Brijesh Patel1, VPS Nihar Nanyam2
1Student, RICS School of Built Environment, Noida, India
2Asst. Professor, RICS School of Built Environment, Noida, India
Correspondence to: VPS Nihar Nanyam, Asst. Professor, RICS School of Built Environment, Noida, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Most of the construction activities in Indian construction projects use concrete which requires huge amount of water for curing. Scarcity of attribute based analysis impede us from adoption of innovative curing methodologies. This paper highlights study of innovative curing methodologies which are not only easy to adopt but also more cost efficient than conventional curing methods. The paper identifies different attributes for evaluation and provides comparative framework of all emerging curing methods. This paper will highlight attributes such as overall curing cost, water requirement, and water wastage, evaporation of water from concrete, electricity consumption, sustainability factor (Green Building material), supervision required, and number of workers required for evaluating emerging curing methods. The paper will provide a comparative framework based on the above mentioned attributes for methods such as: Drip curing technology, conventional curing methods (spraying or fogging and ponding), curing using chemical compounds, curing using waterproof papers, carbon-dioxide (CO2) curing technology (Precast concrete) and curing using plastic sheets and burlap. The comparative framework is tested on the construction projects wherein these methods are adopted. Results obtained from analysis of comparative framework are expected to help the construction professionals in value engineering by providing the cost effective solutions for curing and contributing towards sustainable development.
Keywords:
Curing, Attribute, Framework, Concrete, Construction, Fuzzy Dematel, AHP
Cite this paper: Brijesh Patel, VPS Nihar Nanyam, Multi-Dimensional Analysis of Curing Techniques in Indian Construction Projects, International Journal of Construction Engineering and Management , Vol. 7 No. 5, 2018, pp. 169-177. doi: 10.5923/j.ijcem.20180705.01.
1. Introduction
Concrete is the most important material used in the Indian construction industry. Curing process for concrete requires significantly huge quantities of water. Today, world is trying to contribute towards sustainable development by efficiently using natural resources in every industry. We can contribute significantly towards sustainable development of India by using water efficiently in construction industry as this industry amounts to the second largest contributor to Gross Domestic Product“Curing of concrete is defined as providing adequate moisture, temperature and time to allow the concrete to achieve desired properties for intended use” [13].Well cured concrete helps in achieving good compressive strength and durability of concrete [4]. Curing with adequate amount of water is required to achieve hydration of cement which ultimately contributes towards strength development of concrete [4]. It also helps concrete to increase volume stability, water tightness, abrasion resistance and resistance to freezing and thawing [4]. Effective curing can also help in reducing shrinkage and cracks caused due to shrinkage [13]. Although curing is the most important aspect for concrete, it is one of the most neglected one in Indian construction industry. This paper highlights different methods of curing used in Indian construction projects with an aim of providing comparison based on certain attributes for finding out the use of most effective methods with minimum water wastage. The different methods used for curing in India are (1) Immersion method (2) Spraying method (3) Drip curing method (4) Curing using Hessian cloth/ Burlap (5) Curing compounds (6) Plastic sheets (7) Air drying curing.Immersion method involves submersion of concrete element in water. Spraying method involves spraying of water on concrete element. Drip curing method is inspired by drip irrigation method used in agriculture works. It involves continuously dripping water on the concrete element to keep the surface of concrete moist throughout the hydration of cement process. Curing using Hessian cloth/ Burlap involves covering concrete element moist throughout the concrete duration by periodically spraying water on it. Curing using chemical compounds involves spraying of liquid thin membrane like layer forming compounds like waxes, resins, chlorinated rubber and other materials so as to reduce the rate of evaporation of water from the concrete surface [16]. Curing using Plastic sheets involves wetting of plastic sheets with water and once the concrete gets little hardened it is spread over concrete element so as to prevent evaporation of water from the surface of concrete. Air drying curing involves drying of concrete element under air when atmospheric air contains 90% of moisture [4]. As there are numerous emerging techniques and methods available in the market for curing, there is lack of awareness of those methods which motivated author for this research. The passion to make a change that benefits this construction industry was also one of the reasons that motivated the author for this research.Aim and ObjectivesThe Overarching goal of research work being conducted is to develop a multi-dimensional framework for different curing methods used in Indian Construction Projects. Objectives are:1. To identify emerging curing methods.2. To identify attributes for evaluation.3. To identify suitability of curing methods in different weather conditions.4. To present comparative framework for all the curing methods used in Indian Construction Projects.
2. Literature Review
Most researchers have done various research on different methods of curing and have arrived with various conclusions based on different attributes. This paper uses their significant contribution such results, methodologies and scope of work to finalize the objectives of present work. Various case studies and reports were analysed and studied in detail to finalize the present work.Gowsika et.al. (2017) carried out a research on Experimental Study on Curing Methods of Concrete indicated through their experiments and testing that immersion curing satisfies all the requirements of curing like promotion of hydration for achieving highest compressive strength among all other compared curing methods (when the test specimens were tested on 7th, 14th and 28th day), elimination of shrinkage and absorption of heat of hydration [4]. They also arrived at the conclusion that this method of curing can be used for laboratory and precast works were we can submerge the concrete components in water [4]. Er. Rajesh Sharma and Dr. Hemant Sood carried out a research on Effect of Curing Methods on Various Concrete Grades indicated through their experiments and testing that immersion curing is best method of curing as curing of concrete elements is possible on all the surfaces, but this method of curing can only be used to test laboratory specimens and it cannot be practically used on site [16]. Rohit et al. has carried out the research on The Effect of Curing Methods on Compressive Strength and Durability of Concrete based on methodology of experiment and testing at commercial cum residential building site at vishrambagh, sangli conducted a test on column of size 230*500*3200 mm3 in summer season arrived at the cost per m2 for immersion curing which came out to be Rs. 171.25/m2 [13]. Obam, Ogah carried out a research on Effect of Curing Methods on the Compressive Strength of Concrete in Nigeria through experiment and testing (28 days compressive strength) on M15 grade of concrete an arrived at conclusion that compressive strength obtained from immersion curing is 9.8% and 16.8% higher than the strength achieved compared to Hessian cloth method/ Burlap and polythene sheet methods [12]. Obam et al. also concluded that immersion curing is best method to achieve desired concrete strength, but the other two methods have advantage of achieving large size concrete elements [12].Authors Steven H. Kosmatka, Beatrix Kerkhoff, and William C. Panarese of the book Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures have written that sprinkling method consumes ample amount of water and requires careful supervision contributing towards higher cost by implementing this method [16]. Kanchan et al. carried on research on Developing a New Curing Technique-‘Drip Curing’ stated that spraying method of curing requires higher amount of water and produces maximum wastage of water compared to drip curing and immersion curing methods [9]. Ankita et al. has carried out the research on Membrane Curing of Concrete indicated that spraying method can be used for any types of surfaces like horizontal and vertical [3]. Er. Rajesh Sharma and Dr. Hemant Sood carried out a research on Effect of Curing Methods on Various Concrete Grades indicated through their experiments and testing that strength of concrete is greatly affected by strength of concrete and age of the concrete for a particular grade of the concrete [6]. They also arrived at the conclusion that by sprinkling method used two times in a day does not give desired strength of concrete and it must be improved by increasing the number of sprinkling [6]. Rohit et al. carried out the research on The Effect of Curing Methods on Compressive Strength and Durability of Concrete based on methodology of experiment and testing at commercial cum residential building site at vishrambagh, sangli conducted a test on column of size 230*500*3200 mm3 in summer season arrived at the cost per m2 for sprinkling method which came out to be Rs. 216.61/m2 [13]. They also identified factors on which spraying method is largely dependent like availability of water, availability of manpower and availability of electricity required to operate pumps [9]. Kanchan Ambekar and K.U. Gandhare carried on research on Developing a New Curing Technique-‘Drip Curing’ with the aim of developing new technique of concrete curing which can help in achieving desired strength by minimising wastage of water [9]. They also suggested that Drip curing method can be used in water scarce areas as it consumes very less amount of water compared to spraying method [9]. Through their experiment and testing methodologies they arrived at conclusion that practically drip curing is most effective method of curing [9]. This method allows water ton spread over the concrete surface so as to keep the surface moist throughout the hydration process [9]. A report was prepared showing comparison between Hessian cloth method/ Burlap and drip curing method by conducting an experiment for seven days at Tata Projects Limited on Complete Switchover Project, ICF, LHB Unit, New Avadi Road, Chennai site on a column size of 400*400*2440 mm3. Following were the conclusions drawn after conducting the experiment: Cost of curing by using drip curing was Rs. 600 and cost of curing using hessian cloth method/burlap came out to be Rs. 2196 for seven days, eight hours a day including the cost of material, cost of water required and cost of manpower. It was also found that drip curing method is best suited for vertical concrete elements. It was also concluded that is the best sustainability initiative for green environment.Kamble et al. carried out the research on The Effect of Curing Methods on Compressive Strength and Durability of Concrete based on methodology of experiment and testing at commercial cum residential building site at vishrambagh, sangli conducted a test on column of size 230*500*3200 mm3 in summer season arrived at the cost per m2 for curing using hessian cloth/ burlap came out to be Rs. 221.42/m2 [16]. The requirements for treated burlap those which resist fire and rot is stated in specification for Burlap cloth made from jute or Kenaf (AASHTO M 182) [16]. A report was prepared showing comparison between Hessian cloth method/ Burlap and drip curing method by conducting an experiment for seven days at Tata Projects Limited on Complete Switchover Project, ICF, LHB Unit, New Avadi Road, Chennai site on a column size of 400*400*2440 mm3. Following were conclusions drawn for curing using hessian cloth/ burlap: (1) Initial cost is very less using this method (2) Water loses are more and it requires continuous curing (8 times in a day) (3) Number of repetitions are less, it gives around 3-4 times reuses (4) Dampness duration is very less (5) More manpower is required (6) Easy to damage as it is directly exposed to atmosphere. Er. Rajesh Sharma and Dr. Hemant Sood carried out a research on Effect of Curing Methods on Various Concrete Grades indicated through their experiments and testing that curing using hessian cloth/ burlap gives desired design strength but the condition is that the covering should be kept wet throughout the curing period. They also stated that it the best suited method for vertical and sloped concrete elements [6].Ankita et al. carried out the research on Membrane Curing of Concrete indicated that curing using curing compounds is most suitable for water scarce areas and were economical method of curing is needed (Ankita V.Kalbande, 2017). They concluded that this method can be adopted during summer seasons in order to conserve water. By using this method 90% productivity can be achieved as copared to conventional curing method (Ankita V.Kalbande, 2017). Er. Rajesh Sharma and Dr. Hemant Sood carried out a research on Effect of Curing Methods on Various Concrete Grades indicated through their experiments and testing that curing using curing compounds resulted in achieving 80 to 90% of curing using immersion method (Er. Rajesh Sharma, 2017). They also concluded that this method proved to be cost effective as compared to curing usin hessian cloth/ burlap (Er. Rajesh Sharma, 2017). It was also found that the efficiency can be improved by applying two layers of curing compounds (Er. Rajesh Sharma, 2017). Rohit P. Kamble, Sitaram G. Suryawanshi and Satalingappa P. Deshamukh carried out the research on The Effect of Curing Methods on Compressive Strength and Durability of Concrete based on methodology of experiment and testing at commercial cum residential building site at vishrambagh, sangli conducted a test on column of size 230*500*3200 mm3 in summer season arrived at the cost per m2 for curing using external curing compounds came out to be range of Rs. 21.71/m2 to Rs. 34.52/m2 and curing using internal curing compounds came out to be 280.10/m2 (Rohit P. Kamble, 2016). They also concluded that external curing compounds gives 80% strength of finally set (hardened) concrete than using conventional curing method (Rohit P. Kamble, 2016). They also arrived at conclusion that initial strength is more in case of internal curing compounds than compared to other curing methods like ponding, immersion curing, sprinkling with hessian cloth and without hessian cloth [13]. Authors Steven H. Kosmatka, Beatrix Kerkhoff, and William C. Panarese of the book Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures have recommended that the application of one coat should be at a typical rate of 3 to 4 m2 per liter (150 to 200 Sqft per gallon); but the products may vary, so it was advised to follow manufactures recommended rate [16]. In case were two coats are necessary to apply it was suggested to apply second coat at right angles to the first. It was also stated that complete coverage of the surface is necessary because even small pinholes may increase the rate of evaporation of moisture from the concrete [16]. Curing compounds should conform to ASTM C 309 (AASHTO M 148) [16].Gowsika et al. carried out a research on Experimental Study on Curing Methods of Concrete indicated through their experiments and testing that plastic curing has greater compressive strength by 16% as compared to air drying and 22% greater strength compared to curing compounds [4]. Er. Rajesh Sharma and Dr. Hemant Sood carried out a research on Effect of Curing Methods on Various Concrete Grades indicated through their research that curing using plastic sheets is less effective as there are chances of moisture loss due to damage, theft and it is also compared less effective as compared wet curing and curing compounds [6]. Authors Steven H. Kosmatka, Beatrix Kerkhoff, and William C. Panarese of the book Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures stated that plastic sheets are effective moisture retarder, lightweight and can be applied to complex as well as simple shapes. Polythene sheets can also be placed over wet burlaps which helps in evaporation of moisture from the surface of burlap and prevents labour – intensive need of continuous watering [16]. Plastic sheet should conform to ASTM C 171 (AASHTO M 171). White colour sheets should be used in hot weather conditions to reflect sunlight, whereas black sheets should be used in cold weather conditions [16]. Er. Rajesh Sharma and Dr. Hemant Sood carried out a research on Effect of Curing Methods on Various Concrete Grades concluded through their research that air curing should be avoided because it gives 50% of desired compressive strength [6]. D.Gowsika, P.Balamurugan and R.Kamalambigai carried out a research on Experimental Study on Curing Methods of Concrete concluded through their experiments and testing that air drying curing gives least compressive strength as compared to other methods of curing like immersion curing, pond curing, oven curing, curing compounds and CaCl2 curing [4]. A number of researchers have conducted research on different curing methods and have arrived to certain conclusions based on different attributes. This paper fulfils the research gap on lack of comparative analysis and a framework between different curing methods used in Indian Construction Projects based on required attributes.
3. Methodology
This section discusses the methodology to achieve the objectives set. Steps are highlighted thereafter.Identifying different methods of curing used in Indian Construction Projects: Various curing methods used in Indian construction projects were identified and studied in detail.Literature Review\ on different curing methods and identification of various attributes for comparative analysis: Around twenty to twenty five research papers from different journals were studied and the research gap was highlighted. Most researchers compared various traditional methods of curing with emerging methods. Some did research based on certain attributes like compressive strength, cost of curing using a particular method. Various attributes after going through these research papers were identified. Identify the most important attributes using FUZZY DEMATEL: After finalisation of attributes for the research work, a questionnaire was prepared and floated to 11 experts from various fields having professions like Researcher, Academia, Architect, Project Manager, Construction Manager, Engineer, Consultant and Government Employees in order to know their opinions on the most influencing attribute compared to other attributes. The questionnaire was floated by using Google forms and the responses were collected within a week time. The ratings used in the questionnaire was of the form [7]:0 – No Influence 1 – Low Influence 2 – Medium Influence 3 – High Influence 4 – Very high Influence This scale was used for getting experts opinion in questionnaire for arriving at results using Fuzzy – DEMATEL tool. Using Multiple Criteria Decision Making Tools (MCDM) such as Analytical Hierarchy Process to determine the weightages: After getting responses from respondents Multi Criteria Decision Making Tools such as Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) to arrive at the final result of determining the most important attributes and its weightage as compared to other attributes. This is projected in Figure 1.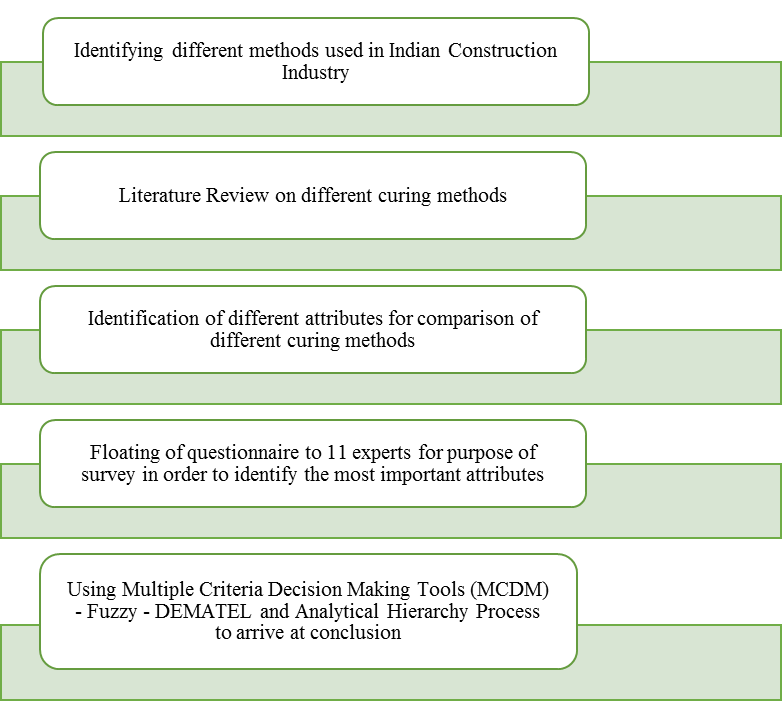 | Figure 1. Research Methodology |
4. Data Analysis
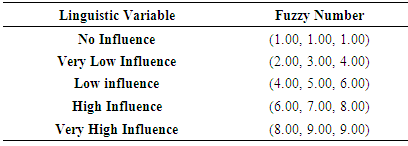
Fuzzy – Decision Software was used in order to determine the most important criteria amongst the six selected criteria’s based on the expert’s opinion [17]. DEMATEL is a tool which is used for pairwise comparison of data obtained by expert’s judgement [17]. This is also used as a decision – making tool during analysis of pairwise criteria [17]. Decision Making Trial and Evaluation Method Laboratory (DEMATEL) method was used to analyse the most important attribute and cause and effect diagram was developed using based on their importance and effect [5]. Fuzzy is introduced to take care of the uncertainty in the expert opinions. DEMATEL method was given by Battelle Memorial. Institute through its Geneva Research Centre [11]. This method.is based on.digraphs which can be used to separate attributes with regards to its cause and effect [11]. DEMATEL tool is used to disclose the relationship in between different factors based on influence of one factor compared to the other factors [11]. As the linguistic judgements can be fraught due to various uncertainties in opinions of experts and vagueness, there is always need to consider ambiguities and hence to obtain efficient results there is a need to integrate them with the fuzzy logic [11].As there are complexities in human judgements, Fuzzy – DEMATEL is used which evaluates the final result using fuzzy logic [17]. The following are the three steps to be followed in order to arrive at required results using Fuzzy Decision software: Insertion of expert data: The data obtained from the expert’s are inserted in two ways: In the form of fuzzy numbers (without scale) [17]Based on the fuzzy scale [17]Define the evaluation spectrum of pairwise comparisons:This step can be further divided into two steps • Evaluation based on default scales [17]• Evaluation by creating new scale [17]The scale that was used in the research is shown in Figure 2:Table 1. Linguistic Variables with Fuzzy Number
 |
| |
|
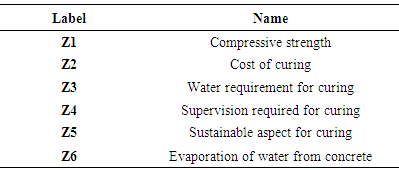
Defining the attributes as listed in Table 2.Table 2. Attributes for Curing
 |
| |
|
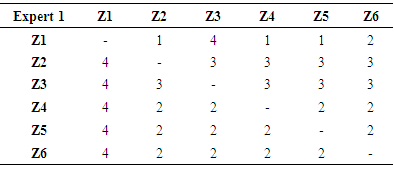
Design the network modelIn this step one of the expert’s sheet is shown in the following table 3 and opinions from other experts are captured. Table 3. Expert Response
 |
| |
|
Pairwise comparison for one of the experts is shown in table 4.Table 4. Pairwise Comparisons - Expert 1
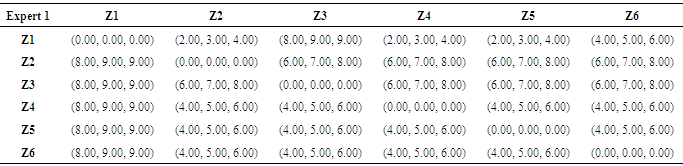 |
| |
|
Mean of pairwise comparison is calculated for all the 11 experts using the below formula and projected in Table 5 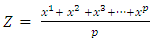 [8]p = Number of expertsZ = Mean of pairwise comparisonx = Individual attribute opinions by ‘p’ number of experts
[8]p = Number of expertsZ = Mean of pairwise comparisonx = Individual attribute opinions by ‘p’ number of expertsTable 5. Mean of Pairwise Comparisons
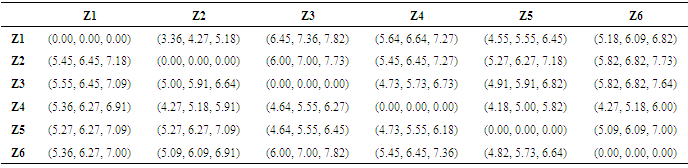 |
| |
|
Matrix as formed earlier is normalized as shown in Table 6.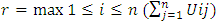 [8]r = normalized matrix
[8]r = normalized matrixTable 6. Normalized Matrix
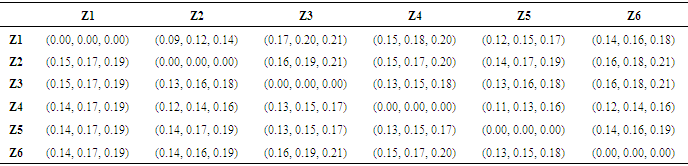 |
| |
|
Total – Relation Fuzzy Matrix: Fuzzy matrix is computed using the following equations and shown in table 7
Table 7. Total - Relation Fuzzy Matrix
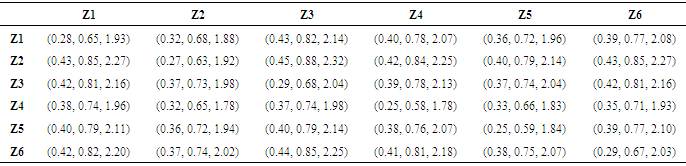 |
| |
|
Importance and cause – effect table: Cause and effect is established using the following equations and shown in table 8 & 9 and figure 2
Table 8. Importance and Cause - Effect Table
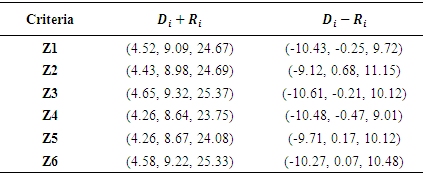 |
| |
|
Table 9. Importance and Cause-Effect Table (CRISP)
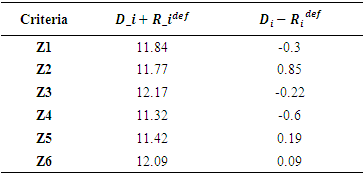 |
| |
|
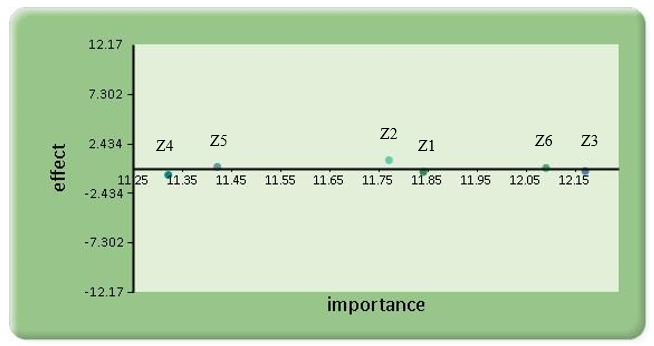 | Figure 2. Importance and Cause - Effect Diagram (CRISP) |
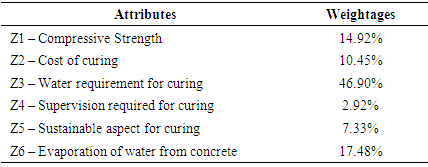
As per the analysis conducted using Fuzzy – DEMATEL tool, almost all the criteria’s equally effect one another. But, the most important criteria identified by using this tool are as follows:Z3 – Water Requirement for curingZ6 – Evaporation of water from concreteZ1 – Compressive strengthZ2 – Cost of curingZ5 – Sustainable aspect for curingZ4 – Supervision required for curingIn order to determine the weightages of the individual attributes, Analytical Hierarchy Process is used.Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a multi-criteria decision making tool proposed by Thomas L. Saaty [2]. This method helps in evaluation of different individual alternatives/parameters identified on the basis of pairwise comparison through expert’s opinion by helping us to calculate the weights of individual criteria’s thereby selecting the best alternative [2]. Process is highlighted in Figure 3.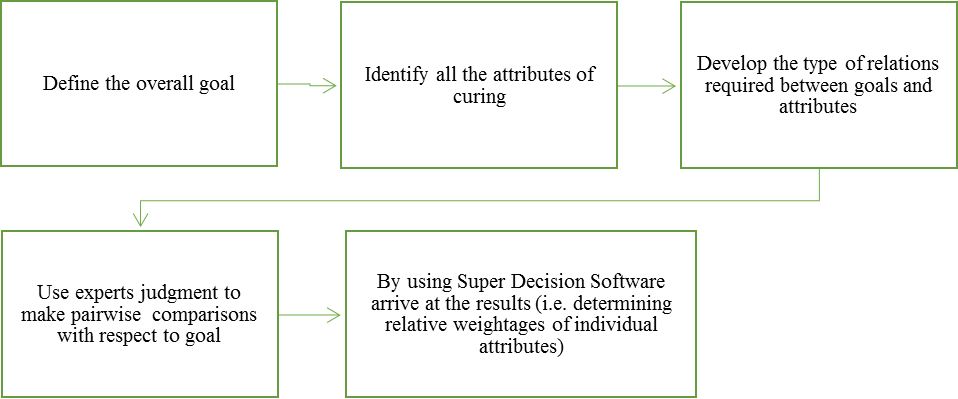 | Figure 3. Analytical Hierarchy Process Roadmap |
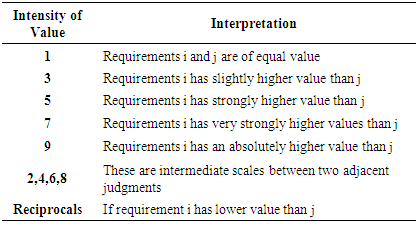
AHP Questionnaire: A questionnaire was prepared on the basis of pairwise comparison between different identified attributes and the scale ranging between 1 to 9 was used to identify responses of the respondents to arrive at results as highlighted in Table 10. The questionnaire was floated among 14 experts. Following represents the scaling approach of AHP:Table 10. Scoring Scale Used for AHP Questionnaire [14]
 |
| |
|
Super Decisions software is a software that helps the researchers to implement AHP and ANP [14]. The maintenance and development is sponsored by Creative Decisions Foundation established by Thomas L. Saaty and his wife Rozann Whitaker Saaty [14]. The following shown in the below figure were analyzed using Super Decisions Software (AHP) and its weightages were calculated.By using this software first the clusters are created and then the nodes lying in the clusters are created. The nodes and the clusters are interconnected and then the software is ready for the pairwise comparison. The geometric mean of all the responses obtained from the experts is calculated and the values are filled in the comparison matrix. This in return generates results based on the relative weightages of the compared attributes.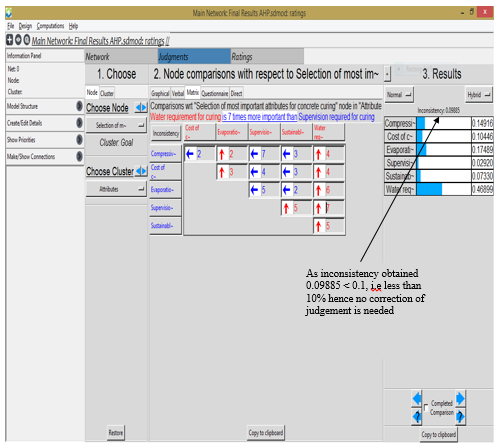 | Figure 4. Relative Weightages of Individual Attributes by using Super Decision Software (AHP) |
Individual weightages of different attributes calculated using Super Decisions Software (AHP) are as shown in the following table 11.Table 11. Relative Weightages of Attributes
 |
| |
|
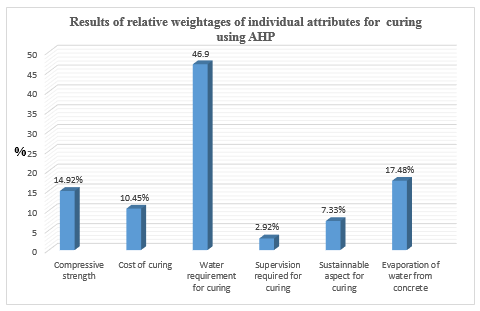 | Figure 5. Graph representing Relative Individual Attributes for Curing |
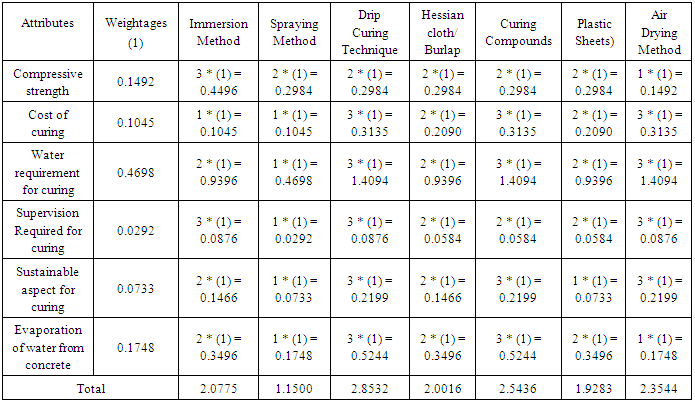
Literature review was taken to finalize the scale and provide relative scoring to different methods of curing. Here, for determining scores of different attributes using this method expert S.V. Ambekar was interviewed who is an Academia with thirty two years of experience.Comparative framework is presented by multiplying the scores assigned to the methods and the weightages obtained and is presented in Table 12.Table 12. Comparative Framework Analysis Table for Curing Methods
 |
| |
|
Following is the order of best curing methods and techniques used in the Indian Construction Industry on the basis of its ranks (top to bottom) derived from above analysis:• Drip curing technique• Curing using Chemical curing compounds• Air drying method• Immersion method• Curing using Hessian cloth / Burlap• Curing using Plastic sheet• Spraying methodDrip curing technique must be widely adopted in Indian Construction Industry as it helps to save significantly huge quantities of water which is a scarce resource [9]. This method is also cost effective and contributes towards sustainable development [9]. It is best suited for horizontal and vertical members on site [9].Curing using Chemical curing compounds cam also be adopted in water scarce area. It is best suited for horizontal, vertical and inclined members on site [16].Although, Air drying method has been ranked at number three position after performing comparative analysis, this method should not be used on site as it provides very less compressive strength which can result into failure of structures. It is many used for laboratory experiments [4].Immersion method is mostly used for laboratory experiments and for small precast members [4]. It also has fast rate of evaporation of water from concrete due to which this method is not used much on construction site and also due to huge size of horizontal and vertical members this method pose problems for its effective usage on construction site [16].Curing using Hessian cloth / Burlap is one of the most used traditional method of curing on construction site [16], it consumes huge quantity of water and requires supervision [10]. Hence, we avoid curing by using this method. In Indian Construction Industry it is generally seen to be used for horizontal, vertical and inclined members.Curing using plastic sheets can be adopted during summers in order to avoid evaporation of water from the concrete surface [4]. It helps to achieve water saving which contributes to sustainable development. It can be used for horizontal, vertical or any other complex shape member [16].Spraying method should be avoided as it consumes huge quantities of water [16]. It is one of the most widely used curing method in Indian Construction Industry contributing a large sum of amount to the overall construction budget and wastage of water which is a scarce resource.
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
Indian Construction Projects are generally based on concrete construction. Curing processes consumes huge quantities of water which is a very scarce resource. The major goal of many countries and its government is reduction of water scarcity. Traditional methods of curing like spraying, ponding, and curing using hessian cloth are mostly used on construction projects which consumes a huge quantity of water.This research provides us with comparative framework analysis between different curing methods used in Indian Construction projects based on certain important attributes for curing. Fuzzy – DEMATEL technique was used in order to determine the most important attributes out of various identified attributes. Further, Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) determines the relative individual weightages of those attributes based on its importance. Based on the results obtained by the analysis of the above two methods, the final scoring of each curing method was carried out separately which helps us to arrive at decision of determining the most feasible method. The limitation of this evaluation framework is that it is completely based on the responses obtained from 11 experts from the construction industry. Another important thing to be considered is that opinion of experts vary from expert to expert based on different geographical conditions in which they have worked, which may affect the final result.However, the results obtained from this research helps us to provide the best curing methods and techniques to be used in Indian Construction Projects in order to save water without affecting the other important attributes of curing and by contributing towards sustainable development.
References
| [1] | Adil Baykasoğlu, V. K. Z. D. U. D. C. Ş., 2013. Integrating Fuzzy DEMATEL and fuzzy hierarchical TOPSIS method for Truck Selection. Expert Systems with Applications: An International Journal, 40(3), pp. 899-907. |
| [2] | ALONSO, J. A., 2006. Consistency in the ANALYTIC HIERARCHY PROCESS: A New Approach. International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems, 15 May, 14(4), pp. 445-459. |
| [3] | Ankita V. Kalbande, A. G. F. H. K., 2017. Membrane Curing of Concrete. International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development, May, 4(5), pp. 11-15. |
| [4] | D. Gowsika, P. R., 2017. Experimental Study on Curing Methods of Concrete. International Journal of Engineering Development and Research, 5(1), pp. 257-260. |
| [5] | Detcharat Sumrit, P. A., 2013. Using DEMATEL Method to Analyze the Causal Relations on Technological Innovation Capability Evaluation Factors in Thai Technology - Based Firms. International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management, & Applied Sciences & Technologies, 4(2228-9860), pp. 81-103. |
| [6] | Er. Rajesh Sharma, D. H. S., 2017. Effect of Curing Methods on Various Concrete Grades. International Journal of Engineering Science and Computing, December, 7(12), pp. 15761-15767. |
| [7] | Gharakhani, D., 2012. The Evaluation of Supplier Selection Criteria by Fuzzy DEMATEL Method. Journal of Basic and Applied, 2(2090-4304), pp. 3215-3224. |
| [8] | Javad Jassbi, F. M. H. N., 2011. A Fuzzy DEMATEL framework for modeling cause and effect relationships of strategy map. Expert Systems with Applications: An International Journal, May, 38(5), pp. 5967-5973. |
| [9] | Kanchan Ambekar, K. G., 2017. Developing a New Curing Technique-‘Drip Curing’. International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET), 5 (VII), pp. 1093-1011. |
| [10] | LIMITED, T. P., 2017. DETAILED REPORT ON CURE IT (DRIP CURING METHOD), Chennai: s.n. |
| [11] | M. Abbasi, R. H. a. B. T., 2013. Application of Fuzzy DEMATEL in Risks Evaluation of Knowledge - Based Networks. Journal of Optimization, 2013(913467), pp. 1-7. |
| [12] | Obam, O., 2016. Effect of Curing Methods on the Compressive Strength of Concrete. International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science, July, 5(7), pp. 17161-17171. |
| [13] | Rohit P. Kamble, S. G. S. P. D., 2016. The Effect of Curing methods on Compressive Strength and Durability of Concrete. International Education & Research Journal [IERJ], December, 2(12), pp. 108-110. |
| [14] | Saaty, T. L., 1980. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation. 2 ed. California: McGraw-Hill. |
| [15] | Saaty, T. L., 2018. Super Decisions CDF. [Online] Available at: https://www.superdecisions.com/about/ [Accessed 18 March 2018]. |
| [16] | Steven H. Kosmatka, B. K. a. W. C. P., 2008. Design and Control of Concrete mixtures. 14 ed. Illinois: Portland Cement Association. |
| [17] | Team, F., 2016. Fuzzy Decision. [Online] Available at: http://www.fuzzydecision.com/en/Product/Info/7/Fuzzy%20Dematel [Accessed 10 March 2017]. |




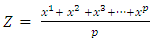 [8]p = Number of expertsZ = Mean of pairwise comparisonx = Individual attribute opinions by ‘p’ number of experts
[8]p = Number of expertsZ = Mean of pairwise comparisonx = Individual attribute opinions by ‘p’ number of experts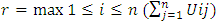 [8]r = normalized matrix
[8]r = normalized matrix
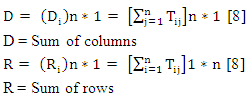




 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML










