-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Biological Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1875 e-ISSN: 2163-1883
2011; 1(1): 1-5
doi: 10.5923/j.ijbe.20110101.01
Study of Calotropis gigantea R. Br. Extracts on Growthand Survival Dynamics of Selected Pathogenic Microorganisms
David M 1, Bharath K R 2, Bhavani M 3
1,3Department of Biotechnology, Sir Padampat Singhania University, Udaipur, 313601, India
2,2Faculty of Biotechnology, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University ,Hyderabad, Hyderabad, 500085, India
3Department of Biotechnology, Vignan University, Guntur, 522213, India
Correspondence to: David M , ,3Department of Biotechnology, Sir Padampat Singhania University, Udaipur, 313601, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The aqueous, methanol and ethanol extracts of Calotropis gigantea leaves, apical buds and flowers were prepared and used to study the effect of Calotropis gigantea extracts on growth & survival dynamics of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicansandXanthomonascampestris. Microbial growth and survival dynamic profiles in the presence of solvent extracts in broth cultures were obtained and in most of the cases the flowers and apical buds extracts have also shown the maximal growth reduction in addition to the leaves, but in some cases growth was rapid and accelerated than the control growth curves. Calotropis gigantea containing active metabolites such as mudarin, anthocyanins, calactin, calotropin, 18, 20-epoxy-cardenolides, non-protein amino acids, protease inhibitors, constitutive α-amylase inhibitors, lectins etc. may be the ones responsible for the obtained growth and survival dynamics in microbial broth culture. Over all the study has provided the potential of Calotropis gigantea as a source for biopesticides and future antibiotics.Keywords Calotropis Gigantea, Medicinal Plant Extracts, Antibiotic Source, Flower Extracts, Microbial Growth and Survival Dynamics
Keywords:
Cite this paper: David M , Bharath K R , Bhavani M , "Study of Calotropis gigantea R. Br. Extracts on Growthand Survival Dynamics of Selected Pathogenic Microorganisms", International Journal of Biological Engineering, Vol. 1 No. 1, 2011, pp. 1-5. doi: 10.5923/j.ijbe.20110101.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Calotropis species is considered to possess anti-inflammatory components[1], due to which it is explored for medicinal and pest control values among the several ethnic groups in Indian subcontinent and several African countries. Although WHO has recognized the role of traditional system of medicine and considered them as a part of the strategy to provide health care to masses[2], it is essential to support their potential use with more of scientific evidences. In this concern there are several reports on Calotropis procera as a potential source of medicine for many diseases[3-10], but there are a few reports on the potential of Calotropis gigantea, even though it is similar in its properties and constituents[11] with that of Calotropis procera. But thenit is also obligatory to carry out the scientific studies to establish the evidence and understand the potential of Calotropis gigantea as source of medicine and biopesticides for the benefit of the society at large.In an attempt to establish and understand the antimicrobial and pest control potential of many plant based metabolites,the scientific studies were carried out using the routine methods of disc diffusion, agar well diffusion etc. where the information seem to be limited to the fact of formation of inhibition zones in a static environment, however it is also vital to understand the survival and growth dynamics of the microorganisms subjected to the presence of antimicrobial or pest control agents under optimal growth conditions in their established dynamic broth medium, over a period of time. This kind of studies can help us to elicit the effectiveness of the antimicrobial or pest control agents and the tolerance of the test pathogenic microorganisms over a period of time. Considering the above facts the present communication is aimed to carry out, the microbial growth and survival dynamics on selected pathogenic microorganisms in the presence of Calotropis gigantea extracts of water, methanol and ethanol.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Calotropis Gigantea Extracts
- Plant extracts of Calotropis gigantea leaves, apical buds & flowers were prepared with the freshly harvested explants by drying, grinding followed by dissolving in distilled water, ethanol and methanol separately for 24 hrs. with reciprocal shaking of 30 cycles per min. and filtering the solvent extracts by 0.45 micron filters followed by drying in water bath at 80℃ for methanol & ethanol and at 100℃ for water followed by dissolving the obtained dry residues or extracts in their respective solvents[12] to obtain the final extract concentrations as aqueous leaves extract of 3.1482mg/ml, aqueous apical buds extract of 2.4317mg/ml, aqueous flowers extract of 0.1434mg/ml, ethanol leaves extract of2.1246mg/ml, ethanol apical buds extract of 4.4352mg/ml, ethanol flowers extract of 1.6455mg/ml, methanol leaves extract of 4.3729mg/ml, methanol apical buds extract of 5.2495mg/ml and methanol flowers extract of 1.6224mg/ml. All these extracts were stored in the refrigerator until use.
2.2. Test Microorganisms
- Microbial strains, namely, Escherichia coli (MTCC 118), Staphylococcus aureus (MTCC 96), Candida albicans (MTCC 183) andXanthomonascampestris (MTCC 2286), were obtained from the Microbiology laboratory, Department of Biotechnology, Sir Padampat Singhania University, Udaipur, Rajasthan, India, and used them for the studies of growth and survival dynamicsin the presence of preparedCalotropis gigantea extracts. All the strains were maintained in the agar slants of their respective media by subculturing at regular intervals.
2.3. Study of Microbial Growth and Survival Dynamics in the Presence of Calotropis Gigantea Extracts
- Standard Nutrient broth (NB); Yeast extract, Peptone & Dextrose (YEPD) &Xanthomonasmedia (MTCC Growth medium No. 179) of 50 ml in 100 ml conical flasks for the respective pathogenic microorganisms were prepared. The media flasks were sterilized at 121℃ &15 psig for 15 minutes. Under aseptic conditions, 0.5ml of the each prepared extract was added separately to all broth media flasks except the control flasks for eachtest microorganism. Broth media were inoculated with 1ml of 0.5 McFarland Standard adjusted inoculum from the overnight grown respective cultures such asE. coli was added to NB media, S. aureus was added to NB media, C. albicans was added to YEPD media and X. campestris was added to Xanthomonasmediaseparately under aseptic conditions. The culture flasks were incubated at 37℃ and 100 rpm in an orbital shaker incubator for a period of 6 hrs. The samples of microbial broth of 2ml inmicrocentrifuge tubes from the respective culture flasks were withdrawn separately in duplicates at 0 time, after the addition of inoculum and then subsequently at an interval of 30 min. during the culturing period. The samples were centrifuged at 10000g & 4℃ for 10 min. using a cooling centrifuge. After centrifugation, the supernatant was discarded and the microbial pellet was re-suspended in 3ml of 1% saline water. OD was measured at 600nm for the microbial suspension and the growth profiles were plotted with OD vs. Time (min.) for 6 hours with respect to each test microorganism as shown in the Figures 1-12.
3. Results & Discussion
- Growth profiles of E.coliin Figure. 1 in the presence of aqueous Calotropis gigantealeaves, apical buds & flowers extracts are much lower for the initial 90 minutes of culturing period, suggesting the presence of growth inhibiting molecules almost stopping the multiplication of E.coli. Later on E.coli is able to overcome the growth inhibiting molecules in the presence of aqueous apical buds & flowers extracts and increased their growth equivalent to that of the control growth curve; where as in the presence of aqueous leaves extract, E.coli still had relatively reduced growth rate.
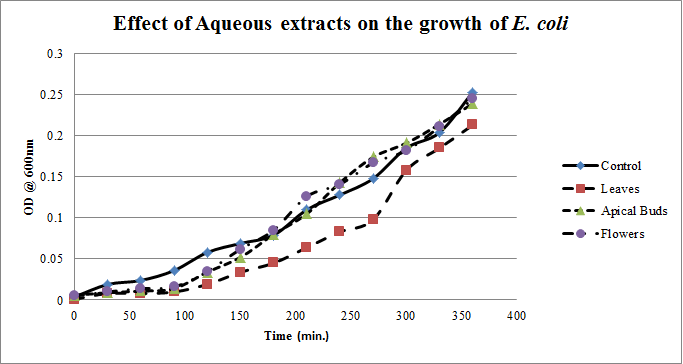 | Figure 1. Growth profiles of E. coli in the presence of aqueous extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
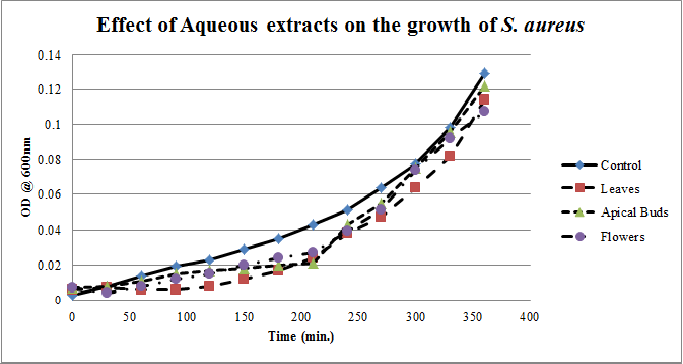 | Figure 2. Growth profiles of S. aureus in the presence of aqueous extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
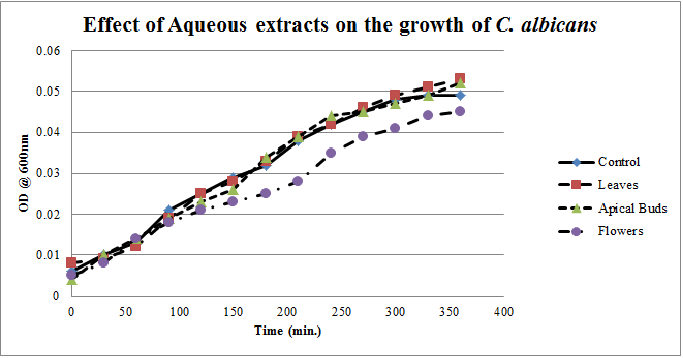 | Figure 3. Growth profiles of C. albicans in the presence of aqueous extracts of Calotropis gigantea.. |
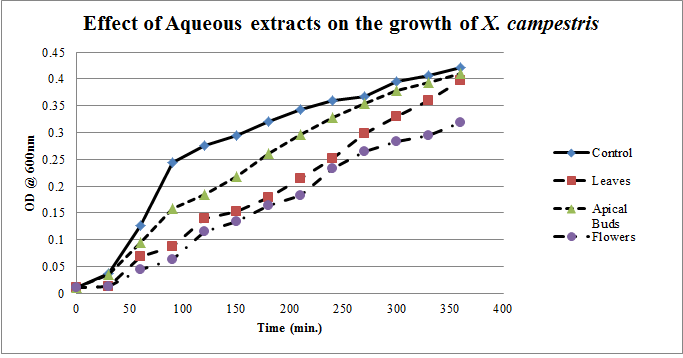 | Figure 4. Growth profiles of X. campestris in the presence of aqueous extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
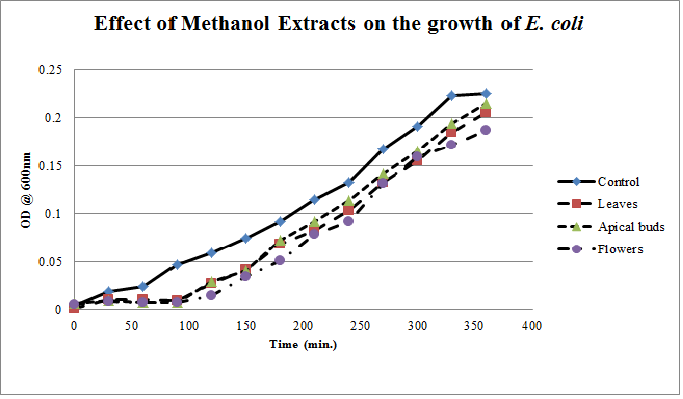 | Figure 5. Growth profiles of E.coli in the presence of methanol extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
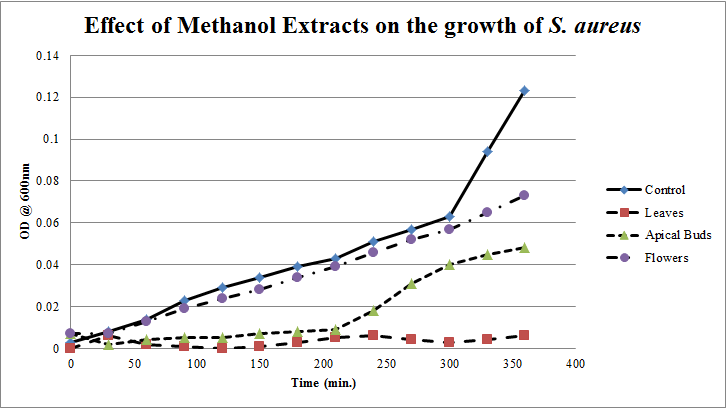 | Figure 6. Growth profiles of S.aureus in the presence of methanol extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
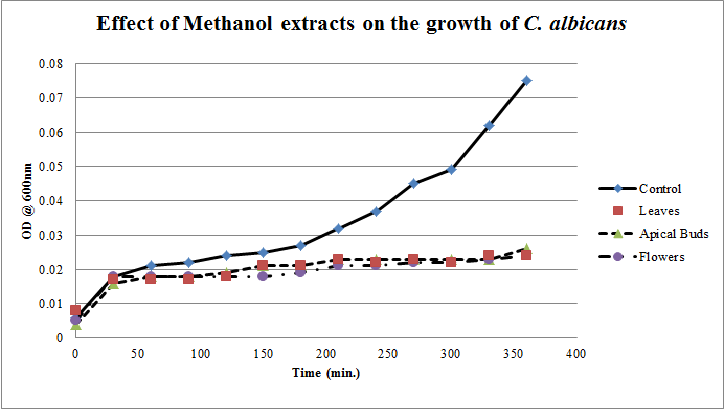 | Figure 7. Growth profiles of C. albicans in the presence of methanol extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
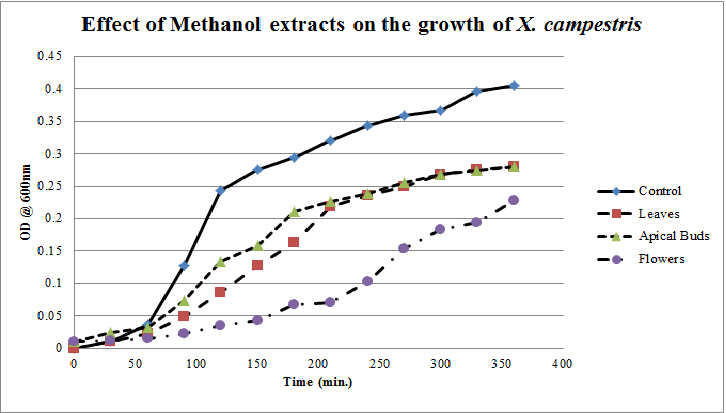 | Figure 8. Growth profiles of X. campestrisin the presence of methanol extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
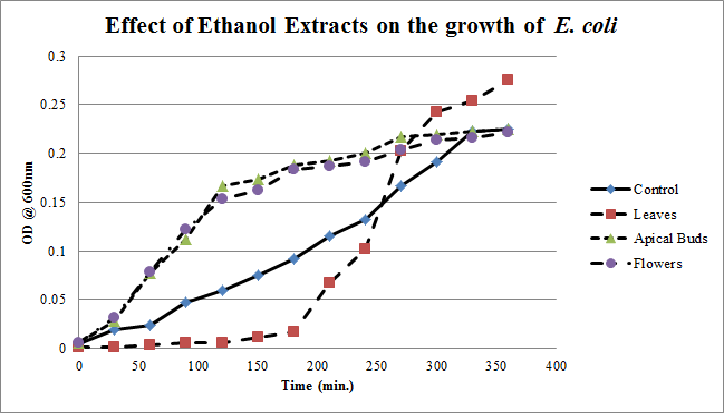 | Figure 9. Growth profiles of E. coli in the presence of ethanol extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
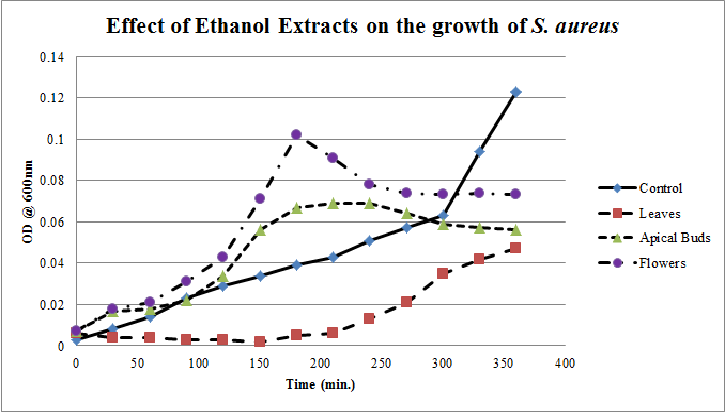 | Figure 10. Growth profiles of S.aureus in the presence of ethanol extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
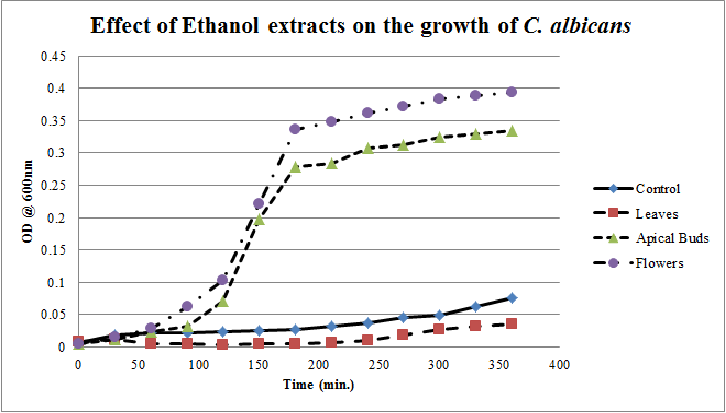 | Figure 11. Growth profiles of C. albicans in the presence of ethanol extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
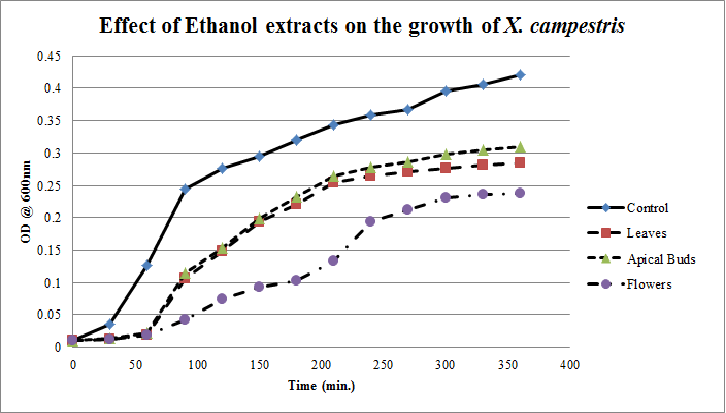 | Figure 12. Growth profiles of X. compestrisin the presence of ethanol extracts of Calotropis gigantea. |
5. Conclusions
- Calotropis gigantea leaves have the active metabolites capable of suppressing the growth of E. coli, S. aureus, C. albicans& X. campestris to greater extent[13] depending on their abundance in the culturing environment. The apical buds have the active metabolites possessing the mild to moderate growth inhibiting capabilities on the tested pathogenic bacteria, whereas the flowers active metabolites has the mild growth inhibitory effect on E. coli&S. aureus and moderate inhibitory effect on C. albicans and X. campestris. The non-aqueous leaves extracts in case of S. aureusand C. albicans have shown more of a bactericidal affect and inhibiting growth effect on X. campestris which may be due to the extraction of active metabolites such as 18,20 –epoxy cardenolides, Calotropin, frugoside, isorhamnetin-3-O-glucopyranoside, non-protein amino acids, protease inhibitors, constitutive α-amylase inhibitors etc[14-17] from leaves. The active metabolites from the leaves, apical buds & flowers were better extracted by non-aqueous solvents, ethanol & methanol; however methanol extracts have shown broader spectrum of activity and they have exhibited bactericidal effect on S. aureus&C. albicans and growth inhibiting effect on X. campestrisand E. coli. These results agree with the reports of other researchers as methanol is the efficient solvent for the extraction of phytochemicals from plant materials[13,18,19]. The flower extracts of methanol has shown bactericidal effect on C. albicans and growth inhibiting effect on X. campestris and E.coli. It is also found that all the used solvent extracts of C. gigantea have shown the growth inhibiting effect on X. campestris concluding that Calotropis sp. may be used for generating biopesticides as an effective substitute for synthetic chemicals[20] to protect the crops from a variety of diseases such as black rot on plant leaves. In case of ethanol extracts of apical buds and flowers the growth of E. coli, S. aureus&C. albicans were stimulated to record the higher growth profiles and this may be credited to the poor efficiency of ethanol to extract the plant lectins used by the plants as one of the defence mechanisms against pathogens; and these lower concentrations of extracted lectins might have caused the increase in bacterial growth rate where as in case of methanol and aqueous extracts the concentrations of the extracted lectins may be abundant or higher to act as growth inhibiting or bactericidal agents[15]. So the presented study has strengthened the use of C. gigantea also as a promising source to generate medicine and biopesticides for the future biopharmaceutical industry. It is also suggested to carry out further studies to isolate and identify the active components specifically and use them either individually or in combination as potential antibiotics and biopesticides to serve the society at large.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors are grateful to Prof. P. C Deka, the Vice Chancellor, Sir Padampat Singhania University, Udaipur, Rajasthan, India, for his kind suggestions and help in the initial stages of the research work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML