Dopamine is important in the occurrence of rewards from good food [24]. There is also a central role of histamine to the control of food intake and energy regulation [25]. Histamergic neurons and histamine H1 receptors are located in the hypothalamic posterior tuberomamilary nucleus and transmit their axons throughout the central nervous system. There is research showing that inhibition of H1 receptors in rats causes obesity, which is accompanied by increased food intake and diurnal diet disturbance [26]. In this study, the results of increased triglycerides in the first month was 10.04 ± 8.03 mg / dl (10.43%), the average increase of triglycerides in the second month was 16.39 ± 8.96 mg / dl (16, 39%). While the total increase of triglycerides after 2 months was 28.43 ± 7.76 mg / dl (28.20%). The increase of triglycerides in the second month is higher than in the first month. In line with other studies patients using atypical antipsychotics experienced elevated triglycerides of 25.8 mg / dl after 3 weeks of therapy [27]. In the study by Kausha et al the average increase in Triglycerides after 8 weeks of treatment using olanzapine (5 mg daily) was: 30.03 mg / dl and at risperidone (2 mg daily) was 13.23 mg / dl. [28] Other studies have shown that samples who received risperidone monotherapy experienced increased of triglyceride levels by 35.2 mg / dl after 3 months of therapy [29]. The difference in these results may be due to the difference in the dose of the given drug, as well as the time of therapy. In addition, the combination of using two atypical antipsychotics, risperidone and clozapine, led to a higher cholesterol increase compared to risperidone alone. The results of this study showed that the percentage of triglyceride elevation was greater than the percentage of weight gain. This suggests that weight gain was not directly correlated with elevated triglycerides. A number of studies have shown that weight gain is generally associated with increased lipid [30, 31]. However, a number of other studies have shown opposite results [21, 32]. A study of patients using atypical antipsychotics showed that weight gain had no significant correlation with elevated lipid profiles including triglycerides [27]. Elevated triglycerides can be caused by weight gain. However, comparison of weight gain and triglyceride for two months was found that the increase of triglyceride has a larger percentage compared to weight gain. This suggests that elevated triglycerides are not solely due to weight gain. Not all metabolic disorders are the result of increased adiposity, a number of patients using atypical antipsychotics, have a new onset of diabetes without weight gain. An experimental study shows the occurrence of insulin resistance caused by the use of atypical antipsychotics independent of adiposity [33]. Metabolic disorders in the use of atypical antipsychotics can be a direct result of changes in insulin sensitivity and / or insulin secretion. Atypical antipsychotic bonds in histamine and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors are associated with weight gain and metabolic disorders [34]. Parasympathetic regulatory disorders in pancreatic beta cell activity contribute to metabolic risk [35]. Triglycerides levels is a marker of insulin resistance, moderate elevations of triglycerides are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular independent from HDL cholesterol levels [36]. Decreased insulin sensitivity may result from a change in the product of the insulin signaling pathway gene and / or increased levels of the circulating factor that alter insulin signaling. There is evidence that antipsychotics can interfere with the direct glucose transport function. Glucose transport is regulated by insulin that actively removes glucose to peripheral tissues (liver, muscle and fat). Decreasing the direct glucose transport function by antipsychotics leads to an increase in glucose in the blood and insulin hypersecretion as a compensation, which, if continuous, results in decreased insulin sensitivity and encourages cascade of metabolic syndromes [37]. Antipsychotic treatment may affect the action of insulin in adipocytes, leading to the progressive accumulation of lipids [38]. Disruption of the effects of insulin on adipocytes may explain the increase of triglycerides that are independent of weight gain [39].The results showed that despite a significant increase in body weight and triglycerides, no samples met the metabolic syndrome criteria after 2 months of therapy. Changes that occurred only increased of overweight subjects from 3.6% to 10.7%. Another study showed that therapy with atypical antipsychotic risperidone for 3 months led to an increase in the number of patients who met the metabolic syndrome criterian from 34.8% at the initiation of therapy increased to 49.3% [29]. This was due to the initial condition of the sample which more than 50% sample were thin based on BMI category so that weight gain and Triglyceride after 2 months of therapy do not reach the category of obesity or hypertriglyceridemia.Limitations in this study, there were no measurement for others variables that were associated with direct effects of atypical antipsychotics on metabolism. In addition, the collected subjects did not represent all types of atypical antipsychotics present. All samples were patients who were hospitalized, where the food provided for the patient was regulated and uniformed.
5. Conclusions
- Weight gain and increase of triglycerides level in schizophrenic patients using atypical antipsiotics occured from the first month, continuing in the second month where the increase in body weight and triglycerides in the second month is higher than the first month. Increase of triglyceride was higher when compared with weight gain. Efforts should be made to maintain a balance of body weight and triglycerides in schizophrenic patients who use antipsychotics, especially atypical antipsychotics by maintaining a balanced diet and adequate physical activity.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors declare no potential conflict of interest in writing this original article. The authors would like to acknowledge the important support and contributions of A. Uleng Bahrun, M.D. (Clinical Pathologist) and Ilhamjaya Patellongi, M.D. (Research Methodology).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML