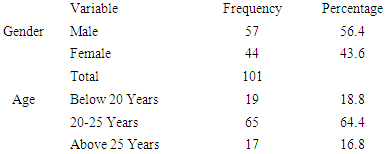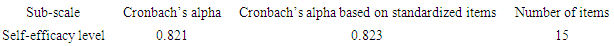-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Applied Psychology
p-ISSN: 2168-5010 e-ISSN: 2168-5029
2023; 13(1): 1-8
doi:10.5923/j.ijap.20231301.01
Received: Dec. 5, 2022; Accepted: Jan. 12, 2023; Published: Jan. 13, 2023

The Level of Students’ Self-Efficacy on E-Learning at Post-COVID-19 Pandemic: Case Study of Rongo University-Kenya
Lazarus Millan Okello, Tom Mboya Omollo
Department of Educational Psychology and Science, Rongo University, Rongo, Kenya
Correspondence to: Lazarus Millan Okello, Department of Educational Psychology and Science, Rongo University, Rongo, Kenya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

COVID-19 contributed a significant portion of the global burden of the killer diseases. The global spread of COVID-19 required not only national-level responses but also active compliance with individual-level prevention measures outside and within the institutions of higher learning. In this context, self-efficacy means individuals' confidence and certainty in their ability to successfully perform specific IT related tasks in response to e-learning after COVID-19 Pandemic. This study investigated the level of students’ self-efficacy on E- learning at Post-COVID-19 Pandemic: Case study of Rongo University-Kenya. The results may guide the University policymakers to focus on increasing the awareness and knowledge of lecturers through conducting training programs on how to use the e-learning system, because the lecturers have an important role in guiding and motivating the students to use the e-learning systems, which in turn affects the teaching performance and students’ self-efficiency in using the ICT gadgets in online classes. The University management should effect changes in learning as well as improving on pedagogical strategies to accommodate needs of different students with varied potentialities in e-learning platforms to promote their confidence level. This could be done through organized trainings and workshops in small manageable clusters, promoting self-efficacy programs on ICT use and ensuring successful address and implementation of issues raised by the concerned students during the learning process.
Keywords: Students’ Self-Efficacy, E-Learning, Pandemic, COVID-19
Cite this paper: Lazarus Millan Okello, Tom Mboya Omollo, The Level of Students’ Self-Efficacy on E-Learning at Post-COVID-19 Pandemic: Case Study of Rongo University-Kenya, International Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol. 13 No. 1, 2023, pp. 1-8. doi: 10.5923/j.ijap.20231301.01.
Article Outline
1. Research Question
- What is the level of Students Self-Efficacy on E-Learning after the COVID-19 Pandemic?
2. Research Methodology
- This study was a descriptive cross-sectional in nature. Convenience samples of 96 Rongo University students were recruited. The COVID-19 SSE questionnaire was administered to the sampled students.
3. Introduction
- Following the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, education shifted to e-learning and students’ personal and professional way of learning has drastically been altered. University lecturers and students have juggled a number of professional and personal changes as a result of this transition. The drastic changes positioned most students to be familiar with using social media platforms while lacking the ability to use technical resources or software for educational purposes. The platform of E-Learning Environments (ELE) became very instrumental in giving learners access to educational resources, connecting students with lecturers and facilitating distance lessons. The selection and the overall impact of ELE crucially depend on lecturers’ pedagogical and technological readiness and on students’ digital competences and hands on experience (accessibility of the internet and availability of appropriate ICT tools are preconditions to this). The choice of the teaching mode appropriately depends on the degree of uniformity and ICT investment a particular University intends to guarantee across different faculties or schools. Various types of E-Learning exist, from basic content repositories, to scaffold curriculum-aligned repositories, to synchronous and asynchronous platforms offering a wide range of tools and services especially within the Library or ICT platforms set for both the staff and the students. Different models should be tested in different contexts and the selection should be based on an accurate analysis of the relative pros and cons of each ELE if the whole process is hoped to be successful and of importance to students during and after the surge of COVID-19 Pandemic.According to Shigemuraet al., (2020); and WHO, (2019), in December 2019 a highly infectious disease, caused by a new coronavirus (the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2; SARS-CoV-2) was officially reported in Wuhan, China, and speedily spread outside China in the first months of 2020. The disease was called Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19) and was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization on March 11, 2020 (WHO, 2020). In Kenya, COVID-19 was first reported on March 13, 2020 and schools were abruptly shut and they remained closed for several months, with learners in most learning levels forced to repeat their 2020 school year in 2021. This affected over 18 million children in Kenya including Universities and middle level colleges. The emergence of this virus to a greater degree hindered Kenya’s Vision 2030 National Development Goals which try to achieve quality education for every child. During the pandemic most learning institutions resorted to online teaching and both students and lecturers were trained on technical components of using IT to effectively carry on with virtual classes. The insight of this paper dwelt on the confidence level of the University students in applying IT related tasks on e-learning after COVID-19 Pandemic.
4. Literature Review
- Student Self-Efficacy on E-Learning after COVID-19 PandemicAmir, Tanti, Maharani, Wimardhani, Julia, Sulijaya and Puspitawati (2020) did a study on student perspective of classroom and distance learning during COVID-19 pandemic in the undergraduate dental study program at the Universitas of Indonesia. This study found out that the COVID-19 pandemic brought the unprecedented universities’ facilities closure and this affected millions of students globally. The study documented that student’s attitude and acceptance toward e-learning became more positive and favorable. According to Rivers (2021), e-learning specialists needed to base their technological solutions and interests on well-researched pedagogical principles with sound theoretical rationale used to direct and moderate the use of technology.Yokoyama (2019) also stated that since a familiarity with online learning devices may affect the relationship between academic self-efficacy (ASE) and academic performance in e-learning settings, those who are not good at using online learning devices may not achieve high enough academic success in an e-learning setting. Second, since task values are closely related to the relationship between ASE and academic performance, students, teachers and parents may need to choose the e-learning software they believe will have the most valuable content and/or tasks for students. The choice on the software made by individual students would build on their confidence level and urge to learn and be conversant with the whole process. Heaperman and Sudweeks (2002) did a study on Achieving self-efficacy in the virtual learning environment. The study outlined that self-efficacy in the VLE will leave the mature student better equipped to deal with technology generally and specifically for the purposes of sustained lifelong learning. The study however, proposed changes in learning as well as pedagogical strategies to accommodate the specific needs of students. Karademas and Thomadakis (2021) equally did a study on the efficacy of online learning during the general lockdown in Kenya and 358 individuals (239 females) participated (mean age = 36.89; SD = 12.15). The study suggested a potential adaptation-promoting synergy between pandemic-related self-efficacy and a more positive representation of COVID-19, as far as psychological distress is concerned. This according to the study would enable the students to synchronize the proposed virtual learning strategies for prosperity. A study done by Maheshwari (2021) found that students’ satisfaction with the e-learning experience is influenced by e-learning self-efficacy. This study revealed that the three domains of learning i.e. cognitive, affective and psychomotor played salient roles in student satisfaction during the emergency shift to remote learning owing to the COVID-19 pandemic. Bellato (2020) concluded that requests that people adhere to government regulations, especially during localized lockdowns, should specifically target individuals’ internal motivation to act, avoiding a diffusion of responsibility. Hussain, Mkpojiogu and Ezekwudo (2021) equally added from their scholarly work that the major causes of students’ low academic self-efficacy are: lack of confidence with 22.73% and others include: low self-esteem (21.05%) and inferiority complex (10.53%). Also the review was able to show the three most important factors necessary for improving the academic self-efficacy of students using mobile educational apps included: teachers’ message (21.05%) and success and failure of others (15.79%). With the inception of mobile applications in schools, teaching and learning have been of great difference. A research done by Peechapol, Na-Songkhla, Sujiva and Luangsodsai (2018) revealed that various factors improved self-efficacy and provided evidence of significant sources of self-efficacy in the context of online learning. The study noted that Self-efficacy is the key to success in all activities including online learning. In carrying out research on Self-Efficacy on the Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) by Dadfar (2021), a convenience sample of Iranian medical students was recruited in July 2020. The sample size was calculated using Cochran's formula. The COVID-19SES was administered to 130 students who were resident in three student dormitories at the Iran University of Medical Sciences. The study provides evidence for the usefulness of the COVID-19SES for assessing self-efficacy in Iranian students and in non-clinical settings. Twenty-four students (36.4%) reported low COVID-19 self-efficacy, and education is necessary to promote self-efficacy in health-related matters. Findings provided evidence for self-efficacy promotion programs and successful implementation of preventive health behavior programs during the COVID-19 pandemic.Alemany-Arrebola, Rojas-Ruiz, Granda-Vera and Mingorance-Estrada (2020) examined the influence of COVID-19 on the perception of academic self-efficacy, state anxiety, and trait anxiety in college students. The findings revealed that the study could cause an increase in stress due to the uncertainty caused by this time of change. This research analyses the relationship between perceived self-efficacy in the confinement period and the level of trait anxiety (TA) and state anxiety (SA) during COVID-19. The results indicated that there was an inversely proportional relationship between anxiety and self-efficacy; men showed the highest perception of self-efficacy, while women had higher scores in TA and SA; the latter was accentuated in cases when a relative died. Ritchie, Cervone and Sharpe (2020) acknowledged the goals and self-efficacy beliefs during the initial COVID-19 lockdown. The study demonstrated a significant drop in self-efficacy beliefs from before to during the pandemic with a large effect based on whether people thought they could still achieve their goal under current conditions. The study analysis of verbal self-efficacy reports mirrored the numerical results, showing significant differences between pre COVID-19 and current self-efficacy beliefs for achieving valued projects. Cadapan, Tindowen, Mendezabal and Quilang (2022) in their study showed that students had a high level of self-efficacy when it comes to online learning during the COVID-19 period. Despite their struggles and challenges in the online classroom, particularly in social interactions and communication with their classmates and teachers, they were eager to complete their respective degrees since they were confident in their learning management system's use. Dash, Akmal, Mehta and Chakraborty (2022) however stated that user satisfaction enhances user intention during this period which then mediated the relationship between self-efficacy, interaction, and user intention. Choice according to this study moderated the relationship between interaction and user intention. Enjoyment moderated the relationship between e-learning contents and user intention. The study under pinned the fact that stakeholders must enhance the required infrastructure and resources to help the stakeholders adapt to the e-learning mode smoothly and for prosperity.
5. Results, Findings and Discussions of the Study
- Return Rate and Demographic InformationThe study sought to explore the demographic information of the respondents. The demographic information investigated includes the students’ gender and age. This information was considered important for the purpose of generalization of the results of the survey. Table 1 shows the demographics of the respondents of the study.
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. Students Demographic Characteristics and Participation in E-Learning
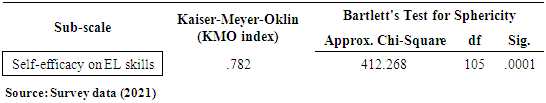
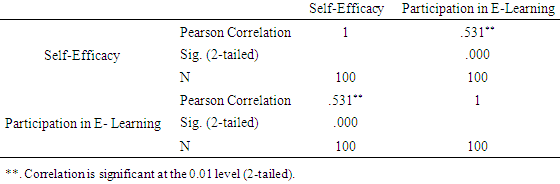
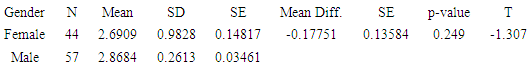
- Students’ Gender on Participation in E- LearningAn independent-samples t-test was conducted to compare the students’ participation in E- learning scores for males and females. The analysis helped to establish whether there is a significant difference in the mean participation in E-learning scores for males and females. Gender, being independent variable was categorical (males/females) and participation in E-learning scores, being dependent variable, continuous variable t-test was the appropriate. Using Levene’s test, assumption of equal variance was not violated (p>.05) as required for an independent t-test. Table 7 shows the summary of an Independent sample t-test results.
|
7. Conclusions
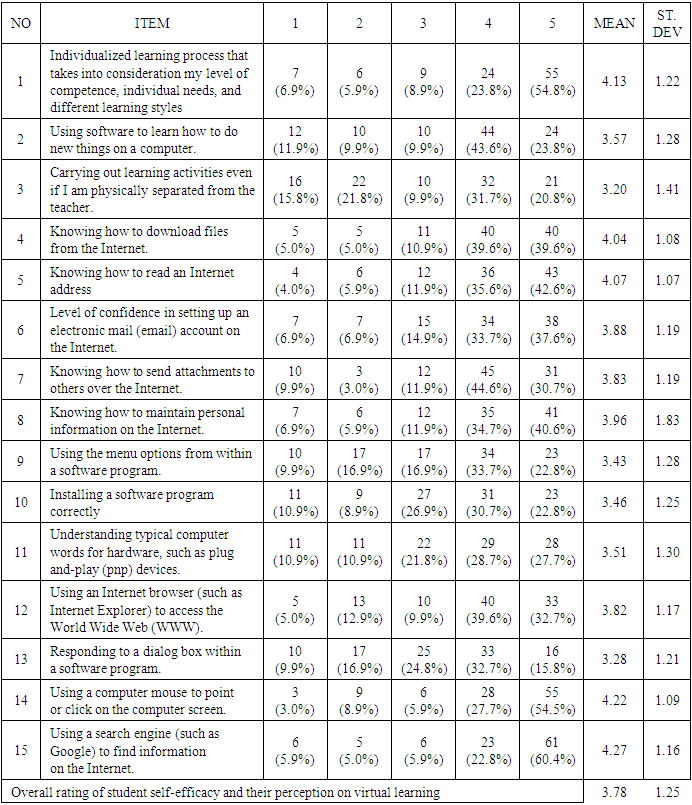
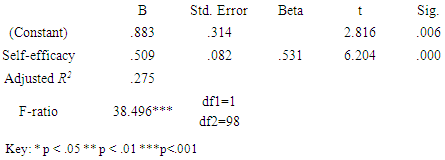
- The objective of the study sought to explore how students rate their own levels of self-efficacy in skills needed to use E- learning after the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings implied that some of the students accepted that they lack confidence in the ability to exert control over their own motivation, behavior, and social environment with regard to E- learning after the COVID-19 pandemic. Causes of low self-esteem after COVID-19 are lack of confidence, low self-esteem and inferiority complex. The study concluded that University management should be more focused in increasing the capacity building programs through ICT skill based trainings on how to use the e-learning system, both to the lecturers and students. The University curriculum developers should effect changes in learning process with an aim to improving on pedagogical strategies to accommodate needs of different students with varied potentialities in e-learning platforms to promote their confidence level. The instructors should also ensuring successful address and implementation of issues raised by the concerned students during the learning process.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML