-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Applied Psychology
p-ISSN: 2168-5010 e-ISSN: 2168-5029
2016; 6(2): 31-36
doi:10.5923/j.ijap.20160602.02

Does Center-based Childcare Play a Role in Preventing Child Maltreatment? Evidence from a One-year Follow-up Study
Tokie Anme 1, Emiko Tanaka 1, Taeko Watanabe 2, Etsuko Tomisaki 1, Yukiko Mochizuki 1
1Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan
2Faculty of Health Science, Japan University of Health Sciences, Satite, Japan
Correspondence to: Tokie Anme , Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Given the increased reports of child maltreatment across Japan, center-based childcare is expected to become more involved in parenting support. The purpose of this study is to clarify the role of center-based childcare in the prevention of maltreatment. This longitudinal project examined parents who used center-based childcare and those who did not over a period of one year. Participants were 3,723 parents who used governmentally authorized childcare centers across Japan and 222 parents who used home care. Indicators of parenting behavior and family background were obtained from a questionnaire completed by parents responsible for the children. Parenting behavior was obtained by a scale based on the Home Observation for Measurement of Environment (HOME). The results suggest that using center-based childcare significantly reduced the risk of child maltreatment. In the center-based care group, 25.7% of parents exhibited positive changes-namely, they engaged in punishment less-but only 11.7% of parents in the home care group did so. Thus, many more caregivers who used center-based care showed positive changes in maltreatment-related behavior. This indicates that center-based childcare would be an adequate early support measure for preventing child maltreatment.
Keywords: Child Care, Prevention, Abuse, Support
Cite this paper: Tokie Anme , Emiko Tanaka , Taeko Watanabe , Etsuko Tomisaki , Yukiko Mochizuki , Does Center-based Childcare Play a Role in Preventing Child Maltreatment? Evidence from a One-year Follow-up Study, International Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2016, pp. 31-36. doi: 10.5923/j.ijap.20160602.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Child maltreatment is a serious social problem requiring urgent address, particularly for infants and toddlers. In Japan in 2013, 73,765 children were identified as victims of abuse or neglect [1], and these rates had increased by more than 10% from the previous year. The effects of maltreatment on children are substantial and long lasting. Compared to children who never experience maltreatment, those who suffer maltreatment have higher rates of socioemotional and behavioral problems, delinquency, and school failure [2, 3]. Maltreatment is believed to occur in particularly high-stress homes, and such escalated stress and its associated effects on parenting—such as increased harshness and decreased consistency of treatment—is believed to undermine children’s emotional wellbeing [4, 5]. Efforts to promote healthy development in children of high-stress families might therefore target how to either reduce family stress or provide more supportive environments for these children outside of the family.Authorized center-based childcare programs have been providing services to families with young children in Japan since 1947. These centers were first implemented after a string of tragic accidents resulted in the deaths of a number of children in low-quality childcare centers, which led the government to enact Child Welfare Act. Part of this act included the establishment of authorized childcare centers. Currently, most parents work for rather long hours, and concerns persist about the efficacy of caring for children outside the home for long periods. Several longitudinal studies suggest that the home environment has a more important contribution to child development and problem behaviors than does the number of hours spent in authorized center-based care [6-8]. Moderating factors outside of the home might also alter the outcomes of stress; finding potential buffers against the negative effects of stress (e.g., maltreatment) would be of particular value from an intervention and prevention standpoint. In the present study, we extend research on maltreatment dynamics by examining a salient developmental context outside of the home—namely, center-based care—as a potential moderator.Quality of care must be considered if the effects of center-based care on child well-being are to be understood [9]. Findings from studies on the quality of care in these authorized childcare centers appear to be inconsistent, particularly over the long-term. Some studies found that children may be less anxious and have less problematic transitions to school if they go to better quality centers, while children placed in non-maternal care in the first three years of their lives have been found to have higher academic achievement and lower behavioral problems in adolescence, compared by having maternal care only [10]. However, the findings of an earlier longitudinal study suggest that the positive effects of high-quality care facilities may not be significant enough to differentiate children as they grow older. Andersson [11] found that by age 13 years, there were no discernible differences in factors such as academic skills and problem behavior between children who had experienced high quality childcare and those who had not. According to previous studies, maltreatment was strongly related to parents’ stress [12-14], loneliness [15, 16], and lack of support [17, 18]. The hypothesis of this study is that using center-based childcare may reduce parental maltreatment of the child. By obtaining support from childcare professionals, parents can reduce their stress and improve their child-rearing skills.This study focuses on whether utilization of center-based childcare can prevent child maltreatment. Specifically, we sought to determine if using center-based care over one year reduces the risk of child maltreatment by caregivers.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
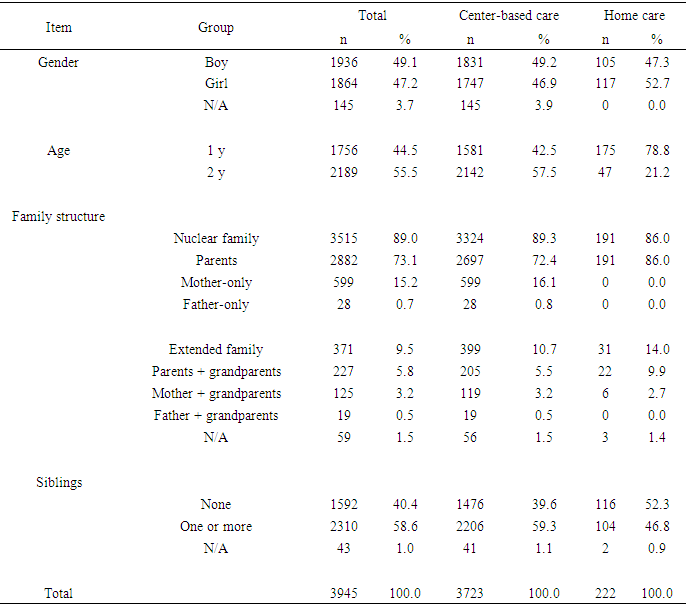
- Participants were 3,723 parents who used governmentally authorized childcare centers across Japan and 222 parents who used home care. We used data of two cohorts: the “Cohort Study for Center-Based Childcare” [6], for participants who used center-based childcare, and the “Japan Children’s Study Cohort,” for participants who used home care [19] to compare changes in rearing behavior between parents who used childcare and those who did not. Both cohorts recruited parents with a distribution of socioeconomic statuses representative of the Japanese population. All parents had at least one child who was either one or two years old. Children with diagnosed disabilities and health problems were excluded from the study because these characteristics were expected to confound results. All 3,945 parents were asked to participate again one year after the initial survey and answered a questionnaire based on the child-rearing environment at that time. Table 1 provides the gender and age composition of the child population that was evaluated, as well as the family structure and number of siblings. The distribution of boys (1,936; 49.1%) and girls (1,864; 47.2%) was fairly even.
|
2.2. Measures and Procedure
- Indicators of parenting behavior and family background were obtained from a questionnaire completed by parents responsible for the children both in the baseline year and one year later. Parenting behavior was measured using a scale based on the Home Observation for Measurement of Environment (HOME), called the Index of Child Care Environment (ICCE). The HOME has been used worldwide and translated into more than 50 languages, and is used to evaluate the quality and quantity of stimulation and support available to children at home [20]. The ICCE measures childcare environment through 13 questions in four subscales: “human stimulation” (5 items: e.g., “How often do you play with your child per week?”), “social stimulation” (3 items: e.g., “How often do you go shopping with your child?”), “avoidance of restriction” (2 items: e.g., “How many times did you hit or kick your child last week?”), and “social support” (3 items: e.g., “How often does your spouse, partner, or other caregiver help you with the child?”). The ICCE can be completed via self-report or interview, meaning that it does not necessarily need a home visit by the researcher. Each item is assessed with a multiple-choice format, such as once a month, once a week, everyday etc., and the answer is then given a binary score according to the manual (1 = good, 0 = not good or not sure). The ICCE shows a high correlation with HOME [21]. In regard to items in “human stimulation” and “social stimulation” subscales, and the item “talking with spouse about child”, the answer “rarely” was coded “0”, due to the reason that “rarely” was considered as the case that needs some support. For the item “Appropriate response to mistakes”, the answer “slap or hit your child” was scored “0”. With respect to the item “Punishment”, the answer “never slap the child” was scored “1”, and others were scored “ 0”. In regard to the items “support for childcare” and “having a consultation”, the answer “no” was scored “0”, and “yes” was scored “1”.The main variables included parents' behavior and existence of support for care at time one (T1) and after one year [time two (T2)]. Two groups were identified according to their changes in these variables over time: “positive change” (low-quality care and no support at T1, and high-quality care and support at T2), and “consistently negative” (low-quality care and no support at both T1 and T2). Chi-square tests were applied to identify the differences in the parents’ behavior and support between the parents who used center-based care and those who used home care.The Statistical Analysis System (SAS) statistical package was used for analysis.
2.3. Ethical Considerations
- All study participants provided written informed consent, and the ethic committee of the University of Tsukuba approved the study design (668). Written Informed consent on behalf of the children was obtained from the parents.
3. Results
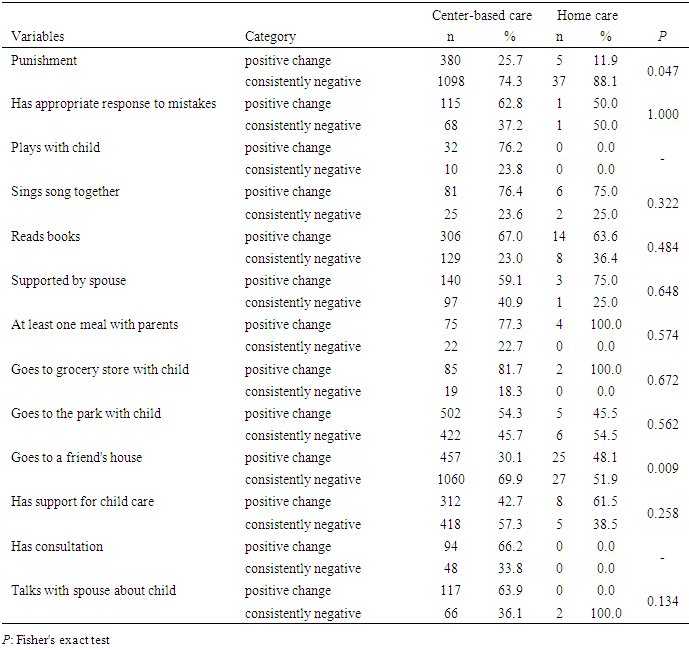
- As shown in Table 2, there were relations between using center-based care and the variables of parents' behavior and existence of support for care. Specifically, using center-based care was significantly associated with a dramatic increase in the number of behaviors that exhibited positive changes, such as reducing “punishment” to the child. In the center-based care group, 25.7% of parents showed positive changes in punishment behavior (i.e., they showed less such behavior), while only 11.7% of parents in the home care group did so. However, one of the behaviors, “Goes to a friend's house” significantly increased to a greater extent for home care children. In the home care group, 48.1% of parents showed positive changes by going to a friend’s house, but only 30.1% of parents for the center-based care group did so. All other items, such as “How often does your spouse, partner, or other caregiver help you with the child,” were not significantly different between center-based care and home care.
|
4. Discussion
- Center-based childcare is important for not only children but also caregivers. However, few studies have focused on the practical benefits of center-based care for caregivers. This study explored the differences in the effects of center-based care and home care on the behavior and support of caregivers of one or two-year-old children. Our results showed that caregivers who used center-based care showed positively changes in maltreatment-related behavior. However, “going to a friend's house” increased more for children receiving home care, likely because such children have more opportunities to go to their friends’ houses when at home.All care centers in this study met governmental standards and attempted to ensure high-quality care for children, such as playing, eating, and sleeping. As the first nationwide Japanese cohort study of center-based care and home care, this study provides unique insight into our understanding of the relation between childcare services and caregivers’ behavior. Outside Japan, several large-scale, center-based childcare studies have been conducted and have documented associations between childcare quality and improvements in parents’ organization of the home environment [22]. Although important, such caregiver-focused research for improving childcare may derail further important child-focused research. In essence, the social and academic skills that children develop in early care may influence parents’ orientations toward better parenting behavior, guidance, and managing their experiences and activities [23].The compensatory-process and lost-resource perspectives suggest that the effects of parental characteristics, including poor mental health and lower socioeconomic status, may be compensated for by high-quality non-maternal care [24, 25]. While the current study provides important findings, the limitations of this study should be mentioned. First, participants were recruited mainly at authorized child care center, and their characteristics are affected by the type of care centers and that they used. Additionally, the information of the factors that previous studies have pointed out to be associated with parenting behavior [26, 27], such as socio-economic status of the family, caregivers’ education background, and professionals were not available in the current study. Furthermore, the parent’s own and the child factor, such as the participant’s temperament, child’s developmental delay and other factors that was shown associated with child maltreatment [28, 29]. A further study with more comprehensive discussion includes these factors is needed in the future. The quality of care may have been a reflection of the maternal and family characteristics of families that participated in this study, meaning that those who did not participate might have had different characteristics and therefore different quality of care, the high response rate and highly homogeneous nature of Japanese society may have mitigated any possible bias. Thus, the principal implication of this large-scale, multisite research project is that center-based care may be more important for reducing caregivers’ maltreatment of children than home care.
5. Conclusions
- The series of studies on center-based care conducted by Anme and her colleagues continue to indicate that while there are some minor differences in the effects of different types of services and care on caregivers, there are a number of major factors that appear to reduce the risk of maltreatment. Parents who used center-based childcare, thereby receiving mental and physical support from professionals, can make positive changes to their behavior after one year.These findings have particular significance for policymakers and service providers working with families of young children. The home life and psychosocial health of caregivers, including their self-confidence and access to childcare assistance, appear to be essential in avoiding abuse. We will be continuing to follow the current sample to assess parenting behaviors and evaluate the effects of childcare that may emerge later in development.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We express our deepest gratitude to the Japan Night Child Care Alliance, particularly President Amahisa and Vice-President Edamoto, as well as all participants and staff. This research was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (23330174) and the Research Institute of Science and Technology for Society.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML