-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Construction Engineering and Management
p-ISSN: 2326-1080 e-ISSN: 2326-1102
2022; 11(3): 65-77
doi:10.5923/j.ijcem.20221103.01
Received: Aug. 29, 2022; Accepted: Oct. 8, 2022; Published: Oct. 21, 2022

Web-Based Building Information Modeling Data Exchange Standardization Protocols for the Architectural, Engineering, and Construction Industry
Kwame B. O. Amoah
Department of Civil and Architectural & Construction Management, University of Cincinnati, OH, USA
Correspondence to: Kwame B. O. Amoah, Department of Civil and Architectural & Construction Management, University of Cincinnati, OH, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Building information modeling (BIM) is an interactive technology that aids the effective collaboration between various disciplines in the architectural, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. The series of methodologies BIM generates helps in managing the requisite building design and project information in an automated format throughout the building lifecycle. However, seamlessly exchanging the properties of BIM applications on a unified platform is a challenge. The aim of this study was to develop a standardized web-based (BIM) platform. A web-based BIM platform is a streamlined diverse system that combines different applications to interact with each other. This study focuses on the perceived problems of exchanging data at a component and itemized level owing to the inefficiencies of inconsistent software. In the first phase, a survey was conducted to thoroughly investigate the methods by which a BIM-based data exchange platform could be used by a firm. The findings identified the need for a unified markup language to exchange datasets for intelligent model objects on an automated platform. In the second phase, the author implemented an extensive markup language (XML) based BIM platform that enabled the exchange of data through web services in real time. This integrated approach promoted vital decisions in the early design and planning phases of projects using rapid information exchange for effective collaboration. The exchange framework system accessed data automatically and seamlessly without the manual effort of a specific project team. The validated model demonstrated an improved standardization process, strengthened project decision-making, boosted communication, and enhanced collaboration across multiple project disciplines.
Keywords: Building information modeling, Interoperability, Classification schema, BIM data exchange protocol, BIM standards, Green building XML, IFC schema
Cite this paper: Kwame B. O. Amoah, Web-Based Building Information Modeling Data Exchange Standardization Protocols for the Architectural, Engineering, and Construction Industry, International Journal of Construction Engineering and Management , Vol. 11 No. 3, 2022, pp. 65-77. doi: 10.5923/j.ijcem.20221103.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Building information modeling (BIM) currently supports data exchange across the architectural, engineering, construction, and facilities management (AEC-FM) industries through various phases, applications, models, and stakeholder engagement. BIM is an integrated informational process that is vital in enabling the effective planning and control of projects at different levels of the project lifecycle. The integration of geometric representations by BIM significantly contributes to the dynamics of the information documentation and exchange methods among various design models. BIM is a connector and acts as an innovative technology that links two-dimensional (2D) drawings to three-dimensional (3D) models to integrate different phases of the project. BIM data exchange issues are technical and process-related. Software workflows using various BIM applications encounter technical difficulties. Each stakeholder has different project responsibilities and requires different information levels to meet the project requirements. In [1], the authors implemented a six-step methodology to support BIM interoperability between the architectural design and structural analysis of AEC-FM projects. The research and development of a new communication platform using BIM and a web-based interface in [2] enabled real-time information updates and interactive visualization of design and construction information. In [3], a systematic methodology of managing asset data flow between building stakeholders throughout the building lifecycle was investigated using the construction operation building information exchange (COBie) standard. In [4], improving the management of information across different stages of a renovation process allowed the interoperable exchange of data among other stakeholders and the development of an innovative BIM-based toolkit. Cloud-BIM represents a new data storage, exchange, and collaboration paradigm that is potentially a considerable departure from existing industry practices. Cloud-BIM is believed to be the second generation of BIM development and studies suggest that it will produce significant changes across the industry [5]. Data exchange is critical for successfully implementing BIM [6], and data interoperability among cloud services is a crucial enabler of cloud-BIM collaboration [5]. In [7], the authors investigated the current limitations and opportunities of cloud interoperability and outlined a framework for loosely coupled network-based BIM data interoperability. Multidisciplinary project teams can collaborate using BIM software solutions to create, use, and share intelligent 3D digital model information, providing all stakeholders a clearer vision of the project and improving their ability to make faster, more informed decisions. Data exchange standards are essential to help project teams move information from one 3D modeling software application to another without loss of data fidelity and facilitate more efficient workflows and higher quality outcomes [8]. In [9], the authors reviewed the progress of software data exchange in the AEC industry. The first-generation data exchange models focused on building geometry data. The second-generation data exchange programs introduced an extended model to integrate domain-specific performance information. Recently developed third-generation data exchange schemes, such as international foundation class (IFC) and gbXML, possess the potential for wider data coverage throughout the building life cycle. BIM outlines a process to prepare, store, exchange, and share information about design, construction, and operation teams [10]. This collaborative philosophy of BIM is beneficial to all phases of the building lifecycle. For example, in the design and construction phases, BIM simplifies the management of the project schedule, optimization of material transportation and logistics, and minimization of storage requirements by knowing exactly when each building component or asset is constructed and installed.Currently, there is a lack of standardized information exchange, which hinders the integration of work processes into the current practices of individual AEC-FM firms. This paper first outlines the features of data exchange protocols aligned with relevant existing BIM standards. The research created a neutral-format data content as an end-user guide to support industry practitioners. BIM data exchange protocols allow individual AEC-FM industry stakeholders to share information with project teams.
2. Literature Survey
- Different BIM authoring tools, including IFC importing and exporting interfaces, interpret native models to IFC files. This is in contrast to the specifications stipulated by coordination view two and COBie.Many studies have described interoperability. According to Eastman et al. [11], interoperability is the ability to flawlessly exchange data between applications to achieve a smooth workflow in which the model's transaction is computerized. This combined data exchange should avoid any possible human error and data repetition and accelerate the reproduction of the model [11]. Others described interoperability as ensuring that the data generated by a BIM authoring tool can be appropriately interpreted by all other tools [12,13]. IEEE STD 610.12 described interoperability as the ability of two or more systems or components to exchange beneficial information [14]. Misconnections or misperceptions among the engaged tools can result in interoperability issues [15]. Interoperability issues between software results in inconsistent and fragmented data that prohibit the automatic flow of information from one tool to another.Moreover, interoperability should permit two-way improvements and data interchanges for building information. In other words, any modification in one of the tools involved in the interchanging process should stream between programs [16,17]. However, information can flow only in one direction irrespective of the exchange format used [11,16,17]. Considerable efforts have been made to demonstrate the automated checking of an IFC translation processes. One of the validation methods for confirming the IFC mapping processes of IFC interfaces is the global testing and documentation server (GTDS) provided by buildingSMART International (bSI) [18]. The web-based validation and certification program helps software developers evaluate an IFC instance file exported from their IFC interfaces according to CV V2.0 [19]. It also provides a buildingSMART certification to identify an approved and compliant IFC interface. BIM solutions for building infrastructure support various industrial standards and file formats. Examples include extensive markup language (XML), DXF, DWF, ODBC, CIS/2, DWG, LandXML, gbXML SAT, DGN, IFC, PDF, WFS, SHP, SDF, WMS, GML, and LAS, and imager formats, such as MrSID, ECW, TIF, DEM, DTED, PNG, and JPEG2K [20]. Additionally, Autodesk supports published application programming interfaces (APIs) for its software and data exchange mechanisms. Autodesk also support published APIs and data-exchange mechanisms through open software. DWF and DXF are Autodesk's published open-format files. These formats are supported by developer tools that provide straightforward and easy ways to interact with the design information created in Autodesk products and many other vendors [21]. Examples of standards that support Autodesk's delivery by open software include published APIs, namely CIS/2 and CIMSteel Integration Standards/Version 2 plug-ins. CIS/2 is an optimized open standard for structural exchange.
3. Methodology
- The research methods involved the development of a blend of various approaches in two main phases. The planned phases were obtained from a series of structured survey questionnaires aimed at a focused group in the industry and a case study. In the initial phase of the study, an extensive literature review was conducted to investigate web-based data exchange possibilities, challenges concerning data exchange formats in BIM software, and methods by which an automated exchange platform may transform information sharing among the project teams using various applications. The literature review phase identified several questions to support the survey. The online poll targeted 120 respondents representing different industry professionals and companies (45 US firms and 15 Canadian companies), 20 general contractors (GCs), 15 owners/owners’ reps, and 25 site supervisors. The other aspect of the survey was centered on direct (face-to-face, emails, phone calls) interviews with subject-matter experts (construction/project managers) in the United States. Forty experts responded to this survey. The objective of this phase was to identify the benefits and investigate the drawbacks of a BIM-based data exchange platform. The initial part of the questionnaire focused on information extracted from the primary survey and experts' opinions. This phase investigated how a standardized BIM-based data-exchange platform could be used by a project team. The case study involved a simulated project test and analyzed BIM-based XML using imported/exported and interoperability plug-ins, which exchanged data between different applications through a web-platform in real-time. By conducting this exercise, the author underscored the capabilities of BIM XML and identified how the process could be integrated with the concept of exchanging data concurrently between different applications using BIM-based web services.The goal of the final phase was to test the information-exchange capabilities of the automated BIM-based exchange platform prototype using the XML schema definition (XSD) features of BIM-based XML. The author tested the service from an end user's perspective to determine whether the research's key objective was realized: to develop a standardized data exchange platform framework that would promote an essential decision-making process for information sharing across project teams (throughout the project life cycle). Based on the survey response, Autodesk Revit 2022 was used to develop, demonstrate, and validate the case study.
3.1. BIM Data Sets Identification
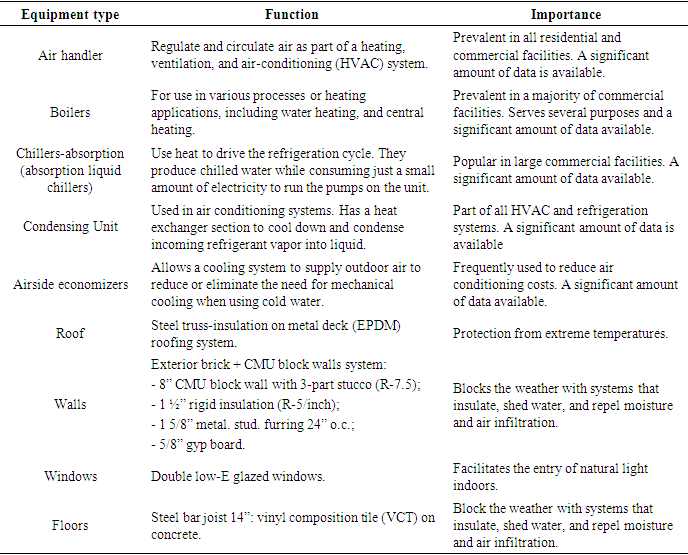
- Based on the survey on different data exchange standards and use case documentation, a set of equipment types and building envelopes were selected for this study, which are listed in Table 1.
|
3.2. Data Exchange Process
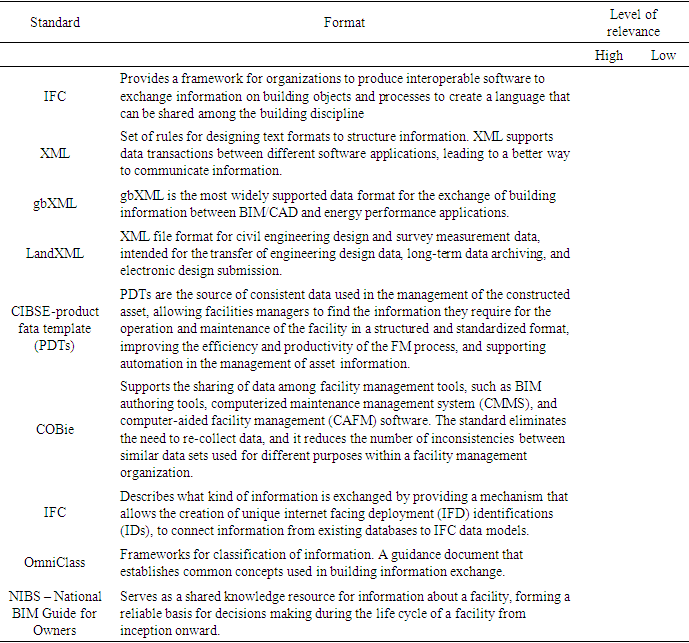
- Owing to the requirement of sharing and transferring BIM data/models between authoring software and performance evaluation tools, 3D models must be interpreted and used in various applications in a straightforward manner. The key challenge in data exchange is the data manipulation between various BIM-based software and the interoperability issues owing to data loss. The exchange protocols identified include gbXML, IFC, open database connectivity, and COBie [22–29]. In addition to completely customizable parameters and other limited computations, extensible parameters can be created and assigned to Revit elements using programming languages such as C# and the Revit API [30]. The extensible parameters can be used for automating the evaluation process. According to Wong et al. [31], building objects can be tagged with features such as “reusable” to automatically retrieve details to access the criteria within Revit. Table 2 lists a summary of different standard data exchange formats and the level of relevance for each type of format related to this research.
|
3.3. Spreadsheet Documentation Development
- The development of a spreadsheet template containing the fundamental properties and features identified in Table 1 was vital for this study. The materials constituted a significant part in the development of BIM toolkit data and exchange process for the end user. The purpose was to create a searchable “rational link” from the selected building component and an added field to develop an essential visual macro. This was to automate the searching and gathering of group objects (with their associated key properties) in an Excel spreadsheet and populate the data on specific equipment or building envelope types. This automated process expedites the retrieval of the current-work data for the asset management use case. Moreover, it also benefits other use cases such as those pertinent to future equipment design and selection activities. Figure 1 shows the process of creating the new building component templates, as described in the following steps: I. Add a column field in the data element worksheets that contains a list of relevant building components. II. Create a blank building component template spreadsheet (e.g., an Air Handling Unit template).III. Specify the equipment/envelope data type as the keyword and search the data element worksheet (in the newly created field) to find the data groups that apply to the building component type. This is achieved by executing the basic visual macro.IV. The component template created in Step 2 is populated with the data retrieved in Step 3. The procedure described above was applied to create the template and populate the template with the data on the selected building component types (Table 1).
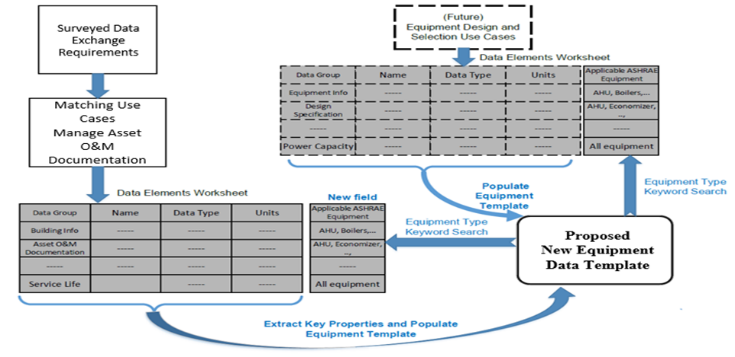 | Figure 1. Example process of automating the creation of new building /equipment templates |
3.4. Adding Classification Scheme to the Spreadsheet
- Table 2 lists the referenced BIM data exchange standards that were used to add a developed classification scheme to the new material data template to support the mapping of building components, such as the COBie template worksheets and CIBSE product data templates (PDTs); the focus of this section was to support this study. The objective was to review the standard properties as part of the data exchange references to harmonize the mapping between the identified building components and the BIM data exchange standards. For example, a specific equipment maintenance property was mapped to the generic properties of the COBie spreadsheet. Figure 2 shows the mapping of equipment properties from the identified data template to the COBie specification and CIBSE PDTs (based on the classification scheme).
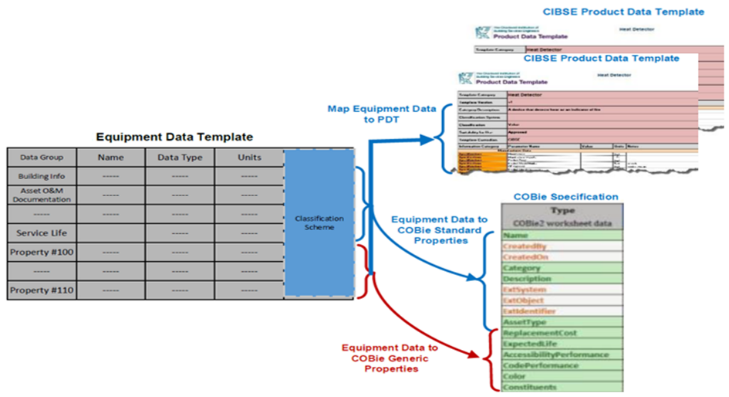 | Figure 2. Conceptual classification scheme for mapping equipment properties to COBie and CIBSE PDTs |
3.5. Neutral Format Schema and Content Document Creation
- XML and JavaScript object notation (JSON) are the two most common human-readable formats used for data exchange on the World Wide Web (W3) today. Neither is superior to the other because each is better suited for different use cases. However, the author chose the XML format to create the standard schema and content based on the spreadsheet template and data content worksheets for the following reasons:• XML can communicate mixed content, that is, its strings contain standard markups that provide flexibility in data mapping.• World-Wide Web consortium (W3C) recommends the XML standard because of its association with powerful capabilities, such as extensibility, flexibility, reusability, maintainability, and generic, robust syntax for developing specialized markup languages.• XML is a vendor-neutral platform and language; hence, it is well suited for satisfying multidisciplinary data content requirements.• The name, attributes, and content model of an XML element are closely related to the class name, properties, and composition association in many use-case documentation.
3.6. Revit Application Interface (APIs)
- The Autodesk Revit API allows developers and users to expand an application’s capacity by writing a program or script that adds new functionality to the software. The Revit API authorizes programmers to change BIM elements directly or access data indirectly to perform specialized tasks. The use of the Revit API improves the capacity of workflows and creates building designs through the process outlined as follows:• Creates add-ins to automate respective tasks in the Autodesk Revit user interface• Extracts project data for analysis reports• Enforces project design standards by checking for errors automatically• Imports external data to create new elements or parameter values• Integrates other applications, including analysis applications into Revit products • Enables Autodesk Revit project documentation automatically. The Web API provides an enabling environment for developing hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) services to access user entities such as browsers and tables [32]. The function of the Web API reduces the computational load for instantly updating the BIM model information for integrated platform users. Figure 3 shows the transmission process between the Revit model information and the unified integrated platform. The model data was uploaded to the cloud space in real-time, and the model information in the cloud was automatically captured during the programming integration phase.
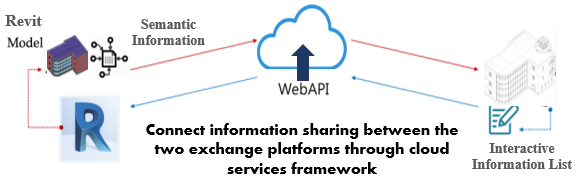 | Figure 3. Cloud service framework (WebAPI) of visual model views |
3.6.1. Programming and Development Options
- The Revit .NET API [33] allows users to program any. NET compliant languages, including VB.NET, C#, and managed C++. Software development toolkits (SDK) provide extensive. NET code samples and documentation to use the Revit API in Autodesk Revit Architecture / MEP / Structure. The Revit API supports in-process dynamic-link library (DLL) and Microsoft’s implementation of a shared library. The two types of DLLs, “External Commands and Applications,” support the creation of the Autodesk Revit API.
4. Discussion and Survey Results Analysis
- A collaborative BIM working environment (archetype) system for automatically creating the data (shared) model exchange framework was developed and implemented in Autodesk Revit. It utilized the Revit API in C# programming to demonstrate the proposed methodology. Figure 4 shows a collaborative data-sharing environment between the user and the archetype system. The collaborative approach defines a system’s ability to communicate, re-use, and share data efficiently without loss, errors, or misinterpretation. This method allows the sharing of information among all project team members. To facilitate a smooth collaboration, each team controls the release of information and data available for project-wide formal access through a shared exchange protocol. All these files are accessible from a central location (an exchange platform) in the project folder structure for each team member.
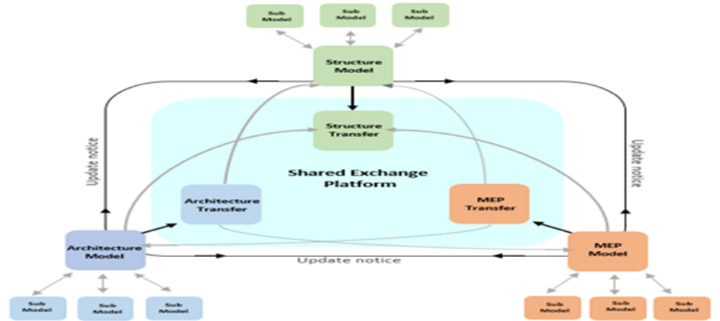 | Figure 4. A collaborative platform for a data sharing environment between the user and archetype system |
4.1. Validation
- To validate and verify the developed framework, a fully assembled collection of design views within the BIM domain was created. An automated BIM framework was developed to integrate practical material standardization and spreadsheet classification into a BIM platform for data-sharing planning. A novel information-based method, shown in Figure 5, was developed and incorporated with BIM, and the proposed seamless data exchange methodology was realized. The process was accelerated by exporting views in the form of output files for assembly and enhancing graphics using 2D detailing tools within the Autodesk Revit environment. Whenever BIM data were referenced in the project, the project teams ensured that the latest validated data information was accessed directly from the project’s shared platform. The input material, system types, and data exchange preference outcomes were inspected to confirm that the automated framework system was competent in supporting the seamless data exchange process.
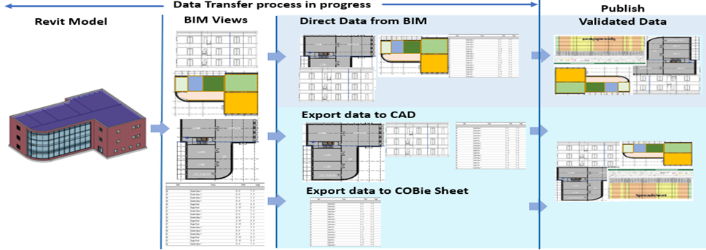 | Figure 5. Collection of views sheets within BIM domain for data sharing though standardized platform |
4.2. The Use Case
- An office building was selected as a case study to test the developed standard. The building shown in Figure 6 consisted of a three-story office, exterior CMU bricks, curtain wall, truss, insulated metal deck (EPDM) roof, single glazed low-E windows, steel bar joist 14”-VCT on concrete, and a precast concrete slab basement. The building model was initially developed using the Autodesk Revit 2022. Various Revit plugins were introduced, including BIM interoperability tools. COBie and the product data template (with an additional introduction of the XML/gbXML export function directly from Autodesk Revit) were enabled using an API and C#. The developed model (incorporated fully with the selected components from Table 1) was launched in Revit to produce the required data exchange protocol. The objective was to ensure that industry-wide practitioners and project teams accessed standardized error-free data that were shared seamlessly.
 | Figure 6. The linked model showing the components in Table 1 |
4.2.1. COBie/PDT Schema Development & Data Sharing Process
- To effectively implement COBie, the author set up a hypothetical project with contact information, configured project parameters, modified the objects associated with COBie elements to support the COBie requirements, and subsequently exported the data from the Web in COBie format. The author used a case study (Figure 7) to demonstrate the (1) setup, (2) modification, and (3) export processes. There were two approaches to generate COBie data automatically using Autodesk Revit, (1) export IFC or IFC XML from Revit, convert it to an XML file, and subsequently convert it back to an Excel file (Figure 7); (2) create a COBie file directly from Autodesk Revit through the BIM interoperability tool plugin.
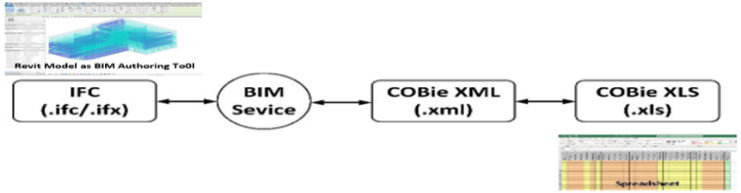 | Figure 7. IFC-COBie, data exchange process [33] |
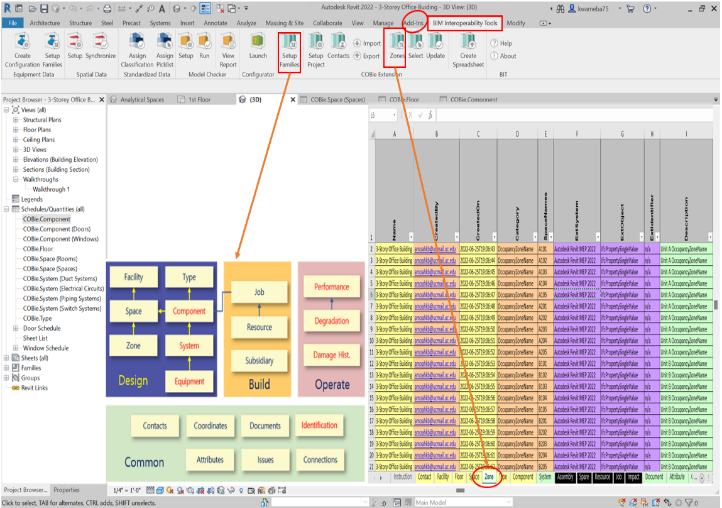 | Figure 8. Project setup and configuration of data exchange BIM-based COBie worksheet |
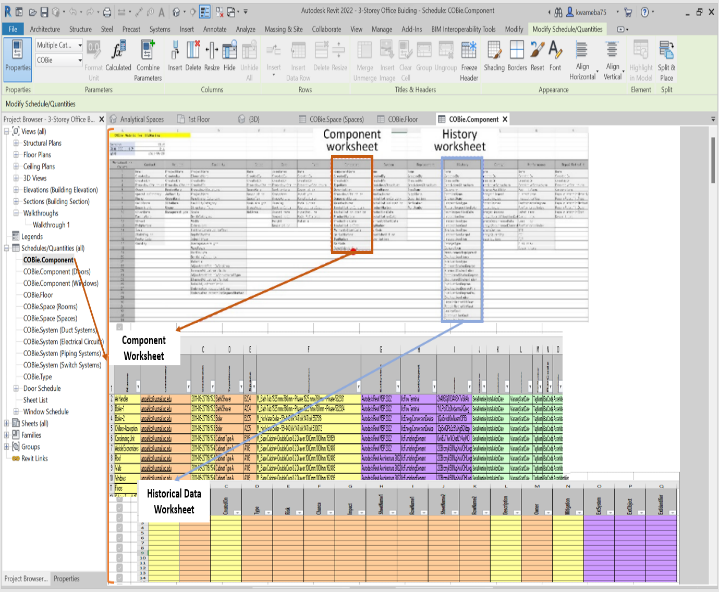 | Figure 9. Setup and configuration of data exchange BIM-based COBie schema |
4.2.2. The Green Building XML (gbXML) Data Sharing Process
- gbXML was developed to enable the transfer of information about a computer aided design (CAD) building [35], making interoperability between the design models and different varieties of engineering analysis tools possible. gbXML is a deterministic open-source language developed to facilitate information transfer between CAD-based building design files and building energy analysis software tools [36]. The use case (Figure 6) was created using Revit 2022 and the corresponding zones were assigned to the model with a defined core perimeter as a gbXML file. Subsequently, the data inputted in the model were manually added to the generated gbXML file by redefined data-mapping rules, following the contemporary gbXML schema. Although the author covered all the building components listed in Table 1, an essential HVAC (boiler) and a building envelope (exterior wall) system were sufficient to prove the effectiveness of the redefined rules. Figure 10 shows the boiler data and outer wall envelope data in the gbXML file.
 | Figure 10. Boiler data and the exterior walls envelop data in the gbXML file |
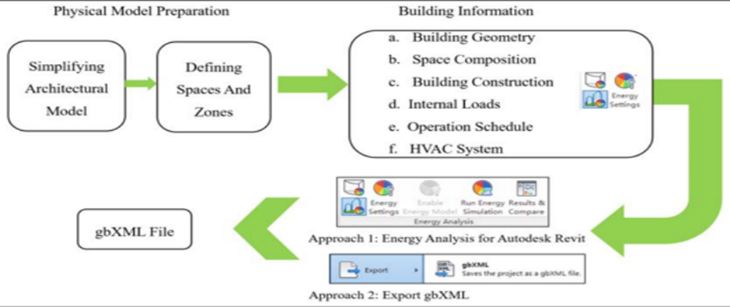 | Figure 11. Process of exporting BIM-based information [40] |
4.3. Investigating the Use of BIM Software and Standardized Data Exchange Framework
- At this stage, the author used an online survey to investigate whether a defined automated data exchange platform through the web supported and advanced a seamless, interoperable BIM-based software solution that could benefit AEC industry stakeholders. The online survey findings were collected from 120 respondents, who were mainly general contractors, owner representatives, site engineers, and superintendents. The objective of the survey was to unravel the benefits and drawbacks of a standardized data-exchange platform to provide easily accessible data sharing among project teams. The survey received feedback from 120 respondents from 205 mail lists. All respondents were well connected and parts of their respective companies' decision-making teams. An average of 75 United States construction companies and 25 Canadian firms, ranging from small, medium, and mega companies were covered. The respondents included general contractors (GCs), architects / designers, civil/structural engineers, construction-related vendor firms, and project managers. The majority of responses came from the GCs/owner's reps, who constituted 25% of the respondents. The architectures / designers constituted 21% of the respondents, civil/structural engineers; 16%, project managers; 19%, construction related vendor firms; 12%, and site superintendents; 7%. The survey mainly focused on establishing the proportions of structured data exchange platforms used by stakeholders, the benefits and challenges, support from software vendor firms, and the business case for seamless interoperability.
4.3.1. The Survey Results Summary
- Concerning the level of BIM usage and its future forecast of growth to develop automated web-based data exchange standards, information management, and applications, the respondents used their respective companies' backgrounds to provide survey feedback. Most respondents thought about the initial cost of purchasing the software instead of life-cycle cost or return on investment (ROI), with a significant focus on the needs and benefits of the software in their firms. The main question in this section was Question 1. “What category of software application is used by your company? If other kindly indicate.” This determinant question provided the respondents with a list of 15 software applications and asked them to choose the application their companies used, from the perspectives of GCs and software vendors. The respondents were also given the option of selecting an alternative software application. Figure 12a shows the combined response for the software primarily used. The main applications identified were Autodesk Revit for design and collaboration. Some GCs used other BIM-based software programmes.
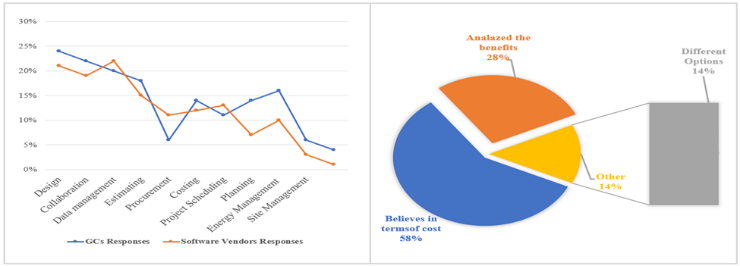 | Figure 12. a. Categories of software mostly used in response to the question; b. Management’s attitude on new products and products currently available |
|
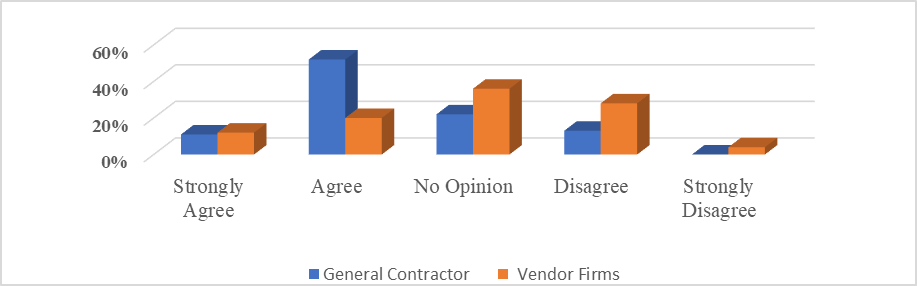 | Figure 13. Opinion and response of the GCs and software vendors |
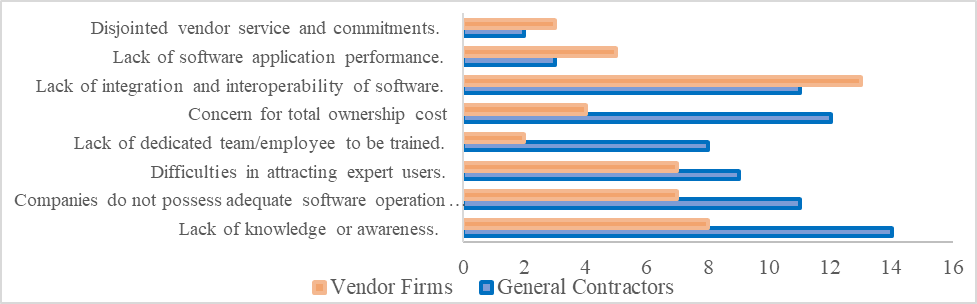
 | Figure 14. Quantitative analysis of the company’s sizes as a reason for low patronage of systemized data exchange protocol |
|
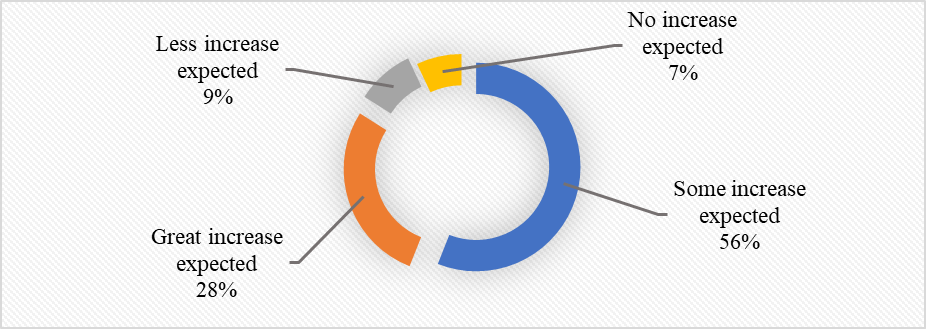
 | Figure 15. Companies’ involvement in developing the use of data exchange for all-inclusive application in the next five years |
4.3.2. Expects Opinion on Advocating for Integrated BIM-Based Data Exchange via Web
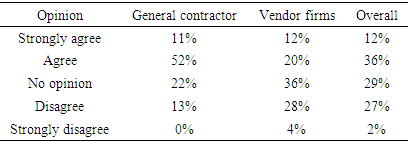
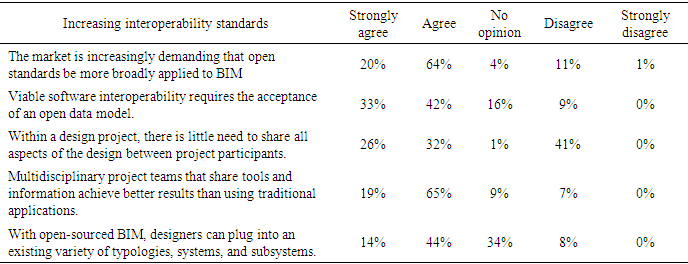
- This section presents the interviews with 25 subject-matter experts on how to significantly improve value, schedule, cost, and carbon reduction by applying an integrated data exchange process that can be rapidly shared among project teams through web-based BIM software. Most experts suggested the modification or elimination of the old methods of importing all data into one drive/drop box/desktop system. They supported the idea of a new system based on CAD-BIM integration (with an extended connection through an automated platform) to facilitate automatic linking with other applications. The interview questions centered on the topics such as standard business practice for data exchange, mode of integrated agreement, new technology adoption, the relevance of web-based data exchange, and the value of using an Internet platform for estimating (4D) and scheduling (5D) and building energy performance simulation software. With end-users in mind, the author addressed the critical issue of developing a standardized information exchange format (for systemized building data) that could contribute to information exchange more efficiently throughout the building lifecycle. An ideal solution includes interconnecting diverse applications using an intermediate repository platform that permitted different applications to interoperate and exchange information openly. Figure 16 and Table 5 show the results and interview questions that investigated experts' preferences for advancing and promoting a standardized BIM-based data exchange protocol. Figure 17 shows the distribution of expert opinions on whether open standard exchange processes (IFC or XML) were more transferable.
|
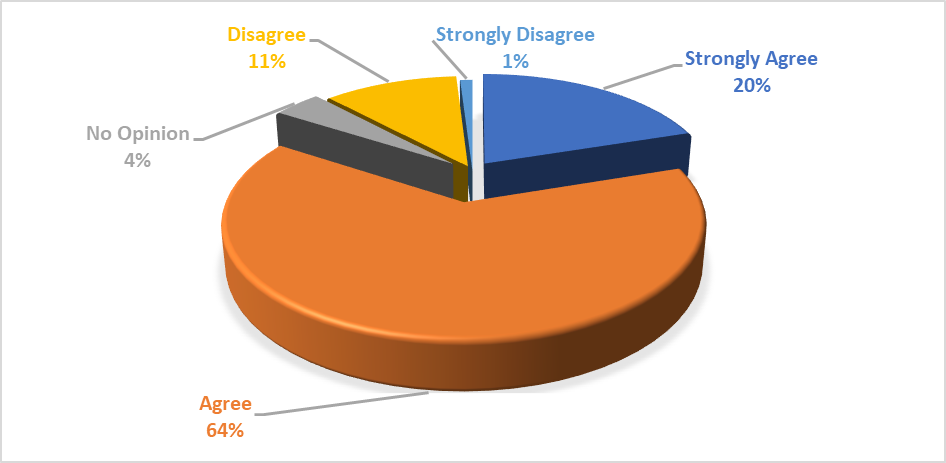 | Figure 16. Subject-matter experts’ preferences towards open standard data exchange protocols |
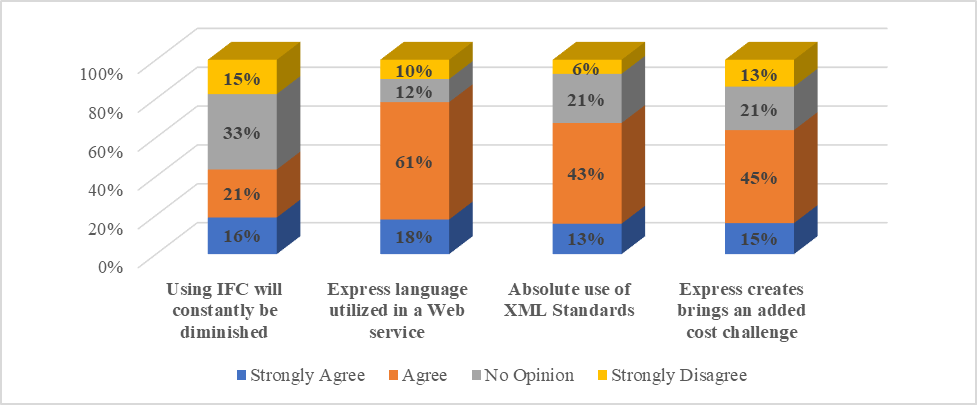 | Figure 17. Subject Matter experts’ preferences of exchanging open standards (IFC-ifc XML) |
4.3.3. Limitations of the Case Study
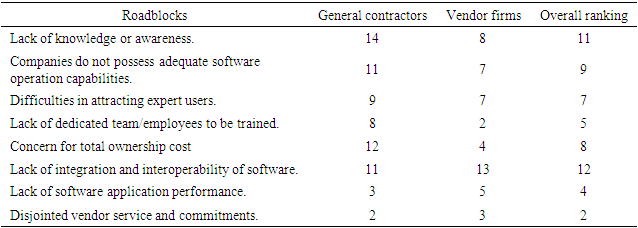
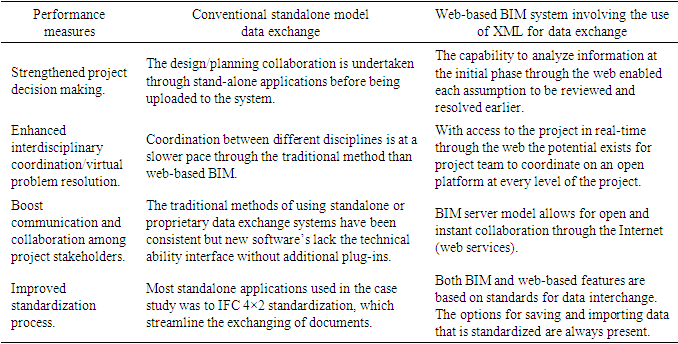
- Autodesk Revit is not equipped with a developed individual XML document web service connection; hence, significant amount of data was lost through the web, such as the data on designing and analyzing the energy efficiency requirement for the building. This exercise had to be conducted separately in the cloud through green building studio (GBS). The 4D and 5D features also required additional plug-ins and IFC to exchange data. A great possibility existed for using web-based services to seamlessly exchange data and presenting the end-user with the ability to activate the information sharing through a defined web application platform. This system permitted the project team to access all the necessary tasks traced to a single interface and exchange the rate of exchanging data between BIM applications. Table 6 lists the advantages and performance standards between the known traditional project stakeholders' collaboration and the novel BIM-based web data exchange process.
|
5. Conclusions
- To embrace interoperability, The AEC industry requires a standardized data exchange structure that is accessible to all disciplines. The importance of a standardized exchange system to advance interoperability was highlighted throughout the survey and discussions were conducted with subject matter experts on the major challenges faced by the industry. The questionnaire and case study analysis identified a standardized information exchange framework as a mechanism to enable collaboration through W3 technologies. Web-based services supported the service-oriented architecture and geographic information technologies using web feature services and have successfully integrated BIM data. Using BIM and web-based services to support the early design, planning, and execution of tasks provided a structure for allowing multiple project teams and experts to seamlessly and simultaneously access different applications. The shared exchange platform demonstrated in the case study underscored the real-time collaboration and economic benefits of using BIM-based web services. From the literature, the author selected XML as a markup language designed for learning, writing, and interpreting data efficiently. The web (Internet) method to access relevant BIM data and validate model views was exchanged in separate batches and provided a process for sharing data. Similarly, the IFC-XML and automated equipment information exchange (AEIx) experiments exhibited differences between the schemas and the structures. The AEIx schema contained more details than that of IFC-related XML; however, the AEIx schema focused only on technical information as compared to that of IFC-XML, which provided information on the entire building. The experts’ opinions from the survey favored using XML data schema. This was because it provided adequate integration of web services with BIM. Moreover, the experts agreed on a centralized web-based database as the leading platform for developing standardized exchanging data between systems. The case study identified three main exchange formats: direct links incorporating APIs to extract data, proprietary exchange formats for interfaces purposely developed for a company’s applications, and public product versions (IFC, text file, and XML). This advantage allowed the initiation of exchange processes without manually manipulating the source code.This study used an experimental case study project to test the interdependence of the data exchange processes. The interoperability experiments were conducted by developing and extracting the COBie via IFC through the Autodesk Revit domain and generating a gbXML file (by redefining the data mapping rules and observing the contemporary gbXML schema procedure). The key contribution of the case study was underlining the ability of the BIM-based standardized data exchange platform to define data in the early stage of a project. However, the results demonstrated typical data exchange challenges, such as varying component types, increasing fill size, model misrepresentation, and property loss. Throughout the survey and case study analysis, it was found that an undefined model presented more interoperability issues. The biggest problem lied in the relationship between the components from the viewpoint of the test indicator. For such data exchange integration challenges, the causes were summarized as follows: (1) data exchange issues such as data loss and misrepresentation existed when software tools imported IFC models created by other software tools. This was a result of semantic differences; (2) the domain-specific software tool correctly demonstrated information from its own domain while information from other disciplines could be lost or misrepresented by software. This was owing to the lack of related knowledge in the internal data schema such as object type and geometric representation.
DISCLOSURE
- All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article. The author had no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML