-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Biological Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1875 e-ISSN: 2163-1883
2013; 3(1): 1-10
doi:10.5923/j.ijbe.20130301.01
Modulation of Reporter EGFP Gene Expression by a Disease-Associated Human Intra-Intronic Minisatellite Upon Transient and Stable Transfection
L. K. Sasina1, E. M. Fedorova1, 2, N. A. Grudinina1, E. V. Belotserkovskaya1, K. V. Solovyov1, I. O. Suchkova1, E. L. Patkin1
1Department of Molecular Genetics, Institute of Experimental Medicine of the NorthWest Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, akad.Pavlov str.,12, 197376, St.Petersburg, Russia
2Pavlov Institute of Physiology, Russian Academy of Sciences, St.Petersburg, Russia
Correspondence to: E. L. Patkin, Department of Molecular Genetics, Institute of Experimental Medicine of the NorthWest Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, akad.Pavlov str.,12, 197376, St.Petersburg, Russia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Currently, our understanding of associations between minisatellite polymorphisms and diseases is far from clear. This is in part due to great differences in human and animal minisatellite structure. Thus, here we have used plasmids which contained the reporter gene EGFP under eukaryotic promoter ROSA26, and different allelles of human minisatellite UPS29 for both transient and stable transfection of F9 cells induced to differentiate, but not terminally differentiated, to establish whether the minisatellite would be capable of affecting expression of EGFP in the episomal state and in a closer to “native” chromatin environment. Upon transient transfection, we found enhanced reporter gene expression for constructs with minisatellite alleles inserts. By contrast, in cells that were stably transfected UPS29 alleles suppressed reporter construct expression compared to controls with no inserted UPS29 allele. The most prominent effect was observed for the shortest UPS29 allele associated with diseases. For stably transfected cell lines, integrated transgene copy number and some epigenetic characteristics of nuclei in situ did not differ among constructs containing different UPS29 alleles. The enhancer effect seen with transient transfection is speculated to be due to accessibility to specific transcription factors. The suppressive effect seen in stable transfectants might be determined mainly by methylation of minisatellite sequences rather than by peculiarities of host genome.
Keywords: Tandem Repeats, EGFP Gene Expression, Embryonal Carcinoma Cell Line F9, Modulation of Expression, DNA Methylation, Heterochromatin, FISH, Transient and Stable Transfection
Cite this paper: L. K. Sasina, E. M. Fedorova, N. A. Grudinina, E. V. Belotserkovskaya, K. V. Solovyov, I. O. Suchkova, E. L. Patkin, Modulation of Reporter EGFP Gene Expression by a Disease-Associated Human Intra-Intronic Minisatellite Upon Transient and Stable Transfection, International Journal of Biological Engineering, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 1-10. doi: 10.5923/j.ijbe.20130301.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- To date it has been established that some DNA polymorphisms, which are localized in non-protein coding sequences and do not influence protein structure, are nevertheless risk factors for several neurological, neurodegenerative and mental diseases [1]. It was shown that such polymorphisms may influence gene expression depending on tissue type and specific endogenous and/or exogenous stimuli[2-4]. Functional significance of such polymorphic DNA can be connected with genetic susceptibility to the specific disease and with individual sensitivity to pharmacological agents and exogenous factors[5-7]. This implies that individuals with various haplotypes of polymorphisms can respond differently to the same medication or external stresses. Thus, it is important to search and identify specific DNA polymorphisms associated with different diseases, and to elucidate the possible mechanisms of such associations. This may help to elaborate individual medication based on genome peculiarities.In humans, the main part of noncoding DNA polymorphisms consists of tandem repeats, stretches of DNA that are repeated head to tail. Tandem repeats are further classified into “microsatellites,” whose repeated units contain up to 6 nucleotides, and “minisatellites” with longer repeated units, up to 100 bp[8,9]. Multiple evidence suggests that highly polymorphic tandem repeats are often functional and that they contribute to aetiology, severity, and progression of simple and complex disorders, especially neurological ones[1]. Some minisatellites, including Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs)[10,11] or non-highly polymorphic minisatellites[12] play a significant role in transcription regulation, translation efficacy, and mRNA stability. For example, tandem repeats in 3'UTR or introns were found to regulate gene transcription[13]. Such regulating activity was demonstrated to be the result of specific binding of several transcription factors to tandem repeated sequences[4, 14]. Repeats may also function as common target sites for regulatory mechanisms involved in the packaging and dynamic compartmentalization of the chromatin into active and inactive regions[15]. Besides, it was recently shown that DNA polymorphisms in promoter and intronic regions of several genes act cooperatively to regulate their transcription[16]. The specific function of some transcription factors in such cooperation was also established[17]. Earlier we demonstrated a shift in different alleles frequency of VNTR minisatellite UPS29 localized in intron 14-15 of centaurin beta 5 gene (ACAP3, former name CENTB5) for patients with different forms of Parkinson's disease (PD) and epilepsy[18]. In healthy individuals this polymorphism exists in the form of seven alleles containing 6, 8, 9, 10, 14, 17 and 24 repeat units with the major allele of 17 repeats (91.5%). The frequency of other alleles (mainly of short ones) varied from 0.3% to 4.4%. A statistically significant increase in the frequency of rare UPS29 short alleles (6-8 units) was observed for females but only in case of early (30–50 years old) and late (> 60 years old) onset of Parkinson's disease and for epilepsy patients. Thus, we found an association of short minisatellite alleles with mentioned pathologies However, any association study gives no explanation of observed statistical dependence. For example, it remains unclear the such important issue as increase or decreased gene expression takes place for different alleles of non-protein coding minisatellites. It is very difficult to study directly such processes in human brain. So it is reasonable to use various models, such as laboratory animals. However, an additional problem is connected with lack of minisatellites in homologous animal genes. Taking into account the above, the main aim of this study was to examine directly the influence of the UPS29 polymorphisms on gene expression in a reporter-gene assay system. We studied quantitatively reporter gene expression depending on different UPS29 alleles upon transient and stable transfection. Transient transfection of different types of cell culture with reporter constructs is widely used, but it is clear that such approach can not mimic natural context, though it is rather simple and fast. Stable transfection is important to establish whether the minisatellite would be capable of affecting transcription in the state more or less resembling “native” or “normal” chromatin environment. Reporter gene constructs were generated containing a 'reporter cassette' which consisted of the EGFP reporter gene under the control of ROSA26 eukaryotic promoter and either without any additional modifications or with the short ("disease") or the long ("healthy") UPS29 allele located upstream of the promoter. Analysis was limited specifically to the minisatellite sequence itself, so that any functional effect detected could be attributed solely to this candidate polymorphism. We have chosen EGFP due to the fact that GFP fluorescence is a reliable and quantitative reporter of underlying differences in gene expression in single cells. [19]. Comparison of transient vs. stable transfection enables evaluation of a relative role of cis- and trans-factors in a potential regulatory function of minisatellite. It was also essential to evaluate possible epigenetical characteristics of stably transfected F9 cells due to well-known modulation of transgene expression by such modifications. Obtained results may be summarized as follows. Upon transient transfection it was found that UPS29 possessed enhancer-like activity compared with control plasmids without minisatellite inserts. In contrast to the results obtained upon transient transfection, after stable transfection integration into host chromosomes resulted in suppressive EGFP expression compared to control plasmids. The most prominent suppressive effect was observed for short “disease” UPS29 allele, ipso facto accordingly to pattern observed in patients with Parkinson’s disease and cryptogenic epilepsy. For all types of reporter plasmids stable transfection has not demonstrated any significant difference in epigenetical characteristics of chromosomes and nuclei with integrated constructs. Thus, suppressive effect is speculated to be determined mainly by minisatellite sequence per se, but not by epigenetical peculiarities of host nuclei and chromosomes. Results of the study point to a potential usage of both types models to elucidate al least partly observed associations of tandem repeats polymorphisms with human disease. Secondly such models might be further used to study the influence of various external compounds (drugs) on modulating function of VNTRs and minisatellites in humans, and their possible role in diseases development.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of UPS29 Reporter Gene Constructs
- To study the potential effect of different alleles on expression, we constructed a reporter system based on the pR26-EGFP vector[20] generously granted by Prof. N.V.Tomilin.Two fragments containing 6 or 17 repeats of UPS29 were amplified with following primers: forward, gtcagaattccgcgagagccctgacagttg, and reverse, tcataagcttcacatgggcagatggtacctgc. The fragment containing the full intron sequence was amplified with the primers: forward, tcataagcttaggctgactccgagaagctg, and reverse, gtcagaattcgagcactcaatgcagagcag. Resulting products were 400, 900 and 1500 bp, correspondingly.Obtained fragments were inserted into multiple cloning site of the pR26-EGFP vector between HindIII/EcoRI sites upstream ROSA26 promoter (Fig. 1).
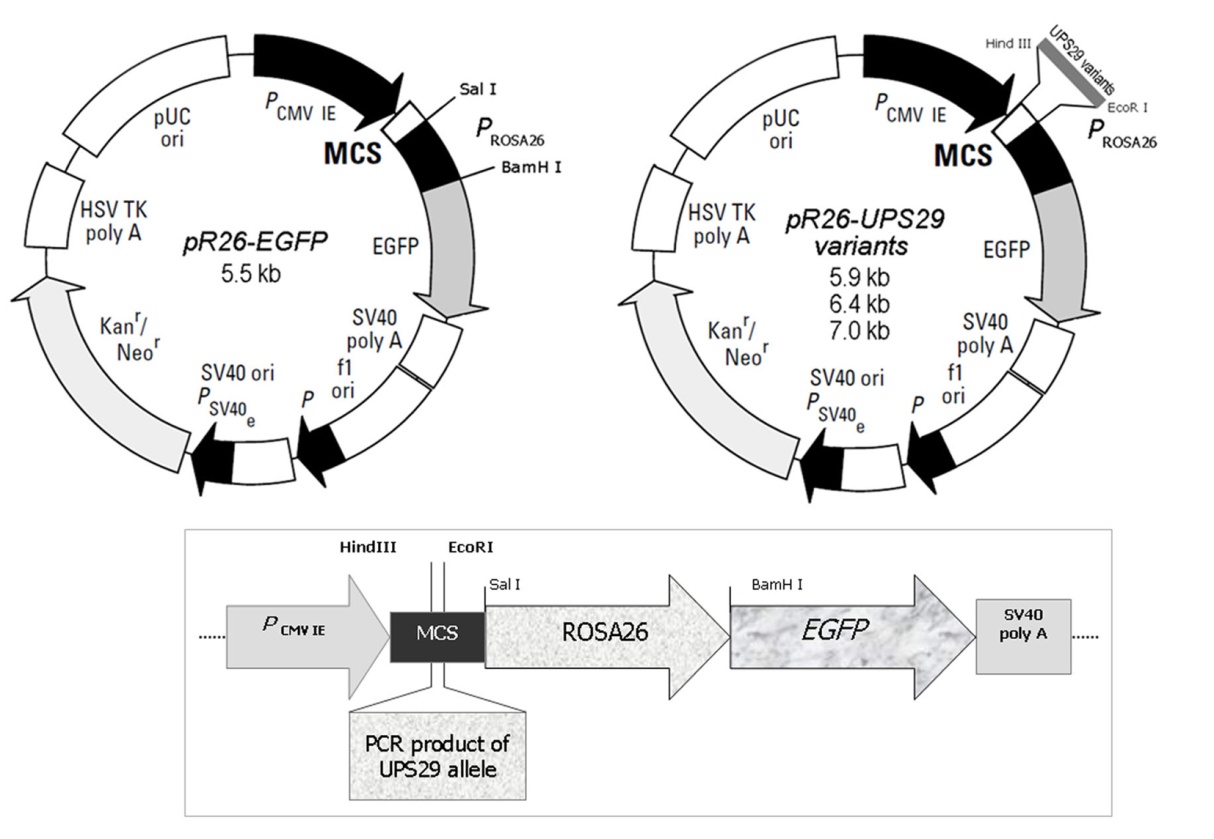 | Figure 1. The map of the vectors used in the present study and the site of the the insert cloning |
2.2. Cell Cultures, Transient and Stable Transfections
- Studies were conducted on undifferentiated or induced to differentiation cells of mouse embryonal carcinoma cell line F9. F9 cell lines were obtained from the Russian bank of cell cultures of The Institute of Cytology of Russia, RAS. Primary rat astrocytes cultures were obtained according to[21]. All stock cultures were cultivated in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS in 6-well plates (Orange Scientific, Belgium) or in 25 cm2 cultural flasks (Jet Biofil, Canada) in 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C. For F9 cells the wells were coated with 0.2% gelatin, and 3.6 g/L HEPES was added for primary rat astrocytes cultures. Cultivation time was 16 hours for F9 cells. Differentiation of F9 EC cells was induced by a 3-day treatment with retinoic acid and dibutyryl cAMP as described earlier[22]. In preliminary experiments, plasmids were linearized before transfection with SalI, but we found no significant differences in transfection efficiencies compared to circular plasmids. Consequently, plasmids were not linearized in the experiments described here. All transfections were carried out at the confluence of 60-70% with 2.5 μg of plasmid DNA using TransFastTM Transfection Reagent (Promega, USA) according to manufacturer's protocol. All transfection experiments were repeated at least three times. Stable transfections of F9 cells were performed with all variants of the vector (carrying 6 or 17 repeats or the full intron), and the cells were subjected to antibiotic selection (400 g/ml G-418[Invitrogen] or 1 g/ml puromycin[Sigma-Aldrich]) 24–48 hours after transfection. Distinct antibiotic-resistant individual colonies appeared after 72-144 h of incubation. For each insert at least five independent stable transfections were performed. For the control, transfections with the pR26-EGFP vector without a UPS29 insert were carried out. Selected stably transfected cells were seeded on coverslips for in situ hybridization and analysis.
2.3. Determination of Copy Number of Integrated Plasmids
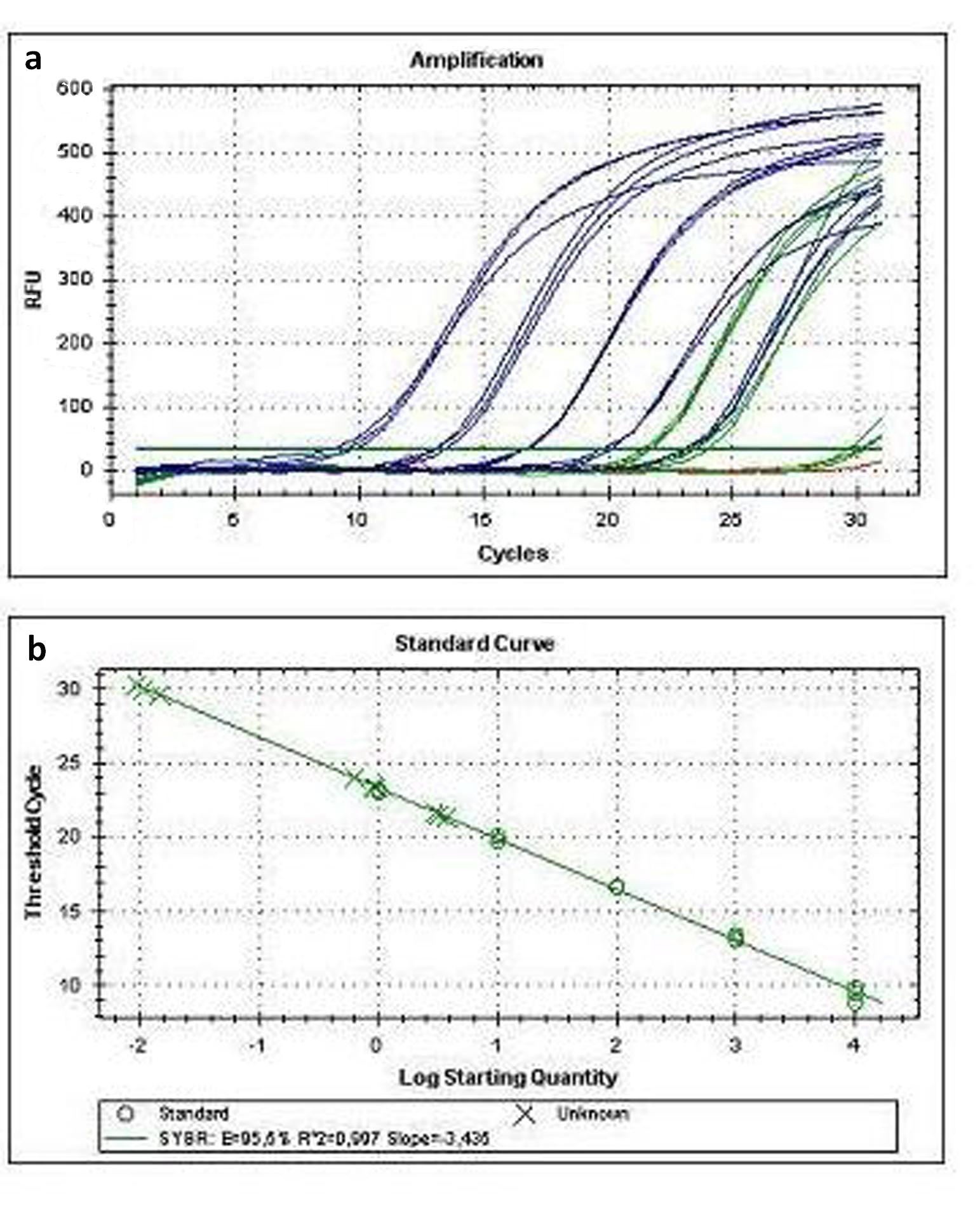
- Since during stable transfection GFP fluorescence increases in direct proportion to the copy number of the reporter gene delivered to cells[19], it was necessary to evaluate the number of integrated copies of the plasmid to avoid misinterpretation of results.DNA was extracted from transfected embryonal carcinoma F9 cells with phenol-chloroform method. Copy number of the plasmid was estimated with Real-Time Quantitative PCR on two targets: the EGFP gene and the UPS29 insert. The primers for EGFP were: forward, cagccgctaccccgaccaca; reverse, cgctgccgtcctcgatgttg, the resulting product was 314 bp. For the UPS29 insert were used the same primers as for the cloning (see above).PCR was performed using SYBR Green PCR Kit (QIAGEN) at following conditions: 15 pmol of each primers, 25 ng of DNA, the final volume of 14 μl; denaturation at 95°C for 15 min, followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 20 s for EGFP (30 s for UPS29), annealing at 61°C for 20 s (57°C for 30 s) and extension at 72°C for 40 s (80 s). Each sample was assayed in triplicate including non-template controls. All assays were conducted using CFX96 thermal cycler (Bio-Rad). Amplification efficiencies (E) were calculated according to the equation E =[10(-1/slope) - 1]. Amplification efficiencies for EGFP and UPS29 were 99% and 90%, respectively.Copy number of EGFP was evaluated with a standard curve generated by Ct values for 5 DNA standard concentrations with 10-fold dilution starting at 1 copy of the corresponding vector DNA per genome. Baselines and thresholds were automatically set by the BioRad software.
2.4. Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization (FISH)
- FISH was performed on stably transfected cells as described[23] with minor modifications described below. Cells were fixed either with ice-cold methanol/acetic acid (3:1) after hypotonic treatment (2D FISH) or with 3.7% formaldehyde in 1xPBS for 10 min at room temperature (3D FISH).As a probe we used the pR26-EGFP plasmid labeled with digoxigenin-dUTP by nick-translation. Hybridization mix contained 3 μl of the probe, 0.6 μl of salmon sperm DNA and 27 μl of hybridization buffer (50% formamide/20% dextran sulfate in 2xSSC). The mix was incubated at room temperature for 10 minutes prior to use, then applied to the preparation and sealed with rubber glue. After 15 min of incubation at room temperature slides were denatured for 3 min at 80°C and hybridized overnight at 37°C. The probe was detected with anti-digoxigenin Rhodamine-conjugated antibodies (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Germany). DNA was counterstained with DAPI (0,5 μg/ml) and cells were mounted in Vectashield (Vector Laboratories Ltd, UK). As a negative control we used untransfected F9 cells.
2.5. Fluorescence Intensity Analysis
- Intensity of the GFP fluorescence was measured as follows: a single cell was selected on the Tiff image of Z-projection and the total area fluorescence was measured with Analyze/Histogram tool of the ImageJ software. An area of same size in the background next to the cell was measured in the same way and its intensity value was extracted from the result of the first measurement. Obtained relative value (in arbitrary units) was placed into a Microsoft Excel sheet. This operation was repeated for at least 1000 cells for each transfection.
2.6. Epigenetical Evaluation of Stably Transfected F9 Cells
- In situ immunodetection of 5-Methylcytosine was carried out according[24]. All slides were counterstaind with DAPI to visualize the DNA and heterochromatin blocks.. Revealing of DNMT1 activity in situ was conducted as descibed earlier[23]. All slides were counterstaind with DAPI to visualize the DNA and heterochromatin blocks.
2.7. Image Acquisition
- Confocal imaging was performed with a Carl Zeiss LSM 510 Meta inverted confocal laser-scanning microscope using the Zeiss LSM 510 software. We used a Plan Achromat 63x oil objective (NA 1.4). Voxel size was 0.10 x 0.10 x 0.5 um. Imaging was performed at room temperature. Bright-field images represent DIC reconstruction done by the LSM software. Images were stored as the series of Z-sections in LSM database format with conversion to Tiff-file series later. Images were analyzed using the ImageJ software version 1.44p (http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/).
2.8. Result Representation and Statistical Analysis
- Representation of numerical data and statistical analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel and integrated tools. Unless otherwise indicated, all data are presented as the mean ± SEM.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. EGFP Activity in Transiently Transfected Cells
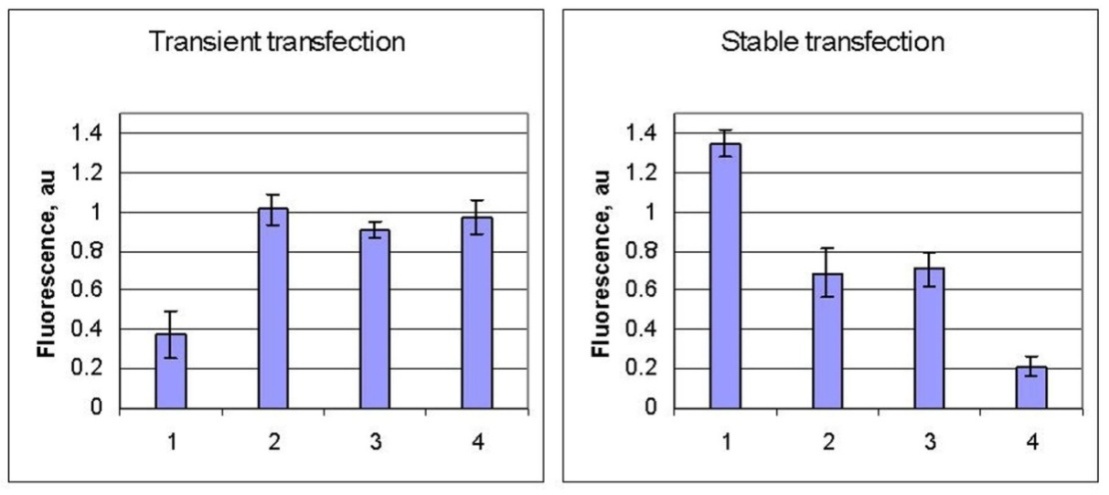
- The effect of the analyzed UPS29 inserts on the reporter gene expression was at first assessed by counting the number of fluorescent cells in cultures of transiently transfected undifferentiated and differentiated F9 cells. Quantitative analysis of transient transfection in differentiated F9 cells confirmed above mentioned enhancing effect of UPS29 inserts without a significant difference between analyzed UPS29 variants (Fig.2, left).
3.2. EGFP Activity in Stably Transfected Cells
- In order to know if the minisatellite would be able to affect transcription in vivo we determined whether the reporter gene was transcriptionally active in a chromatin environment. Results of stable transfections of differentiated F9 cells with the four plasmids were at variance with the results of transient transfections with the same constructs. The most striking difference lies in the fact that integration into the host genome of plasmids with minisatellite UPS29 alleles resulted in decreased fluorescence intensity compared to control plasmids. Also, the most prominent declining was observed for cells with the short ("disease") UPS29 allele insert (Fig 2, right).
3.3. Copy Number and Transgene Stability
- The number of integrated pR26-UPS29 plasmids, evaluated with qPCR for two DNA targets (i.e. EFGP and UPS29) in various passages of transfected F9 cells, revealed that cells of the first passage contained an average of 3 copies per genome, whereas already after the third passage the number of copies became 1 copy per genome and this was observed for all repeated transfections (Fig. 3). Thus, since the number of integrated copies did not differ between the plasmids variants used, a possibility that the GFP fluorescence intensity depends on the number of integrated copies may be excluded. Also, presence of both PCR products in each cell line indicates a complete integration of pR26 based plasmids in transfected cells.Transfection was stably preserved in selected clones for at least 10 passages. However, in all F9 cells carrying modified pR26 EGFP expression slowly fell with time, while PCR analysis revealed the presence of EGFP DNA in all the cells derived from the initially EGFP-expressing clones. This implies that the loss of the reporter gene expression might be attributed to progressive gene silencing and possible rearrangements of the transgene.
3.4. Epigenetical Characterization of Stably Transfected F9 Cells
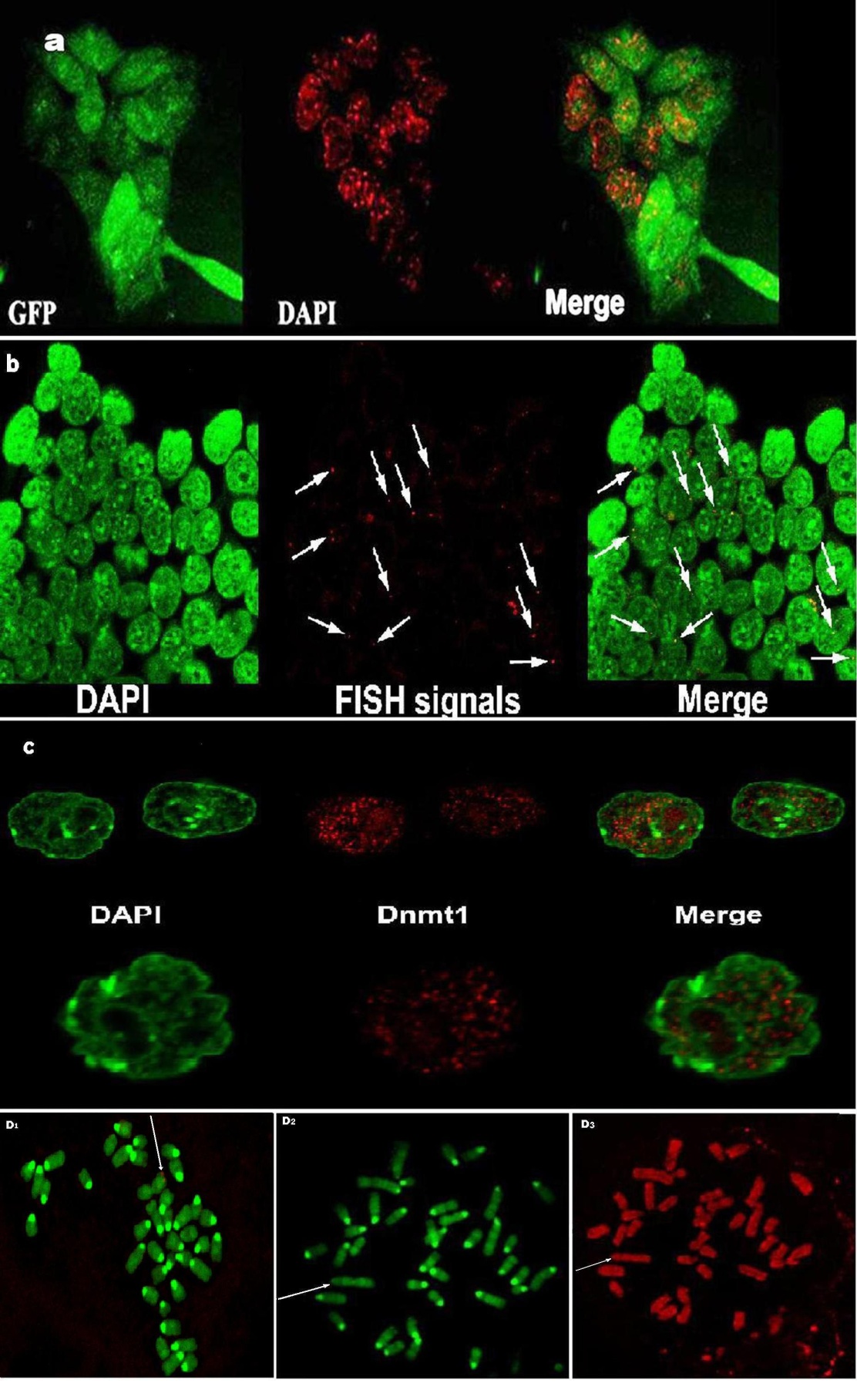
- Results of epigenetical analysis and FISH are summarized in Figure 4a,b,c,d. One of the factors affecting transgene expression is the site of the vector construct integration into the genome. In our case it could be a significant issue, since integration of a transgene upon transfection is stochastic and thus the probability of integration into the same locus in repeated experiments is almost zero as we had only a single integration per genome. We found reverse correlation between number of heterochromatin blocks and intensity of EGFP fluorescence (Fig. 4a), but FISH signals were localized more or less stochastically inside nuclei of transfected F9 cells (Fig. 4b). Results of immunodetection of 5-Methylcytosine and DNMT1 in nuclei of stably transfected induced to differentiation F9 cells are shown in Figures 4c,d. These data show that F9 cells are characterized by rather high activity of maintenance methylase DNMT1 (Fig. 4 c). This is confirmed by labeling of 5-methylacytosine in nuclei and chromosomes with specific antibody against 5-Methylcytosine (Fig. 4d). We did not observe any significant difference between cells transfected with different constructs which contained UPS29 alleles. As was above mentioned suppressive effect could be determined by integration into heterochromatin or near it. However at least in one of obtained stable clones the plasmid with 900bp UPS29 insert, integrated into telomeric euchromatic locus of the metacentric marker chromosome of F9 (Fig. 4d1), but mentioned reverse correlation was found for all clones. It is noteworthy that this locus was nevertheless methylated in such metacentric chromosomes in all clones (Fig. 4d3,4).
3.5. Discussion
- The potential for varying number of repeat elements of UPS29 minisatellite to support or suppress reporter gene expression was assessed by transient and stable transfection of induced to differentiation and undifferentiated mouse embryonic carcinoma F9 cells using appropriate EGFP expression plasmids. Upon transient transfection, we observed an enhancing effect of all tested UPS29 alleles on EGFP expression in F9 cell, compared to control plasmids. To explain this effect, it is necessary to take into account that during transient transfection naked plasmid DNA, containing minisatellite tandem repeats, and especially GC-rich repeats like UPS29, may fold into non-canonical structures such as cruciforms/hairpins, triplexes, slipped conformations, quadruplexes, and left-handed Z-DNA[25,26]. In turn, such non-canonical DNA structure may serve as a binding site for TF, for example SP1[27]. Indeed, neuron-specific enhancing was shown earlier for VNTR from 3’UTR and introns of the human dopamine transporter gene[28,29] and of the serotonin transporter gene in vitro[3] and in vivo[2]. Such enhancer activity was shown to result from VNTR-specific binding of several cell-specific transcription factors[4,17]. To evaluate effects of the UPS29 minisatellite on the reporter gene expression in conditions resembling “natural” genome environment, we performed stable transfection of F9 cells with constructs enclosed different alleles of UPS29. In contrast to transient transfection, we observed a suppressive effect of all used UPS29 variants on EGFP fluorescence compared to control. The most prominent decrease was found in cells transfected with the short "disease" insert (6 repeats). Thus, all minisatellite inserts suppressed fluorescence, and additionally differed in their suppressive capabilities. Why there was observed suppressing and not enhancing effect upon stable compared to transient transfection? What determined different suppressive effect between allelic variant inserts in plasmid? In theory, such suppressive effect could be a result of several probably interrelated reasons. Firstly, it could be dictated by number of integrated transgene copies[30]. Secondly, integration into or near to heterochromatin regions, and localization of transgene near nucleus border are also well-known reasons of suppression of transgene expression[31-33]. For example, we earlier showed that Integration of transgene consisted of minisatellite could induce heterochromatinization de novo[34]. This effect might have been also caused by a complete or partial methylation of the insert. Indeed, it is known that many transgenes undergo substantial methylation de novo upon integration in F9 and stem cells genomes[34, 35] Moreover, transgene integration was shown to induce methylation not only of the transgene per se, but also of the adjacent regions of the host genome[36]. In turn, methylation will likely result in a decrease of the reporter gene expression or even in its complete suppression, possibly by formation of “closed” chromatin conformation [37]. So, it was reasonable to check above mentioned markers to try to understand, whether observed suppressive effect was determined by the integration into specific domain of host genome or was connected with peculiarities of tandem repeat per se inside construct. We did not observe any difference in number of integrated transgene copies between control and between cultures with different allele inserts in constructs. In all cases there was once copy of transgene after three passages. Here we did not find any spatial association between the integration site and heterochromatin domains, Thus, heterochromatin and heterochromatinization most likely were not the reason for observed decrease in the EGFP fluorescence intensity. Moreover, it is interesting that FISH showed the localization of transgene in euchromatic telomeric region of marker translocated chromosome for one of stable clones. That clone had integrated plasmide with minisatellite insert (900 bp), and demonstrated decreased EGFP fluorescence. In situ methylation analysis showed that such marker chromosomes in different clones were nevertheless stained by monoclonal antibodies against 5-methylcytosine in their subtelomeric regions. This also points to relative independence of suppressive effect on heterochromatinization of transgenes, and suggests that the role of DNA methylation must be considered. It is important, that the main varying factors, such as differences between the cell batches used, the number of integrations per genome or localization of integration sites were equalized by repeating at least five independent transfections for each vector. Taken together epigenetical analysis of nuclei and chromosomes following stable transfection indicates crucial role of different UPS29 alleles sequence and their modifications, but not nuclear environment in observed suppressive effect of EGFP fluorescence. What peculiarities of this minisatellite could lead to this effect? As was mentioned before, the DNA binding of some transcription factors is sensitive to the local methylation state inside chromatin. So, level of methylation can affect their binding to the target DNA. Each repeat of UPS29 has at least three potential sites for methylation. It was shown by Down and coauthors (2008), that at least in mature spermatocytes cytosine methylation level was unequal in different repeat units of this minisatellite and that internal repeats were methylated weaker than terminal ones[38]. Short alleles of UPS29 lack namely internal repeats compared to the long allele. As a result, it is possible that a short minisatellite variant will have all its CpG sites methylated. This may at least partly explain the observed difference in the reporter gene expression between the alleles. Besides this, the complete silencing might be explained by recombination of the adjacent regions in the transgene due to the presence of repeated units. This supposition is based on the fact that, in one of the lines transfected with long allele of 17 repeats a subpopulation of cells, carrying the intermediate 12 repeats cassette, was detected (results are not shown here). Such rearrangement could affect or disturb the promoter activity leading to the absence of EGFP expression, though, the EGFP gene itself was still integrated in the genome of transfected cells. Further experiments are necessary to elucidate this question. Determination of integration site and transgene methylation per se are necessary for more definite conclusions. The supposed here role of minisatellite methylation in gene modulation could be connected with natural human context. Indeed, age-dependent accumulation of DNA methylation was shown for several genes[39,40]. So, it can be possible that such progressive methylation of UPS29 repeats during life will affect the level of ACAP3 gene expression. This will lead to decrease of centaurin beta 5 level and to age-dependent development of Parkinson's and Alzheimer diseases. If it is the case, people whose genome contains short alleles of the minisatellite will be more predisposed to disease development upon ageing. Besides this, the presence of source of methyl groups in diet could also influence of development and progression of disease. Sure, this supposition needs further evidences. Similar mechanisms may also operate for other genes containing tandem repeats in introns.
4. Conclusions
- In the present study we identified the effects of long and short alleles of minisatellite UPS29 on the reporter gene expression and found that upon transient transfection there was an enhancing effect independently on insert length. However, upon stable integration to the genome the minisatellite demonstrated clear suppressive and length-dependent effect, with the short allele being most effective. We propose a methylation-related mechanism of observed effect during integration into the mouse genome and believe that similar mechanism plays a role in natural environment in the human genome. We could not evaluate this directly using animal as model organism. The main problem is connected with the lack of analogous minisatellite in genome of any laboratory animal. For example, the mouse genome does not contain this minisatellite, which is instead replaced by a microsatellite in the corresponding intron of homologous centb5 gene. Results of the study point to a potential usage of transient and stable transfection models to elucidate, frequently observed associations of tandem repeat polymorphisms with human disease. However, it seems that it is necessary to use appropriate type of model depending on specific aim. Secondly such models might be further used to study the influence of various external compounds (drugs) on modulating function of VNTR and minisatellites in humans, and their possible role in diseases development.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This study was supported by grants from Russian Foundation for Basic Research (Projects № 11-04-00254).
Abbreviations
- DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DMEM, Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium; EC, embryonal carcinoma; FBS, fetal bovine serum; FISH, Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization;EGFP,enhanced green fluorescent protein; HEPES, 2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethanesulfonic acid; PD, Parkinson's disease; UTR, untranslated region; VNTR, variable number tandem repeats
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML