-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Brain and Cognitive Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1840 e-ISSN: 2163-1867
2018; 7(2): 36-41
doi:10.5923/j.ijbcs.20180702.02

Anxiolytic Effects of Senna singueana in Mice after Exposure to Chronic Restraint-Stress
Mairaira Véronique1, Jean Pierre Omam Omam2, David Pahaye Bougolla1, Moto Fleur Clarisse Okomolo2, Ngo Bum Elisabeth1
1Department of Biological Science, Faculty of Sciences, University of Ngaoundéré, Ngaoundéré, Cameroon
2Higher Teachers’ Training College, University of Yaoundé I, Yaoundé, Cameroon
Correspondence to: Mairaira Véronique, Department of Biological Science, Faculty of Sciences, University of Ngaoundéré, Ngaoundéré, Cameroon.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Senna singueana (Cesalpiniaceae) root is traditional medicine used in many countries in Africa to treat epilepsy, agitation, malaria. In the present study, the anxiolytic effect of decoction of S. singueana root was evaluated on chronic stress induced biochemical and psychological changes in mice. Chronic stress was induced by chronic restraint stress method and the effects of S. singueana at the doses of (40, 100, 200, 400 mg/kg) was evaluated on levels of plasma serotonim and corticosterone after the final exposure to chronic stress the elevated plus-maze tests were performed to measure the level of anxiety. These results suggest that S. singueana shows the ameliorating effects on chronic restraint stress by modulating the activity of the serum levels of corticosterone and serotonin.
Keywords: Senna singueana, Chronic restraint stress, Corticosterone, Serotonin, Anxiety
Cite this paper: Mairaira Véronique, Jean Pierre Omam Omam, David Pahaye Bougolla, Moto Fleur Clarisse Okomolo, Ngo Bum Elisabeth, Anxiolytic Effects of Senna singueana in Mice after Exposure to Chronic Restraint-Stress, International Journal of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Vol. 7 No. 2, 2018, pp. 36-41. doi: 10.5923/j.ijbcs.20180702.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Anxiety is a normal response to stress, a feeling of apprehension or fear, combined with the symptoms of increased sympathetic activity. A clinical problem may arise if anxiety becomes persistent that interferes with every day performance [1]. Anxiety disorders are among the most common psychiatric disorders that affect all age groups of the general population [2]. The biology of anxiety is considered as an integral part of the human response to threat or danger and it affects about one-eighth of the world population [3]. Various stresses can cause physical changes as well as mental performances. Acute and chronic stresses are characterized by the physiological changes that occur in response to novel or threatening stimuli. Chronic stress has been linked to the pathophysiology of various psychiatric disorders, including anxiety disorders and depression [4]. Both acute and chronic stresses activate the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis, which are characterized by a sudden rise in adrenocorticotrophic hormone followed by the release of glucocorticoids, such as corticosterone and cortisol [5]. In the conditions of chronic stress-induced anxiety disorders and depression in the brain decreased. In contrast, the serum levels of glucocorticoids such as corticosterone and cortisol are increased by various chronic stresses, and this is mediated by the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis [6].Many stress models, including electric footshock (EF) stimulus, forced swimming, noise stimulus, restraint and immobilization have been employed to examine the stressful responses in mice and rats [7-9]. In the field of anxiety disorders induced by chronic stress, the elevated plus-maze and marble burying tests are widely used in response to threatening stimuli [10, 11].According to Cameroonian traditional healers, roots of S. singueana are used in the treatment of agitation, epilepsy, fever and pain. Previous experiments have shown that S. singueana possesses antiplasmodial, antibacterial, antinociceptive, antipyretic and hepatoprotective properties [12-14]. However, no previous work was reported on this plant used as anxiolytic agent. Moreover, phytochemical screening of the plant revealed the presence of tannins, phenols, saponins, terpenes, alkaloids, sterols, guinoids, antraquinones [14, 15] which, may be involved in the anxiolytic activity.The present study aimed to evaluate the anxiolytic effect of S. singueana roots decoction on chronic stress induced biochemical and psychological changes in mice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
- Male Mus musculus Swiss mice (22-23g) were used for this study. Animals were housed in stantard cages at 25°C on a 12/12-hour light –dark cycle. They were supplied with food and water ad libitum. The study was conducted in accordance with the nationally (N° FWA-IRB00001954) and internationally accepted principles for laboratory animal use and care as found in the USA guidelines.
2.2. Plant Material
- The dued roots of S.s were ground. 10g of the plant powder were boiled in 50ml of distilled water for 20 min. After cooling the supernatant was collected and filtered with whatman N° 1 filter paper. 20ml of the decoction were obtained. Part of the decoction was diluted to less concentrated solution by adding distilled water. The initial decoction and the diluted solution were then ready to be used. After filtration (another experiment) the decoction was evaporated in a drying oven at 45°C and 0,8g of dark brown solid was obtained. The field of the extraction was 8%. The decoction was administered orally (p.o). The following doses were 400, 200, 100, and 40mg /kg.
2.3. Chemical
- Diazepam (Valium(R), Roche, France) was used as reference drug (positive control) for anxiolytic activity.
2.4. Experiment Procedure
- In the present study stress was induced using chronic immobilization stress (CIS) [16]. Model with minor modifications. The restraint stress was produced by restraining the animals inside an adjustable a cyclic hemicylindrical plastic tube (for 3 hours for mice: 3cm diameter; 6,5cm long). The mice were divided into seven groups of six animals. Group 1 animals served as normal control were administered distilled water and were not exposed to stress. Group 2: served as negative control as untreated stress induced. Group 3, 4, 5, 6 animals were administered S.s Extract Orally at the doses of 40, 100, 200, and 400 respectively. Group 7 animals were administered Diazepam (2mg/kg). The animals were pretreated with the extracts and the reference drug for a period of 10 days before induction of stress. Following the induction of stress the male Swiss mice were evaluated for behavioral changes on the elevated plus maze test. The animals were sacrificed post stress induction by cervical decapitation; the blood was withdrawn from the jugular vein and was then centrifuged to obtain a serum. Corticosterone and serotonin levels were assessed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit.
2.5. Elevated Plus Maze Test (EPM)
- On the 11th day, mice were tested in an elevated plus meze test for 5 minutes. This test has been widely used to measure anxiety in rodents [17]. The wooden apparatus, consisted of two open arms (16×5cm each), two enclosed arms (16×5cm×10cm; each) and a central plat form (5×5cm) arranged in such a way that the two arms of each type were opposite to each other. The maze was elevated 70cm above the floor. After the induction of stress (10 days), each animal was placed at the center of the maze, facing one of enclose arms. During the 5 min test period, the number of open and enclosed arms entries, the times spent in open or closed arms, rearing and head dipping were recorded with stop watches [18, 19].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
- The value of the negative control was compared to the values of the tested groups and control. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Dunnett (HBD) were done. A value of P>0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Anxiolytic-like Effects of S. singueana on Elevated Plus Maze Test
- Treatment with S.singueana (200 and 400 mg/kg) once a day for 10 days did not alter the results of the elevated plus-maze test in terms of open arm entries and time spent on open arm entries compared with the control groups (Figure 1 A and B). In contrast, the reduction percentage in the open arm entries and the reduction percentage of the time spent on open arms significantly decreased to 52.94% (F(6,28)=5.63; P=0.001) and 66.46% (F(6,28)=66.74; P<0.0001), respectively by chronic restraint stress, as compared with the control groups. However, treatment with S. singueana at 200 and 400 mg/kg for 10 days recovered to 42.85% and 40.90% the number of open arm entries respectively which had been reduced by chronic restraint stress. The reduction in time spent on open arms due to chronic restraint stress was also recovered to 39.36% and 35.69% that of the control groups by S. singueana at 200 and 400 mg/kg, respectively as compared with the chronic restraint groups (Figure 1A and 1B).
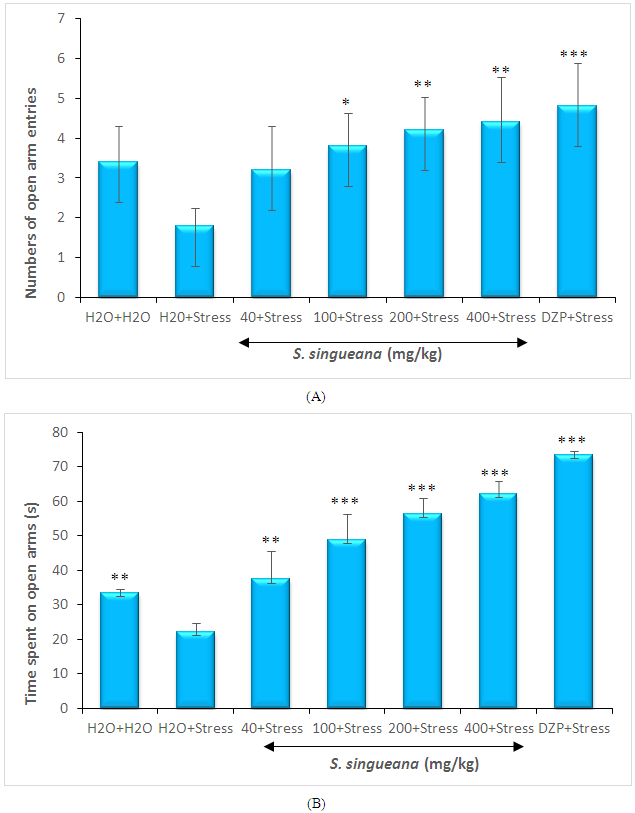 | Figure 1. Effects of S. singueana on the number of open arm entries (A) and time spent on open arms (B) in the elevated plus-maze in mice |
3.2. Effects of S.singueana on Serum Corticosterone Levels
- The induction of stress by restraining in mice was confirmed by measuring the serum corticosterone levels. The animals on exposure to chronic restraint stress showed a significant (F(6,28)=21.26; P<0.0001) increase in blood corticosterone levels as compared to the normal mice. Further treatment with S. singueana decoction at a dose of (40, 100, 200, and 400 mg/kg) significantly (F(6,28)=21.26; P<0.0001) countered this elevation in blood corticosterone level (Figure 2).
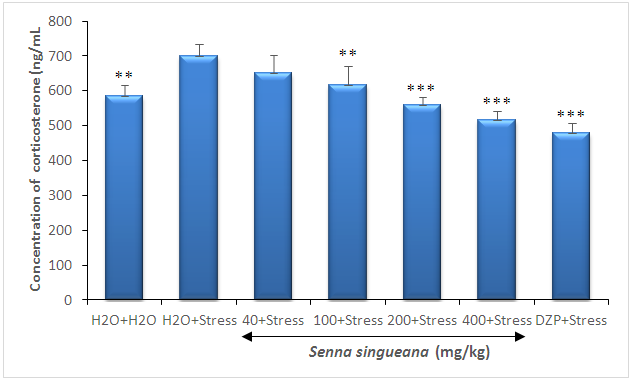 | Figure 2. Effect of S. singueana on the levels of corticosterone in the serum |
3.3. Effect of S. singueana on Serum Serotonin Level
- Serotonin level in the negative control significantly (F(6,28)=15.32; P<0.0001) decreased by 52.57% by chronic restraint stress, compared to the normal control group (figure 3). However, serotonin level induced by chronic restraint stress significantly (F(6,28)=21.26; P<0.0001) increased by 56.26% and 44.82% when treated at doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg S. singueana root decoction, respectivement, compared to with chronic restraint-stressed group (Figure 3).
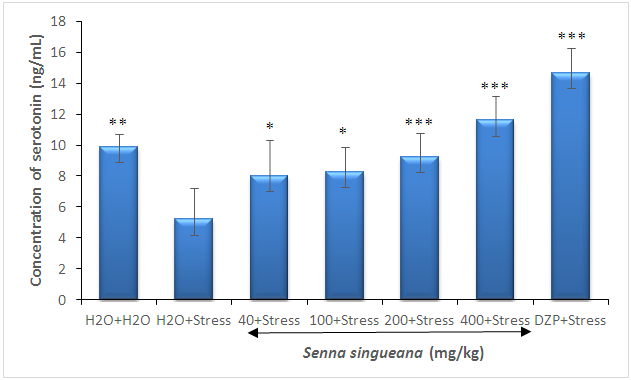 | Figure 3. Effect of S. singueana on serotonin level in the serum |
4. Discussion
- Homeostatic survival mechanism of all living organisms regulates their internal environment, and helpss maintain a stable healthy condition. Imbalance in this survival mechanism is caused or followed by stress induced responses involving diverse neuro-endocrine and biochemical mechanism [20]. These alterations in neurotransmitter activity result in behavioral changes as well as a cascade of hormonal release from the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis [21].The elevated plus maze (EPM) is the prime apparatus that is responsible for finding the anxiolytic potential of a drug. The test is based on assumption in which encounter to an open arm maze elicits an approach avoidance conflict that was considerably stronger than elicited by exposure to a closed arm [22]. We have demonstrated that chronic stress produced an anxiolytic effect in the EPM. Oral administration of S. singueana (200 and 400 mg/kg) had shown a significant increase in open arm entry and time spent in open arm.The central monoaminergic system (including serotonin (5-HT), NE and DA) has been widely implicated in the pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies for emotional disorders [23, 24]. Chronic stress-induced anxiety disorders decreases dopamine and serotonin levels in the brain [6]. Anxiolytic-like behavioral responses in the elevated plus-maze test are mediated by the serotonin receptor functions. In this study serotonin level are reduced by chronic restraint stress in the plasma, and increased by treatment with S. singueana and Diazepam a dose dependent manner. In contrast, the corticosterone serum level increased by chronic restraint stress and they were also reversed by treatment with S. singueana (40, 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg) in a dose-dependent ways. Thus, these results suggested an anxiolytic profile of S. singueana decoction and might improve chronic stress-induced anxiety disorders by modulating serotonin and corticosterone levels.
5. Conclusions
- The results of this present study demonstrated the significant effect of Senna singueana on the HPA axis dysfunction and anxiety induced by chronic stress and may be related to its modulating effect on neurotransmitters. Oral administration of S. singueana to the chronic stress mice significantly reduced anxiety-like behavior under restraint stress. These effects were found to be concomitant with the regulation of monoamine neurotransmitter levels in serum.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors are very thankful to the laboratory of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, University of Ngaoundéré, Cameroon for the realization of the experiments in their laboratory and some facilities provided.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML