-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Brain and Cognitive Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1840 e-ISSN: 2163-1867
2015; 4(3): 41-49
doi:10.5923/j.ijbcs.20150403.01
Anxiolytic (Benzodiazepine-Like) Properties of Mimosa pudica in Mice
Rigobert-Espoir Ayissi Mbomo1, Jean Pierre Omam Omam1, Antoine Kandeda Kavaye2, Stephanie Jacqueline Njapdounke Kameni3, Elisabeth Ngo Bum3
1Department of Biological Sciences, High Teacher Training College University of Yaoundé I, Yaoundé, Cameroon
2Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Sciences University of Ngaoundéré, Ngaoundéré, Cameroon
3Department of Animal Biology and Physiology, Faculty of Sciences University of Yaoundé I, Yaoundé, Cameroon
Correspondence to: Rigobert-Espoir Ayissi Mbomo, Department of Biological Sciences, High Teacher Training College University of Yaoundé I, Yaoundé, Cameroon.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Mimosa pudica Linn. (Mimosaceae) is a plant widely used in traditional African medicine to treat anxiety. The aim of the present study was to assess the anxiolytic and myorelaxant properties of M. pudica using behavioural tests. Two months old mice, Mus musculus Swiss were acutely treated by different doses of M. pudica (3, 10 and 30 mg/kg) and anxiety related responses evaluated by analyzing stress-induced hyperthermia (SIH), elevated plus maze (EPM), open field and hole board parameters. The horizontal wire and rota-rod tests were also used to highlight possible myorelaxant properties of M. pudica. The decrease of SIH was observed with M. pudica (30 mg/kg) treatment. In the EPM, significant increase of open arms entries and percentage of time spent in the open arms with M. pudica (10 mg/kg) was observed. Neither diazepam (3 mg/kg) nor M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg) produced changes of motor activity. However the change of motor activity was observed with M. pudica (30 mg/kg). In the hole-board test, M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg) significantly increased the number and duration of the head-dips respectively. The anxiolytic properties of M. pudica as assessed using the EPM test were abolished by flumazenil (3 mg/kg), by bicuculline (5 mg/kg), and FG 7142 (10 mg/kg). In the Horizontal wire test, both M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg) and distilled water allowed animals to grasp within 30 s. M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg) did not impair the duration of the time spent on the rota-rod. However at the dose of 30 mg/kg, up to 60 min, the M. pudica significantly reduced the time that animals remained on the rota-rod. This study indicates that M. pudica contains an effective psychotropic agent that acts via the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor complex as an anxiolytic at low doses and as a muscle relaxant at higher doses. These results in part could justify the use of this plant extract as an anxiolytic agent.
Keywords: Anxiety, Behaviour, Benzodiazepine, Myorelant, Mimosa pudica
Cite this paper: Rigobert-Espoir Ayissi Mbomo, Jean Pierre Omam Omam, Antoine Kandeda Kavaye, Stephanie Jacqueline Njapdounke Kameni, Elisabeth Ngo Bum, Anxiolytic (Benzodiazepine-Like) Properties of Mimosa pudica in Mice, International Journal of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2015, pp. 41-49. doi: 10.5923/j.ijbcs.20150403.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Generalized anxiety affects 10% of the world population, making them the most common of problems encountered in psychiatry [1, 2]. Despite the wide range of chemical substances that act against different anxiety states, benzodiazepines continue to face numerous problems, including a lack of specificity of action and side effects. Minor tranquilizers (anxiolytics) from plants, could provide at low doses the beneficial effect. The present study was conducted on sensitive plant (M. pudica) to ascertain the anxiolytic properties of this plant claimed by traditional medicine. M. pudica is a plant species belonging to the Fabaceae family, commonly found in the wetlands of the tropics. For a long time, various extracts of M. pudica were successfully used in traditional medicine in Africa, South America and Asia to treat a variety of human diseases [3, 4]. In Cameroon, a preparation of M. pudica is used both short and long-term to treat of a variety of problems, including headache, migraine, insomnia and anxiety disorders [5]. Despite the wide use of this plant, very little is known about the neuroactive substances it contains and neurobiological substrates it targets. Previous studies suggested an implication of GABAA receptor in the anxiolysis induced by M. pudica [6]. The main objective of this work was to evaluate the anxiolytic effects of M. pudica and further characterize the molecular mechanisms on anxiolysis in mice.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
- For the present study, fresh plants of M. pudica were collected at Oliga neighborhood in Yaoundé (Cameroon) during the month of April 2012 (rainy season). The collected samples were dried in a shad room for a month (to comply with traditional practices). The dried plants were crushed to obtain a green powder used for the preparation of the decoction.
2.2. Preparation of Decoction
- To prepare the decoction, 30 g of powder of M. pudica leaves were placed in a beaker containing 500 mL of water, then covered. The mixture was boiled for 20 min on a hot plate (100°C). After cooling, the preparation was filtered. The filtrate obtained (thick and sticky 265 mL) was the stock solution. Serial dilutions of this stock solution in well-defined volumes of distilled water provided different doses of the decoction used in this work (3, 10 and 30 mg/kg). Furthermore, to determine the amount of dry matter absorbed, the filtrate of M. pudica was evaporated in an oven at 60°C, until obtaining 1.77 g of brown powder (ie a yield of 5.9%).
2.3. Animals
- White mice, Mus musculus Swiss strain from a colony bred at the University of Dschang (Cameroon) were used. Animals were keept in a controlled environment (normal light cycle of 12 h, a temperature of 23ºC and a humidity of 55%). Animals were bred in wooden cages, in a quiet environment. During behavioral tests, the animals had free access to food and tap water. All animal handling procedures were done in accordance with National Ethic Guidelines (FWA-IRB00001954), and the experiments were designed to minimize the number of animals used and to minimize their suffering.
2.4. Procedure
2.4.1. Stress-Induced Hyperthermia in Group-Housed Mice
- When mammals are faced with stressful situations, their body temperature rises, referred to as stress-induced hyperthermia (SIH). The group-housed animals version of SIH is based on is based on the principle that, in a group of animals maintained together in the same cage, when removed from the cage at the regular interval of time, it observed the raise of body temperature from the first animal removed to the last one [7]. The equipment used to perform the SIH test is a thermometer (Harvard Apparatus) with a probe 2 mm in diameter and 2 cm in length. 24 h before all manipulations, animals were transferred from the animal room to the laboratory according to the protocol described by Bourin in 1992 [8]. To perform the test, male mice (24-31 g body weight) were divided into 5 groups (n = 10). The first group, the positive control, received phenobarbital (20 mg/kg). The second group that received distilled water served as control. The test groups were treated with one of three doses of the decoction of M. pudica (3, 10 or 30 mg/kg). Except for phenobarbital administered intraperitoneally (i.p), all the other substances were administered orally. One hour after treatment, the animals were removed one by one from the cage in the same order as the administration and the body temperature measured anally. The SIH (ΔT) was calculated by the method used by Borsini in 1989, and represented the difference between the basal T1 (mean temperature of first three mice) and the end T2 (mean temperature of last three mice) of group-housed male mice [7].
2.4.2. Elevated Plus Maze
- The elevated plus maze (EPM) is a model based on unconditioned fear [9]. The maze was made of wood and disposed on a support of 50 cm of height. The animals were taken to the experimental room 24 h before the test. After habituation to the experimental environment, each animal was individually removed from the home cage, and received one of the substances of interest. White mice of both sexes, aged about two months and weighing 20-30 g were used. The animals were first divided into 5 groups (n=6 each) thereafter, animals of each group received orally one of three doses of the decoction of M. pudica (3, 10 and 30 mg/kg) for test groups, distilled water for negative control group or diazepam at the dose 3 mg/kg administered i.p for the positive control group. 1 h after treatment of the first mouse, one after another, animals of each group were tested on the EPM for 5 min.
2.4.3. Spontaneous Behaviour in the Open Field Test
- This test examines the responses of rodents to new and unfamiliar environments where escape is prevented by the presence of the walls surrounding the paradigm [10, 11]. This test was here used to assess the level of anxiety and locomotor activity of animals subjected to various treatments. The open field test was conducted according to the procedure described by Belzung in 1999 [11]. The open field system design used in this work was made of wood (square floor of 40 cm surrounded by walls of 20 cm high, on the floor 16 tiles of 10 x 10 cm were marked and using another marker in red ink, it was brought to the center of the floor one tile with the same dimensions). Mice of both sexes weighing (20-30 g) were divided into groups (n=6 each). Each group received specific treatment: distilled water for the negative control, one of three doses of the decoction of M. pudica (3, 10 and 30 mg/kg) administered orally in a volume of 10 ml/kg. Two groups that received diazepam at the doses of 3 and 4.5 mg/kg (i.p) as positive. After randomized treatment (1 h), animals were individually placed in the center of the arena, and behavior of each mouse was observed for 5 min. Total ambulatory distance, time spent in the center of arena and the return delay in the centre tile noted.
2.4.4. Hole-Board Test
- Like the EPM test, the hole-board test is based on an unconditioned conflict between a motivation to explore new areas and tendency to avoid open and illuminated spaces by rodents [12]. However, the main behavior considered here is a specific ethological parameter called «head dip». For the hole-board test used in this work, the equipment used was a wooden made box (2.2 cm thick, square with 40 cm sides and protected by walls 15 cm high). Using a permanent marker, tiles 10 cm sides were drawn on the floor. The center of each tile was perforated with a hole 3 cm in diameter, the whole device was raised to 25 cm above the ground with a support. Mice of either sexes weighing 20-30 g were divided into 5 matched groups. Each group was given a specific treatment (distilled water for the negative control, diazepam at the dose of 3 mg/kg and 4.5 mg/kg for the positive control, or one of three doses of M. pudica for testing groups). All these substances were administered orally with the exception of diazepam administered (i.p) at the same volume (10 ml/kg). After 1 h treatment of each group, animals were placed in the center of the floor with the look turned away from observers, and then the behavior was recorded for 5 min. During the observation, the number and the length of time the animal lowered the head into the hole (head dip) were noted.
2.4.5. Study of Mechanism of Action of M. pudica in the Elevated Plus Maze
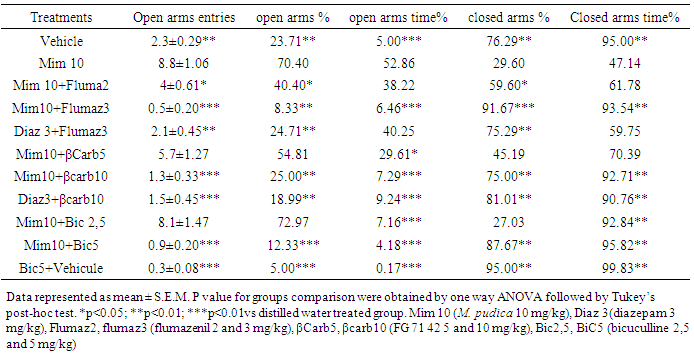
- Animals in groups of six were treated with a single dose of M. pudica (10 mg/kg). After oral administration of decoction for 30 min, test groups received the following substances (i.p): bicuculline antagonist on complex GABAA receptor, in 2.5 and 5 mg/kg; flumazenil (or RO 151788) (a competitive antagonist of benzodiazepine receptor site on the GABAA receptor), in 2 and 3 mg/kg; N-methyl-β-carboline-3-carboxamide or FG 7142, (partial inverse agonist of benzodiazepine receptor site on the GABAA receptor complex), in 5 and 10 mg/kg. Control animals (n=6) received 30 min after administration of distilled water, bicuculline (2.5 and 5 mg/kg), flumazenil (2 and 3 mg/kg) or the FG 7142 (5 and 10 mg/kg). Three groups designated positive control that received diazepam 3 mg/kg, were treated 30 min after administration of diazepam or bicuculline (5 mg/kg), flumazenil (5 mg/kg) or FG 7142 (3 mg/kg). A last negative control group for all test received distilled water 30 min after administration of distilled water. For each group, 1 h after administration of the first substance (30 min after administration of the second), mice were individually placed at the center of the EPM with the head turned to one open arm, and the behavior observed for 5 min.
2.4.6. Rota-Rod Test for Motor Coordination
- The rota-rod test, was described by Dunhand and Miya in 1957 to assess potential non-specific muscle relaxant or sedative effects of plant extracts [13]. The paradigm consists of a rotating cylinder of 23 cm in diameter. For the present study the cylinder was set at a speed of 16 rev/min as previously described by Pieretti [14]. The test was carried out on two consecutive days. One day before the experiment, the animals were subjected to a preliminary test, and only mice that could grab the rotating mat for a period of 180 s were selected for the test. On the test day, animals were divided into groups of six and treated orally with distilled water (negative control), different doses of M. pudica (3, 10 and 30 mg/kg) (test groups), and diazepam in doses of 3 and 4.5 mg/kg (i.p) (positive control group). One h after the various treatments, the animals were placed individually on the rotating cylinder of the rota rod and the time spent on this latter recorded at intervals of 30, 60, 90 and 120 min for a period of 120 s.
2.4.7. Horizontal Wire Test
- This test is based on the principle that the muscle relaxant substances inhibit the ability of rodents to grasp a horizontal wire [15, 16]. Immediately after the EPM test, the animals were subjected to the test of the horizontal wire. The experimental device was composed by a nylon wire of 1 mm in diameter and measuring 60 cm length, taut between two supports and high 40 cm above the bench. Briefly after the EPM test, one after the other, the mice were raised by the tail and allowed to hang with the front legs to the horizontal string taut. Once gripped the string, the animals were released. In each group, the number of mice that remained suspended on the string for a period of 30 s was recorded.
2.5. Statistics
- Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a Tukey’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. Values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. p<0.05 as threshold was considered statistical significance.
3. Results
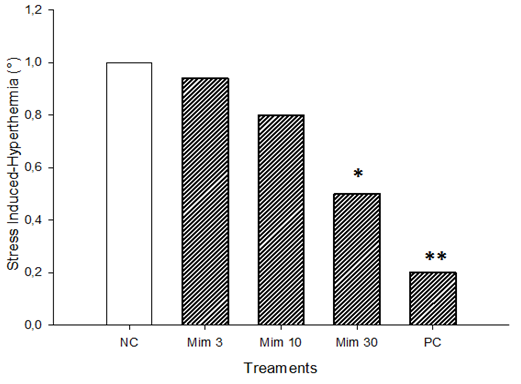
3.1. Effects of Single of Decoction of M. pudica on Stress-Induced Hyperthermia
- The value of SIH was 1°C in the negative control group; and 0.2°C in those treated with phenobarbital (20 mg/kg). The treatment of animals with gradual doses of M. pudica led to a significant (p<0.05) decrease of SIH up to 0.5°C with M. pudica (30 mg/kg), representing 50% of the value obtained with the negative control group (Fig. 1).
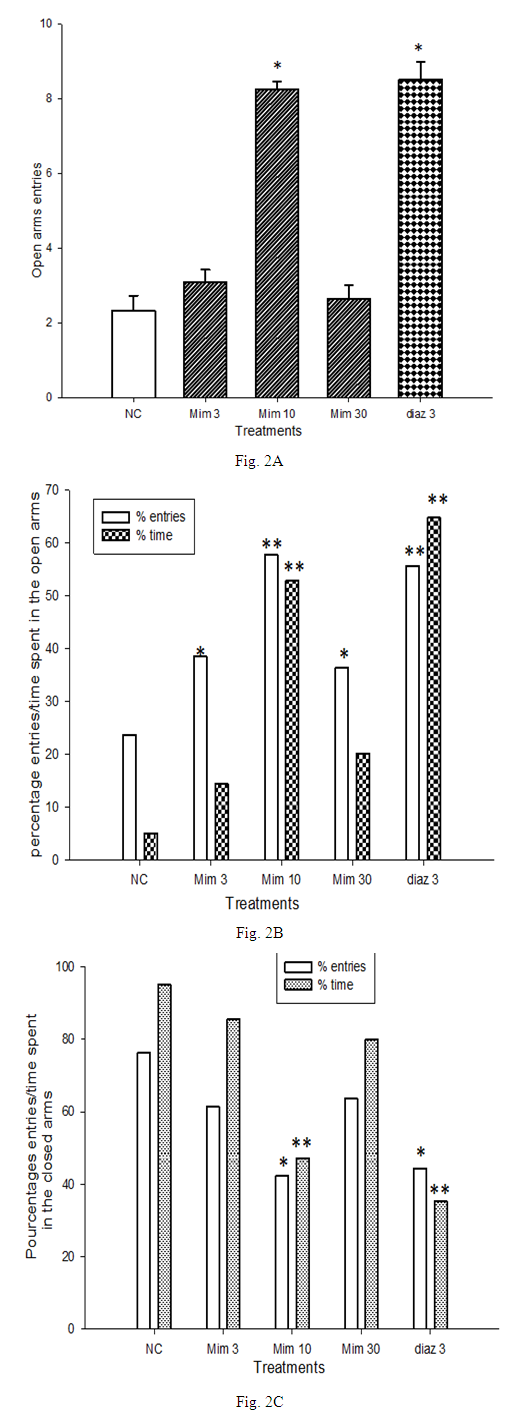
3.2. Effects of a Single Administration of Decoction of M. pudica on elevated Plus Maze Parameters
- The number of open arms entries was 2.33 in the negative control group, and 8.5 in the group treated with diazepam (3 mg/kg). The treatment of mice with M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg) resulted in a significant (P <0.05) increase of this parameter. The increase of open arms entries to 8.33 at the dose 10 mg/kg was approximately 300% of the effect observed with the negative control group (Fig. 2A). The value of 23.66% of open arms entries obtained with the negative control group increased to 38.48% and 57.74% with M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg respectively) (Fig. 2B). Animals of the negative control group spent 4.99% of observation time in the open arms, and those of the positive control, which were treated with diazepam (3 mg/kg) spent 64.76% (Fig. 2B). The percentage of time spent in the open arms rose to 52.86% in the group treated with M. pudica (10 mg/kg), representing a significant increase (p <0.01) of 1321% compared to the negative control group. The treatment of mice by M. pudica led to a decrease of closed arms avoidance (Fig. 2C). The percentage of closed arm entries of 76.33% in mice of negative control significantly decreased (p <0.01) to 42.25% with mice treated by M. pudica (10 mg/kg). A parallel decrease (47.13%) of the percentage of time spent in the closed arms was observed after treatment with the dose 10 mg/kg of M. pudica. Table 1 summarize the effects of bicuculline (2.5 and 5 mg/kg); flumazenil (2 and 3 mg/kg) and N-methyl-β-carboline-3-carboxamide (5 and 10 mg/kg) on Elevated plus maze parameters induced by M. pudica (10 mg/kg).
|
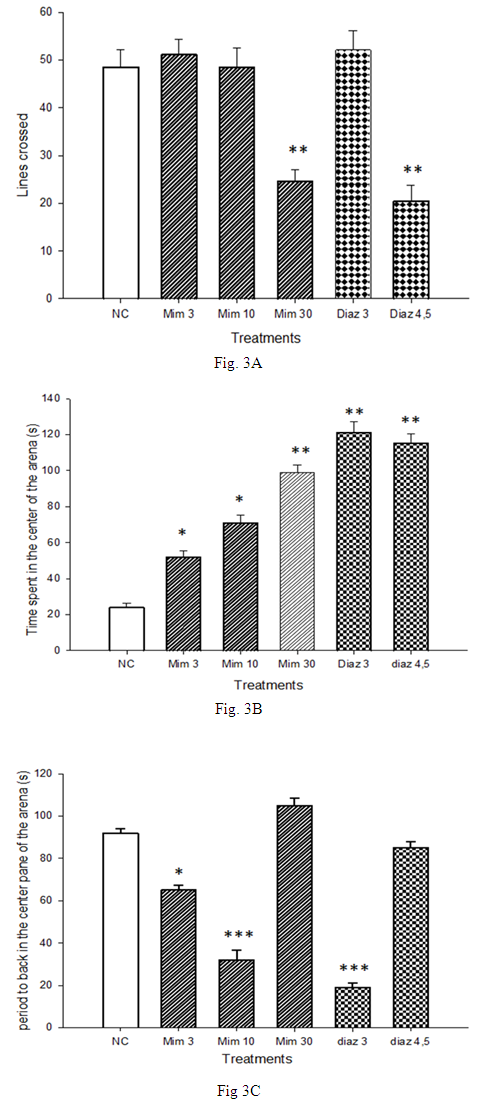
3.3. Effects of a Single Administration of Decoction of M. pudica on Open Field Parameters
- Mice of the negative control group crossed 48.5 ± 9 lines. Neither M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg) nor diazepam 3 mg/kg affected this parameter (Fig. 3A). However, the time spent in the center tile of the arena increased from 24 ± 2.40 s with mice of the negative control group to 52 ± 3.65 s in the group treated with M. pudica (10 mg/kg). Treatment of mice with diazepam (3 mg/kg) also significantly increased (p <0.01) this time to 121 ± 6.15 s, an increase of 504.17% compared to the negative control group (Fig. 3B). Mice of negative control group explored the peripheral zone of the open arena during 92 ± 2.0 s prior to the first back in the central area. Treatment with 10 mg/kg led to a significant decrease (p <0.001) of nearly 66% of the results obtained with the negative control group. Treatment with reference drug, diazepam (3 mg/kg), also induced a significant decrease in time of onset the first back in the center tile to 19 ± 2.01 s, a reduction of about 80% of the effect observed with the group that received distilled water (Fig. 3C).
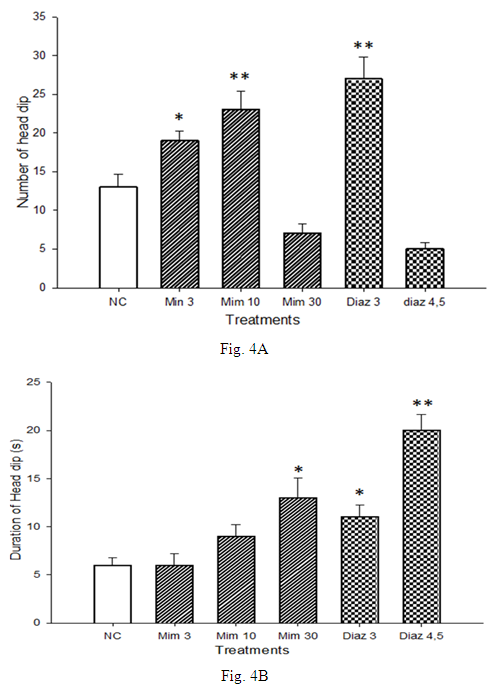
3.4. Effects of a Single Administration of Decoction of M. pudica on Hole Board Parameters
- The effects M. pudica on the hole-board paradigm are summarized in Fig. 4. The number of head dips increased from 13 ± 1.33 with animals of the negative control group to 23 ± 2.46 with mice treated by M. pudica (10 mg/kg), and 27 ± 2.85 with those receiving diazepam (3 mg/kg) (Fig. 4A). Duration of «head dip» increased from the value of 6 ± 0.8 s in the negative control group to 9 ± 1.23 s with mice treated with M. pudica (10 mg/kg). With the single dose of diazepam used (3 mg/kg), a significant (p <0.05) increase to 11. 3 ± 1.3 s was also observed (Fig. 4B).
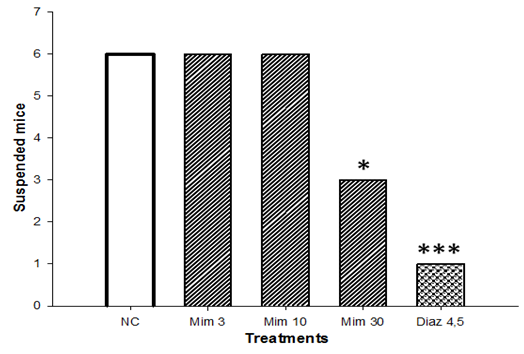
3.5. Effects of a Single Administration of Decoction of M. pudica on the Horizontal Wire Test
- After single administration of M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg), mice were kept in suspension on the horizontal wire for 30 s. In the groups treated by M. pudica (30 mg/kg) and diazepam (4.5 mg) a decrease to 3 and 1, respectively, was observed (Fig. 5).
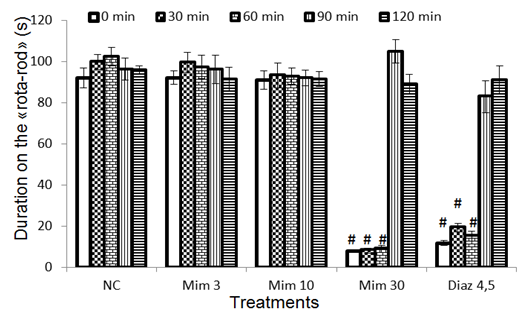
3.6. Effects of a Single Administration of Decoction of M. pudica on Time Spent on the Rota-Rod
- At 0, 30, 60, 90 and 120 min intervals, no difference (compared to the negative control) of the time spent by animals on the rotating mat of the rota rod was observed after treatment with M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg). However, treatment with M. pudica (30 mg/kg) and diazepam (4.5 mg/kg) significantly reduced the time animals spent on the rotating mat until the 60th min. After the 60th min, no effect of different treatments was observed on this parameter (Fig. 6).
4. Discussion
- The major finding of the present study is the ability of M. pudica to reduce the level of anxiety in mice in multiple behavioral paradigms, including the SIH, the open field, the EPM, and the hole board. The SIH is a physiological phenomenon that appears when animal including human are faced to stressful situation. In this experiment, the handling by the experimenter was the stressful situation. In this procedure, anxiety and fear increased by anticipation the body temperature. Thus, in group-housed mice, mice removed late showed higher body temperature than those removed earlier, and substances that prevent this increase of temperature induced by stress are refer as anxiolytic. The three incremental doses of M. pudica administered orally to mice significantly inhibited (up to 50%) the increase of body temperature induced by stress. The SIH was also attenuated by anxiolytic dose of phenobarbital, suggesting that M. pudica contains anxiolytic substances. This conclusion is supported by previous studies [17, 18]. EPM has been widely used to assess in rodent anxiolytic and even anxiogenic effects of several pharmacological substances including plant extracts [19, 20]. From the present study, oral administration of M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg), resulted in a significant four-fold increase in the number of entries and time spent in the open arms of the EPM. Furthermore, it was observed that when given distilled water, mice placed at the central platform directly returned into the closed arms. This is consistent with previous observations showing that once placed in the center of the EPM, unlike the treated mice, the mice not treated with anxiolytic substances avoided the open arms [21]. In contrast to low doses, the highest dose (30 mg/kg) of M. pudica, which obviously had no effect on the open arms entries and duration, reduced by 70% the total entries. At this dose, M. pudica decreases arousal [22, 20] a finding which is in line with a previous report of a sedative effect of M. pudica at high doses [23]. This sedative profile of M. pudica at high doses is comparable to that previously observed with diazepam [24, 25]. Consequently we suggest that M. pudica contains substances that reduce anxiety in mice, but may induce sedation and muscle relaxation as side effects at higher doses. Given similarity of the physiological effects of M. pudica and diazepam it is conceivable that these agents act by binding to the same sites of the GABAA receptor complex [26].It has long been known that the responses of mice in the paradigm of open field primarily represent a fear response to a new environment, the isolation of the social environment or finally a motivation to reconnect with others mice [27, 28]. Acutely administered to mice, M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg) did not affect horizontal activity (general locomotion) on the open field paradigm. The treatment of animals by gradual doses of M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg) has led to a decrease of the latency to return to the central area. At the higher doses used M. pudica (30 mg/kg) and diazepam (4.5 mg/kg), symptoms of sedation were observed, similarly to those reported previously with high doses of diazepam [29]. In addition, a gradual increase in time spent in the central red tile was observed. An increase in central locomotion or time spent in the central area of the open field without altering the locomotor activity could be interpreted as an anxiolytic effect, while a decrease in vertical activity and locomotion involved sedation [30, 28]. Thus the results of the present study suggest that M. pudica is anxiolytic at low doses and sedative at higher doses as assessed by the open field paradigm. The hole-board test is a simple procedure to measure the response of animals to new unfamiliar environments, and is widely used to evaluate the emotional, anxiety and stress responses in animals [31]. The hole-board test was used in the present study to assess the anxiolytic properties of M. pudica administered orally. Head dip behavior is sensitive to changes in emotional states suggesting that the expression of anxiety in animals could be reflected in the change in the frequency and the duration of the head dip [12]. In the present study it was observed that M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg) increased the number of head dips without having an impact on locomotor activity. The low frequency of head dip observed with the larger dose of M. pudica (30 mg/kg) could be explained by sedation. The treatment of animals by gradually increased doses of M. pudica also resulted in a dose-dependent increase of the duration of head dip. As previously observed in the open field paradigm, the results of this test suggest that low doses of M. pudica have anxiolytic properties.The present results also indicate a significant effect of co-treatment with M. pudica (at the dose of 10 mg/kg) and FG 7142 (10 mg/kg) on the open arm entries and percentage of time spent in the open arms of the EPM. These results are consistent with those previously observed on the anxiogenic effects of FG 7142 and indicate that this substance counteracts the effects of M. pudica on the parameters of the EPM [32]. These findings support the assumption that substances of M. pudica could induce their anxiolytic effects by binding to the benzodiazepine site of the GABA receptor complex. Co-treatment with flumazenil (3 mg/kg) completely abolished the effects of diazepam and M. pudica (10 mg/kg) on behavioral parameters of the EPM, indicating that like diazepam, M. pudica acts via the benzodiazepine binding site of the GABAA receptor, this is consistent with a previous study showing, M. pudica like diazepam enhance the inhibitory effect of the GABA agonist THIP on neuronal firing rate [6]. These effects of M. pudica on EPM parameters (open arms entries and time spent into the open arms) are similar to those obtained by Medina. In fact Medina and his colleagues showed that co-administration of chrysin (a flavonoid isolated from Passiflora), with flumazenil (or diazepam with flumazenil) counteracted the effects of chrysin (or diazepam) [33]. Although the competitive GABA antagonist site bicucullline at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg showed no effect on EPM parameters induced by M. pudica, bicuculline at a dose of 5 mg/kg coadministrated with M. pudica (10 mg/kg) reduced the percentage of time spent in the open arms induced by M. pudica. Dalvi and Rodgers showed that the reduction of this standard parameter of the EPM was an indicator of decreased anxiety [20]. Although deep anxiogenic effects are evident when the larger dose of bicuculline was co-administered with M. pudica, the level of active behavior was markedly reduced. Since bicuculline at high doses could be convulsant, considerable evidence has confirmed that this inhibition of movement was more characteristic of a high degree of fear in animals [34, 35, 36]. Behavioral tests revealed a decrease of anxiety’s level after treatment with M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg). With M. pudica (30 mg/kg) symptoms of sedation and immobility were observed, and then rota rod and horizontal wire tests were used to assess the effects of M. pudica on coordination of motor activity. Up to 120 s after the treatment, M. pudica (30 mg/kg) decreased the time spent on the rotating mat. Previous studies demonstrated that, substances which decrease the residence time of rats and mice on the rotating mat were muscle relaxants [37, 14]. Furthermore treatment with M. pudica (3 and 10 mg/kg) allowed mice to grab a horizontal wire, but M. pudica (30 mg/kg) decreased the number of mice maintained in suspension. Huen and his colleagues have showed that, muscle relaxants decreased the ability of rodents to cling on a horizontal wire [16]. These findings suggest that M. pudica could be a muscle relaxant at higher doses.
5. Conclusions
- In summary, results of the present study provide evidence that M. pudica manifests anxiolytic properties at low doses, in addition to the sedative and muscle relaxant properties at high doses. These activities may modulate, at least in part, via the benzodiazepine receptor on the GABAA receptor complex. Further studies are necessary to clarify the molecular anxiolytic mechanisms of action of specific components of M. pudica.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- To Pr Marina BBENTIVOGLIO and Pr Roger BUTTERWORTH for their kindle reading in the account of the first SONA Workshop on «Getting your article ready for submission» in Rabat (Morocco), 2013.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML