-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Brain and Cognitive Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1840 e-ISSN: 2163-1867
2018; 7(1): 9-16
doi:10.5923/j.ijbcs.20180701.02

Relationship between Self-Esteem and Impostor Syndrome among Undergraduate Medical Students in a Nigerian University
J. N. Egwurugwu1, P. C. Ugwuezumba1, M. C. Ohamaeme2, E. I. Dike3, I. Eberendu4, E. N. A. Egwurugwu5, R. C. Ohamaeme6, Egwurugwu U. F.7
1Department of Human Physiology, College of Medicine, Imo State University, Owerri, Nigeria
2Department of Community Medicine, Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital, Nnewi, Nigeria
3Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Imo State University Teaching Hospital, Orlu, Nigeria
4Department of Paediatrics, Imo State University Teaching Hospital, Orlu, Nigeria
5Department of Social Science Education, Faculty of Education, Imo State University, Owerri, Nigeria
6Department of Educational Foundation and Counseling, Faculty of Education, Imo State University, Owerri, Nigeria
7Department of Internal Medicine, Imo State University Teaching Hospital, Orlu, Nigeria
Correspondence to: J. N. Egwurugwu, Department of Human Physiology, College of Medicine, Imo State University, Owerri, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

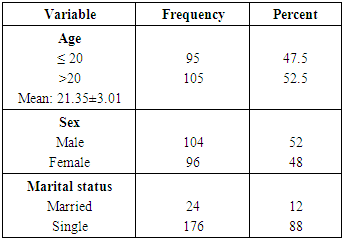
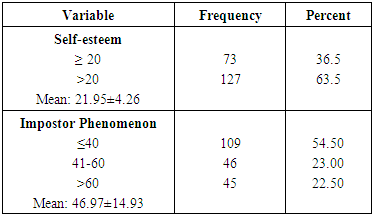
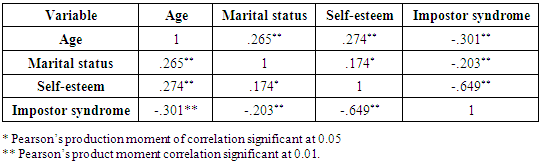
Most medical educators, patients, caregivers, health team members and stakeholders would prefer a medical practitioner and /or a future doctor that has high self-esteem and low impostor scores. This cross-sectional descriptive study among the medical students of Imo State University, Nigeria, was under taken to assess the relationship between self-esteem and impostor phenomenon. Two hundred students participated in this study. Rosenberg Self-Esteem scale and Clance Impostor Phenomenon scale were the research instruments used to measure self-esteem and impostor syndrome respectively. The results showed that self-esteem correlated significantly and positively with age (r =.274, p = 0.001) and marital status (r = .174, p = 0.05) and negatively with impostor syndrome (r = -.649, p = 0.001). Impostor syndrome correlated negatively and significantly with age (r = -.301, p= 0.001), marital status (r= -.203, p= 0.001) and self-esteem(r= -.649, p = 0.001). Majority of the students (63.5%) had high self-esteem and low impostor (54.5%) scores. Married students had high self-esteem and low impostor scores compared to their single peers (p<0.05). Prevalence of marriage among the medical students was low (12%). Statistically significant difference was noted in the age of the males and females (p<0.05). No statistically significant gender differences in the scores for self-esteem and impostor syndrome. In conclusion, the students had high levels of self-esteem and low levels of impostor phenomenon, self-esteem correlated positively and significantly with age and marital status and negatively with impostor syndrome. Marriage rate was low and married students had high levels of self-esteem and low impostor score compared to their single peers. No significant gender differences in self-esteem and impostor syndrome.
Keywords: Self-esteem, Impostor phenomenon, Medical students, Marital status, Nigeria
Cite this paper: J. N. Egwurugwu, P. C. Ugwuezumba, M. C. Ohamaeme, E. I. Dike, I. Eberendu, E. N. A. Egwurugwu, R. C. Ohamaeme, Egwurugwu U. F., Relationship between Self-Esteem and Impostor Syndrome among Undergraduate Medical Students in a Nigerian University, International Journal of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2018, pp. 9-16. doi: 10.5923/j.ijbcs.20180701.02.
1. Introduction
- The term impostor phenomenon (IP) was first used by Clance and Imes in 1978. [1] Clance in 1985 defined IP as “an internal experience of intellectual phoniness that those who feel fraudulence and worthlessness in spite of outstanding academic or professional accomplishment have”. [2] Holmes et al. in 1993 described the concept as the inner experience of intellectual phoniness in high-achieving women who seemed to be unable to internalize their experiences of success. [3] It is the experience of people who attribute their success to luck, while feeling that they are truly incompetent, with the consequent anxiety that others may discover their weaknesses despite their objectively outstanding accomplishments. [4] Therefore, IP is a set of feelings of fear, doubt, apprehension and a defected cycle of post-success anxiety, which involves successful young people. This psychological deficit can be an obstacle to progress and use of their hidden talents. [3, 5] The factors contributing to the emergence of impostorism include perfectionism [2, 6-8], family environment, personality variables, destructive beliefs and unpleasant consequences of progress [2, 9-13, parenting styles [11, 14], attribution styles [15-18], and gender differences [5, 19-22]. Clance has also suggested four main features of the family that can contribute to the development and perpetuation of IP: (i) perception of imposters that their talents are atypical compared with other family members, (ii) family messages that convey the importance of intellectual abilities and that success requires little effort, (iii) discrepancy between feedback about impostors’ ability and success derived from family and other sources, and (iv) lack of positive reinforcement. [2] It has also been opined that parental overprotection is a strong factor in development of impostor fears. [11]The characteristic features of people who experience IP include: ability to fulfill academic or work requirements despite their self-perceived fraudulence [23], they attribute their success to external sources such as luck [24-27], they experience passing satisfaction, display low level of confidence in their own competence, and cannot acknowledge the evidence of their high ability [28], they fear that they will not be able to fulfill the expectations of others at some future time [29] and the demands they make on themselves are extra-ordinarily high, to the point where they sometimes expect perfection [2, 6]. IP is a personality construct [30-31], affects both genders [9, 32], occur in people with different occupations such as college students [9, 32], academics [33], medical students [34], marketing managers [35], physician assistants [36, 37], and physicians [38], they exhibit failure avoidance behaviours such as lack of self-worth protection, self-handicapping, negligence, impostor fears and defensive pessimism. [39] It has been estimated that seventy percent of people may experience at least one episode of IP in their life time. [40]Self-esteem has been defined as the rate of validity, approval, acceptance and worthiness that a person feels about himself /herself. [41] It is the evaluation and experience associated with self value, perception of self ability and acceptance of whole self which a person imbibes during the process of socialization. [42-43] It has also been described as an individual’s feelings, thoughts and evaluations of his/her abilities in social, educational, familial and body image domains. [44] It cuts across all age brackets and it’s the totality of one’s self-evaluation. [45] High self-esteem has been associated with good mental health and self-harmony [46], competence, confidence, high productivity, optimistic attitudes, ability to solve problems and ability to control emotions. [45, 47-51] Conversely, low self-esteem often leads to desperation, inferiority, hopelessness, sadness, depression and may predispose to suicide. [47, 51-53] Self-esteem affects both present and future physical, mental health and associated health-related behaviors. [54] Health care givers with high self-esteem have greater tendency to influence, stimulate and induce a positive and sustainable well-being in the patient, health care team, and hospital management. [54-56] Studies have demonstrated strong relationship between IP and low self-esteem. [11, 27, 57] Experience of IP is also associated with psychological distress [34, 58], anxiety [59], and depression. [60, 61] A good doctor and by inference, a good medical student requires high self-esteem and minimal impostor characteristics to impact positively on the healthcare system, this prompted the research on the undergraduate medical students of Imo State University, Owerri, Nigeria.
2. Materials and Methods
- This is a cross-sectional descriptive study involving all the undergraduate medical students of Imo State University as the statistical community during the 2016/2017 session. Sampling was done via proportional stratified random sampling in the five levels of the core medical programme according to Morgan and Krejcie’s sample size table [62], though modified. Sample size was 200, that is 40 students from each level. The aim and objectives of the research were explained to the students and those who consented in writing participated in the study. Thus, participation was voluntary, anonymous and confidentiality of the data generated was ensured. This research was approved by the Ethical Committee of Imo State University, Owerri.Standardized self-reporting questionnaires of the Rosenberg Self-Esteem scale and Clance’s Impostor Phenomenon Scale (CIPS) were used for the study. Clance’s Impostor Phenomenon Scale, consisting of 20 items, is the best scale to measure impostor syndrome in a student sample. Each statement on the scale is answered on a five point scale (Likert scoring 1-2-3-4-5) with the scoring ranging from 0-100. The lower the score, the less the manifestation of impostor syndrome. CIPS has a high level of internal consistency (α = .84, [63]; α = .96, [3]. Cronbach’s α (alpha) was used to compute the internal similarity of the scale and the estimated internal consistency reliability was .83.The Rosenberg Self-Esteem scale is one of the best instruments used in assessing self-esteem. It is a 10-item self –reporting scale that assesses a person’s overall sense of self-esteem. Each statement on the scale is answered on a four point scale (Likert scoring 0-1-2-3) with the scoring ranging from 0 to 30. Rosenberg self-esteem scale has strong internal reliability: test-retest correlations are in the range of 0.76 to 0.88, and Cronbach’s alpha in the range of 0.77 to 0.88 [64-67]. A cronbach alpha of 0.84 and two week test-retest reliability coefficient of 0.76 has been established in a Nigerian study [67]. For the present study, the calculated internal consistency reliability was 0.79.Two hundred undergraduate medical students invited for the study, filled and returned their questionnaires (participation rate of 100%) within 10-15 minutes, thus the intensity of their self-esteem and impostor were measured in a given period of time.Data generated from the study was entered, cleaned, coded and analyzed using SPSS-IBM version 21. Descriptive statistics (mean, standard deviation, frequency, and percentage) was used. Pearson’s product moment correlation method was used to study the association between self-esteem and impostor phenomenon. The statistical level of significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
|
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
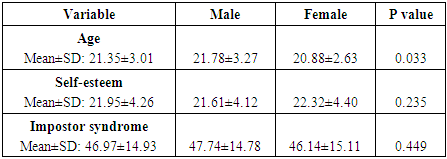
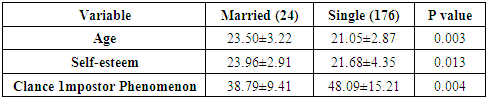
- High self-esteem and little or low features of impostor phenomenon are necessary for effective and sustainable medical practice. Therefore, medical students, the future doctors, should imbibe such good qualities and many more to play the expected vital roles in the health care system.This study showed a negative significant correlation (r=-0.649, p= 0.002) between self-esteem and impostor syndrome. That is, any increase in self-esteem is accompanied by a decrease in impostor syndrome and vice versa. These findings corroborate earlier works. [1, 3, 13, 31, 39, 68-74] However, our findings do not support other works which noted no significant correlation between self-esteem and impostor syndrome. [27, 75] The results of this study also indicated that majority (54.5%) of the students had impostor score of 40 and below. That is, majority of the respondents exhibit few characteristics of the impostor syndrome. Twenty three percent had moderate features while 22.5% had severe features of the syndrome. Furthermore, 63.5% of the students had high level of self-esteem while the rest had low self-esteem. Individuals with high levels of self-esteem attribute their achievements and successes to their internal capabilities such as intelligence, abilities and competencies (internal attribution), while an individual with impostor phenomenon attributes his/her achievements and successes to external factors like chance and coincidence, luck, interpersonal attractions or external events. [26, 27, 38, 69] Impostor phenomenon or perceived fraudulence is a type of personality trait in which people imagine that their competencies are not real. [30] This feeling of phony intelligence is often accompanied by some sense of guilt, dissatisfaction and worries about interpersonal relationships with their colleagues. [72] Evidences abound that the mental state of those who experience frequent impostor phenomenon tends to fall into present psychological distress [34], anxiety [59, 57] and depression. [60, 61] Our results also indicated that no statistically significant difference was observed between self-esteem (p= 0.235) and the impostor phenomenon (p= 0.449) in males and females. Age was statistically significant between males and females (p=0.033). The no gender difference in this study is consistent with other earlier works. [27, 35, 72] Conversely, some researchers have observed statistically significant difference between males and females. [21, 76] This study noted significant and positive correlation between marital status and age and self-esteem and negative with the impostor syndrome. That is, marital status is associated with increase in age and self-esteem and a decrease in impostor syndrome. There has been a significant increase in marriage age during the last two centuries. [77] This significant increase in marriage age tends to be more among medical students and physicians. [78-81] This study showed that married students had higher self-esteem and lower characteristic features of impostor syndrome compared to their unmarried counterparts. This finding is contrary to earlier work [82] which showed a positive relationship between self-esteem and marital status and that unmarried subjects had higher self-esteem than their married, divorced or separated peers. High self-esteem has been associated with superior social skills and interpersonal successes [83], coping better with stress and adversity [84], better romantic relationships [85-89], less likely to engage in destructive behaviours [90], overall life satisfaction and happiness. [91-95] Married students tend to attract better emotional and social support, better finances, better time management than their single peers. [96-97] These plausible good attractions of marriage and high self-esteem could explain low features of impostor syndrome seen among the studied married medical students. Despite the said attractions of married life, the rate of marriage among the medical students is low (12%). The rate of marriage among medical students seems to be generally low. A study among Saudi Arabian medical students found a rate of 18% [98]. Medical education and training is stressful and very demanding, can affect physical and mental health, and contribute to the development of psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety and behavioural problems. [64, 98-108] Marriage on its own can also be stressful, therefore medical students’ marriage can be additional burden on the already existing challenges of medical education. The challenges of medical marriage include: burden of marriage, pregnancy and child bearing on academic performance, balancing the demands of medical studentship and that of marriage, housing problems, financial difficulty, divorce risks, lack of similarity of interests, differential rates of intellectual growth when only one spouse is enrolled in medicine, and lack of leisure time. [78, 96-97, 109] It has also been noted that because of the prolonged period of medical education training, compared to other young people, students of medical sciences, are usually faced with more obstacles and problems in their marriage and family formation. [79-81] The above reasons and many more may explain why majority of medical students would prefer completing their training before getting married.
5. Conclusions
- There is high level of self-esteem and few characteristic features of impostor syndrome among the medical students of Imo State Univeristy, Owerri, Nigeria. Among the students studied, self-esteem is significantly and positively correlated with age and marital status and negatively correlated with impostor syndrome. Married students had high levels of self-esteem and low scores of impostor syndrome compared with their single peers (p<0.05). The prevalence of marriage is low (12%) among the medical students. We therefore recommend that measures should be put in place to increase and sustain the level of self-esteem while at the same time, reduce to the barest minimum, the features of impostorism among the students.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML