-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Applied Sociology
p-ISSN: 2169-9704 e-ISSN: 2169-9739
2015; 5(2): 76-83
doi:10.5923/j.ijas.20150502.02
Analysis of the Influence of Leadership Styles of Chief Executives to Organizational Performance of Local Organization in Thailand (A Case Study of Transformational, Transactional and Laissez-Faire Styles of Leadership in Pattaya City, Laemchabang City Municipality and Chonburi Provincial Organization)
Supit Wongyanon1, Andy Fefta Wijaya2, Mardiyono2, M. Saleh Soeaidy2
1Doctoral Program of Public Administration, Faculty of Administrative Science, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
2Department of Public Administration, Faculty of Administrative Science, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Supit Wongyanon, Doctoral Program of Public Administration, Faculty of Administrative Science, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Organizational achievement is an ability of the leader to influence others to do the right things. It is called leadership. There are many leadership theories that have been written but there is no one theory that works best in a given situation because organizations have different environments and cultures, especially the public sector. This study would encourage new empirical findings to public administration. The purposes of this study are to analyze and to examine the influence of transformational, transactional and laissez-faire leadership styles of the chief executives to organizational performance in case of Thai local organizations. They are Pattaya City, Laemchabang City Municipality, and Chonburi Provincial Organization. Self-administered surveys distributed to a randomly selected sample within the three local organizations. Participants consisted of 820 respondents who had returned the questionnaires from 953 invitations. The results demonstrated that transformational, transactional and laissez-faire leadership styles have a significant and positive influence to the organizational performance. The findings revealed individual consideration leadership style in transformational exhibited in two locations, while others displayed only one location. Contingent reward and management by exception-active in transactional leadership style and laissez-faire leadership style also indicate independent influence to the organizational performance but there is no leadership style overlaps. Therefore, it is concluded the leadership styles of the organizational achievement are the best from regression equation. Those are charisma, inspiration motivation and intellectual stimulation in transformational leadership, contingent reward and management by exception-active in transactional leadership and laissez-faire leadership style.
Keywords: Transformational leadership, Transactional leadership, Laissez-faire leadership, Chief executives, Organizational performance, Thai local organizations
Cite this paper: Supit Wongyanon, Andy Fefta Wijaya, Mardiyono, M. Saleh Soeaidy, Analysis of the Influence of Leadership Styles of Chief Executives to Organizational Performance of Local Organization in Thailand (A Case Study of Transformational, Transactional and Laissez-Faire Styles of Leadership in Pattaya City, Laemchabang City Municipality and Chonburi Provincial Organization), International Journal of Applied Sociology, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2015, pp. 76-83. doi: 10.5923/j.ijas.20150502.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Leadership is an important element of the directing function of management. Wherever there is an organized group of people working towards a common goal, some types of leadership become essential. Leadership theory has been an important area of study in the social sciences arena. Leadership is described as the ability to influence and inspire the performance of those around them with an active and spontaneous attitude [1]. However leadership style theories are categorized into four areas [2]: Trait theory, Behavior theory, Contingency theory and transformational theory. Transformational theory is described as a modern leadership theory. It was introduced by [3] and developed by [4]. It contends that a transformational leader creates visions, accepts new ideas, makes quick decisions, encourages cooperation, and avoids being over cautious [5]. Moreover it is believed that leadership behavior that facilities changes with regard to technical, political, and cultural aspects is important when organizations exist in a dynamic environment and highly technical environment [6].Leaders in public organizations must be capable of personally managing environmental change whilst at the same time preparing and developing their team to handle not only environmental change but also changes to mission and direction. This type of leadership requires individuals to have the ability to assess threats and opportunities both internal and external and take steps to create the necessary organizational energy necessary for action [7]. Researchers have noted that the structure of bureaucratic organizations become more flexible and engaging in order to support economic modernization [8]. To continue with the reform initiative, public organizations have adopted their work systems and processes to become more flexible and adaptable. Therefore the leaders’ behavior influences efficiency and effectiveness in order to provide the highest levels to the organization. The chief executive must be involved, not only in the day– to–day activities but also to create the vision to lead, inspire and motivate his team.The leader in the local organization has an important role to direct work in the local administration. In a context of social, environmental, and cultural that it always change along with globalization and frequent crises. Despite pressures in local administration it has to maintain close contact with its citizens and public services to effectively and efficiently manage. For a few local organizations in Chonburi Province, Thailand, it is quite a different situation in term of environment, population, some regulations etc. They are Pattaya City, Laemchabang City Municipality, and Chonburi Provincial Administrative Organization. Pattaya City is a special status local government organization. This is related to Pattaya’s popularity and tourist attraction involving people from all over the world. Indeed, the Administrative Act is different from other local organizations such as Bangkok metropolitan, provincial, municipality, and sub districts with more autonomy. On the other hand, Chonburi Provincial Administrative Organization and Laemchabang City Municipality are similar in law but different in environment. Laemchabang City Municipality comprises a large shipping port and industrial area so they have large income from those areas. Chonburi Provincial Administrative Organization is located in an urban area so most of its population is commercial. All of the local organizations that are mentioned should have leadership style differences as researchers offered.
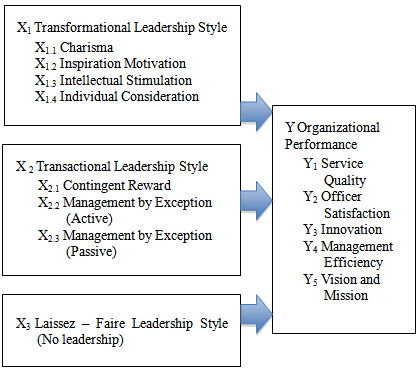
2. Theoretical Framework and Research Hypotheses
- The hypotheses for this study, based on the literature review previous and conceptual model, are as follows:Hypothesis one: There is a significant and positive influence of transformational leadership style of chief executives to organizational performance of Thai local organizations. Hypothesis two: There is a significant and positive influence of transactional leadership style of chief executives to organizational performance of Thai local organizations.Hypothesis three: There is a significant and positive influence of laissez-faire leadership style of chief executives to organizational performance of Thai local organizations.Hypothesis four: There is a significant and positive influence of transformational, transactional, and laissez-faire leadership style of chief executives to organizational performance of Thai local organizations.
3. Leadership Theories
3.1. Transformational Leadership Style
- Transformational leadership theory argues that leader could improve their effectiveness by developing their understanding of differing principles that would influence follower as:(a) Charisma: a leader with charisma is one who can see where the organization wants to go, develops a strong vision, instills pride, gains respect and trust, and can motivate others to follow this or her feeling.(b) Inspiration: the leader builds trust, keeps follower focused on the vision, uses symbols, and works on bringing other follower on board who may not have agreed with the vision of the organization.(c) Intellectual stimulation: the leader usually takes the vision and finds the steps needed to implement the vision while gathering the follower to follow this new path. The leader is one who can see the picture with fewer details and who explore new ideas to arrive at the new vision.(d) Individualized Consideration: the leader remains visible, give individual attention, coach, advise, lead by example, encourage follower, and promote the vision to different groups. Also, leader keeps the follower excited about where the organization is going and how they can maintain their focus to achieve their goals.Additionally, it states the following:“Transformational leaders have better relationship with their supervisors and make more of a contribution to the organization than do those who are only transactional. Moreover, employees say they themselves exert a lot of extra effort on behalf of managers who are transformational leaders [9].Transformational leadership style can be categorized into idealized influence attributes, idealized influenced behaviors, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation and individualized consideration [10]. Idealized influence attributes refer to personality of the leader whether he or she is perceived as confident and powerful whereas the idealized influence behavior refers to the charismatic actions of the leader that are focused on values, beliefs and principles [10]. Inspirational motivation refers the behaviors of the leaders that motivate followers to view the future optimistically, stress on the team spirit, project idealized vision and communicate a vision that is achievable [10]. As for the intellectual stimulation, the leader stimulates innovation and creativity in their followers by questioning assumptions and approaching old situations in new ways [11]. Individualized consideration refers to the leader pay more attention each follower's need for achievement and growth by acting as a mentor [11]. Transformational leaders can spin a view that will have followers believing in their message. They become role models, they have power over their followers through their speaking ability, and they make eye contact and are very demonstrative. A research offers that there is a higher level of trust from followers because they show a genuine concern for both the followers and the path of the organization [12] [13].
3.2. Transactional Leadership Style
- Transactional leadership theory is developed as a reward system to match leadership’s desired outcomes with the follower’ expected performance. The leaders would be counterproductive and would encourage follower to be stagnant at one level while followers maintain their level of production at a minimum level, management left them alone to do their work, but when their production dropped below the required level, their pay, level of responsibility, and even their job level may be affected [9]. There are three dimensions of transactional leadership styles [9] stated:a. Contingent Reward, this style exchanges reward for effort and promote good performance with reward and recognition.b. Management-by-Exception (Active), this style looks at any deviation from the rule and making correction to any changes as they arise.c. Management-by-Exception (Passive), this style watches and only intervenes when standard is not achieved.According to three sub-constructs, Contingent reward covers behaviors intended to clarify performance expectations, and to establish follower credibility that valued rewards (verbal or tangible) will follow in exchange for good performance. Management-by-exception passive includes watching for deviations from the expected performance norms and standards, and providing feedback to correct deviations from the norm. Management-by-exception active spans behaviors intended to proactively prevent potential problems before they arise [14].
3.3. Laissez-faire Leadership Style
- Leaders use a variety of different approaches. Some are autocratic and prefer to tell their teams exactly what to do. Others use a much more participative style. Still others may use a style somewhere between these two extremes. Continuum describes running from high authority at one extreme (Tells) through the team having complete freedom to threat at the other. It can say laissez-faire that is the similar defines to other authors when the leaders use abdicates style. The leaders ask team to assign the problem, develop options, and make a decision. The team is free to work what is imperative to solve a problem whilst still working under reasonable limits, given organizational needs and targets.The laissez-faire style is referred as “Abdicates responsibilities avoid making decisions” [15]. Similar to defined laissez-faire style states as “Abdicates responsibilities avoid making decisions” [16]. Laissez-faire is uninvolved in the work of the unit. It is difficult to defend this leadership style unless the leader’s subordinates are expert and well-motivated specialists, such as Scientists. “Leaders let group members make all decision” [17]. The concept of laissez-faire is also given as “Abdicates responsibilities and avoiding decisions” [18]. Above all the Authors define the laissez–faire leadership style with their own words according to their given definitions the idea of this type of leadership is the same. Authors define majority of those meaning that in laissez-faire leadership style the leaders normally do not want their intervention in the decision-making of subordinates’ process. The leaders allowed subordinates that they have power to get their personal decisions about the work. They have freedom to do work in their own way and they response for their decision. Normally leaders avoid to making decisions, are not involved in working units, they are absent when they are required because the leaders give t completely freedom to their subordinates to drive the job into goals. Sometimes the leaders provide subordinates with essential material and they just associate the answer and question but avoid feedback.
4. Organizational Performance in Government (Local) Organization
- According to the revised balanced scorecard (BSC) [19][20], it claims that the BSC is applicable to both for-profit and non-profit organizations alike, the financial focus of the BSC appears to conflict with the mission-oriented nature of non-profit organizations. Hence, to break the impasse between the resistance to tools conceived with a for-profit motive and the need to apply proven for-profit management tools, such as the BSC, in the non-profit sector, the BSC is redesigned by replacing the financial aspects of the original model with the customer as the ultimate measure of success in determining whether the non-profit's mission has been achieved [19]. BSC for non-profit organizations has retained all four perspectives, which are financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth as well as strategy mapping process although it differs as follows [19] [20]:Mission moves to the top of the BSC. All of the measures appearing on the for-profit scorecard are designed to lead to improved bottom-line performance. By moving the mission to the top of the BSC, the non-profit nature of third sector organizations is underscored.Strategy is still at the core of the scorecard system for non-profit organizations. Most non-profit organizations have a difficult time developing their strategies. Many statements of strategy amount to little more than detailed lists of programs, corresponding to their funding sources [19]. The customer element is elevated. It is placed the customer in a very high position, linked directly to the non-profit organization's mission [19]. This positioning of the customer contrasts with Kaplan and Norton's model, where they consider the customer element as supporting financial performance, leading ultimately to improved shareholder value.The financial element positioning is changed. For BSC, the question put forth for the financial element is: To succeed financially, how should we appear to our shareholders? [20]. In Niven's model, by placing the financial element as subordinate to the customer, the question. In the overview of BSC that is revised [19], this study is going to determine to appropriate dimension to Thai local environment. These dimensions will be measured through subordinate in organization. Five dimensions that are translated into organizational performance variables are (a) service quality, (b) officer satisfaction, (c) innovation, (d) management efficiency, and (e) vision and mission.
5. Relationship of Transformational, Transactional and Laissez-Faire Leadership Styles to Organizational Performance
- According to research background, the organization’ administration must be changed by using the reform to adapt with strategy, vision, knowledge skills, and so on. The personality of leadership is different depends on characteristics and situation as there is no single leadership style that is effective in all situations. Rather, certain leadership styles are better suited for some situations than for others. However, we cannot discriminate against any person into completely either and each person is a various mixture in any way, but rather than focus on it. Over the last two decades, in both profit and non-profit organization they measured effectiveness and efficiency in administration by leaders or chief executives in organization. There are two leadership styles that still exist and could display leader behaviors in obviously and also contemporary is transactional, transformational and laissez-faire leadership style. How difference between transformational leadership theory and transactional and the transformational leader. Transactional leadership focuses on role and task requirements and utilizes rewards contingent and punishment on performance with monitoring and intervention process. By contrast, transformational leadership focuses on development mutual trust, foster the abilities to lead others and to set goals that go beyond the requirements short-term of the team. Transformational leadership theory identifies by Bass, are four aspects of effective leadership including charisma, inspiration motivation, intellectual stimulation, and individual consideration. According to Bernard Bass, transformational leadership occurs when a leader transforms, or changes, his or her followers in three important ways that together result in followers trusting the leader, performing behaviors that contribute the achievement of organizational goals, and being motivated to perform at a high level. Transformational leaders:a) Increase subordinates’ awareness of the importance of their tasks and the importance of performing well.b) Make subordinates aware of their needs for personal growth, development and accomplishment.c) Motivate their subordinates to work for the good of the organization rather than exclusively of their own personal gain or benefit.Leadership can be best understood as either a transactional or a transformational process [3]. Transactional suggests that most managers engage in a bargaining relationship with employees [21], using a system of rewards and punishments. Transactional leadership is often used in business; when employees are successful, they are rewarded; when they fail, they are reprimanded or punished. For public organization also utilized both things to implementation for subordinate but the different way because they have to drive follow the act. The leader views the relationship between managers and subordinates as an exchange. Furthermore, rules, procedures, and standards are essential in transactional leadership. Followers are not encouraged to be creative or to find new solutions to problems. Research has found that transactional leadership tends to be most effective in situations where problems are simple and clearly defined. Also, Robbins defined the transactional leadership as “leaders who lead primarily by using social exchanges for transaction” [14].Several researchers have indicated that chief executives leadership influence organizational performance. Chief executive leaders have a direct and significant effect on their organization's performance. They further noted that because organizations are open systems and must interact with their environments leaders affect organizational performance. Most of the researcher comparing transformational, transactional and laissez-faire leadership style has used MLQ. The MLQ is a multi-rater survey tool that asks the respondent the frequency with which a particular leader exhibits particular behaviors or traits. The tool assesses the full range of specific behavior associated with the two leadership styles through self-reporting, perception of colleagues and supervisors or self-reporting and perception of colleagues and supervisors.The empirical findings exhibit some leader’ characteristics they displayed in two styles especially both transactional and laissez-faire that is mentioned by Tannenbaum & Schmidt and Kurt Lewin. The leaders do not want to carry many styles but they need properly styles that suit to the crisis so sometimes the results would show in more one form.
6. Methodology
- In research the researcher uses the quantitative method. The population for this study is the staffs who are working in three local organizations as Pattaya City (PC), Laemchabang City Municipality (LCM), and Chonburi Provincial Organization (CPO). The random sampling is utilized together with the Taro Yamane technique for sample group (953 participants). The Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire (MLQ) is used to survey leadership behavior and organizational performance via translation to Thai language. The data is analyzed using SPSS (version 17.0) for windows including analysis techniques such as frequency, percentile, Pearson Correlation, Multiple Regressions (stepwise) to examine the influence of leadership styles to organizational performance.
7. Results
- The analysis statistics with correlation coefficients and multiple regressions for all study variables are exhibited in Table 1-2. The overall of three locations (Table 1) concludes that transformational leadership being “strong” while CR and MBEA in transactional leadership “moderate”, and MBEP and LF “weak” influence to organizational performance of three locations. Those mean transformational displayed stronger influence than others to organizational performance so that made the locations effective being as “strong”.
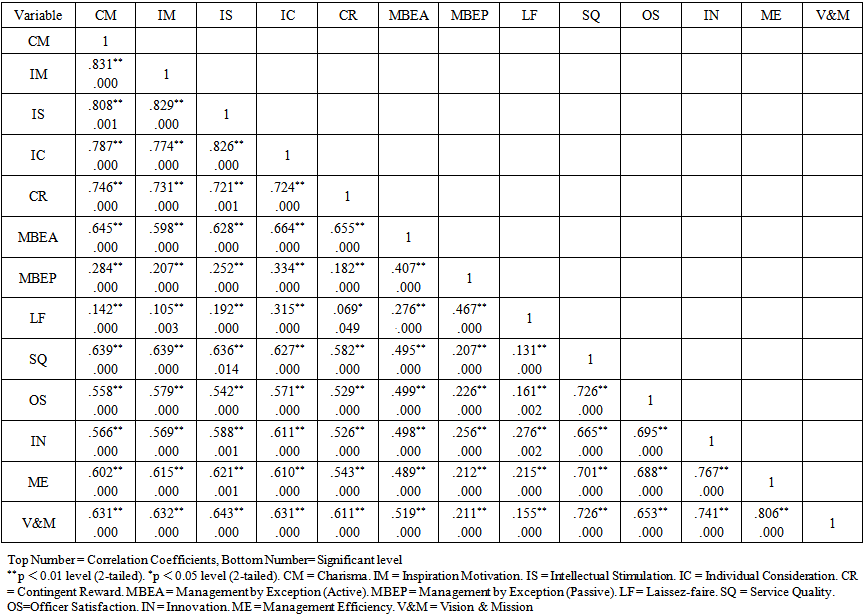 | Table 1. The Correlation Matrix and Reliability Coefficients (Overall) |
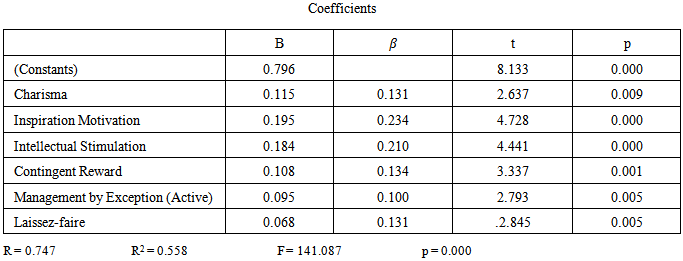 | Table 2. Multiple Regression Results of the Influence of three Theories (Transformational, Transactional and Laissez-Faire Leadership) Dimensions to Organizational Performance (Three locations) |
8. Hypotheses Testing
- Hypotheses one is examined significant and positive influence of transformational leadership style of chief executives to organizational performance of Thai local organizations. The correlation matrix in Table 1 indicates that there is a positive linear relationship between all four transformational factors and organizational performance variables (service quality, officer satisfaction, innovation, management efficient, and vision and mission). Coefficients range from 0.542 to 0.643 with significant levels p < 0.01. Therefore, the alternative is accepted. Hypotheses two is examined the significant and positive influence of transactional leadership style of chief executives to organizational performance of Thai local organization. The correlation matrix in Table 1 indicates that there is a positive linear relationship between three transactional factors and organizational performance variables (service quality, officer satisfaction, innovation, management efficient, and vision and mission). Coefficients range from 0.207 to 0.611 with significant levels p < 0.01 for all five variables. Therefore, the alternative is accepted.Hypotheses three is examined the significant and positive influence of laissez-faire leadership style of chief executives to organizational performance of Thai local organization. The correlation matrix in Table1 indicates that there is a positive linear relationship between laissez-fair factor and organizational performance variables (service quality, officer satisfaction, innovation, management efficiency, and vision and mission). Also, the correlation coefficient of laissez-faire leadership factor (non- leadership) and five organizational performance variables is positive influence as ranging from 0.131 to 0.276 with significant levels p < 0.01. Therefore the null hypothesis is rejected or the alternative is accepted.Hypotheses four is examined the significant and positive influence of transformational, transactional and laissez-faire leadership style of chief executives to organizational performance of Thai local organization. Due to multiple regression analysis results exhibited as table 2, the alternative hypothesis is accepted based on B (Positive) and p values (p < 0.01). According to multiple regression results as Table 2, the multiple regression equation of this research is:
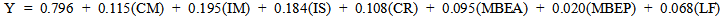 | (1) |
9. Discussion
9.1. Theoretical Discussion
- As the methodology in quantitative approach, the theoretical review is at the heart of the case, transformational, transactional and laissez-faire leadership theories are utilized to study in the case of Thai local organizations. Figure 1 is exhibits the overview leadership theories to investigate from followers’ perception.
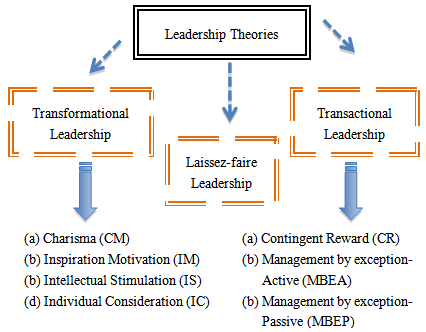 | Figure 1. Theoretical leadership styles of local organization |
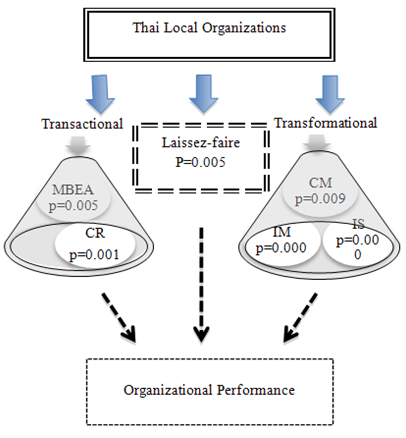 | Figure 2. The leadership styles of chief executive of Thai local organizations |
10. Conclusions
- The results of the study indicate that transformational, transactional and laissez-faire leadership styles positively influence organizational performance. It revealed that the three leadership styles have effect to organization effectiveness via people perception. Therefore, a new finding for leadership in local organization encouraged other empirical findings in leadership term. As we know the current environment around the local organization is constantly changed through globalization. From the findings, it is imperative that the leaders of today, when managing staff in the present look to the future and become progressive in dealing with people within their organization. Adapting appropriate styles, depending on the situation will be a core feature in organizations of the future and an expectation of staff.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML