-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Construction Engineering and Management
p-ISSN: 2326-1080 e-ISSN: 2326-1102
2015; 4(1): 26-34
doi:10.5923/j.ijcem.20150401.03
A Study of Time and Cost Relationship of Private Building Projects in Abuja
John Ebhohimen Idiake, Abdullateef Adewale Shittu, Abdulganiyu Adebayo Oke
Department of Quantity Surveying, Federal University of Technology, Minna, Nigeria
Correspondence to: John Ebhohimen Idiake, Department of Quantity Surveying, Federal University of Technology, Minna, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Time, cost and quality targets have been identified as the main criteria for measuring the overall success of construction projects. However, previous research shows that little evidence exists of projects where these factors were successfully balanced. How then are the completion times of building projects in Abuja related to their costs? This was the research question of this research, which aimed at achieving a result that will show whether time is effectively related to cost of construction or not. The following objectives were examined: (i) computation of the expected duration of sampled building projects, (ii) determination of the differences between the actual and expected durations and (iii) derivation of an average value for time performance of sampled building projects. Time-cost relationship data for 30 completed private projects in Abuja were obtained from consultant Quantity Surveyors. Objective One was realized by calculating the expected effective duration for each project using the Ogunsemi and Jagboro (2006) model which is given as T = 168.895 + 0.491C (if C ≤ 557) or 709.66 + 0.884C (if C ˃ 557); where T = effective project duration in relation to a given cost from date of site possession to practical completion (in working days) and C = cost of the project (in millions of Naira). From analysis of the research data, it was found that at a given cost, private building projects in Abuja are executed within a duration that is 34% later than the required time. This represents an improvement over the 51% time overrun published in previous works. At the same time, it was found that larger building projects are more susceptible to time underrun. It was recommended that since the time-cost relationship appeared effective in reducing time overrun from 51% to 34%, this should be continuously maintained.
Keywords: Building, Contract Sum, Cost, Duration, Performance, Private projects
Cite this paper: John Ebhohimen Idiake, Abdullateef Adewale Shittu, Abdulganiyu Adebayo Oke, A Study of Time and Cost Relationship of Private Building Projects in Abuja, International Journal of Construction Engineering and Management , Vol. 4 No. 1, 2015, pp. 26-34. doi: 10.5923/j.ijcem.20150401.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Time, cost and quality are three major variables that are of primary concern to the main parties involved in procurement of building projects (client and contractor). This fact was pointed out by Dissanayaka and Kumaraswamy [1]. According to them, Time, Cost, and Quality target are recognized to be the major criteria used to measure project delivery level of success. The clients of building projects are primarily interested in their projects being delivered within a short time, for an effectively lower cost, and at a higher quality.On the part of the contractor, executing projects at an effective time and at a given standard of quality in relation to a given cost gives him an edge ahead of others when bidding for subsequent contracts. For the purpose of successful planning, management and execution of projects, these aforementioned major parameters (Time, Cost and Quality) have to be taken into consideration. Hughes and William [2], in their opinion concerning how the aforementioned parameters are considered so as to meet requirements of the client, proposed that the parameters can be simply identified as three points comprised in a triangle. Underestimating any of them will definitely cause resultant negative effects on the remaining two. But Rwelamila and Hall [3] argue that there exists little evidence of projects where these three factors have been successfully balanced. The need arises therefore to embrace Time, Cost and Quality relationship.According to Jagboro [4] the Nigerian Institute of Quantity Surveyors in 1981 conducted a survey which showed that costs of construction in Nigeria were about 40% higher than similar types in Brazil and Kenya, 35% higher than in Britain and 30% higher when compared to construction in United States of America. This was further buttressed by Newcombe [5], who opined that there exists global criticism of the construction industry’s failure to deliver projects on time. According to Charles and Andrew [6], construction clients are increasingly perplexed with the general level of effectiveness and accountability of projects. Cost overruns, in connection with project delays have more often than not, been recognized as one of the prime factors that leads to high cost of construction.In Nigeria, besides investigating cause and consequences of time overrun, little research was identified to have been done in the study of Time, Cost and Quality relationship of building projects. The Nigerian construction industry is of overriding significance in terms of providing employment and economic growth. Efforts geared toward the improvement of construction competence in terms of timeliness, cost-effectiveness and quality efficiency will be meaningful and contribute to cost savings for the country at large. This research therefore attempts to study time, cost and quality relationship in order to determine whether or not time and quality are effectively related to the cost of private building projects in Abuja. The objectives of this paper include (i) computation of the expected duration of sampled building projects, (ii) determination of the differences between the actual and expected durations and (iii) derivation of an average value for time performance of sampled building projects. Only private building projects were covered in this study. This paper reports the study of time and cost, while the study of cost and quality was reported in a separate paper.
2. Time in Relation to the Execution of Building Projects
- Time in the execution of building projects is the duration from the date of site possession to the date of practical completion of that particular project, usually considered in weeks. Effective time control is one of basic goals of parties involved in constructing projects. From the initial stage the client is interested in the time required for the project to be delivered. The client’s goal is to shorten as much as possible, the time needed for each phase of the project, beginning from the initial planning stage to the completion stage. Time, it is said, is money. This economic significance of time is why clients assert that "time is of the essence" in any contract. The construction process contains many aspects where time can be controlled by the building project owner indirectly through contract clauses and contracting procedures. The contractor is in the best position of exercising the most direct control over construction duration. Contractors use network schedules to control project durations, which are mostly a contract agreement between the two parties. Clients may stipulate contract durations based on economics, weather, or other considerations. The project executor (the Contractor) only generates a detailed network schedule after signing the contract. The initially scheduled duration might be longer than the actual time required in the contract, hence there is the need for adjustment so as to meet contract requirements. The contractor might want to finish the project earlier in order to avoid winter season, to take advantage of bonus payments, or to free up resources for different projects. In addition to this, the contractor might fall behind schedule as the construction progresses, and as a result require action to get back on track. In these cases, the contractor needs to define the project duration at which construction costs are minimized.According to Newcombe [5], there exists global criticism of the construction industry’s failure to execute projects on time. Chan and Kumaraswamy [8] are of the view that duration of construction is of increasing importance due to the fact that it serves as a vital benchmark for assessing project performance and project organization efficiency. It is therefore observed that the timely completion of projects is commonly regarded as one of the major criteria by which the success of the projects are measured by building owners, consultants and contractors alike.
3. Concept of Cost in Relation to Building Projects Execution
- The concept of cost in executing building projects entails every constituent of cost incurred in relation to that particular project right from the inception to practical completion and occupation stage. Throughout the construction process of building projects, cost is seen as one of the major considerations. The importance and significance of cost is portrayed when a proposed project with estimated cost significantly higher than the client’s budget is either redesigned or abandoned. An ongoing project can also suffer abandonment as a result of cost overrun. These go a long way in proving that no matter how important a proposed building project might be to the client, cost is one of the major determinants as to whether the project will be realistic or not.It is important to note that cost has continuous influence on building projects. It dictates the major characteristics of the building embryo (height, plan, shape and type of finishing), throughout the design development stage. Cost will be inescapable even after completing the building project; this is because uneconomical distribution of cost at the inception can adversely impact on lifecycle costs.Cost is what must be given in order to obtain something valuable, that is to say it is a measure of the utility of the items. Cost is also seen as the total financial liability of the client, according Douglas and Peter [9]. Ashworth [10] sees the cost sensitivity of an element in a building as dependent upon its total cost in relation to the total cost of the building. A structural component is said to be cost sensitive, if a substantial change in its cost or quantity has a significant effect on the total cost of building.Ambrose [11] stated that dealing with cost is a painstaking but necessary operation in construction process. For the building structure itself, the bottom-line cost is the delivered cost of the finished structure, which is measured usually in cost per square meter units of the building. Cost factors such as cost of materials, labor, transportation, testing and inspection must be combined to produce a single unit cost for the structure. Designing for the control of cost of a structure is just an aspect of the design problem. It is noteworthy to mention that possible cost saving efforts applied to a structure may end up increasing the cost of other parts of the structure.William et al [12] opined that an effective means of representing cost is necessary to keep cost of jobs in line with original estimates. They further pointed out that adequate cost recording and control systems provide opportunities for savings in future jobs.The terms cost and price are used interchangeably on several occasions, but it is important to note that builder’s cost is quite distinct from builder’s price. Thus Seeley [7] sees it this way: cost is the consequential of labour, plants, and material deployed for precise activities which are charged in accordance with the accounting system of an organization. Price on the other hand can be defined as the sum a buyer, for example a client will pay for an item, an element or a product, such as a complete building.Some of the previous researches carried out have focused on the technical aspects of management of construction projects cost for the realization of client’s objectives. According to Ayeni [13] cost is the calculation aimed at ascertaining what will be spent on part or the whole of a building for the purpose of submitting a tender. In such a case it is not proper to think of cost in terms of money alone, as Benneth and Ormerod [14] explained that there are other factors that must be taken into consideration in order to arrive at a realistic tender.
4. Time and Cost Relationsip in Building Projects
- Time in relation to construction of building projects is recognized to be one of the benchmarks used to assess project performance and project organization efficiency. Timely completion of a construction project is one goal of both the client and contractor because each party tends to incur an additional cost and lose potential revenues when such completion is delayed (Thomas et al., [15]).According to Chan and Kumaraswamy [16] a building project is said to be successful if such project is completed within effective time, at a predetermined budget and to the standard of quality specified by the owner at the initial stage of the project. Rigorous criticism has trailed the construction industry when projects are executed at durations longer than planned.The issue of project time overrun may safely be described as being of global concern, as Chan and Kumaraswamy [16] found out in Australia that seven-eighth of building contracts surveyed in the late 1960s were completed after scheduled completion while in Hong Kong, 70% of building projects were delayed. Al-Khalil and Al-Ghafly [17] confirmed in a study they carried out in 1995 that contractors agreed that 37% of all their projects were subject to delay whereas consultants admitted that delayed projects accounted for 84% of projects under their supervision. All these, according to Kumaraswamy and Chan [16], have made construction projects one of the most visible ‘failure models’, attracting criticisms on the industry’s efficiency and effectiveness profile.
4.1. Factors Affecting Time and Cost Performance
- Chan and Kumaraswamy [8] remarked that studies in various countries appear to have contributed significantly to the body of knowledge relating to time performance in construction projects over the past three decades, whereas Iyer and Jha [18] opined that project performance in term of cost has been studied since the 1960s. These studies include theoretical work based on experience of researchers and structured research works. According to Kuprenas [19] the frequency of design team meetings and the written reporting of design phase progress were found to be significant in reducing design phase costs. On the other hand, the use of project manager training and a project management based organizational structure were found to be processes that did not significantly reduce design phase costs.Iyer and Jha [18] remarked that factors affecting cost performance include: project manager's competence; project manager's coordinating and leadership skill; top management support; monitoring and feedback by participants; decision making; coordination among project participants; owners' competence; economic condition, social condition and climatic condition. Coordination among project participants was the most significant of all the factors having maximum influence on cost performance of projects.
4.2. Time-Cost Relationship Using Critical Path Method
- Ever since the technique of critical path method (CPM) was introduced in 1950, it has always been used as a base for calculating and scheduling project time and cost. Nevertheless, CPM only calculates the project’s total duration as the sum of the duration of activities lying on the critical path; CPM does not respect the project time deadline. To defeat this predicament, time-cost trade-off (TCT) analysis was developed. According to Hegazy and Ayed [20], the purpose of TCT analysis is to decrease the CPM original duration of the project thereby meeting a precise deadline in the least costly way. This is achievable optimally by selecting certain activities to be performed by using faster and costlier construction processes.Figure 1 confirms the result of research carried out by Feng et al [21], which shows that there exist a trade-off between Time and Cost when executing a given task, and as a result, the lesser the expenses on the resources, the longer it will take to complete the task. According to them, the total cost of a given project is the sum of direct and indirect costs thereby resulting in optimum duration for the least cost. This is shown in Figure 2.
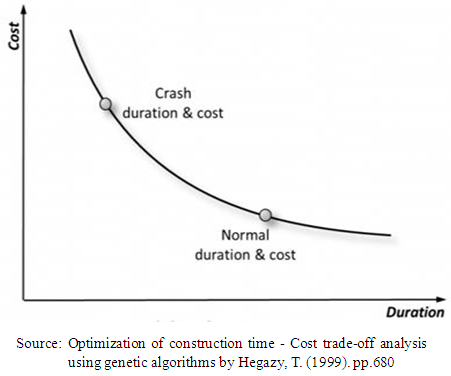 | Figure 1. Activity Time-Cost Relation |
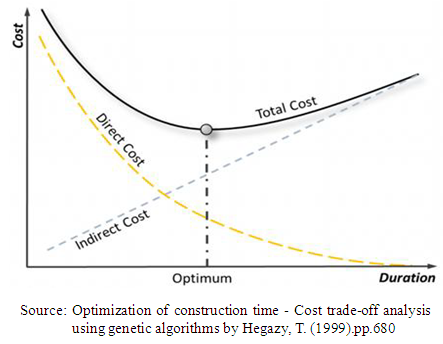 | Figure 2. Project Time-Cost Curve |
4.3. Time-Cost Trade-Off Analysis
- According to Liao et al [22], Time-Cost Trade-off (TCT) is employed in meeting project deadline especially when considering such projects whose deadline is fixed or a project that is already behind schedule. Siemens [23] added that TCT analysis involves replacing some activities found on the critical path with shorter methods of construction for the purpose of saving time, even though this might increase the cost of such critical activities. Non-critical activities were left undisturbed to save cost. According to Hegazy and Ayed [20], the outcome of such analysis results in a Time-Cost trade-off curve as shown in Figure 3. This helps in selecting construction methods that provide an effectively balanced project cost and duration.
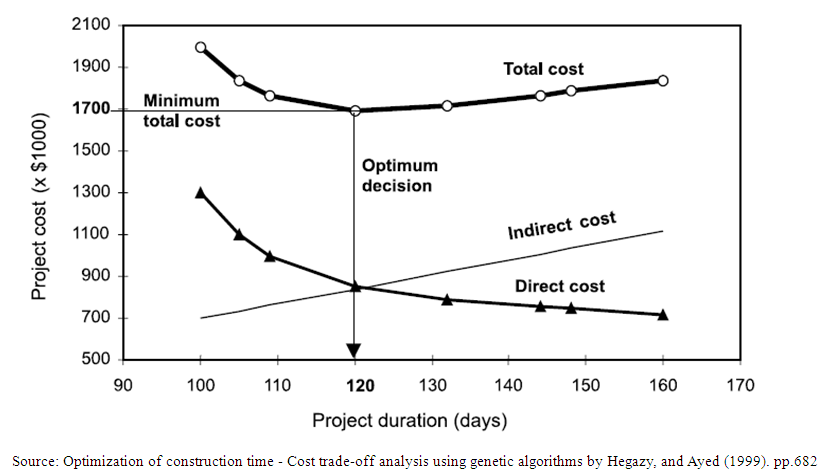 | Figure 3. Time-Cost relationships |
 | Figure 4. Linear and Discrete Relationships of Activity Modes |
5. Research Mehodology
5.1. Research Population
- This refers to the total number of elements making up the target group. For the purpose of this study, the population is focused on registered Quantity Surveying firms and owners of selected private buildings in Abuja. The research population was not static, and was liable to vary in size from one point in time to the other.
5.2. Method of Data Collection
- The method applied in collecting data for the purpose of study involved both primary and secondary data collection methods. Primary data on cost-quality relationship were obtained through the use of structured questionnaires administered to owners of selected private buildings in Abuja, Nigeria. The analysis of cost-quality data was however reported in a separate paper. Secondary data on Time-Cost relationship were obtained from contract administration documents prepared by consulting Quantity Surveyors who had been professionally involved in delivering the buildings under consideration.
5.3. Sampling Size
- Time-cost relationship data for 30 building projects were obtained, along with the retrieval of 30 questionnaires which were administered to the owners of the buildings under consideration.
5.4. Sampling Technique
- The study area, Abuja, is made up of six area councils namely; Abaji Area Council, Abuja Municipal Area Council, Bwari Area Council, Gwagwalada Area Council, Kuje Area Council and Kwali Area Council. For the purpose of this study, the research considered each area council as a separate cluster, irrespective of size; five building projects were drawn from each of the area councils. The samples eventually collected were randomly picked, based on the requirement that each item in the population studied has equal chances of being selected.
5.5. Research Instruments
- Time-Cost data required for this research was collected in a tabular form; column headings included information such as project name, location, initial contract sum, final cost and duration of the selected projects. The cost-quality data required for this study was gathered through the use of self administered questionnaire, which were designed in a structured manner.
5.6. Method of Data Analysis
- The method adopted in analyzing the data obtained for this research is the descriptive method of data analysis. Time-Cost relationship data obtained from consulting Quantity Surveyors for the selected building projects were subjected to the time-cost relationship model developed by Ogunsemi and Jagboro [24] which was stated as;
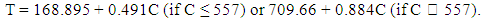 where:T = effective project duration (time) in relation to a given cost from date of site possession to practical completion, given in working days.C = cost of the project given in millions of Naira.To achieve Objective One of this paper, the model was used to calculate the effective time (T) required to execute each of the sampled projects at a given cost.To achieve Objective Two, the difference between the computed effective project duration (T) and the actual project duration (t) will be determined by subtraction, and then converted to percentage in relation to the value of (T).
where:T = effective project duration (time) in relation to a given cost from date of site possession to practical completion, given in working days.C = cost of the project given in millions of Naira.To achieve Objective One of this paper, the model was used to calculate the effective time (T) required to execute each of the sampled projects at a given cost.To achieve Objective Two, the difference between the computed effective project duration (T) and the actual project duration (t) will be determined by subtraction, and then converted to percentage in relation to the value of (T).6. Data Analysis and Discussion of Results
- This study went beyond what was available in previous research by categorizing projects into those completed before planned durations and those completed after planned durations. About half of the projects (14 in number) had experienced time underrun, while sixteen projects had been involved with time overrun. From the statistics presented in Table 2, sixteen projects were completed at durations that exceeded planned or expected periods of time; the average extra time required for project completion was 34.2%, with a standard deviation of 22.2%. Published records of previous research on time-cost relationship of private building projects in Abuja are thin; the result obtained compares well with that of Odusami and Olusanya [25] in which construction projects in the Lagos metropolitan area suffered an average delay of 51% of the planned duration.Table 2 also revealed that fourteen out of the thirty projects sampled were completed in less than the expected duration. An average time underrun of 43.0% was observed in this case. From this result, it was adduced that in the execution of private building projects in Abuja, up to 43.0% of the planned time could be saved. In other words, some private building projects take only 57% of the required time to complete in Abuja, representing a time saving of 43%.
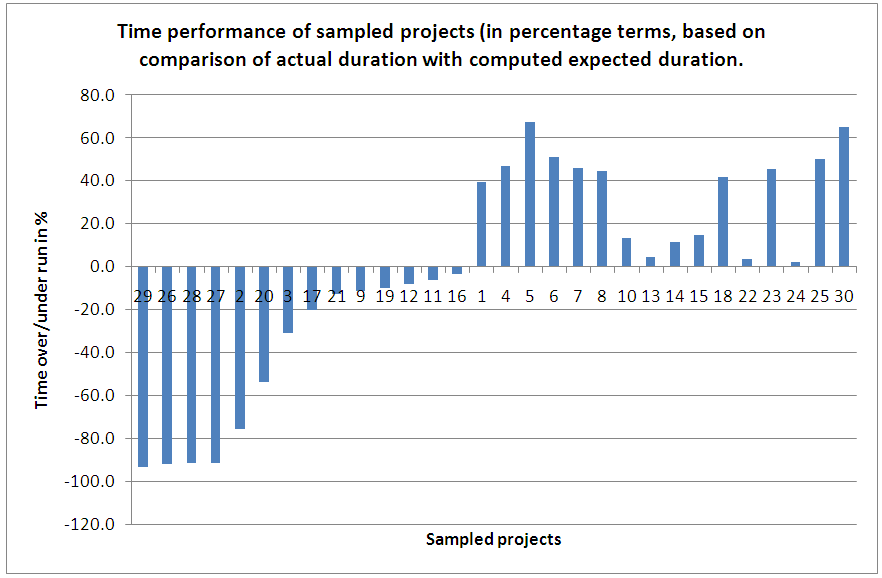 | Figure 5. Time performance of private building projects in Abuja |
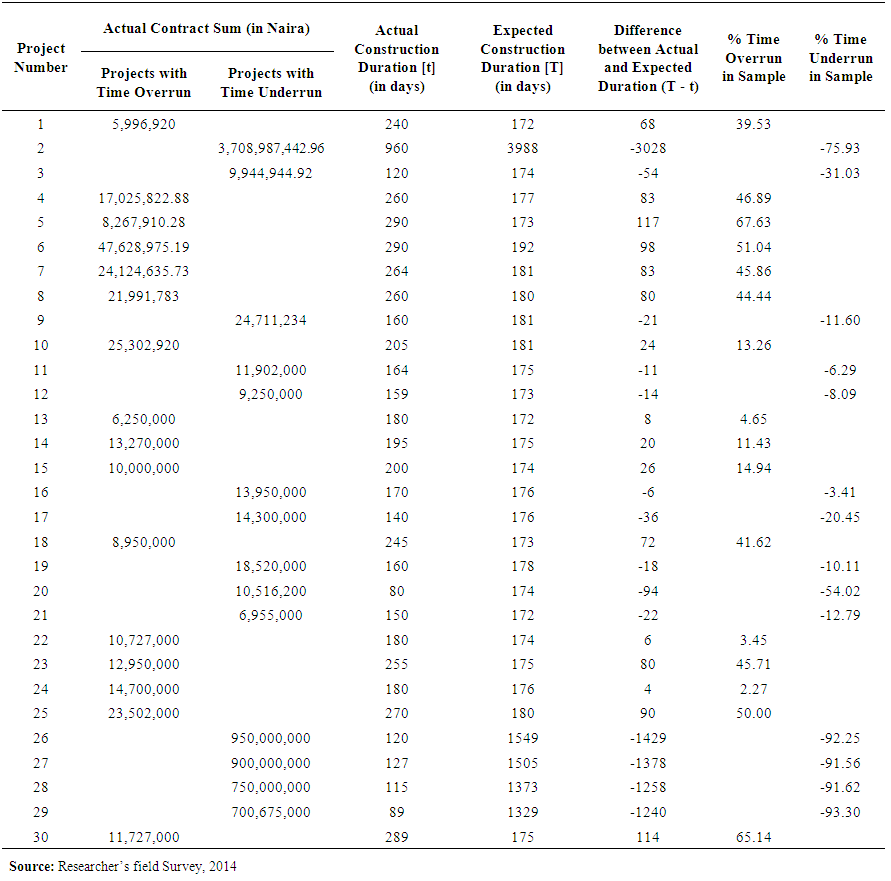 | Table 1. Comparison of Actual and Expected Construction Durations |
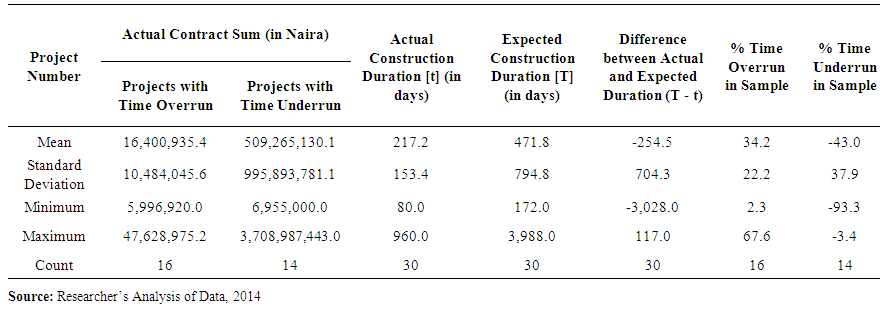 | Table 2. Key Statistics associated with Actual and Expected Construction Durations |
7. Conclusions
- Review of previous research has shown that the balancing of time, cost and quality expectations in the execution of building projects has always been a challenge. There are records of projects executed at a cost far higher than expected. Others suffer high percentage of delay whereas relatively less attention has been paid to quality deviations.This paper has applied the Ogunsemi and Jagboro [24] time-cost relationship model in determining the expected durations of 30 building projects; the differences between the actual durations of the projects and the expected durations were also computed. The mean time overrun was found to be 34%, while a corresponding value of 43% was computed as the mean time underrun (or time saving). In the light of previous research, the average time overrun of 34% discovered represents an improvement in the time-cost relationship for building projects. This is because the level of time overrun in previous works was 51%, thus a reduction of 17% (51% minus 34%) implies an improvement in the management of the time-cost relationship. Another significance of the findings in this paper is the discovery that up to 43% savings were realized in the planned durations of some construction projects. One of the questions that remain in this area include what differences between projects account for why overrun/underrun in time occur.
8. Recommendations
- Based on the research carried out, the following recommendation was made;1. In executing private building projects in Abuja, the time-cost relationship maintained in recent times appears to be effective, going by the reduction in the level of time overrun previously documented. It was therefore recommended that this should be continuously maintained and improved upon.2. Additional attention is required in the areas of time-cost relationship for large private building projects in Abuja. This was necessitated by the discovery that cost underrun occurred predominantly on large projects. Further research in this direction would provide explanations for the behavior of the time-cost relationship in these cases.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The effort of Mr. Loya Osusha Samuel who helped to supply the data used in this research paper is gratefully acknowledged.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML