-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Construction Engineering and Management
p-ISSN: 2326-1080 e-ISSN: 2326-1102
2017; 6(2): 35-45
doi:10.5923/j.ijcem.20170602.01

Lightweight Concrete Cast Using Recycled Aggregates
ALaa A. Bashandy 1, Fatma M. Eid 1, Ebrahim H. Abdou 2
1Civil Engineering Department, Menoufia University, Egypt
2Civil Engineer, M.Sc. candidate
Correspondence to: ALaa A. Bashandy , Civil Engineering Department, Menoufia University, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Lightweight concrete (LWC) has been successfully used since the ancient Roman times. It has gained its popularity due to its lower density and superior thermal insulation properties. LWC can significantly reduce a dead load of structural concrete elements compared to normal weight concrete. Concrete cast using recycled aggregates considered as green concretes as their positive impact on the environment. This research conducted to study the efficiency of obtaining structural LWC cast using recycled aggregates as coarse aggregates. In this research, the main variables are; type of recycled coarse aggregates used (crushed light brick, crushed glass, and crushed red brick compared to dolomite), the dosage of Lightweight aggregate used (ADDIPOR-55 as 0, 10, 20 and 30% of coarse aggregate volume). The investigated physical properties included the unit weight and slump values as well as the main mechanical properties of hardened concrete in terms of compressive, tensile, flexural, and bond strengths.
Keywords: Lightweight concrete, Lightweight aggregate, Recycled aggregates
Cite this paper: ALaa A. Bashandy , Fatma M. Eid , Ebrahim H. Abdou , Lightweight Concrete Cast Using Recycled Aggregates, International Journal of Construction Engineering and Management , Vol. 6 No. 2, 2017, pp. 35-45. doi: 10.5923/j.ijcem.20170602.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In recent years, the demand for structural lightweight concrete increased at several applications of modern constructions. This was owing to many advantages such as lower density results in a significant benefit in terms of load-bearing elements of smaller cross sections and reduction in the size of the foundations [1]. The aggregates considered the former of concrete, which is, actuates about 75% of concrete volume. Using lightweight aggregate (LWA) in the concrete industry contributes to producing the lightweight aggregate concrete (LWAC). LWA are broadly classified into two types; natural (pumice, diatomite, volcanic cinders, etc.) and artificial (perlite, expanded shale, clay, slate, sintered PFA, etc.). Lightweight concrete can easily be produced by utilizing lightweight aggregate such as pumice or perlite aggregate [2, 3].Recycling concrete provides a sustainable concrete that the re-use of the demolitions of concrete constructions reduces the amount of material that must be landfilled. The concrete, bricks, ceramics become aggregate and any embedded metals can be removed and recycled as well [4, 3]. In addition, that reduces the economic impact of the concrete used and reduces the need for virgin aggregates. This, in turn, reduces the environmental impact of the aggregate extraction process. By removing both the waste disposal and new material production needs, transportation requirements for the project significantly reduced [5-7]. Lightweight concrete enhanced from non-structural to structural concrete. Also, it used as high strength light concrete [8-15].
2. Research Significance
- This investigation aims to study the possibility of using lightweight concrete cast using recycled aggregate as coarse aggregates. In this research, the fresh and hardened properties of recycled aggregate lightweight “LWC” concrete are studied. The main variables in this investigation are; recycled aggregate used (crushed light brick, crushed glass, and crushed red brick compared to dolomite as coarse aggregates), lightweight additive (ADDIPOR-55 as 0, 10, 20, and 30% of coarse aggregate volume). The importance of this research is based on the need to know green alternatives to the conventional lightweight natural aggregates to obtain structural lightweight concrete. This research provides data for researchers concerning the behavior of lightweight concrete cast using recycled aggregates as green concrete.
3. Materials and Test Specimens
- All tests in this research are carried out in the quality control and testing of the building materials research laboratory in Civil Eng. Dep. at Faculty of Engineering, Menoufia University. The materials used, the preparation of test specimens and testing procedures are discussed in the following sections.
3.1. Materials
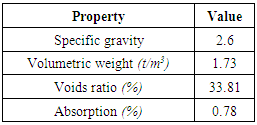
- The cement used is ordinary Portland cement CEM I) 42.5 N) from the Suez cement factory. It satisfies the Egyptian Standard Specification (E.S.S. 4756-1/2009) [14]. The fine aggregate used is natural siliceous sand that satisfies the Egyptian Code (E.S.S. 1109/2008) [15] and ASTM C-33 [16]. It is clean and nearly free from impurities with a specific gravity 2.6 t/m3 with a fineness modulus of 2.61. Its main properties are shown in Table (1).
|
|
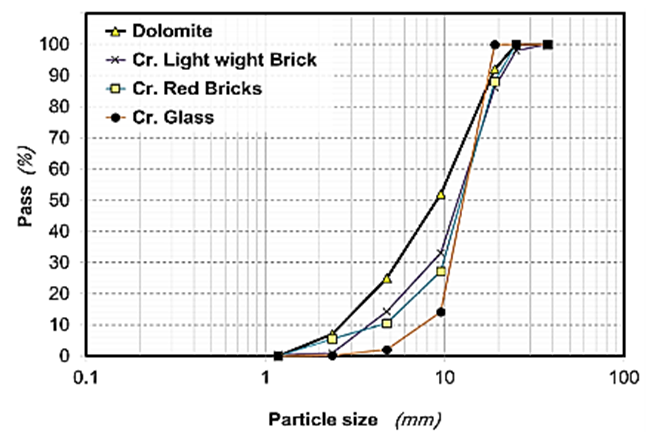 | Figure (1). Sieve analysis of coarse aggregates used |
3.2. Concrete and Test Samples
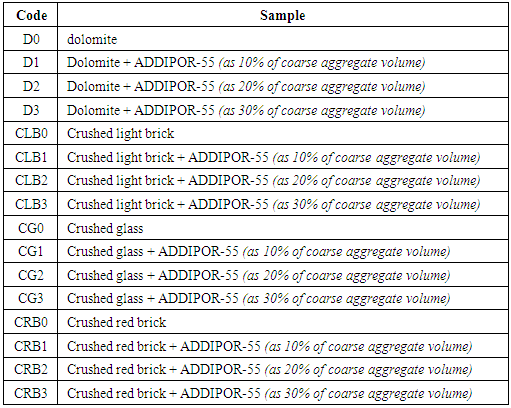
- The start point of choosing the proportions of lightweight concrete mixes was conducted firstly based on previous researches [17].The present experimental program conducted using different valid recycled aggregates compared to natural aggregates as coarse aggregates for lightweight concrete as shown in Fig. (2). ADDIPOR-55 as a lightweight additive was used as a ratio of recycled aggregate (as 10, 20, 30% of aggregate volume) to study the feasibility of mixing it with recycled aggregates to light the weight of concrete to have lightweight concrete.
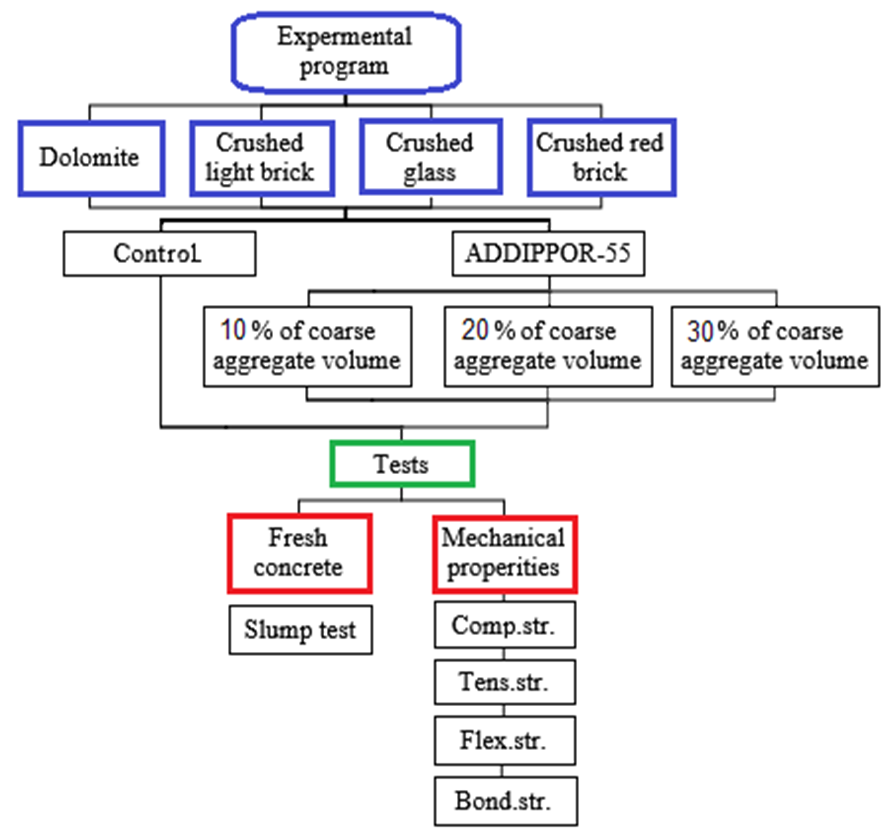 | Figure (2). The flow chart of the experimental program |
|
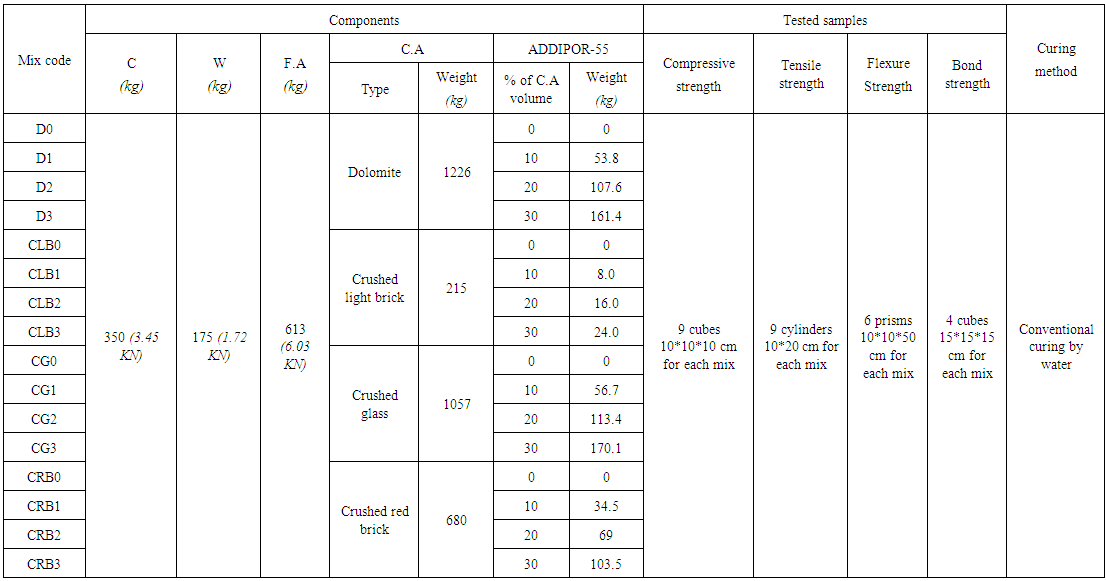 | Table 4. Mixture proportions of concrete mixes used per cubic meter |
3.3. Performed Tests
- The fresh concrete properties obtained in terms of slump values. The standard cone of dimensions 100mm upper diameter, 200mm bottom diameter, and 300mm height was used according to the Egyptian Code of Practice (E.C.P. 203/2007). The main mechanical properties of tested samples obtained in terms of compressive, splitting/ indirect tensile, flexural and bond strengths. Cubes of dimensions 100x100x100 mm were used to obtain compressive strength values. Cylinders of dimensions 100mm diameter and 200 mm height were used to obtain indirect tensile strength values. Prisms of dimensions 100x100x500 mm were used to obtain flexural strength values. Cubes with dimensions of 150x150x150 mm with embedded rebars (12 mm diameter and 160mm length) were used to determine the bond strength between steel bars and concrete. The concrete-steel bond strength is formulated according to E.C.P. 203/2007 as Fbu= fs .φ /(4.Ld) where, Ld (mm) is the bond length of steel; φ (mm) is the diameter of the steel, and fs (N/mm2) is the tensile stress in steel. If in the previous equation fs= F / (π.φ2 /4), where F (N) is the applied force on the rebar, it then comes out as, Fbu= F / (Ld .π. φ).A compressive strength testing machine of 2000 kN capacity was used to obtain compressive strength, indirect tensile strength, and bond strength. A flexure testing machine of 100 kN capacity was used to obtain flexural strength values.
4. Test Results and Discussions
- The results of fresh and hardened lightweight concrete properties discussed in this section. The fresh properties are drive in term of slump values while the hardened properties are drive in terms of compressive, splitting tensile, flexure and bond strengths. The concrete cast using dolomite was considered as the referee structural concrete compared to LWC.
4.1. Effect of Using Lightweight Additive (ADDIPOR-55)
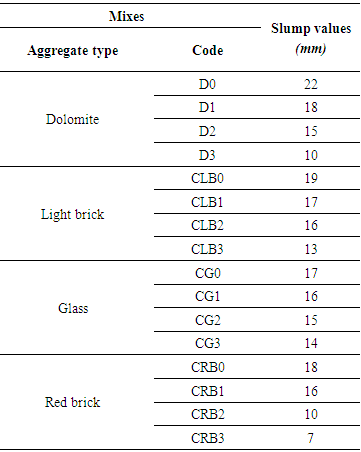
- The results of slump tests due to the effect of using ADDIPOR-55 are shown in Table (5) and Fig. (3).
|
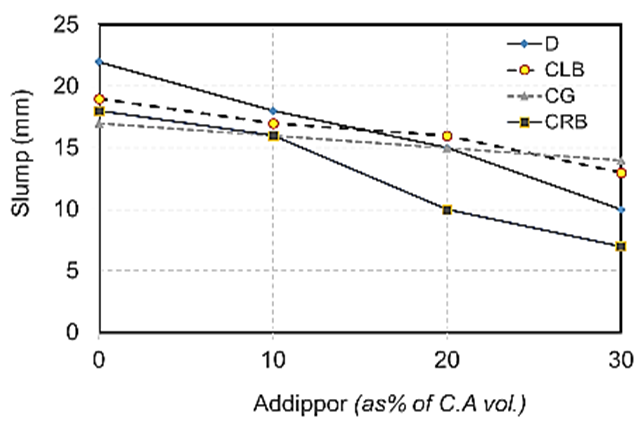 | Figure 3. Slump values for different aggregates used |
|
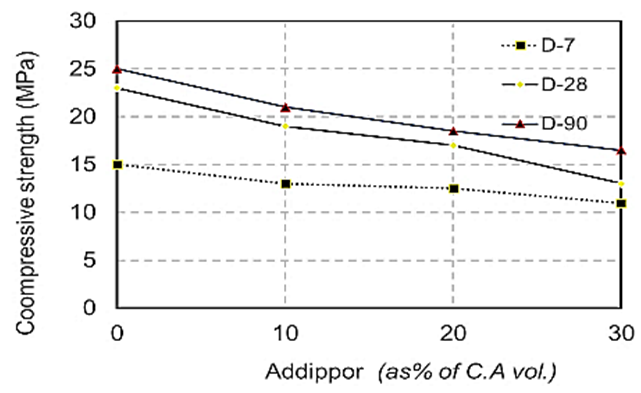 | Figure 4. Compressive strength values when using dolomite at different ages due to ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
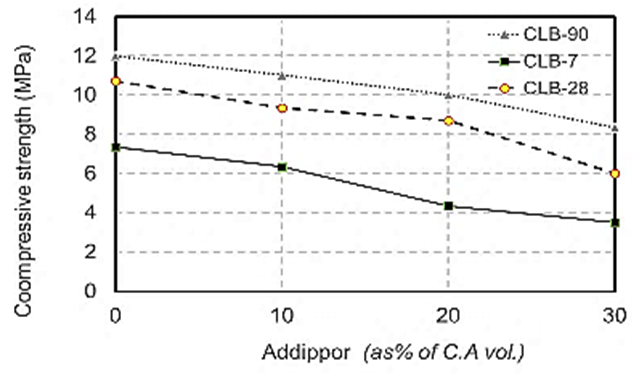 | Figure 5. Compressive strength values when using crushed light brick at different ages due to ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
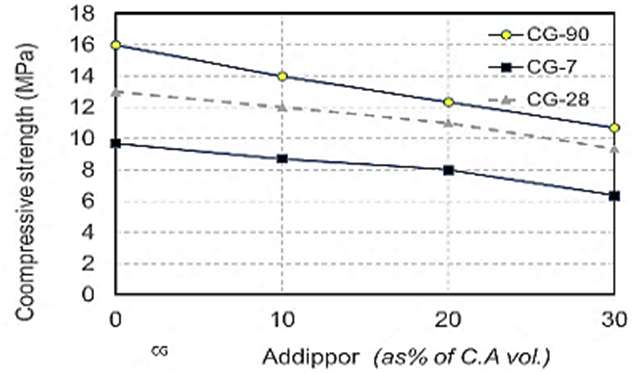 | Figure 6. Compressive strength values when using crushed glass at different ages due to ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
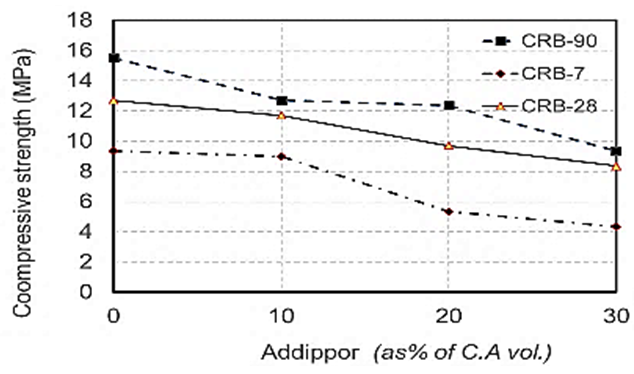 | Figure 7. Compressive strength values when using crushed red brick at different ages due to ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
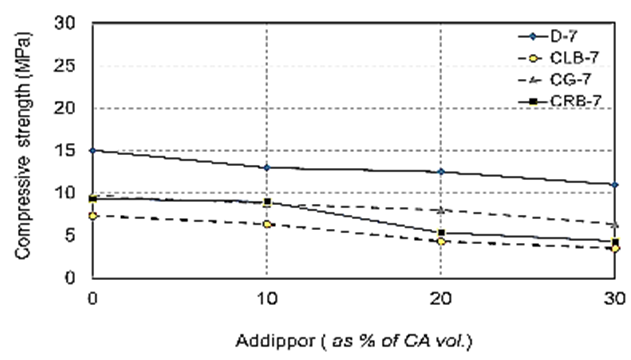 | Figure 8. Compressive strength values at 7 days for different recycled aggregate types used with different ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
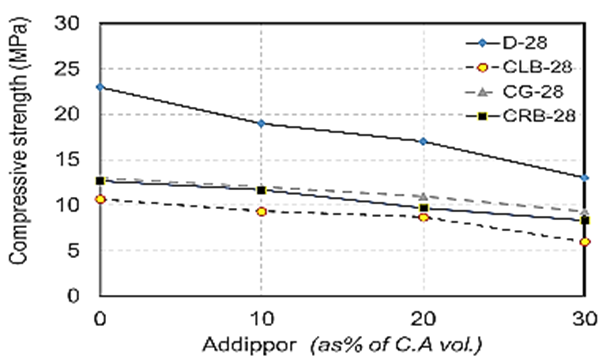 | Figure 9. Compressive strength values at 28 days for different recycled aggregate types used with different ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
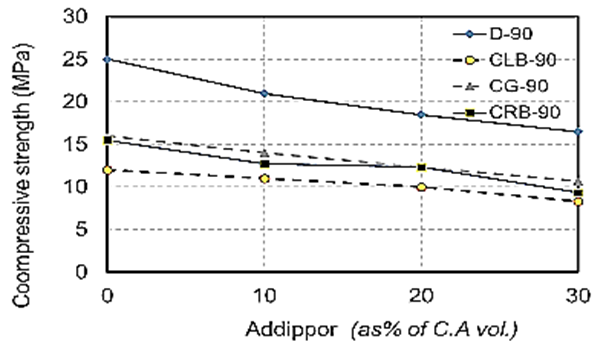 | Figure 10. Compressive strength values at 90 days for different recycled aggregate types used with different ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
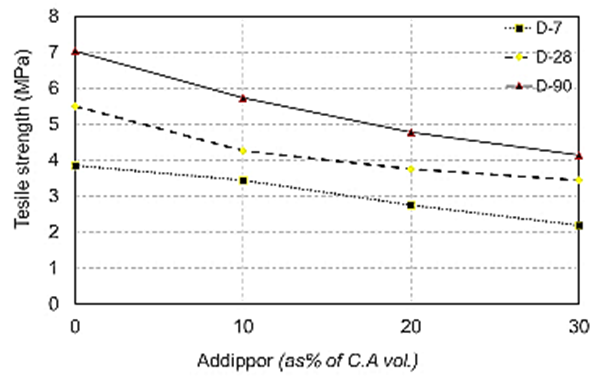 | Figure 11. Splitting tensile strength values when using dolomite at different ages due to ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
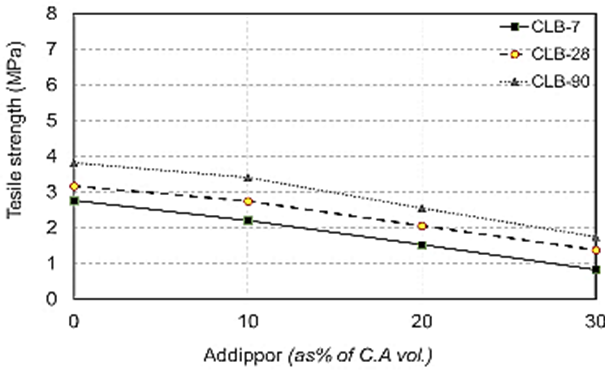 | Figure 12. Splitting tensile strength values when using crushed light brick at different ages due to ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
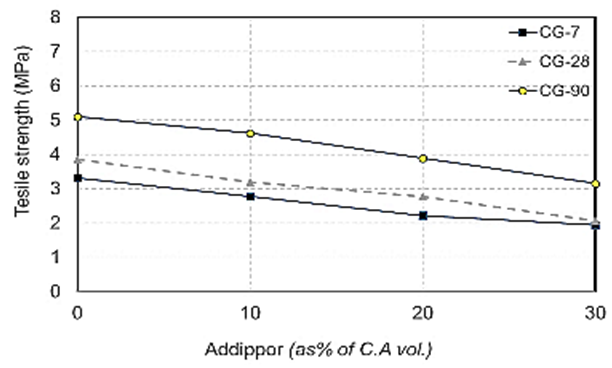 | Figure 13. Splitting tensile strength values when using crushed glass at different ages due to ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
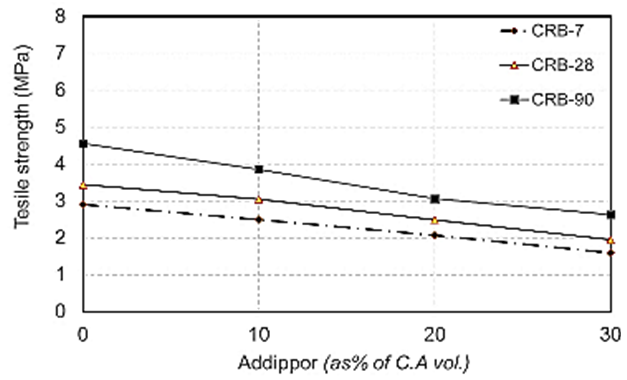 | Figure 14. Splitting tensile strength when using crushed red brick at different ages due to ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
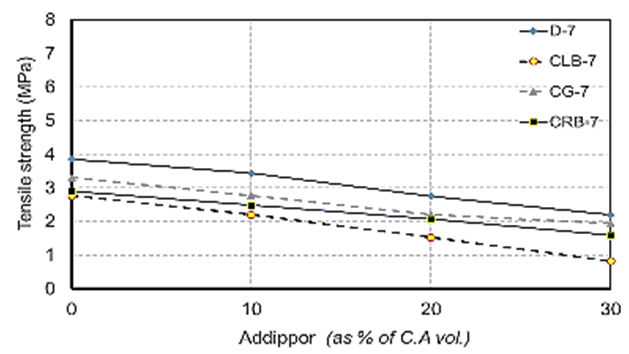 | Figure 15. Splitting tensile strength values at 7 days for different recycled aggregate types used with different ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
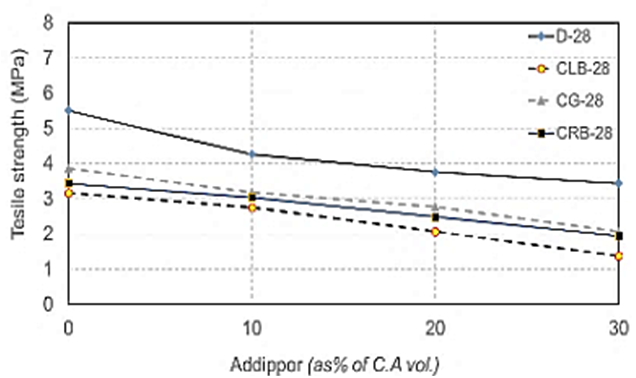 | Figure 16. Splitting tensile strength values at 28 for different recycled aggregate types used with different ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
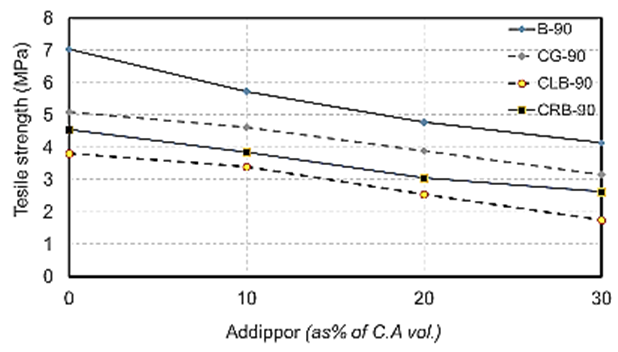 | Figure 17. Splitting tensile strength values at 90 days for different recycled aggregate types used with different ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
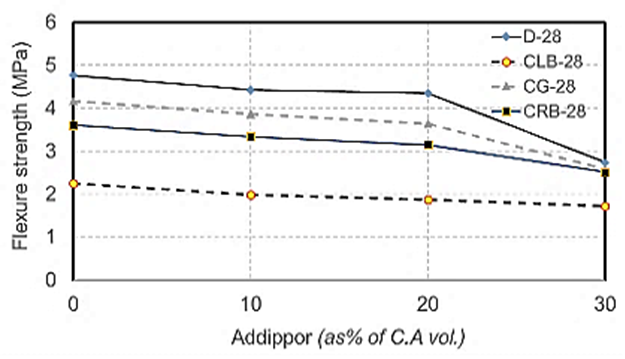 | Figure 18. Flexure strength values at 28 days for different recycled aggregate types used with different ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
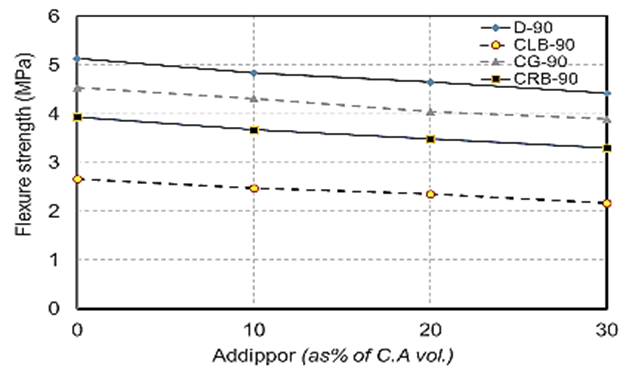 | Figure 19. Flexure strength values at 90 days for different recycled aggregate types used with different ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
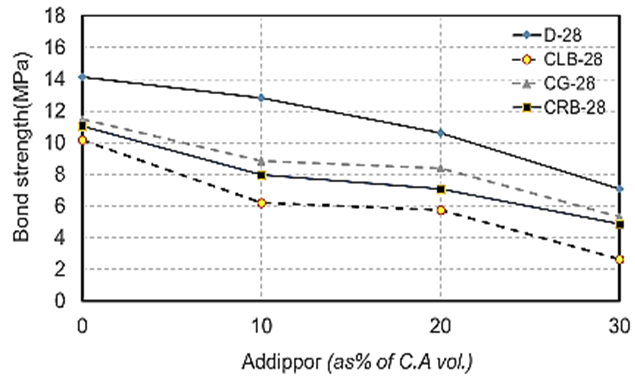 | Figure 20. Bond strength values at 28 days for different recycled aggregate types used with different ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
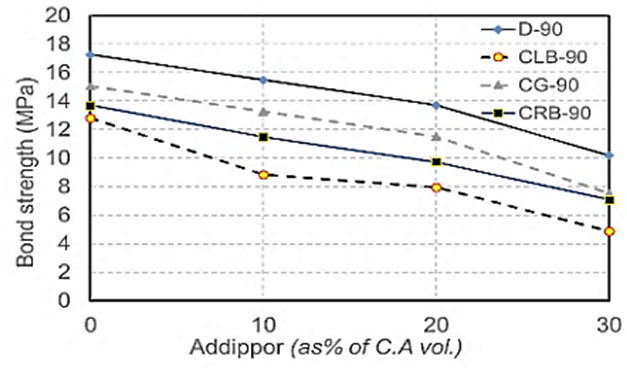 | Figure 21. Bond strength values at 90 days for different recycled aggregate types used with different ADDIPOR-55 dosages |
|
4.2. Effect of Using Recycled Aggregates
4.2.1. Fresh Concrete Properties
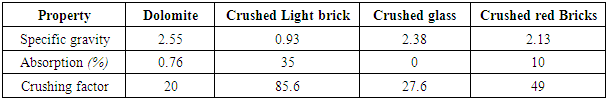
- The results of slump tests due to the effect of using different aggregate types used in this study are shown in Table (5) and Fig. (3).The results showed that the slump values decreases when using recycled aggregates compared to using dolomite. When using light brick as concrete aggregates slump values decreased compared to using dolomite with a decrease in weight by about 13%. Using crushed glass decreases the value of slump comparing to using dolomite while the weight decreased by about 7.5%. Also, using crushed red brick decreases the slump values comparing to using dolomite with a decrease in weight by about 9.25%.At 10 % of ADDIPOR-55 as an optimum ratio of coarse aggregate volume, the better slump value (better workability) occurs when using crushed light brick with a decrease in weight by about 14% compared to dolomite. The worst workability was observed when using crushed glass and crushed red brick comparing to dolomite with a decrease of about 8.3% and 9%, respectively compared to dolomite.
4.2.2. Hardened Concrete Properties
4.2.2.1. Compressive Strength
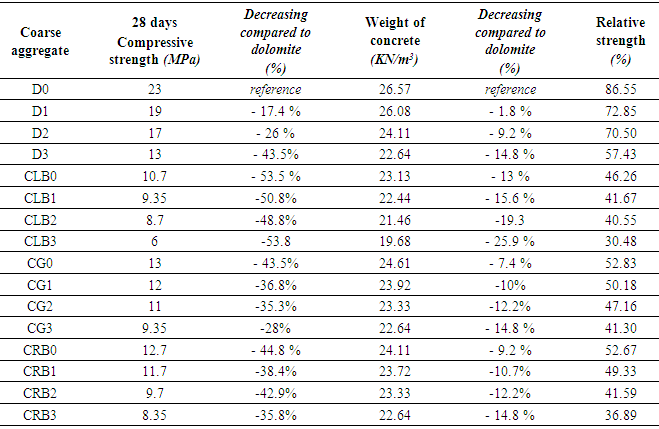
- The results of compressive strength tests shown in Table (6) and Figs. (4) to (10). Figs. (4) to (7) showed the splitting tensile strength at different ages for each aggregate type used. Figs. (8) to (10) showed the differences between splitting tensile strength values at each age for different aggregate types used. The results show that the compressive strength values when using crushed light brick as coarse aggregate decreased by about 53.5% compared to using dolomite with a decrease in weight by about 13% due to the lighter in weight, which makes lower strength than dolomite. Using crushed glass decreased the values of compressive strength by about 43.5% compared to using dolomite while the weight decreased by about 7.5% that is why the voids of glass are too small but its weight is less than dolomite that makes concrete with dolomite is higher in compressive strength. Using crushed red brick decreased compressive strength values by about 44.8% compared to using dolomite with a decrease in weight by about 9.25% as a red brick has more voids ratio than dolomite in addition to its lower weight comparing to dolomite.When using 10 % of ADDIPOR-55 as a lightweight additive, the better compressive strength values obtained with using crushed glass with a decrease in weight and strength by about 8.3% and 36%, respectively compared to dolomite. The worst strength values occur when using crushed light brick with a decrease in weight and strength by about 14% and 50.8%, respectively compared to dolomite. That may referee to the presence of voids and the high crushing factor compared to dolomite.
4.2.2.2. Tensile Strength
- The results of splitting tensile strength tests shown in Table (6) and Figs. (11) to (17). Figs. (11) to (14) showed the splitting tensile strength at different ages for each aggregate type used. Figs. (15) to (17) showed the differences between splitting tensile strength values at each age for different aggregate types used.The results showed that the splitting tensile strength values decreased when using crushed light brick by about 42.5% compared to using dolomite with a decrease in weight by about 13% due to the high voids ratio of light brick, which decreases both weight and strength. Using crushed glass decreased the value of tensile strength by about 30% comparing to using dolomite with a weight loss of about 7.5% as glass has much lower voids ratio than light brick. When using crushed red brick values decreased by about 37.6% compared to using dolomite with a decrease in weight by about 9.25% as a red brick has lower voids ratio than light brick but higher than glass.When using 10% of ADDIPOR-55, it was found that the better tensile strength values obtained when using crushed glass compared to using dolomite with a decrease in weight by about 25.5%. The lowest values obtained when using crushed light brick with a decrease in weight by about 35.5% compared to using dolomite.
4.2.2.3. Flexure Strength
- The results of flexure strength tests are shown in Table (6) and Fig. (12). The test results showed that the flexure strength values decreased by about 52.8% with a decrease in the weight by about 13% when using crushed light brick compared to using dolomite. Using crushed glass decreases the value of flexure strength by about 12.6% and decreases the weight by about 7.5% compared to dolomite. Using crushed red bricks decreases the flexure strength values by about 24.4% with a decrease in the weight by about 9.25%.compared to dolomite. When adding ADDIPOR-55 (as 10% of coarse aggregate volume), the better flexure strength obtained when using crushed glass compared to using dolomite with a decrease in weight by about 11%. The lowest values obtained when using crushed light brick with a decrease in weight by about 49% compared to using dolomite.
4.2.2.4. Bond Strength
- The results of bond strength tests are shown in Table (6) and Fig. (15). The results showed that the bond strength decreases by about 25.6% with a decrease in weight by about 13% when using crushed light brick compared to dolomite and this may be because of the highest lightweight comparing to other coarse aggregates that affect widely on the bond between steel and concrete. Using crushed glass decreases the values of bond strength by about 14% with a weight decrease of about 7.5% compared to using dolomite as glass has heavier than light brick and as a result, it has more bond strength than light brick. Also, using crushed red brick decreases the bond strength values by about 20% compared to dolomite with a weight decrease of about 9.25%.When ADDIPOR-55 was used (at the optimum value of 5%), the better bond strength obtained with crushed glass compared to dolomite with a decrease in weight by about 14%. The lowest values obtained when using crushed light brick compared to dolomite with a weight decrease by about 43% comparing to dolomite.
4.3. Effects on the Weight of Samples
- Using suggested recycled aggregates in this research producing lightweight concrete. The weight of samples cast using light brick, crushed glass and crushed red bricks are lighter than that cast using dolomite by about 13%, 7.4%, 9.2%, respectively with strength loss of about 53.3%, 43.5%, and 44.8%, respectively at 28 days tests. Increasing the ADDIPOR-55 dosage decreasing the weight of concrete samples up to 25.9% with a strength loss for dolomite, light brick, crushed glass and crushed red bricks up to about 43.5%, 43.9%, 28.1%, and 34.3%, respectively compared to using those aggregates without ADDIPOR-55.
5. Economic Study
- From the economic point of view (without taking in to consideration labour costs), using recycled aggregates is more economic than using neutral aggregates especially crushed glass then crushed red bricks from the point of strength but as non-structural uses (in the range of this study). Using light bricks is cost less compared to dolomite used. Concrete using Light brick costs about 513 L.E. for one cubic meter of concrete while dolomite costs about 1300 L.E. /1 m3 when using the optimum percentage of ADDIPOR-55. The strength of concrete obtained by using dolomite with optimum percentage of ADDIPOR-55 is better than that using light brick at the same percentage of ADDIPOR-55 by about twice but the light brick is lighter in weight than dolomite by about 1.13 times.
6. Conclusions
- In this research, a series of experiments have been performed to investigate the behavior and the properties of recycled aggregates lightweight "LWC" concrete. Based on the experimental results presented in this paper, the following conclusions could be drawn as follow: 1. Recycled aggregate concrete "RAC" is less suitable for structural concrete compared to conventional concrete with natural aggregate.2. Using suggested recycled aggregate decreases the concrete weight. The decrease in weight for concrete cast using crushed light brick, crushed glass, and crushed red brick are 13%, 7.4%, and 9.2%, respectively with strength loss of about 53.5%, 43.5%, and 44.8%, respectively compared to that cast using dolomite only. 3. For lightweight concrete with all suggested aggregates used, the optimum ADDIPOR-55 dosage is 10% of coarse aggregate volume.4. The Slump value of the lightweight concrete with dolomite is higher than the lightweight concrete with crushed light brick, crushed glass, and crushed red brick by about 13.6%, 22.7%, and 18 %, respectively. When using ADDIPOR-55 the weight of samples decreased by about 14%, 8.3%, and 9.1%, respectively with a decrease in slump values by about 5.6%, 11%, and 11%, respectively.5. Using ADDIPOR-55 as a lightweight aggregate additive decreases the concrete weight and strength. The decrease in weight at 10% of ADDIPOR-55 for concrete cast using crushed light brick, crushed glass, and crushed red brick are 14%, 8.3%, and 9.1%, respectively with strength loss of about 50.7%, 36.8%, and 38.4%, respectively compared to those cast using dolomite with the same dosage. 6. The tensile strength of the lightweight concrete cast using dolomite is higher than lightweight concretes cast using crushed lightweight brick, crushed glass and crushed red bricks as aggregates by about 42.5, 30 and 37.5%, respectively. Using ADDIPOR-55 decreases the tensile strength by about 35.5%, 25.3%, and 28.7%, respectively with a decrease in weight by about 14%, 8.3%, and 9.1%, respectively compared to those cast using dolomite with the same dosage.7. The flexure strength of the lightweight concrete cast using dolomite is higher than lightweight concretes cast using crushed lightweight brick, crushed glass and crushed red bricks as aggregates by about 52.8%, 12.6%, and 24.4%, respectively. Using ADDIPOR-55 decreases the flexure strength by about 11.5%, 7.2%, and 7.3%, respectively with a decrease in weight by about 14%, 8.3%, and 9.1%, respectively compared to those cast using dolomite with the same dosage.8. The bond strength of the lightweight concrete with dolomite is higher than lightweight concretes with crushed lightweight brick, crushed glass and crushed red bricks as aggregates by about 28%, 18.7%, and 21.9%, respectively. Using ADDIPOR-55 decreases the bond strength by about 51.7, 31 and 38%, respectively with a decrease in weight by about 14%, 8.3%, and 9.1%, respectively compared to those cast using dolomite with the same dosage.Generally, it can be concluded that recycled aggregates can be used in lightweight concrete because it can gain a lighter weight. In addition, using recycled aggregates decrease environmental impact and save natural resources. Lightweight aggregate can be used with recycled aggregates to produce suitable structural lightweight concrete for small to medium loads. As an application, it can be used for last floor slabs, which can guarantee suitable strength and heat isolation for those slabs.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML