-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Brain and Cognitive Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1840 e-ISSN: 2163-1867
2014; 3(1): 6-24
doi:10.5923/j.ijbcs.20140301.02
Brain Plasticity Associated with Meditation Experience: Neurofunctional Approach and Structural Findings
1Department Basic Psychology II (Cognitive Processes), Complutense University of Madrid, Madrid, 28223, Spain
2Faculty of Education, International University of La Rioja, Logroño, 26002, Spain
Correspondence to: Carlos Valiente-Barroso, Department Basic Psychology II (Cognitive Processes), Complutense University of Madrid, Madrid, 28223, Spain.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The study of neurofunctional structure associated with the practice of meditation along with its neural, cognitive and emotional implications, has increased exponentially in recent years, forming a regular line of research in neuroscience production. We review published studies that have used different experimental paradigms (neurophysiological and neuroimaging testing, cognitive tests), which, through indirect evidence and direct findings, highlight both functional and structural changes evidencing a neuroplasticity phenomenon. Thus, our results establish the existence of significant changes in brain plasticity correlated with the time devoted to their practice, and regardless of the specific style or tradition, manifested primarily through (1) changes in the bioelectrical brain pattern, (2) metabolic activation of specific brain areas, (3) cognitive functions supported by idiosyncratic neural networks, and (4) neuroimaging studies that show measurable increases in different subcortical and cortical brain structures, belonging mainly to the prefrontal region. In turn, revealing any shortcomings in this line of research, provides for future initiatives aimed at the optimization of experimental approaches, conceptual clarifications, control of intervening variables and inclusion of new instrumental paradigms.
Keywords: Cerebral plasticity, Cognition, Executive functions, Meditation, Neuroscience
Cite this paper: Carlos Valiente-Barroso, Brain Plasticity Associated with Meditation Experience: Neurofunctional Approach and Structural Findings, International Journal of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2014, pp. 6-24. doi: 10.5923/j.ijbcs.20140301.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- This recent years have witnessed an increase in studies focusing on the neuroscientific implications associated with the practice of meditation. [1]. The clinical application of meditation and its role in understanding human consciousness have come into the focus of psychological research [2, 3]. Meditation has been a spiritual and healing practice in some parts of the world for more than 5,000 years [4]. Historically, religious or spiritual aims were intrinsic to any form of meditation. These traditional practices held some type of spiritual growth, enlightenment, personal transformation, or transcendental experience as their ultimate goal [5]. During the last 40 years, the practice of meditation has become increasingly popular and has been adapted to the specific interests and orientation of Western culture as a complementary therapeutic strategy for a variety of health-related problems [6, 7]. Both secular forms of meditation and forms rooted in religious and spiritual systems have increasingly attracted the interest of clinicians, researchers, and the general public, and have gained acceptance as important mind-body interventions within integrative medicine (the combination of evidence-based conventional and alternative approaches that address the biological, psychological, social, and spiritual aspects of health and illness). With an estimated 10 million practitioners in the United States and hundreds of millions of practitioners worldwide [8], meditation was the first mind-body intervention to be widely adopted by mainstream healthcare providers and incorporated into a variety of therapeutic programs in hospitals and clinics in the United States and abroad [9, 10].The word “meditation” is derived from the Latin “meditari,” which means “to engage in contemplation or reflection.” Meditation has been characterized in many ways in the scientific literature and there is no consensus definition of meditation. This diversity in definitions reflects the complex nature of the practice of meditation and the coexistence of a variety of perspectives that have been adopted to describe and explain the characteristics of the practice. Therefore, we recognize that any single definition limits the practice artificially and fails to account for important nuances that distinguish one type of meditation from another [11].It has been developed a detailed operational definition of meditation broad enough to include traditional belief-based practices and those that have been developed specifically for use in clinical settings. Using a systematic approach based on consensus techniques, we can to define any practice as meditation if it (1) utilizes a specific and clearly defined technique, (2) involves muscle relaxation somewhere during the process, (3) involves logic relaxation (i.e., not “to intend” to analyze the possible psychophysical effects, not “to intend” to judge the possible results, not “to intend” to create any type of expectation regarding the process), (4) a self-induced state, and (5) the use of a self-focus skill or “anchor” for attention [12]. From a cognitive and psychological perspective, it has been defined meditation as a family of self-regulation practices that aim to bring mental processes under voluntary control through focusing attention and awareness [13]. Other behavioral descriptions emphasize certain components such as relaxation, concentration, an altered state of awareness, suspension of logical thought processes, and maintenance of self-observing attitude [14]. From a more general perspective, Manocha [15] described meditation as a discrete and well-defined experience of a state of “thoughtless awareness” or mental silence, in which the activity of the mind is minimized without reducing the level of alertness. Meditation also has been defined as a self-experience and self-realization exercise [16]. Despite the lack of consensus in the scientific literature on a definition of meditation, most investigators would agree that meditation implies a form of mental training that requires either stilling or emptying the mind, and that has as its goal a state of “detached observation” in which practitioners are aware of their environment, but do not become involved in thinking about it. All types of meditation practices seem to be based on the concept of self-observation of immediate psychic activity, training one’s level of awareness, and cultivating an attitude of acceptance of process rather than content [5]. Meditation practices may be classified according to certain phenomenological characteristics: the primary goal of practice (therapeutic or spiritual), the direction of the attention (mindfulness, concentrative, and practices that shift between the field or background perception and experience and an object within the field) [5, 17], the kind of anchor employed (a word, breath, sound, object or sensation) [10, 18, 19], and according to the posture used (motionless sitting or moving) [10].Mindfulness meditation has been reported to produce positive effects on psychological well-being that extend beyond the time the individual is formally meditating. Over the last three decades mindfulness meditation practices have been increasingly incorporated into psychotherapeutic programs, to take advantage of these benefits [10, 20]. A large body of research has established the efficacy of these mindfulness-based interventions in reducing symptoms of a number of disorders, including anxiety [17, 21, 22], depression [20, 23], substance abuse [24, 25, 26], panic disorders [27], eating disorders [10; 28], emotional distress [27], and cognitive abilities [29]. The effects of meditation practices as complementary treatments for medical conditions other than mental illness have been evaluated using a variety of methods and outcomes. These clinical conditions include hypertension [30] and other cardiovascular disorders [31, 32], pain syndromes and musculoskeletal diseases [20, 33, 34, 35], respiratory disorders (e.g., asthma, congestive obstructive pulmonary disease) [36], dermatological problems (e.g., psoriasis, allergies) [37], immunological disorders [34], treatment-related symptoms of breast and prostate cancer [20], as well as improving well-being and quality of life [37]. These outcomes are complemented by reports of alterations in physiological parameters and biochemical measures as a consequence of meditation [38, 39].Finally, meditation practice has been demonstrated to affect higher functions of the central nervous system, reflected in increased performances and altered brain activity. Less is known about the link between meditation and brain structure.
2. Objective and Methodology
- This paper aims to clarify the effect on human neural structure caused by the practice of meditation, through published findings from studies on different types that are part of their typology. In particular, any possible changes in cortical and subcortical structures are being studied directly, as evidenced by neurostructural effects, and indirectly, as inferred by neurofunctional changes produced by extended practice.We are implementing a review on this topic, analyzing the state of this issue through significant research gathered from benchmark neuroscience publications (PubMed, Science Direct and PsycINFO). We use this research to analyze and summarize various studies based primarily on Electroencephalographic (EEG) studies, positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and functional imaging magnetic resonance (fMRI) studies, as well as through neurocognitive tests.The findings of the phenomenon of neuroplasticity produced by extended practice of meditation can be exposed through two perspectives. So on the one hand, we refer to anatomical changes in the brain, which are tangible and measurable, originated through this practice, visible through structural neuroimaging. From another point of view, we will discuss the most relevant data, which in indirectly, show us the neurofunctional changes generated by the practice of meditation sustained over time, as evidenced by EEG, PET, SPECT, fMRI and cognitive tests.
3. Neurofunctional Approach (Indirect Evidence)
- Given that a specific neural functioning is based on a specific neuroanatomical structure, we highlight the studies demonstrating the idiosyncratic aspects of brain functions, which associated with the practice of meditation, provide us with plausibility arguments to infer the existence of underlying brain changes related with the practice. For this purpose, we will present the key findings arising from studies with EEG, functional neuroimaging and neuropsychological testing. Aware that these tests, strictly, do not have the ability to show neuroanatomical changes, we base our argument on the inferential ability derivable from its results. In the case of EEG and fMRI, we consider most scientific value the studies showing neural functioning during meditation, comparing brain activation in expert meditators with brain activation in novice meditators, provided that the latter, possess sufficient skills to execute the meditative technique analysed. Consequently, if neurofunctional differences were found with identical performance, the cumulative effect of meditative practice could be regarded as the differentiating factor between both groups, and therefore, the independent variable to justify this contrasting assumption. However, the studies comparing different types of mind exercises are more numerous (e.g. comparing meditation vs. relaxation), as well as between meditator groups and control groups, ignoring the synergistic effect produced between the activation associated with the state of meditation requested at a particular moment and the possible underlying, present and permanent neuroplastic changes in the analysed meditator, derived from years of practice.
3.1. Neurophysiological Findings
- Early studies of meditators implicated alpha (8-12 Hz) power increases as both a state and trait effect of meditative practice -Yogic, Zen, and Transcendental Meditation- [40, 41, 42, 43]. Later studies have failed to replicate the early findings of increased alpha in advanced practitioners but have reported increased alpha coherence, especially in assays of TM practitioners [44, 45, 46, 47]. Advanced, but not beginner, Qigong meditators increased alpha power selectively over frontal cortex; decreases in alpha power over occipital cortex and concomitant decreases in peak alpha frequency were observed [48]. Theta (4-8 Hz) power increases for meditative practice have been widely reported, especially in the assays of concentrative/focused attention practitioners [49, 50, 51, 52]. Some studies of yogic meditative practice found increases in theta to be associated with proficiency in meditative technique [49, 53, 54, 55], and early investigations with Zen meditation indicate theta increases to be characteristic of only the more advanced practitioners [55]. Relative increase in frontal theta (4-8 Hz) power was observed during meditation with long-term Vipassana meditators [56]. Increased frontal midline theta power during meditation has been observed [57, 51, 58, 52], although a similar activation occurs in non-meditation- related studies of sustained attention [59, 60, 61, 62]. Frontal midline theta activity is generated by anterior cingulate cortex, medial prefrontal cortex, or dorsolateral prefrontal cortex [59, 61]. This activity is correlated with attention-demanding tasks [60, 62]. Recently, Baijal & Srinivasan [50], investigated the temporal dynamics of oscillatory changes during Sahaj Samadhi meditation (a concentrative form of meditation that is part of Sudarshan Kriya yoga) and they found that the generation of distinct meditative states of consciousness was marked by distinct changes in spectral powers especially enhanced theta band activity during deep meditation in the frontal areas. Meditators also exhibited increased theta coherence compared to controls. Interestingly, increased frontal theta activity was accompanied reduced activity (deactivation) in parietal-occipital areas signifying reduction in processing associated with self, space and, time.Das & Gastaut [63], first reported widespread increased high frequency gamma (20-40 Hz) activity in association with meditation, reporting that after a long period of meditation some of the more advanced Yogis studied exhibited increased gamma states associated with periods of subjective deep meditation/samadhi [63]; more recent meditation gamma findings have been reported as well [64; 65, 66, 67]. They specifically reported that relative occipital increases in gamma were observed in a meditation focused on visualization of the Buddha relative to other meditative states not incorporating visualization. Another recent study of meditation and gamma activity indicated that long-term meditators relative to controls exhibited decreased negative emotional stimulus-induced gamma power activation, likely related to decreased emotional reactivity due to such practice [64]. One report of widespread increases in gamma power assessed expert Tibetan Buddhist meditators engaged in a loving-kindness/compassion meditative practice and found both trait and state associations between meditation and gamma activity [66]. Midline frontoparietal gamma power was higher at baseline (trait) in advanced Tibetan Buddhist practitioners, and upon engaging in compassion meditation gamma power increased in magnitude (state) to a very significant degree. Significantly increase in parieto-occipital gamma power has been observed during meditation with long-term Vipassana meditators [56].Previous assessments of meditation have not often reported effects on the delta frequency band (1-4 Hz), but it is unclear whether it has been systematically analyzed. Recently, using LORETA to analyze EEG, two reports of increased trait frontal delta in long-term Zen and Qi-Gong meditators suggest that there may be an important interaction between meditative practice and delta brain activity [68, 69]. Decreased delta activity in the temporo-parietal junction, secondary motor cortex, and sensory association cortices appeared indicative of increased brain activation associated with detection and integration of internal and external sensory information, with detachment from the same as indexed by inhibited activity (increased delta) in prefrontal areas responsible for analyzing, judging, and expectation [69]. Moreover, as studies examining the neurofunctional impact of meditation, witnessing permanent changes after its extended practice, using specifically, the comparison between expert and novice meditators, highlights those who gather higher theta and alpha power [53], only increased theta [70], increased alpha power and and alpha coherence at rest [45], increased 6-10 Hz spectral power in Stage III-IV sleep with increased meditation and reports of awareness during sleep [71], increased theta-alpha (6-10 Hz) power and increased frontal coherence across all bands during cognitive CNV task [47].In conclusion, there is an increase of alpha power related to internally driven mental operations, like the imagery of tones, internal attention, or working memory retention and scanning. Furthermore, EEG biofeedback studies indicate that alpha activity is the brain rhythm, which can be most easily controlled. Subjects can be trained to either produce or suppress alpha activity. Moreover, taken together, the general findings of theta activity related to meditative processes do not provide sufficient evidence to correlate its form of appearance with a specific step of meditative development. One may speculate that theta activity occurs after the specifically altered alpha patterns related to the beginner/student level have already been established in the brain, possibly as a correlate of increased relaxation. Theta activity would then be closer associated with an advanced level of meditative practice. Finally, synchronized gamma activity is highly relevant for neural plasticity and the implementation of new processing circuits. The findings of strongly increased synchronized gamma activity in meditation experts may thus be related to processes of cortical restructuring and learning. These processes may provide a permanent neural basis facilitating specific meditation-related states of consciousness, as well as altered perception and cognition outside meditation practice.
3.2. Functional Neuroimaging Studies
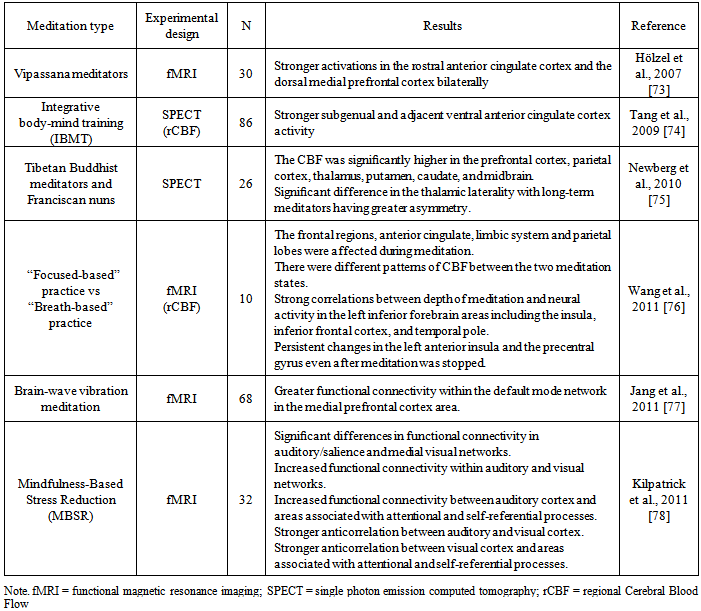
- There are numerous studies that show changes in brain function motivated by the practice of meditation. Most of the studies compare an experimental group of meditators against a control group not involved in the practice. For a revision covering up to what was published in 2006, refer to Cahn and Polich [72]. Currently, we are highlight results from recent research (see table 1).
|
3.3. Neuropsychological Approach
- The majority of Meditation studies have investigated the physiological and neurobiological correlates of the acute effects of Meditation. As we will see later, several studies of this type, which record the brain activation of meditators, highlight the influence the meditation exercises on some cognitive functions, highlighting those that refer specifically to attentional capacity. Fewer still are the investigations that focus exclusively on the effects that this practice carries on cognitive functions in terms of both enhancement and preservation.Although both sustained attention and the efficiency of inhibitory mechanisms have been shown to be reduced in the older adults [83], and this weakened inhibitory control leads [84] to increased distractedness and is thought to result from altered prefrontal cortex function in aging populations [83], the results of research have indeed suggested that attentional training in the form of meditation counteract these aging effects, helping to preserve attentional resources. In this way, evidence exists for long-term improvements with Meditation in cognitive skills, mainly in the domains of attention, perceptual sensitivity and inhibitory control [85]. Thus, long-term Meditators have been shown to be superior to controls in selective and sustained attention and inhibitory control as well as in EEG neurophysiological correlates of performance [72]. Furthermore, several studies have shown enhanced perceptual acuity and enhanced attentional and inhibitory skills in long-term practitioners of Mindfulness Meditation practice [86, 87, 88] and onepointedness Tibetan Buddhist Meditation [89]. Improvements in reaction time and executive functions have also been reported in practitioners of other Buddhist Meditation techniques [90]. These benefits in tasks of inhibitory self-control, attention and perception are likely to reflect the long-term effects of concentrative practices that teach attentional focus and the inhibition of task-irrelevant external and internal activity such as thoughts or environmental distraction. Remarkably, there is evidence that even very short-term Meditation based mental training of weeks to months can enhance performance on attention tasks [88]. Moreover, a study by Tang et al. [91] revealed that 20 min of meditation a day over a five-day period improves executive attention. In this study executive attention was assessed by determining the efficiency of mental conflict resolution. In turn, Zeidan et al. [92], found benefits after four days; brief meditation increased sustain attention, visuo-spatial processing, working memory, and executive functioning. Recently, Moore & Malinowski [93], discovered the link between meditation, self-reported mindfulness and cognitive flexibility as well as other attentional functions. The study of Van Leeuwen et al. [94], show that long-term meditation practice leads to a reduction of the attentional blink, and their results support the hypothesis that meditation practice can alter the efficiency with which attentional resources are distributed and help to overcome age-related attentional deficits in the temporal domain. Likewise, Lutz et al. [95] suggest that 3-months of intensive training in meditation enhances attentional stability, reduces task effort and amplifies the phase-consistency of the brain responses to task-related sensory inputs. Moreover, Van den Hurk et al. [96] discovered better orienting and executive attention (reflected by smaller differences in either reaction time or error score, respectively), observed in the mindfulness meditation group; furthermore, extensive mindfulness meditation appeared to be related to a reduction of the fraction of errors for responses with the same reaction time. A more recent study by Kilpatrick et al., [78], suggest that 8 weeks of mindfulness meditation training alters intrinsic functional connectivity in ways that may reflect a more consistent attentional focus, enhanced sensory processing, and reflective awareness of sensory experience. More recently, we have analyzed the impact of another style of meditation (Catholic contemplative in cloistered convents), which, to date, can be considered as unique in this research field. Thus, by applying neuropsychological tests assessing executive functions, better cognitive performance has been found in older meditators, with a more extensive experience of contemplative meditation-compared with young less experienced meditators, both in cognitive flexibility and attentional control, and also in relation to their performance on verbal fluency, abstraction and conceptualization, stunningly evading the foretasted decline associated with aging [97, 98].Since these cognitive functions are crucial for other processes such as learning, awareness, decision making, etc., and this positive influence, which would bring the practice of meditation, seems to be demonstrated by sustainable neuroplastic mechanisms, we emphasize the importance of meditation practice in order to optimize brain function and cognitive development.
4. Structural Brain Changes (Direct Evidence)
- The findings on structural brain changes associated with the practice of meditation are still in their infancy. In this section, we describe in more detail some of the most important research conducted from this perspective.One of these studies, which could be considered as a pioneer, was carried out by Lazar et al. [99], conducted using a sample of twenty participants with extensive training in insight meditation. These participants were not monks, but rather typical Western meditation practitioners who incorporate their practice into a daily routine involving career, family, friends and outside interests. Cortical thickness was estimated from two magnetization prepared rapid gradient echo (MPRAGE) structural images collected from each participant that were then motion-corrected and averaged together to form a single high-resolution image [100, 101, 102]. An initial estimate of the gray/white matter boundary was constructed by classifying all white matter voxels in a magnetic resonance imaging volume using a combination of geometric and intensity-based information. A surface-deformation procedure was then used to obtain subvoxel resolution in the gray/white boundary and in the pial surface using a combination of smoothness constraints and intensity terms. The resulting cortical surface models for all participants were aligned to an atlas of cortical folding patterns using a high-dimensional nonlinear registration technique. Their data indicate that regular practice of meditation is associated with increased thickness in a subset of cortical regions related to somatosensory, auditory, visual and interoceptive processing. Further, regular meditation practice may slow age-related thinning of the frontal cortex. Previous studies of cortical plasticity in animals and humans have shown that when a task requires that attention be consistently directed towards a behaviorally relevant sensory stimulus (e.g. a somatosensory) [103] or auditory stimulus [104] over repeated practice sessions [105] robust changes in sensory cortical maps result [106]. Increased cortical thickness could be due to greater arborization per neuron, increased glial volume or increased regional vasculature. The methods employed do not distinguish between these possibilities; however, each of these mechanisms is supportive of increased neural function. Within the search territory, a large region of right anterior insula and right middle and superior frontal sulci corresponding approximately to Brodmann areas (BA) 9 and 10 were significantly thicker in meditators than in controls. The left superior temporal gyrus and a small region in the fundus of the central sulcus (BA 3a), showed trends towards a significantly thicker cortex in meditation participants than in controls. Analysis of the right frontal BA 9/10 subregion resulted in a significant age by group interaction, with typical age-related decreases observed in the control group but not in the meditation group. The most experienced participants were also among the oldest. As age-related decreases in cortical thickness are greatest in frontal regions [102], it is possible that the effect of age may obscure the modest effects of meditation practice in these areas, thereby minimizing our ability to detect significant correlations. Such age-related effects may account for the fact that the strongest correlation with experience was found in the occipitotemporal region, while other regions of interest, which all lie in frontal regions, had only low correlation with experience. Interestingly, despite the effects of aging on the prefrontal cortex, in one focal region of BA 9/10 the average cortical thickness of the 40-50-year-old meditation participants was similar to the average thickness of the 20-30-year-old meditators and controls, suggesting that regular practice of meditation may slow the rate of neural degeneration at this specific locus. Future longitudinal studies will be required to verify this finding. Finally, most of the regions identified in this study were found in the right hemisphere. The right hemisphere is essential for sustaining attention [107], which is a central practice of Insight meditation. The largest between-group difference was in the thickness of right anterior insula. Functional imaging and electrophysiological studies in humans and monkeys have implicated the right anterior insula in tasks related to bodily attention and increased visceral awareness [108, 109]. Structural measures of gray matter volume of the right anterior insula predict accuracy of objective measures of interoceptive performance, as well as subjective ratings of global visceral awareness [109]. The differential thickness between groups in this region is consistent with increased capacity for awareness of internal states by meditators, particularly awareness of breathing sensations. Right BA 9/10 has been shown to be involved in the integration of emotion and cognition [110]. It has been hypothesized that by becoming increasingly more aware of sensory stimuli during formal practice, the meditation practitioner is gradually able to use this self-awareness to more successfully navigate through potentially stressful encounters that arise throughout the day [111, 112].Pagnoni & Cekic [84], observed a similar effect for gray matter volume in the prefrontal cortex by difference between meditators and controls in the correlation of age and cortical thickness of prefrontal areas. This research, had a sample which consisted of Thirteen Zen meditators with more than 3 years of daily practice were recruited from the local community and meditation centers, along with 13 control subjects who never practiced meditation. Were employed Voxel-based morphometry for MRI anatomical brain images and a computerized sustained attention task. Furthermore, they observed a difference in the age-related decline rate of cerebral gray matter volume in the putamen between regular Zen meditators and control subjects, with total cerebral gray matter volume displaying a trend of significance for the same effect. These findings were complemented by a similar pattern in the capacity for sustained attention, a cognitive process that occupies a central position in the meditative exercise. While an observed difference in anatomical structure correlating with an individual ability can be generally interpreted as either an innate neural predisposition to that ability or a learning-dependent alteration, there is strong evidence in humans that intensive practice of a task for a period of only a few months can in fact induce anatomical plasticity [113, 114]. The cross-sectional design of the present study cannot rule out the possibility of a selection bias (i.e., subjects less prone to cognitive and neural aging could also be more inclined to practice meditation or could differ from controls on some hidden variable, such as diet), albeit it is worthwhile to consider the mechanisms that could underlie a potential neuroprotective effect of meditation. Zen meditation is a task that is likely to influence brain function at several levels, from autonomic and hormonal regulation to emotional and executive processes [115]. The finding of a reduced rate of decline with age of both global and regional gray matter volume in meditators may in fact indicate the involvement of multiple mechanisms of neuroprotection. Potential causal factors for the observed changes include autonomically mediated vascular effects, modulation of hypothalamic-pituitary- adrenal (HPA) axis activity [116], and CNS-mediated influence on immune function [117]. Although the evidence is quite sparse, effect of meditation on stress reduction [118], autonomic regulation [53, 58, 119], and immune activity [120] have all been previously reported in the literature. The observed regional effect in the putamen, on the other hand, may be more specifically related to the cognitive processes engaged by meditation, such as the conscious regulation of attention and posture. The basal ganglia’s corpus striatum, which includes the putamen, is a predominantly dopaminergic structure that beyond its classical role in motor control and learning is also implicated in cognitive flexibility and attentional processing [121].Hölzel et al. [122], extends the findings by Lazar et al. [99] and suggests also a wider network of brain regions involved in meditation show long-term structural differences. Using voxel-based morphometry, this study investigated MRI brain images of 20 mindfulness (Vipassana) meditators (mean practice 8.6 years; 2 h daily) and compared the regional gray matter concentration to that of non-meditators. In ROI analyses, gray matter concentration in the right hippocampus and right anterior insula was significantly greater in meditators. The cluster at the left inferior temporal gyrus showed a trend towards significance. The other structures tested in ROI analyses, namely the DLPFC, ACC and left postcentral gyrus were not significant. Controls did not show any cluster of greater gray matter concentration compared to meditators. A cluster of gray matter concentration that was found to correlate with the amount of meditation training was located in the bilateral gyrus rectus and medial orbitofrontal cortex (OFC). It has to be emphasized that this region was not significant when correcting for the whole brain. The present study showed a distinct pattern of gray matter concentration in meditators, who spent a significant part of their lifetime training non-judgmental acceptance towards internal experiences that arise at each moment. Data did not confirm the expected differences at the DLPFC, ACC and left postcentral gyrus. Also, no effect of meditation training has been found on the cortical thickness in these regions [99]. Possibly, the activation of these regions during meditation training does not lead to alterations in cortical structure. It is conceivable that some brain regions are more amenable to structural modifications than others. Moreover, meditators mean gray matter concentration within the relevant regions in the left inferior temporal gyrus was predictable by the amount of meditation training, corroborating the assumption of a causal impact of meditation training on gray matter concentration. Gray matter concentration in the left inferior temporal gyrus not only differed between groups, but also significantly correlated with the hours of meditation training. Temporal lobe activation during meditation has been found in several studies [123, 124, 73], suggesting it plays an important role in meditation [125]. The right insula, which showed greater gray matter concentration in meditators in this study and greater thickness in the study by Lazar et al. [99], is involved in interoception and visceral awareness [109]. This difference between meditators and non-meditators presumably reflects the specific training during Vipassana meditation, namely the awareness of bodily sensations. Farb et al. [126] found that participants trained in mindfulness showed increased activation of viscerosomatic areas, including the right insula, during a momentary experiential focus. This finding further supports the crucial role of the insula for the experience of a mindful state. Further, Hölzel confirmed the hypothesis that the hippocampus exhibits greater gray matter concentration in meditators. An investigation of subcortical structures was not possible with the methods employed by Lazar et al. [124]. The usage of VBM in the present study enabled us to go beyond these limitations and made it possible to confirm the group difference in the hippocampus. In their neuropsychological model of meditation, Newberg & Iversen [127] ascribe an important role for meditative experiences to the hippocampus, due to its involvement in modulating cortical arousal and responsiveness. The hippocampus also modulates amygdalar activity and its involvement in attentional and emotional processes. The region identified in the group comparison extends into the parahippocampal region, which participates in emotional memory and sensory functions and is the essential link between the hippocampus and neocortex [128]. The exploratory whole-brain regression analysis revealed that gray matter concentration in the medial OFC was positively correlated with the cumulated hours of meditation training. The OFC plays a crucial role in emotion regulation, during which it is thought to down-regulate activity of the amygdala. Thickness of the medial OFC is directly correlated with extinction retention after fear conditioning, suggesting that its size might explain individual differences in the ability to modulate fear [129]. It is thus critical for the modification of learned emotional responses. Greater gray matter concentration in the medial OFC dependent on meditation training might reflect the improved ability to modify emotional responses. It has to be kept in mind that gray matter in the OFC was not found to be greater in meditators than in non-meditators in the present study. The absence of a group difference in gray matter concentration in the OFC might be a sample artifact. The difference in gray matter concentration between the groups could be an effect of the extensive meditation training of meditators. However, the causal direction of influence cannot be determined by this study. Alternatively, people with greater gray matter in the relevant regions might be prone to take up meditation practice. Though correlational data provide support for the causal role of meditation practice, it is possible that meditators with greater gray matter concentration in the relevant regions maintain practice for a longer period of time. Randomized longitudinal studies could adequately address this question. it has to be emphasized that their results are not directly comparable to those of Lazar and colleagues because different variables were measured: Lazar investigated cortical thickness while Hölzel and colleagues examined gray matter concentration. Only very few studies have compared cortical thickness and gray matter concentration analyses so far [130, 131], and more investigation is required on the concordance of both measures.Luders et al. [132], conducted a study with a sample of 22 active meditation practitioners and 22 controls from the International Consortium for Brain Mapping (ICBM) database of normal adults(http://www.loni.ucla.edu/ICBM/Databases/), matched for gender and age; there were 9 men and 13 women in each group. Using high-resolution MRI data of the 44 subjects, they set out to examine the underlying anatomical correlates of long-term meditation with different regional specificity (i.e., global, regional, and local). For this purpose, they applied voxel-based morphometry in association with a recently validated automated parcellation approach. In agreement with previous studies, the present analyses revealed significantly larger cerebral measurements in meditators compared to controls. More specifically, they detected significantly increased gray matter in the right orbito-frontal cortex (as well as in the right thalamus and left inferior temporal lobe when co-varying for age and/or lowering applied statistical thresholds), and also significantly larger volumes of the right hippocampus. In addition, we observed increased gray matter in two clusters of the left and right paracentral lobe. The current study revealed increased gray matter in meditators within an orbito-frontal region, located more inferiorly (compared to Lazar et al. [99]) and more laterally (compared to Hölzel et al. [122]). Moreover, meditation-associated effects in the thalamus [123, 133, 127, 81] and in the temporal lobe [123, 124, 73, 122] have been reported in prior studies. In particular, Newberg et al. [133] detected an increased regional cerebral blood flow during meditation in the right thalamus. In a subsequent review on the neural basis of meditation, they comment on the potential role of the thalamus as a regulator of the flow of sensory information. They suggest, for example, that an increase in thalamic activation during meditation might result in a decrease of sensory input entering the posterior superior parietal lobule which, in turn, might lead to an enhanced sense of focus [127]. The latter is often attained during the state of meditation, and is also known as a characteristic trait in active meditation practitioners. With respect to the observed effect in the left inferior temporal gyrus, there is a striking spatial correspondence between the location of the current cluster and a cluster in a previous VBM analysis of Hölzel et al. [122], that showed a trend towards significance when comparing meditators against matched non-meditators. Furthermore, they observed significantly enlarged hippocampal volumes in the right hemisphere in meditators, which is in good agreement with the increased GM concentration in the right hippocampus in meditators, as reported by Holzel et al. [122]. Moreover, functional studies using PET or fMRI revealed increased brain activation during meditation or mindfulness of breathing in hippocampal and parahippocampal regions [123, 124,73]. Davidson, Jackson, & Kalin [134] propose an active role of the hippocampus in emotional responding. They hypothesize that individuals who habitually fail to regulate their affective responses in a context-sensitive fashion may have a functional impairment of the hippocampus. Thus, it is likely that the observed larger hippocampal volumes may account for meditators' singular abilities and habits to cultivate positive emotions, retain emotional stability, and engage in mindful behavior. Aside from its involvement in emotional processes, the hippocampus has also been shown as relevant for attentional processes and “certain types of imagery”, as summarized by Newberg & Iversen [127]. Thus, the observed increased hippocampal volumes in meditators might be partly driven by subjects of the current sample who pay attention to external and internal stimuli/events and who engage visualization. Finally, the hippocampus has also been suggested to modulate cortical arousal and responsiveness via rich and extensive interconnections with the prefrontal cortex and in close interaction with the thalamus [127]. Their observation of larger right hippocampal volumes together with increased voxel-wise GM in the right orbito-frontal cortex and in the right thalamus is in striking agreement with this postulate. Finally, the authors of this study suggest that the observed regionally increased GM volumes in meditators constitute part of the underlying neurological correlate of long-term meditation independent of a specific style and practice. Moreover, they postulate that There were no differences between meditators and controls with respect to global cerebral measurements (i.e., total brain and GM volumes), suggesting that links between meditation and brain anatomy exist on a relatively small scale.Hölzel et al. [135], conducted a longitudinal MRI study to investigate the relationship between changes in perceived stress with changes in amygdala gray matter density following a stress-reduction intervention. Stressed but otherwise healthy individuals (N=26) participated in an 8-week mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) intervention. Perceived stress was rated on the perceived stress scale (PSS) and anatomical MR images were acquired pre- and post-intervention. The amygdala has been implicated in both human and animal studies as playing a crucial role during stress responses, including the detection of stressful and threatening stimuli and the initiation of adaptive coping responses [136, 137], and some studies found enlarged amygdala volumes in subjects with affective disorders [138, 139]. Although, in contrast to studies of humans, the stress literature with animals is more consistent; several studies have shown that prolonged stress exposure leads to increases in measures of amygdala structure in rodents [140, 141, 142]. PSS scores decreased pre- to post-intervention, indicating that the participants benefited from the course and pre- to post-intervention analyses of the MRI data in SPM confirmed a correlation between change in PSS scores and change in gray matter density within the right amygdala. Larger decreases in perceived stress were associated with larger decreases in amygdaloid gray matter density. The identified region appears to be located in basolateral/lateral regions of the amygdala, based on the atlas by Mai, Assheuer, & Paxinos [143]. Their results suggest that ameliorating the subjective experience of stress through a behavioral intervention may actually decrease amygdala gray matter density in humans. This finding is particularly interesting as it suggests that an active re-learning of emotional responses to stress (such as taught in MBSR) can lead to beneficial changes in neural structure and well-being even when there is presumably no change in the person’s external environment. Although a correlation was found between changes in amygdaloid structure and perceived stress, the present study did not show a significant overall main effect of the training on amygdaloid gray matter density. Thus, the results do not support the conclusion that MBSR training per se leads to decreases in gray matter in this region. Amygdaloid gray matter density increased for some participants, though it should be noted that a lot of those subjects also reported increases in perceived stress following the MBSR program. Some of the participants with improved perceived stress scores appear to have slight increases in gray matter density, but these small deviances may reflect noise. Alternatively, changes in amygdala gray matter may be temporally delayed relative to changes in perceived stress, perhaps requiring habitual activation in this region to subside prior to longer term structural changes. The results do support a bidirectional correlation; further work will be required to determine the precise relationship between the self-report measure and cellular changes. PSS values and gray matter density were not correlated at the pre-intervention timepoint. This is in line with previous findings [144] and is not unexpected, as numerous factors can influence brain gray matter variables [145, 146]. Importantly, Hölzel et al. [135] assessed the relationship between the change in one variable, namely perceived stress and changes in gray matter density within the amygdala. By employing a longitudinal design most within-subject variables were kept relatively constant, while the factor of interest, perceived stress, varied. Previous studies identified several regions of altered brain morphology, but none within the amygdalae. This is the first study to demonstrate neuroplastic changes in the amygdala associated with the measure of a psychological state, through the influence of meditation.Tang et al. [147] hypothesized that 11 h of training with integrative body-mind training (IBMT), a meditation method adopted from traditional Chinese medicine, over 1 mo, would increase fractional anisotropy (FA) in the anterior corona radiate, an index indicating the integrity and efficiency of white matter in the corona radiata, an important white-matter tract connecting the ACC to other structures. In their previous work, as little as 3 h of IBMT, in comparison with a randomly assigned control group given relaxation training (RT), reduced the time to resolve conflict in the Attention Network Test and increased ACC activation [74, 148]. However, neither 3 nor 6 h of training changed white-matter FA or gray-matter volume as measured by voxel-based morphometry [149]. Recently they reported that 11 h of training with IBMT over a 1-mo period improved the efficiency of executive attention and alerting attention networks [148]. To test this hypothesis, they randomized 45 undergraduates to an IBMT or relaxation group for 11 h of training, 30 min per session over a 1-mo period. Before and after training we acquired brain images from each participant at rest for analysis of white matter by diffusion tensor imaging and gray matter by voxel-based morphometry. No areas showed significantly greater FA after relaxation training but a number of areas showed significantly greater FA following IBMT. The largest significant increase in FA following IBMT was found in the left anterior corona radiata, indicating that white-matter changes from training in this structure were significantly greater after 11 h of IBMT than those following relaxation training. Because changes in myelination lead to FA changes in diffusion tensor imaging, a possible mechanism for the observed FA change is increased myelination after training [150]. However, these changes may also reflect differences in the organization of white-matter tracts rather than changes in myelination. It might also be possible that these white-matter changes were due to changes in ventricle volume induced by training. Although this seems unlikely, we performed structural analysis for cerebral spinal fluid using voxel-based morphometry before and after 11 h of training, neither the IBMT nor the relaxation group showed significance in ventricular volume. They also found significant FA increases in the body and genu of the corpus callosum, superior corona radiata, and superior longitudinal fasciculus. We do not know whether this difference in laterality between the anterior and superior corona radiata reflects different functions or differential sensitivity, but the result warrants further investigation. The increased white matter FA in the body and genu of the corpus callosum could lead to increase interhemispheric transfer between the ventral and dorsal anterior cingulate. They used voxel-based morphometry to assess gray-matter differences between the two training conditions after 11 h of practice. Clearly, neither group showed significant changes in gray-matter volume. One possible explanation of the result is that the methods used to detect alterations in white and gray matter (FA from diffusion tensor imaging and voxel-based morphometry from T1 images) may have different sensitivities. It is also possible that the training can result in changes in both white and gray matter, but with different time courses. Finally, these findings suggest a use of IBMT as a vehicle for understanding how training influences brain plasticity observed in functional activation, functional connectivity, white matter anisotropy, EEG coherence, gray matter volume, and other measures.Hölzel et al. [151], report a controlled longitudinal study to investigate pre-post changes in brain gray matter concentration attributable to participation in a Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) program. Anatomical magnetic resonance (MR) images from 16 healthy, meditation-naïve participants were obtained before and after they underwent the 8-week program. Changes in gray matter concentration were investigated using voxel-based morphometry, and compared with a waiting list control group of 17 individuals. Thus, this study demonstrates longitudinal changes in brain gray matter concentration following an 8-week Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction course compared with a control group. Hypothesized increases in gray matter concentration within the left hippocampus were confirmed. Exploratory whole brain analyses identified significant increases in gray matter concentration in the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC), the temporo-parietal junction (TPJ), and the cerebellum. The hippocampus has been postulated to play a central role in mediating some of the benefits of meditation, due to its involvement in the modulation of cortical arousal and responsiveness [127], and morphological differences between meditators and non-meditators in the hippocampus have previously been reported [122, 132]. The hippocampus also contributes to the regulation of emotion [152, 153, 129] and the structural changes in this area following mindfulness practice may reflect improved function in regulating emotional responding. Moreover, as we know, the hippocampus is a region well known for its ability to remodel synapses and generate new neurons [154], and volume loss in this region seems to be reversible [155, 156]. However, the structural changes in the hippocampus identified here might be related to improvements in one of the other well-being-related variables that have been reported to improve following participation in an MBSR course. Moreover, it has been suggested that the TPJ is a crucial structure for the conscious experience of the self, mediating spatial unity of self and body [157], or embodiment [158], and impaired processing at the TPJ may lead to the pathological experience of the self, such as disembodiment or out-of-body experiences [157]. Furthermore, there is evidence of greater activation of this region during feelings of compassion in meditators [81]. Mindfulness training involves both the establishment of an awareness of oneself as a ‘complete whole’ [159], and the cultivation of compassion. The morphological changes in the TPJ might be associated with increases in compassion attributed to meditation training [160] and the cultivation of an embodied self. Correspondingly, several studies suggest that the PCC is engaged when assessing the relevance or significance of a stimulus for oneself [161, 162] and it has been suggested to be particularly important for the integration of self-referential stimuli in the emotional and autobiographical context of one's own person [163]. These functions also are closely related to mindfulness practice, which involves the introspective observation of phenomenal experiences as they are encountered [159]. Structural increases might be related to the repeated activation of this region during this process. Moreover, one of the two extensive clusters identified in the cerebellum was located in lateral parts of the posterior and flocculonodular lobe, and the other one was located in the vermis, reaching into the brainstem. Aside from the well-known function of the cerebellum in the integration of sensory perception, coordination, and motor control [164], this structure also plays a crucial role in the regulation of emotion and cognition. It has been suggested that in the same way that the cerebellum regulates the rate, force, rhythm, and accuracy of movements, it also regulates the speed, capacity, consistency, and appropriateness of cognitive and emotional processes [165], i.e., it modulates behavior automatically around a homeostatic baseline. Given the importance that the regulation of emotions and cognition play in healthy psychological functioning, the morphological changes in these regions might contribute to the positive effects of mindfulness meditation on the salutary changes in well-being. While significant Pre-Post changes in the TPJ, PCC, and cerebellum have been found in the present study, it is unclear why previous cross-sectional studies of meditators have not identified group differences in these regions. It is possible that small differences existed but were not detected due to the lack of power in the previous small cross-sectional studies, or that structural changes are transient and change might be maximal when a skill is newly acquired [166]. Interestingly, the hippocampus, TPJ, and PCC (as well as parts of the medial prefrontal cortex not identified in the present study) form a brain network [167] that supports diverse forms of self-projection [168], including remembering the past, thinking about the future [169], and conceiving the viewpoint of others [170]. These abilities have been suggested to share a common set of processes, by which autobiographical information is used adaptively to enable the perception of alternative perspectives [168]. Literature on the mechanisms of mindfulness proposes that the positive benefits of the practice might be mediated by a perceptual shift that modulates the internal representation of the self [171] and it is possible that structural changes in the brain network involved in the projection of oneself into another perspective may underlie this perceptual shift.Recently, this findings (structural neuroplasticity) has been reinforced by several authors. Theirs findings suggest that long-term meditators have structural differences in both gray and white matter [172, 173, 174].
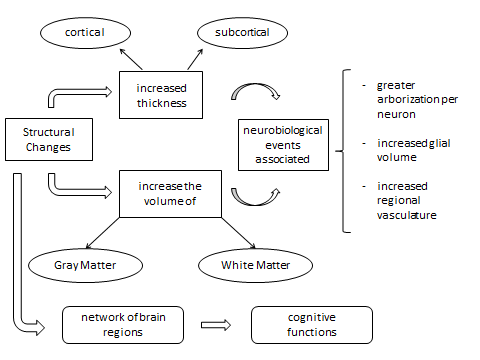 | Figure 1. Structural Brain Changes and implications: neurobiology, neurophysiology and cognition |
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
- Extensive practice of meditation, regardless of technique's specific subtype or tradition that is practiced, seems to generate stable changes in brain structure and function. Neuroanatomical changes can be verified, both through direct findings showing cortical and subcortical structural changes, as through variations of neurofunctional patterns that show the possible structural changes to which they would relate. To summarize, research to date shows significant results linked to its sustained practice over time:1) Neurophysiological analyses highlight the increase in consistency of alpha wave power, increased selectively in the frontal cortex. Also, increases in theta power have been significantly reported, mainly in meditation types characterized by the use of concentration and focused attention, specifically in frontal midline, generated by anterior cingulate cortex, medial prefrontal cortex, or dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Increase in Midline frontoparietal and parietooccipital gamma power has been observed during meditation with long-term meditators. Decreased delta activity in the temporo-parietal junction, secondary motor cortex, and sensory association cortices appeared indicative of increased brain activation associated with detection and integration of internal and external sensory information, with detachment from the same as indexed by inhibited activity (increased delta) in prefrontal areas responsible for analyzing, judging, and expectation. Bioelectrical patterns linked to the extended practice of meditation, emphasize the crucial role played by frontal brain areas which would modulate its level of activation depending on the cognitive and emotional demands of meditation, specifying a plausible neuroplastic change.2) From studies based on neuroimaging, by comparing brain activation in meditators with control groups of non-meditators, a more significant activation of the frontal regions (dorsal medial prefrontal cortex, inferior frontal cortex, medial prefrontal cortex area) is emphasized, with a significant involvement of the anterior cingulate cortex, as well as parietal and subcortical areas, having verified increased activation in the thalamus, putamen, caudate, and insula. All this, in line with the attentional requirements and affective states associated with the practice of meditation (limbic region). Regarding studies that have been developed through the comparison between meditators with varying degrees of experience, considered in our case as having the most inferential value, greater activation is noted in those most expert in DLPFC and ACC, associated with higher performance in sustained attention and attentional control. In turn, these experts demonstrate high activation of limbic areas (insula and amygdala) and in right TPJ, and right pSTS, suggesting a greater detection of the emotional sounds and alters the activation of circuitries previously linked to empathy and theory of mind in response to emotional stimuli.3) Through neuropsychological research developed via the application of neurocognitive tests, we have found a positive impact on attentional and executive functions, such as a boost and/or preservation before the decline expected with age-, highlighting its specific influence on sustained and selective attention, inhibitory control, cognitive flexibility, verbal fluidity, abstraction, conceptualization, and perceptual sensitivity. These cognitive functions that are essential for the functioning of other more complex processes, denote the role of the prefrontal cortex in the exercise of meditation. And, along with data on the activation of this brain area, we note as a most important finding, the evidence that seem to demonstrate a striking conservation of the functions, even a boost associated with this brain region, whose decline is remarkably significant with aging.4) Building on research that examine neuroanatomical changes, we can say that there would be a broad network of brain regions involved in the long term practice of meditation, which show structural brain changes associated with its practice. Several studies show increased cortical thickness and increase the volume of gray and white matter, correlated with the hours devoted to meditation. Increased cortical thickness could be due to greater arborization per neuron, increased glial volume or increased regional vasculature; each of these mechanisms is supportive of increased neural function. Specifically, neuroplastic changes have been discovered in the integrity and efficiency of white matter in the anterior corona radiata, an important white-matter tract connecting the ACC to other structures. In turn, other studies have shown a higher concentration of gray matter in right thalamus and right OFC, PCC, TPJ, the cerebellum, and a large region of right anterior insula, right middle and right and left hippocampus, superior frontal sulci, and also in the left inferior temporal gyrus and a small region in the fundus of the central sulcus and putamen. In addition, there appears to be a similar effect on the body and genu of the corpus callosum, superior corona radiata, and superior longitudinal fasciculus. We stress the importance of these cortical and subcortical areas in the performance of functions such as attentional effort, cognitive flexibility, awareness of internal states, emotional regulation, somatosensor, auditory, visual and interoceptive processing, consistent with the results obtained from other parameters and experimental methodologies.5) From the standpoint of therapeutic intervention, the clinical potential derived from the practice of meditation, with its influence on brain function at different levels (hormonal regulation, plasticity, cognitive function, etc.) is clearly established. Thus, we find its effects on both structural and functional levels (neuroprotection) as strictly psychotherapy (cognitive and emotional). These benefits associated with the extended practice of meditation have been verified after few practice sessions, and, in turn, through various methods and meditative traditions.6) From the study of the state of this issue in the field of neuroscience-meditation interaction, we consider timely to suggest future research that will enable the advancement of knowledge in relation to the neurofunctional network involved. Thus, we propose:a. Clarification on the brain substrate that justifies the changes in brain function, caused by meditation, by analyzing the specific role of neural phenomena such as increases in dendritic arborization, glial volume or regional vascularization.b. Promoting additional longitudinal studies, which are almost unprecedented to date, in order to provide greater inferential power to our conclusions. At the same time, this will help clarify the role of innate and acquired components in the optimal neurofunctional performance found in elderly expert meditators.c. Delineate the concept of meditation practice in a more operational manner, together with the differential study on the effects of different styles and traditions, to deepen the distinction between practices that emphasize the emotional-empathy, affection, compassion aspects, etc. in relation with those experiences that focus on introspective experiences, relaxation, inner awareness, avoidance of the external stimulating demand.d. Consider the religious factor associated with some styles of meditation as an element that has proved relevant in several studies on general health, and in particular, on brain functions, and cognitive and emotional functions. This phenomenon is explained by an underlying psychophysiological mechanism and by the lifestyle linked to religion in question, with its corresponding behavioral prescriptions connected with them. In this regard, and referring also to non-religious meditative style, it is required to analyze the possible role of lifestyle, regardless of the proper exercise of meditation, in relation to the neurofunctional performance shown, so it is important to further study factors such as diet, aerobic exercise, psychosocial stimulation, and so on.e. Using the comparison of meditators with non-meditators, to analyze the differences in brain activation associated with the differential state of rest and with cognitive functions relevant to meditation (attention, cognitive flexibility, abstraction, etc..), in order to detect possible neuroplastic changes that would be the basis of these hypothetical differences. In turn, the same experimental paradigm of meditators versus non-meditators lead to studies that seek to compare activation during meditation vs. rest and meditation vs. relaxation, since they are of different activities, whose specific neurophysiological imprints are known. f. Promotion of research comparing the differences between meditators (novices vs. experts), considering the experience of its operational practice by its temporal quantification (hours, years, etc.), making this its independent differentiating factor or variable. This sets a more appropriate experimental adjustment.g. Promoting neuropsychological studies based on neurocognitive testing, as a paradigm which is still in its infancy on this line of research. Through this type of work at the same time that the cognitive impact of meditating is shown, major scenarios of the structure-function relationship would be shown by comparing its results with those arising from neuropsychological tests and brain imaging.h. Inclusion of a new methodology, not yet used in this field, based on magnetoencephalography analysis evidence; through it, we could provide valuable data to elucidate the neurofunctional substrate underlying meditation, through an instrument that combines an optimal ratio of the spatial and temporal resolutions for the sake of further clarification of the where and when, compared to brain activation simultaneous to meditation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The heading of the Acknowledgment section and the References section must not be numbered.SAP Productions wishes to acknowledge all the contributors for developing and maintaining this template.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML