-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Applied Psychology
p-ISSN: 2168-5010 e-ISSN: 2168-5029
2019; 9(4): 110-116
doi:10.5923/j.ijap.20190904.03

Exam Anxiety among Nursing Students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University and Its Relationship with Some Variables
Husam Al Khatib
Al-Ahliyya Amman University, Jordan
Correspondence to: Husam Al Khatib, Al-Ahliyya Amman University, Jordan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study aims at investigating exam anxiety among nursing students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University. One hundred nursing students from Al-Ahliyya Amman University were selected out of 174 who represented the population of the study. For data collection, Test Anxiety Scale developed by (Sarason, 1980) has been employed in this. The results showed that more than one-third of participants had a high level of exam anxiety and half of them had a medium level of anxiety. Regarding gender of students, the study showed that one-third of male students had a high level of exam anxiety. While, less than one-fourth of female students had a high level of exam anxiety. Finally, there was no statistically significant differences between male and female students in terms of exam anxiety and its dimensions.
Keywords: Exam Anxiety, Nursing Students, Al-Ahliyya Amman University
Cite this paper: Husam Al Khatib, Exam Anxiety among Nursing Students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University and Its Relationship with Some Variables, International Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol. 9 No. 4, 2019, pp. 110-116. doi: 10.5923/j.ijap.20190904.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Exam Anxiety is one of the most common complaints among students at all level and secondary school and university students are no exception. An exam is a formal assessment and a summative evaluation of student's cognitive achievement which determines students’ success or failure. A certain level of anxiety affects students’ performance and therefore influences their academic progress (Timothy & Donna, 1992). Since the 1950s, psychologists have recognized the importance of the relationship between anxiety and learning. The findings of the previous studies have shown that some students achieve lower than their actual ability level because of their increased anxiety. Hence, the term “exam anxiety” has been coined to refer to a type of anxiety that appears in certain situations associated with examinations and evaluation processes (Al- Wahsh, 1998).Exam anxiety has two types: a) disruptive anxiety which is a form of anxiety that affects an individual's behavior during examinations and may significantly affect an individual's performance in exam; and b) facilitative anxiety which is the moderate or a normal level of anxiety that does not significantly affect an individual's performance in exam (Abdul Khaliq and Hafez, 1987). The psychological research studies which were conducted to investigate exam anxiety indicated that both high and low levels of anxiety were the main obstacles that negatively affect students’ level of academic achievement and the accomplishment of their goals. A high level of anxiety hinders students' ability to remember, think, judge and perform mentally. On the other hand, a low level of anxiety leads to weakening motivation, while a medium level of anxiety increases motivation (Zahran, 2000). Hence, exam anxiety can be considered as a motive or an obstacle to mental and academic achievement based on its severity level and the individual differences within the study groups at educational institutions at any learning stage. Spielberger (1980) posits that exam anxiety increases when performance is associated with life decisions of students who aspire to achieve their special goals. The more individual's performance is associated with the exam to achieve their special goals, the higher the level of exam anxiety will be and vice versa. Furthermore, academic achievement can be influenced by the general mental ability of students and can be also considered as an important pattern of the student's mental activity during their study (Spielberger, 1980). Exam anxiety is a pattern and a form of general anxiety that can be provoked by different exam situations. It represents an individual emotional psychological issue experienced by students during exam period which can be signified and intensified by fear from failure (Abdul-Rahim, 1989). As the study of nursing specialization is one of the areas that requires a lot of time, tremendous effort and sufficient cognitive abilities to succeed, these factors may contribute to increasing the level of anxiety among nursing students at all levels.
2. Problem of the Study
- Studying at university is a distinguished stage within the educational pyramid because it differs from others educational stages in terms of method of teaching, requirements, and results that may lead to either success or failure of students. Academics and teaching faculties at universities consider that the study of nursing subjects' needs more complex abilities and skills such as: time management, effort, cognitive knowledge, language proficiency and technical and soft skills. The main purposes of university education are cognitive achievement, skills acquisition and the extent to which these requirements are achieved. There should be a set of examinations and formal evaluations to determine whether students have successfully passed the stage or not. While this is usually obtained through achievement exams at this stage, exams become the only available means to judge the success or failure of students in the various educational stages. This makes exams associated with awe and fear in the eyes of both students and parents (Khairallah, 1981). Given the great role they play in the educational process, tests and exams remain an obsession for students. Moreover, their results serve as measures to distinguish students to move from one stage to another. Based on the results of the exams, the certificates are issued to determine the fate of students to join a job or pursue a postgraduate position which help them get the desired social status. Success is a dream for every student, while failure is the destructive factor of all aspirations, which might cause severe disappointment and dissatisfaction. Sometimes, there are factors that affect students’ success and their ability to reach their goals such as: fear of the exam and a sense of awe which is known as exam anxiety. Hence, this can affect their performance negatively and impede their success despite having the cognitive and skills knowledge which necessary to succeed. Based on the aforementioned, the problem of the study can be identified in the following main research question: What is the level of exam anxiety among nursing students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University?
3. Objectives of the Study
- The study aims at:1. identifying the level of exam anxiety among nursing students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University.2. examining whether there is a statistically significant difference between the levels of exam anxiety among nursing students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University which can be attributed to the variables of sex, age and level of study.
4. Questions of the Study
- This study aims at answering the following research questions:1. What is the level of exam anxiety among nursing students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University?2. To what extent is the level of exam anxiety among nursing students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University attributed to students’ gender, age and level of study?3. What are the most prevalent symptoms of exam anxiety among nursing students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University?
5. Important of the Study
- Investigating the level of exam anxiety among nursing students has a significant importance for the following reasons:First: Theoretical importance:1. Knowing the level of exam anxiety among nursing students and understanding its relationship with some variables can contribute to increasing scientific knowledge about the exam anxiety levels.2. Lack of studies that targeted Arab students and lack of Arabic studies that investigated exam anxiety among nursing students. Therefore, this study sheds more light on a specific sample of university students who have certain study requirements.Second: Pedagogical implications: 1. The results of this study will contribute to raise the awareness of instructors, test designers and educators about the state of exam anxiety in order to take into account the students’ psychological and social status during exam period as a proactive and protective measure and criterion. 2. The results of this study will further help psychologists and counsellors to recognise one of most central problems that faces university students which may require psycho-therapy and psychological support.
6. Terminology
- Exam anxiety: Sarson & Sarson (1960) define exam anxiety as the response to perceived danger and inability to carry or perform a mission which is characterized in the students’ feeling of incompetent and weak motivation to do the mission he/she is working on. It is also defined as having ideas that significantly underestimate their values, assume failure, and weaken the consideration of others.
7. Concept of Exam Anxiety
- Exam anxiety consider as a common psychological phenomenon that psychologists have been interested in new era. it has become a noticeable phenomenon in individuals, as a result of difficult and complex life conditions. also, anxiety is part of the human life and a dynamic aspect in building personality and basic variable of human neurological, mental and behavioural disorders. Anxiety is a normal phenomenon experienced by human being, as part of human life and forcing him to choose things inconsistent with his desires to meet the demands of society, or the inability to fulfil his desires, tendencies and aspirations that are hampered by many obstacles with increasing life and demands stresses (Abu Azab, 2008). There are many definitions that deal with concept of exam anxiety. In this regard, the researcher will review some of definitions and opinions of psychologist on exam anxiety as follows: -Gohn (1985) says the exam anxiety is a student's state as a result of increase in degree of fear and tension during passage the exam conditions as well as disturbance in emotional, cognitive and physiological aspects. Spielberger sees the anxiety in general “a personal trait in a specific situation and consists of discomfort and emotion. Also, he defined the discomfort as a cognitive concern of fear of failure, whereas the emotional state is the reactions of the autonomic nervous system, these two components discomfort and emotional are the main factors of exam anxiety (Al-Daheri, 2005:207). Spielberger (1980) posit that the exam anxiety is a temporary emotional state caused by perception of evaluation position as threatening situations of personality accompanied by tension and stimulate emotional unity, and negative mental preoccupations, overlap with the concentration required during the exam, which negatively affects in mental and cognitive missions in exam position. Abdul-Khaliq and Hafez (1987) believes that exam anxiety is sometimes called as achievement anxiety, it is a type of anxiety related to exam situations make the individual feel fear. Types of exam anxiety 1. Facilitator exam anxiety: its affects positively and as motivation anxiety drives the student to study, high achievement, and good preparation for exams.2. Difficulty exam anxiety: it’s a high level of exam anxiety effects negatively in the students, where he/she feels nervous, fear, discomfort, and awe increase. this impedes the student's ability to remember, understand, and confuses him when prepares for the exam, also makes it difficult (Zahran, 2000:98). Symptoms and aspects of exam anxietyThe exam anxiety is a type of a state anxiety, to distinguish it from anxiety attribute, and the symptoms of exam anxiety include (Dhamen, 2003 and Zahran, 2000): -1. Stress, insomnia and loss of appetite, dominate some thoughts and obsession before and during the nights of the exam.2. The deeply thinking about exams and preoccupation before and during the exam.3. Tachycardia, Xerostomia, lips, rapid breathing and sweating, abdominal pain and nausea.4. Shortness of breath before and during the exam.5. Disorders of mental processes such as attention and thinking.6. Emotional horror in which the student feels inability to remember anything. These symptoms and physiological and emotional behaviour and mental confusion and disruption of the student to perform the necessary missions in the exam. It may be reinforcement by family and school as a result of exam will lead to fateful situations in the future of the student. Causes of exam anxiety According to mental health and educational researchers, the exam anxiety is due to many reasons such as (Zahran, 2000:99):1. Weak of subject’s knowledge.2. Weak of motivation to succeed.3. Having learning problems, organizing, reviewing information before the exam. 4. Frequency of failure and the relation of exam with student’s failure experience. 5. Failure in prepare for the exam.6. Low of self-confidence.7. The negative attitudes of students, teachers and parents towards exams.8. The difficulty of exams and feeling that the future depends on it.9. Environmental and family stress to achieve an ambitious level that is not commensurate with a student's abilities.10. Learner's inability and expectation of failure.Sources of exam anxietyEducators in this field indicate that the exam anxiety has several sources, including the following:1. Ambitions, expectations and family concerns.2. Student motivations.3. Teacher and teaching methods.4. Methods of assessment and the circumstances surrounding the exams.5. Studying Habits (Tayeb, 1996:98).Al-Kuhaimi (2011) considers that the most important sources of anxiety are psychological stress, life stress, and environment stress which saturated with: fear, illusion, unity, deprivation, and parental disorder.
8. Literatures Review
- Hayawi’s (2018) identified the effectiveness of a cognitive behavioural counselling program to reduce exam anxiety among students of the University of Basra. Sample of the study consisted of 30 students from social sciences faculty, were distributed into two groups, experimental group 15 participants and a control group 15 participants. Results of the study showed that the participants of experimental group had a significantly lower level of exam anxiety compared with participants of control group.Mahdi’s (2017) investigated the relationship between exam anxiety and cognitive representation among university students. Sample consisted of 241 students from Iraq republic, the exam anxiety scale and the cognitive representation scale have been used. Results of the study founded a negative statistically correlation between exam anxiety and cognitive representation. Hawash’s and Olimat’s (2004) identified the achievement motivation relation to exam anxiety and its impact in english language achievement in primary and secondary school students in Mafraq governorate. Sample of the study consisting 180 students (99 male & 81 female) from two different school, for purpose of the study, the achievement motivation, exam anxiety, and achievement scales have been used. To obtain the results, means, standard deviation, and ONE-WAY ANOVA have been calculated. Results of the study presented that the level of student’s achievement in English subject differ according to their level of motivation. This cannot be attributed to the exam anxiety, class level, or interaction between them. Results also showed that there is no different between students in their motivation for achievement according to their grade levels. While, there is different between students in test anxiety according to level of the students in favor of ninth grade.Adibi’s (2001) studied the relationship between creative thinking abilities, recall habits and exam anxiety on the other and includes innovative thinking. Sample of the study consisted of 227 male and female students from university students from (education, science and Arts faculty), and students from general secondary school and in Bahrain state. The researcher adopted on creative thinking abilities, recall habits and exam anxiety scales, and one-way analysis of variance, t-test and correlation coefficient of Pearson are used. Finally, results of the study indicated that there is a positive statistically significant correlation between ability of creative thinking (emanation, originality and creative ability) and work methods; and there are significant statistical differences among highly creative ones in their work methods. It was also found that there is a positive statistically significant correlation between originality and creative ability on one hand and recall manners and attitudes towards learning on other hand, whilst there are no statistical correlations between ability of creative thinking ad learner satisfaction variables.
9. Methodology
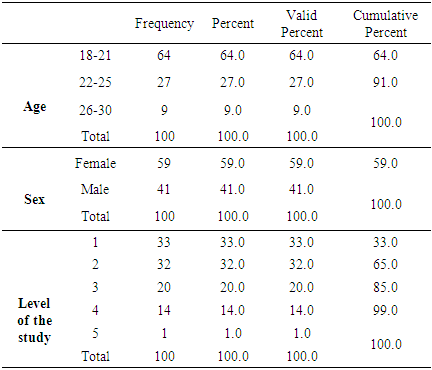
- Following the objectives and research questions of the current study, the researcher adopted the descriptive analytical method. Population and study Sample The population of the study includes 174 nursing students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University for the academic year 2018/2019. The sample of the study consists of 100 students representing 58% of the population of the study as illustrated in the following table:
|
10. Results of the Study
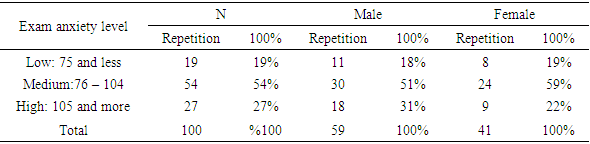
- Q1: 1. What is the level of exam anxiety among nursing students in Al-Ahliyya Amman university?
|
|
|
|
|
11. Discussion and Conclusions
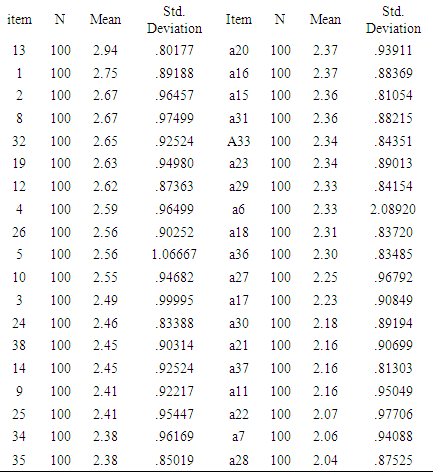
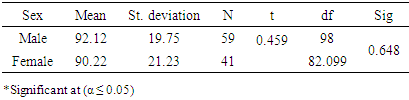
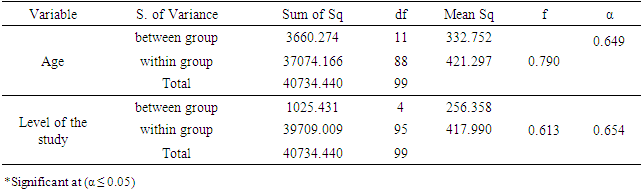
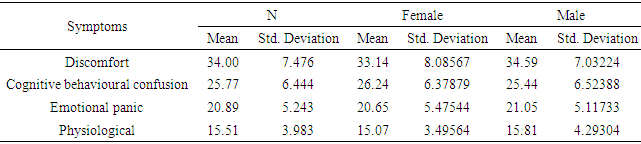
- Results of the study indicated that more than half of the participants were suffering from medium levels of exam anxiety. Whereas one-third of the participants were suffering from high levels of exam anxiety. Regarding the effect of the gender of participant, the results revealed that one-third of male students were suffering from exam anxiety, while less than one-fourth of female students were suffering from exam anxiety. Furthermore, the results of the study revealed that the most influential item was: I feel nauseous, shivering when the teacher asks a question. Whereas, the least influential items among the participant was: I feel anxious and worry when the teacher declares how much time is left for the exam. The findings further proposed that there was no statistically significant difference between students’ level of exam anxiety and their gender, age, and level of study. Finally, the results showed that the most prominent symptom among both male and female students was discomfort symptom, while the least prominent symptom was the physiological symptom. The high level of exam anxiety among nursing students at Al-Ahliyya Amman University can be explained according to lack of subject’s knowledge and expertise, study method problems, or the feeling that the students’ career future depends on the results of exams. Moreover, a large number of Al-Ahliyya Amman University students’ sample of the study are foreign students. Therefore, such a high level of anxiety might be due to environmental and family pressure to achieve high and reach an ambitious level that is not commensurate with the students’ abilities. It seems that such a pressing environment with high demands are difficult to achieve in light of the student's stress caused by homesickness. These potential reasons affect both male and female students. Thus, the results showed that no significant differences in exam anxiety between both genders. Moreover, the level of study at university did not interact with exam anxiety because the students who had exam anxiety in the first year of the study, he/she would suffer from exam anxiety throughout all university study years. Severe exam anxiety requires psychological care and treatment and cognitive behavioural programs. It is predicted that such services were not provided to the participants in this study. Therefore, the results of the study showed that students from different levels of the study suffered from exam anxiety.The most common symptoms between students were discomfort symptoms and the lowest on was physiological symptoms. This might be due to the youth age stage in which students’ physical health is a good and therefore they might have resistant to exam anxiety. It is also possible that some students may be more resistant because of their prevailing culture which does not accept any physical complaints. More than half of the participants are male, and hence they may express fewer physical complaints. The results of this study are in line with results Adibi (2001) and Hawash and Olimat (2004).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML