-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Biological Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1875 e-ISSN: 2163-1883
2011; 1(1): 11-17
doi: 10.5923/j.ijbe.20110101.03
Bioextraction of Cu (II) Ions from Acid Mine Drainage by Bacillus Thuringiensis
Reza Marandi
Department of Environmental Engineering, Islamic Azad University, North Tehran Branch, Tehran, Iran
Correspondence to: Reza Marandi , Department of Environmental Engineering, Islamic Azad University, North Tehran Branch, Tehran, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In this study, biosorption of Cu and Mn ions from Sarcheshme copper mine wastewater by a locally available bacterium, Bacillus Thuringiensis, was investigated in batch mode. Optimum amounts for various parameters such as contact time, pH, initial ion concentration, biosorbent dosage and temperature were determined. In the first 30 minutes, most of Cu and Mn ions were removed by the sorbent. Optimum pH and temperature were determined to be 6 and 308৹K. The experimental data were fitted to both Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption models. Desorption studies showed that bacterial biomass can be eluted by 1M HCL solution and reused in five biosorption-desorption cycles.
Keywords: Biosorptoin, Cu and Mn ions, Bacillus Thuringiensis, Bioextraction, Acid Mine Drainage
Cite this paper: Reza Marandi , "Bioextraction of Cu (II) Ions from Acid Mine Drainage by Bacillus Thuringiensis", International Journal of Biological Engineering, Vol. 1 No. 1, 2011, pp. 11-17. doi: 10.5923/j.ijbe.20110101.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Heavy metal ions in wastewater cause serious problems on human health and environment. The main sources of these ions are mining and electroplating. Cu, Mn, Pb, Cr, Zn, Ni, Cd are some metals that these industries discharge into environment. Various conventional treatment methods such as coagulation and flotation[1], reverse osmosis[2], reduc- tion and precipitation[3], adsorption[4], ion exchange, mem- brane technologies and electrolysis[5] have been used so far. Most of these methods are expensive or ineffective especial- ly when the metal concentration is less than 100 ppm[6]. Some generate secondary wastes and toxic sludge that also need other treatments[7].Biosorption is known as an alternative method for removing heavy metals from soil and water. Metal cations can be absorbed by living and nonliving biomass. Various kinds of biosorbents have been used including: Bacteria[8- 10], yeast[11], fungi[12-14] and algae[15-17]. Bacteria are the most abundant and versatile of microorganisms [biotech] and are used as biosorbents because of their small size, their ubiquity, their ability to grow under controlled conditions, and their resilience to a wide range of environmental situations[18]. Bacteria species such as Bacillus, Pseudo- monas, Streptomyces, Escherichia, Micrococcus, etc, have been tested for uptake metals or organics[19]. In literature, there are several reports showing that Bacillus Sp. Is an appropriate sorbent of heavy metal ions. Some studies are listed in table 1.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Biosorbent
- Sarcheshme mine`s wastewater was transferred to a microbiology lab under sterile condition and Bacillus Thuringiensis was isolated by pour plate method. Bacterial biomass was cultivated in nutrient broth medium using the shake flask method as following. Isolated bacteria were inoculated from nutrient plates to 500 ml Erlenmeyer flasks containing 200 ml growth medium. After inoculation, flasks were shaken at 310৹K and 100 rpm for 24 hours. In order to deactivate bacteria, flasks were autoclaved at 393৹K, then centrifuged and culture media was discarded. Remaining biomass was dried at 333৹K oven for 24 hours and then crushed and sieved to obtain homogeneous powder.
2.2. Wastewater Analysis
- Samples from wastewater were collected 4 times with 2 months intervals. They were analyzed and some solute metal ions detected. Table 2 shows concentration of these metals in the first sample.In other samples similar concentrations were detected. As seen in table 2 Cu and Mn had more concentrations than other ions. So their biosorption was investigated in this study. Table 3 shows Cu and Mn concentration in all four samples.
2.3. Biosorption Studies
- In order to optimize effective parameters on metal uptake, batch biosorption experiments were performed. In all steps, 200 ml wastewater containing conical flasks, stirred at 100 rpm using an incubator-shaker. The effects of pH, contact time, biosorbent dose and temperature were examined using the first sample of wastewater with Cu and Mn concentration of 5.5 and 8 mg.l-1 respectively. At the end of each experiment the biosorbent was filtered and residual Cu and Mn ions in the filtrate were analyzed by an Atomic Absorption Spectrometer. All the experiments were conducted in triplicate and the average of the measurements were used.Equilibrium uptake (the amount of ion sorbed at equilibrium) was calculated using following equation.
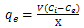 | (1) |
2.3.1. Effect of Contact Time
- To investigate the effect of contact time on Cu and Mn biosorption, samples were drawn at pre-determined time intervals and residual ion concentrations were measured. Other sorption parameters were 6, 1g.l-1 and 308 ৹K for pH, biosorbent concentration and temperature respectively.
2.3.2. Effect of Biosorbent Concentration
- Effect of biosorbent concentration on the value of equilibrium uptake (qe), for Cu and Mn ions was investigated in the range of 1 to 10 g.l-1 at pH 6, temperature 308 ৹K and contact time of 180 minutes.
2.3.3. Effect of pH
- Batch biosorption experiments were done at pH range of 2-6. It was adjusted using NaOH/HCl. Biosorbent dose 1g.l-1, temperature 308 ৹K and contact time 180 minutes.
2.3.4. Effect of Initial Ion Concentration
- Effect of initial ion concentration on biosorption was investigated by contacting 0.1 g.l-1 of biosorbent with 4 samples of wastewater. Cu and Mn initial concentrations are presented in table 3. During the experiment pH, contact time, biosorbent dose and temperature were constant values of 6, 180 minutes, 1g.l-1 and 308 ৹K respectively.
2.3.5. Effect Temperature
- Investigating effect of temperature on biosorption was performed at the thermal range of 298 to 318 ৹K for a contact time of 180 min, biosorbent dose of 1gr.l-1 and pH value of 6.
|
| |||||||||||||||||
2.3.6. Sorption-Desorption Studies
- Sorption- desorption experiments were conducted by taking 200 ml of wastewater on to 0.1g of the sorbent in following conditions; pH=6, temperature 108 °K, stirring time was 180 minutes at 100 rpm. Then it was filtered and residual Cu and Mn ion concentrations in filtrate were measured. Metal loaded biosorbent was shaken at 108 °K with 100 ml of 1M HCL for 30 minutes. Then eluted biomass was extracted and washed with generous amounts of deionized water till neutrality. HCl was analyzed for Cu and Mn ions. Another 4 sorption –desorption cycles were done to investigate reusability of the bacterial sorbent.
3. Results and Discussion
- Fig. 1 shows the effect of contact time on Cu and Mn uptake by the bacteria. It is seen that the sorption capacity of the sorbent increased with an increase in time for both metals.
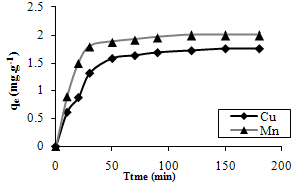 | Figure 1. The effect of contact time on biosorption of Cu and Mn ions. |
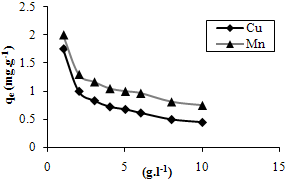 | Figure 2. The effect of biosorbent concentration on biosorption of Cu and Mn ions. |
3.2. Effect of Biosorbent Concentration
- By increasing biosorbent dosage, ion uptake per unit weight of the sorbent (qe), was decreased for both metals (fig. 2). Increasing biosorbent dosage may result in more biosorbent surface area and more available adsorption sites. These sites remain unsaturated during biosorption process so equilibrium uptake decreases by increasing biosorbent dose[30].
3.3. Effect of pH
- Among factors influencing biosorption, pH strongly determines the speciation and biosorption availability of the metal ions and seems to affect the solution chemistry of metals and the activity of functional groups of the biomass [31,32]. The charge of the adsorbate and adsorbent often depend on pH of the solution.In literature during the biosorption of metal ions by bacterial biomass pH 3 to 6 has been found favorable for biosorption due to the negatively charged carboxyl groups which are responsible for the binding metal cations via ion exchange mechanisms[33].The effect of wastewater pH on biosorption is shown in fig. 2. The low metal uptake under pH 3 is due to high concentration of hydrogen ions and competition for binding to the active sites by metal ions and H+ in the wastewater.
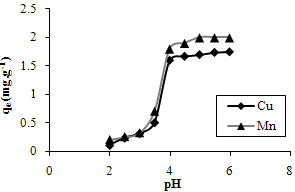 | Figure 3. The effect of wastewater pH on biosorption of Cu and Mn ions |
3.4. Effect of Initial Ion Concentration in Wastewater
- The initial ion concentration plays an important role in biosorption. Figs. (3 to 4) exhibit that the equilibrium uptake increased by increasing initial ion concentrations for both Cu and Mn ions. Higher amounts of metal ions in wastewater increased the contact probabibility between these ions and active binding sites on the surface of the biosorbent and subsequently enhanced the metal removal.
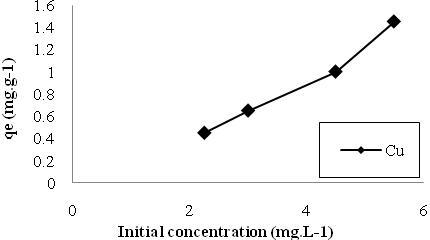 | Figure 4. The effect of initial ion concentrations on biosorption of Cu. |
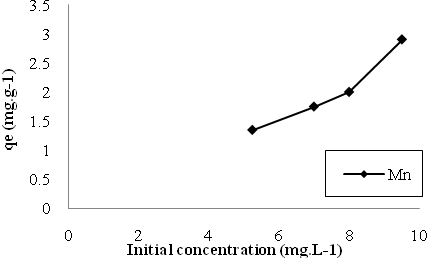 | Figure 5. The effect of initial ion concentrations on biosorption of Mn. |
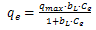 | (2) |
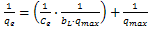 | (3) |
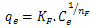 | (4) |
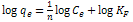 | (5) |
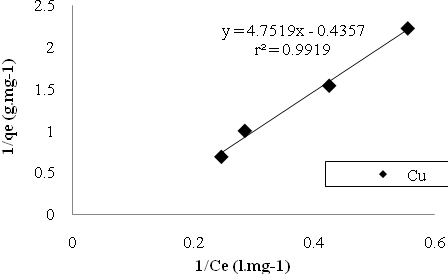 | Figure 6. Cu sorption isotherms based on the Langmuir model. |
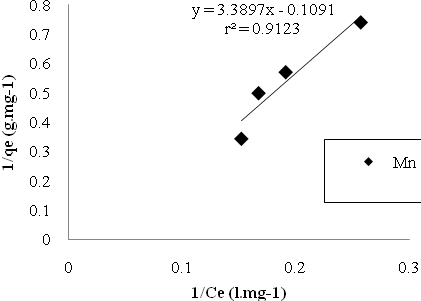 | Figure 7. Mn sorption isotherms based on the Langmuir model. |
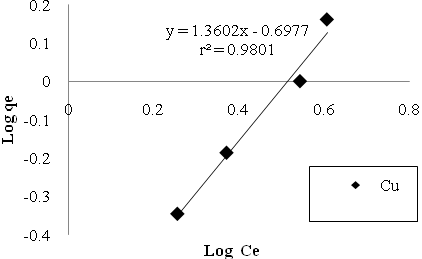 | Figure 8. Cu sorption isotherms based on the Freundlich model. |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
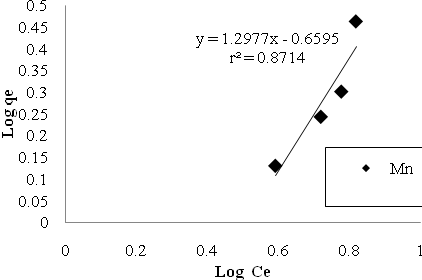 | Figure 9. Mn sorption isotherms based on the Freundlich model. |
 | Figure 10. The effect of temperature on biosorption. |
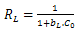 | (6) |
3.5. Effect of Temperature
- High temperatures usually enhance sorption due to the increased surface activity and kinetic energy of the solute [41-43]. But in some cases high temperature may cause damage of active binding sites on the biosorbent surface.As seen in fig. 6 an increase in the temperature from 293 to 318˚K led to an increase from 1 to 1.93mg.g-1 and 1.27 to 2.2 mg.g-1 for Cu and Mn ions respectively. Maximum equilibrium uptake occurred at 318˚K for both metals. This proved that the adsorption of Cu and Mn ions to bacterial biomass was controlled by an endothermic process. As mentioned rising metal uptake capacity was the result of increasing collision frequency between metal ions and the biosorbent active sites.
3.6. Sorption-Desorption Studies
- Sorption-desorption results are summarized in table 5. As seen both metal ion sorbed and metal ion desorbed decreased from cycle 1 to 5. Strong sorbent-sorbate affinity may be the main cause of difference between amount of sorbed and desorbed ions. Although sorption-desorption efficiencies decreased they were high in all cycles for both Cu and Mn ions.
4. Conclusions
- In the study of removing Cu and Mn ions by Bacillus Thuringiensis following conclusions were drawn:1. Using native microorganisms can be very effective due to their high resistance and compatibility to the environment.2. The natural biomass of Bacillus Thuringiensis that isolated from Sarcheshme mine`s wastewater can be consider as a very effective and low cost sorbent for the purpose of mine`s effluent treatment.3. Finding and optimizing effective parameters on batch mode operation was very important to achieve high sorption capacity.4. Biosorption was very fast at first and 75% and 90% of total Cu And Mn uptake occurred after first 30 minutes.5. The adsorption equilibrium data were fitted well both Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models, but Langmuir isotherm gave the better fit.6. The biosorption capacity increased with increasing temperature up to 320৹K.7. In five consecutive cycles biosorbed metal ions were easily eluted using 1M HCl and the biomass was regenerated and reused with high sorption/desorption efficiency.
References
| [1] | Zouboulis, A.I., Matis, K.A., Lanara, B.G. and Loos-Neskovic, C., 1997, Removal of cadmium from dilute solutions by hydroxyapatite. II. Floatation studies. Sep Sci Technol, 32(10):1755–1767 |
| [2] | Ahmady-Asbchin S., Yves A., Ge`rente C., Le Cloirec P. (2008) “Biosorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solution by Fucus serratus:Surface characterization and sorption mechanisms” J. of. Biores. Technol., 99, (2008), pp 6150–6155 |
| [3] | Esalah, O.J., Weber, M.E. and Vera, J.H., 2000, Removal of lead, cadmium and zinc from aqueous solutions by precipitation with sodium di-(n-octyl) phosphinate. Can J Chem Eng, 78:948–954 |
| [4] | Ravindran, V., Stevens, M.R., Badriyha, B.N. and Pirbazari, M., 1999, Modeling the sorption of toxic metals on chelant-impregnated adsorbent. AIChE J, 45(5):1135–1146 |
| [5] | Canet, L., Ilpide, M. and Seta, P., 2002, Efficient facilitated transport of lead, cadmium, zinc and silver across a flat sheet-supported liquid membrane mediated by lasalocid A. Sep Sci Technol, 37(8): 1851–1860 |
| [6] | Schiewer, S. and Volesky, B., 1995, Modeling of the proton–metal ion exchange in iosorption. Environ Sci Technol, 29:3029–3058 |
| [7] | Kapoor A., Viraraghavan T., Cullimore D. R. (1999) “Removal of heavy metals using the fungus Aspergillus niger”, J. of. Biores. Technol., 70, (1999), pp 95-104 |
| [8] | T. Srinath, T. Verma, P.W. Ramteke, S.K. Garg, Chromium (VI) biosorption and bioaccumulation by chromate resistant bacteria, Chemosphere 48 (2002) 427–435 |
| [9] | S. Tunali, A. C¸ abuk, T. Akar, Removal of lead and copper ions from aqueous solutions by bacterial strain isolated fromsoil, Chem. Eng. J. 115 (2006) 203–211 |
| [10] | A. Iyer, K. Mody, B. Jha, Biosorption of heavy metals by amarine bacterium,Mar. Pollut. Bull. 50 (2005) 340–343 |
| [11] | Padmavathy V. (2007) “Biosorption of nickel(II) ions by baker’s yeast: Kinetic, thermodynamic and desorption studies” J. of. Biores. Technol., 99, (2008), pp 3100-3109 |
| [12] | G. Yan, T. Viraraghavan, Heavy-metal removal from aqueous solution by fungus Mucor rouxii,Water Res. 37 (2003) 4486–4496 |
| [13] | S. Tunali, T. Akar, Zn(II) biosorption properties of Botrytis cinerea biomass, J. Hazard. Mater. 131 (2006) 137–145 |
| [14] | T. Akar, S. Tunali, Biosorption characteristics of Aspergillus flavus biomass for removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions from an aqueous solution, Bioresour. Technol. 97 (2006) 1780–1787 |
| [15] | A. Sari, M. Tuzen, Biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution using green alga (Ulva lactuca), J. Hazard. Mater. 152 (2008) 302–308 |
| [16] | K. Chojnacka, A. Chojnacki, H. Górecka, Biosorption of Cr3+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ ions by blue–green algae Spirulina sp.: kinetics, equilibrium and the mechanism of the process, Chemosphere 59 (2005) 75–84 |
| [17] | P. Lodeiro, B. Cordero, J.L. Barriada, R. Herrero, M.E. Sastre de Vicente, Biosorption of cadmium by biomass of brown marine macroalgae, Bioresour. Technol. 96 (2005) 1796– 1803. |
| [18] | Mann H. Removal and recovery of heavy metals by biosorption. In: Volesky B, editor. Biosorption of heavy metals. Boca Raton: CRC press; 1990. p. 93-137 |
| [19] | Urrutia MM. General Bacterial Sorption Processes. In: Wase J, Forster C, editors. Biosorbents for metal ions. London, UK: CRC Press; 1997. p. 39–66 |
| [20] | Jianlog W., Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future, Biotechnology Advances 27 (2009) 195–226 |
| [21] | Srinath T., Verma T., Ramteke PW., Garg SK. (2002) “Chromium (VI) biosorption and bioaccumulation by chromate resistant bacteria” J. of. Chemosphere., 48, 2002, pp 427–35 |
| [22] | Zhou M, Liu Y, Zeng G, Li X, XuW, Fan T. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of Cr (VI) biosorption by dead Bacillus licheniformis biomass. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2007;23:43–8 |
| [23] | Şahin Y, Öztürk A. Biosorption of chromium(VI) ions from aqueous solution by the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis. Process Biochem 2005;40:1895–901 |
| [24] | Tunali S, Çabuk A, Akar T. Removal of lead and copper ions from aqueous solutions by bacterial strain isolated from soil. Chem Eng J 2006;115:203–11 |
| [25] | Nakajima A, Yasuda M, Yokoyama H, Ohya-Nishiguchi H, Kamada H. Copper biosorption by chemically treated Micrococcus luteus cells.World JMicrobiol Biotechnol 2001;17:343–7 |
| [26] | Yilmaz EI, Ensari NY. Cadmium biosorption by Bacillus circulans strain EB1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2005;21:777–9 |
| [27] | Green-Ruiz C. Mercury(II) removal from aqueous solutions by nonviable Bacillus sp. from a tropical estuary. Biores Technol 2006;97:1907–11 |
| [28] | Öztürk A. Removal of nickel from aqueous solution by the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis. J Hazard Mater 2007;147:518–23 |
| [29] | Nakajima A, Tsuruta T. Competitive biosorption of thorium and uranium by Micrococcus luteus. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 2004;260:13–8 |
| [30] | E. Schnepf, N. Crickmore, J. Van Rie, D. Lereclus, J. Baum, J. Feitelson, D.R. Zeigler, D.H. Dean, Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62 (3) (1998) 775–806 |
| [31] | W.H. Zou, R.P. Han, Z.Z. Chen, J. Shi, H.M. Liu, Characterization and Properties of manganese oxide coated zeolite (MOCZ) as adsorbent for removal of copper(II) and lead(II) ions from solution, J. Chem. Eng. Data 51 (2006) 534–541 |
| [32] | Yang J, Volesky B. Modeling the uranium-proton ion exchange in biosorption. Environ Sci Technol 1999b; 33:4079–85 |
| [33] | Esposito A, Pagnanelli F, Vegliò F. pH-related equilibria models for biosorption in single metal systems. Chem Eng Sci 2002;57:307–13 |
| [34] | Vijayaraghavan K, Yun YS. Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption. Biotechnol Adv 2008;26:266–91 |
| [35] | Volesky B. (2007) “Biosorption and me” J. of. Water Res., 41, (2007), pp 4017-4029 |
| [36] | I.C. Hancock, The use of Gram-positive bacteria for the removal of metals from aqueous solution, in: R. Thompson (Ed.), Trace Metal removal from Aqueous Solution, Royal Soc. Chem., London, 1986, p. 25 (Spec. Publ. 61) |
| [37] | M.N. Hughes, R.K. Poole, Removal or recovery of metal ions and compounds from solution by microbiological methods, in: Metals and Microorganisms, Chapman and Hall, London, 1989, p. 328 |
| [38] | Langmuir I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 1918; 40: 1361– 403 |
| [39] | Freundlich H. Ueber die adsorption in loesungen. Z Phys Chem 1907; 57: 385–470 |
| [40] | Kratochvil D, Volesky B. Advances in the biosorption of heavy metals. TIBTECH 1998; 16: 291–300 |
| [41] | Weber, T.W., Chakraborti, R.K., 1974. Pore and Solid diffusion models for fixed bed adsorbers. J. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. 20, 228–232 |
| [42] | Sağ Y, Kutsal T. Determination of the biosorption heats of heavy metal ions on Zoogloea ramigera and Rhizopus arrhizus. Biochem Eng J 2000; 6: 145–51 |
| [43] | Vijayaraghavan K, Yun YS. Utilization of fermentation waste (Corynebacterium glutamicum) for biosorption of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 2007b; 141: 45–52 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML