-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Applied Psychology
p-ISSN: 2168-5010 e-ISSN: 2168-5029
2016; 6(1): 15-19
doi:10.5923/j.ijap.20160601.03

Family Burden of Stroke Patients in Rayong Hospital Thailand
Nimnual Chuyingsakultip1, Rapin Chayvimol2, Doldao Purananon2, Chompunut Srichannil2
1M.N.S., Ph.D. Student Counseling Psychology, Burapha University, Thailand
2Ph.D. Professor of Counseling Psychology, Burapha University, Thailand
Correspondence to: Nimnual Chuyingsakultip, M.N.S., Ph.D. Student Counseling Psychology, Burapha University, Thailand.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Especially when one member of a family illness will affect the other members of the same family. Sometimes a member may feel a greater burden of responsibility. The purpose of this mixed methods study is to examine the burden that the family members experienced by caring for individuals with stoke at Rayong hospital, Thailand (from March 1, 2015 to April, 2015). 40 relatives of stroke patients were recruited using systematic random sampling. The participants completed the Zarit Burden Questionnaire and ten of them were interviewed with semi structural interviews for qualitative study and analyzed using analytic induction. Quantitative analyses showed that stroke has a moderate burden moderate) X = 30.3, SD = 13.7 (for the family. Participant’s gender, age, income, marital status, degree of relationship between the caregivers and the stroke patients, and degree of patient’s disability produced no significant result. There were two significant effects of the hours of care) F (2, 37) = 4.173, p = .023) and participant’s level of education) F (2, 37) = 5.424, p=.009) on family burden. In-depth interviews with ten caregivers of patients with stroke revealed 3 main dimensions of family burden, including personal strain, personal or inner conflict and guilt. The results suggested that Zarit Burden Interview were appropriated for measured family burden of stroke.
Keywords: Stroke patients, Family burden, Thailand
Cite this paper: Nimnual Chuyingsakultip, Rapin Chayvimol, Doldao Purananon, Chompunut Srichannil, Family Burden of Stroke Patients in Rayong Hospital Thailand, International Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol. 6 No. 1, 2016, pp. 15-19. doi: 10.5923/j.ijap.20160601.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The changes that happen to a family member whether it is with any given subject. Causing changes to the roles and responsibilities of the members who had originally performed. It causes problems as a consequence. Especially when one member of a family illness will affect the other members of the same family. Sometimes a member may feel a greater burden of responsibility. The concept of Zarit, Reever, & Bach-Petersons (1980) The study of the family burden has the meaning that means response emotions and attitudes that unwanted physical, mental, emotional, social and economic conditions as a result of experience in direct care. The second measure including personal tensions that need to be role (role strain) and paradoxical self (personal strain). The burden on families caring for family members with the disease, whether any given time. What is relevant is inevitable illness with a stroke, which is a major public health problem of global population issues. World Stroke Organization: WSO report that stroke is the second leading cause of death of people aged over 60 years and is the fifth leading cause of death for persons aged 15-59 years, each year there are an estimated 6 million people died from the disease so stroke is a silent disease threatens the lives of people around the world (WSO, 2012). Patients may become disabled as a result of disease. Affect patient caregivers cannot function in the family. Unable to work or profession again. Some cannot attend social events or communicate to others who understand all the aspects that affected the body, mind and emotions caused from patient care. Severe anxiety, depression and physical impact on patient care, such as fatigue, body pain, back pain, lumbar health problems are increasing. The impact on the family found that families are concerned about the patient's condition that can be healed or not. Will be how to help or what it does. In addition, when patients discharged from hospital often found that physical disability of patients attending social events was low. Some creditors could not attend any social events. The problem of the ever-changing roles in the family self-sufficiency or relied on other people to have to rely on others. Almost every family to family turmoil, such as changing the home environment.The changing lifestyle of the family members. Family expenses increased revenue decreased liability and the lack of opportunities for professional care. The impact of these occurrences Jonghongklang (2006) study on The effect of the program is to promote the potential administrative burden of caring for stroke patients found that the samples are taken care of with potential caregivers there is a lower that significant p<.05. Foreign research In line with Thailand's research found that illness caused by stroke patients who lost previous job was a burden. Increased levels of anxiety and depression to the administrator. The caregiver was a woman will feel a burden than men financial problems and feel the burden will increase if long-term care patients and the severity of the disease. Moreover, the worsening of the health care worse. It also enables administrators to loss of job as well decreased quality of life (Inez, 2013; Sapna Erat Sreedharan, et al, 2013; Kamel, Bond, & Sivarajan, 2012). Moreover, the development of programs to reduce the burden of care is called Psycho-education intervention program (Farkhondeh, Maryam, & Arash, 2012; Ho, Sek, & Janita, 2014) the research sample is a group of psychiatric patients Schizophrenia and Mental disorder, which the study found to reduce the burden of care to the caregivers.
2. Research Purposes
- 1. To study the family burden and factors affecting the families of patients with stroke.2. To compare the factors that affect the family burden, including gender, age, education, marital status, relationship with the patient, the number of hours of care per week, and the ability to perform daily activities of patients (disability).
3. Research Questions
- 1. Gender, age, education, marital status, relationship with the patient, the number of hours of care per week and the ability to perform daily activities of patients (disability) affects the patient's family burden or not.2. Gender, age, education, marital status, relationship with the patient, the number of hours of care per week, and the ability to perform daily activities of patients (disability) that are different made the family burden of stroke patients different or not.
4. Hypotheses
- 1. Gender, age, education, marital status, relationship with the patient, the number of hours of care per week and the ability to perform daily activities of patients (disability) affects the patient's family burden.2. Gender, age, education, marital status, relationship with the patient, the number of hours of care per week, and the ability to perform daily activities of patients (disability) that are different made differently on the family burden of stroke patients.
5. Research Methodology
- This research was mixed method model that consisted of quantitative and qualitative method.Population: Caregivers of stroke patients which is responsible for the primary caregiver and family members of patients with stroke that as admitted to hospital in Rayong hospital.SampleSystematic Random Sampling for 40 the primary caregivers.
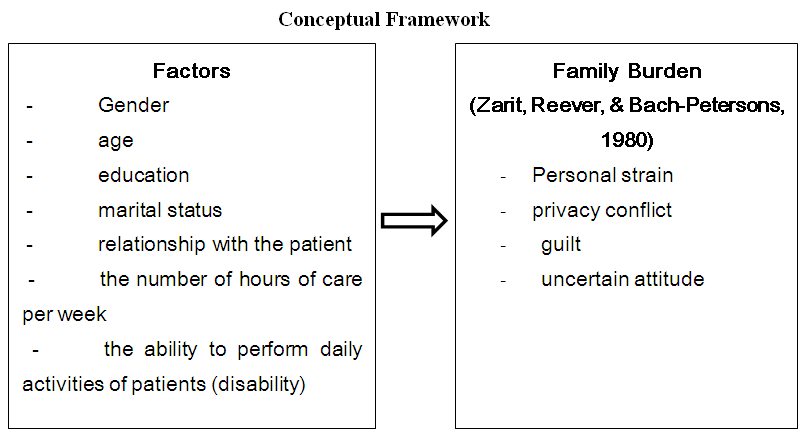 | Figure 1. Conceptual Framework: Family Burden of Stroke Patientsin Rayong Hospital Thailand |
6. Research Instrumentation
- Research Instrumentation include1. The quantitative research used questionnaires to examine the family burden of patients with stroke divided into two steps:The first is a questionnaire about general information of caregivers of stroke patients. Which is responsible for the primary caregiver and family members of patients with a survey items (Check list) include sex, education, marital status, relationship with the patient, the number of hours of care per week, and the ability to perform daily activities of patients.The second questionnaires about the family burden 22 items by TulsiriC., et. al. (2011) that translated from Zarit Burden Interviews: ZBI (1980) about 4 dimensions thuspersonal strain 9 itemsprivacy conflict 4 itemsguilt 5 itemsuncertain attitude 4 itemsInterpretation of the high score means a higher burden. No clear criteria for the interpretation of results thus, the criterion adopted in interpreting the results by Hebert R., Bravo G., & Preville M. (2000) for applications details0 – 20 little or no burden 21 – 40 mild to moderate burden 41 – 60 moderate to severe burden 61 – 88 severe burden2. The qualitative research used semi-structured Interview Protocol
7. Quality Monitoring Tools
- 1. The family burden 22 items by TulsiriC., et. al. (2011) that translated from Zarit Burden Interviews (1980) Trial with the primary caregivers in families of patients with stroke that looks similar to the sample 30 patients analyzed for Cronbach’s alpha coefficient .88.2. The semi-structured Interview leading to the 5 experts check the content validity to the IOC is 1.00.
8. Data Collection
- The researcher collected data manually by following procedure1. Conducted a systematic random sample2. Ask and record personal information of patients3. Estimates of the family burden by ZBI and interview burden of care in high score of burden by question “How do you feelings and experiences in patient care in the past”
9. Data Analysis
- Check the accuracy of the data. The data were analyzed by a computer program. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the basic information (percentage, average, standard deviation). Test the difference of the family burden by independent t-test, One-way analysis of variance and test different pairs by Fisher’s Least Significant Difference: LSD. The qualitative data analysis, interpretation created by inductive conclusion and presented as a lecture.
10. Advocacy Groups
- Received approval from the Ethics Committee in humans at Rayong Hospital Thailand in April, 2015.
11. Conclusions and Discussion
- 1. SamplesPrimary caregivers of stroke patients, mostly female (85) corresponding with the research administrative burden of Michael O. O., Olumide O. D., Olajire S. O., Adesola C. O., & Morenike O. O. (2013) and Melissa S. D., Patrick J. G., Glenn D. G., Marco D. D., Amir G., Sepi F. V., & Richard Z. (2013) both studies found that most primary caregivers were female. Also, research the development of caregiver burden by Tulsiri C., et. al. (2011) found that most caregivers are women as well (76.4%).2. The family burden of patients with stroke, most are moderate (52.5%) and family burden, the average 30.33 points corresponding with the research of Tzu-Jung W., Chi-Chung H., Siang-Han L., Mei-Hua L., & Wen-Jiuan Y. (2011) found that the burden of caregivers is moderate in the term of rehabilitation3. The results of the comparative analysis family burden in patients with strokeSex: There was no effect on the average scores of family burden, as opposed to the study of the Tzu-Jung W., Chi-Chung H., Siang-Han L., Mei-Hua L., & Wen-Jiuan Y. (2011) which was conducted in patients with stroke, 80 cases by random sampling criteria (purposive sampling) by the findings showed administrators who are women To feel the financial burden than men. But in this study, It found that the number of samples differ too muchthe number of respondents were 34 female while male only 6 cases are limitations in data analysis in this research as well. But if you look at the average burden of care it found that caregivers are female scores family burden of care than male caregivers.Income: Do not affect the rating of the family burden of care for stroke patients (F (3, 35) = 1.764, p = .172)The ability to perform daily activities of patients (disability) had no effect of the family burden of care in stroke patients (F (2, 37) = 2.603, p = .088)The results of this study as opposed to the education of Kamel A. A., Bond A. E., & Sivarajan F.E. (2012) which was conducted in patients with stroke and caregivers of 116 cases, the results showed that the ability to practice the routine of patients relations with the burden of care patients who have the ability to perform daily activities is high administrative burden of care is low. In this study, the features of patients with stroke is the ability to perform daily activities no more than 50 points, and the study found the ability to perform routine daily average of 35.13 points (SD = 19.98, minimum = 0, maximum = 50), the rate of dependence on the care of patients in similar levels thus not affected administrative burden of care.The number of hours of careper week: Affect the average burden of family burden in patients with stroke level of statistical significance. 05 (F (2, 37) = 4.173, p = .023) Consistent with studies Tzu-Jung W., Chi-Chung H., Siang-Han L., Mei-Hua L., & Wen-Jiuan Y. (2011) which was conducted in patient with stroke, 80 cases by random sampling criteria (purposive sampling) found that social factors are related to the occurrence of the most, followed by emotional and duration of care.Education: Affect the average burden of family care in patients with stroke level of statistical significance. 05 (F (2, 37) = 5.424, p = .009). In the study found education differences in the burden of care varied by level of primary education the burden of care is higher than higher education and secondary education. Affect the perception of the disease the proper conduct towards patients to seek what is useful to promote the recovery and rehabilitation phase of the disease. Education will be involved, clearly from this study, and education of Tulsiri C., et. al. (2011) found that most caregivers are primary education (52.7%), thus reducing the administrative burden of care for this group there should be an emphasis on Psycho-education ProgramSemi structural interview about the family burden of caregivers of stroke patients found that primary care is perceived burden of care in three dimensions: personal strain, privacy conflict and guilt. The administrator of the samples in this interview the caregiver provides care to patients just in the last two weeks later due to illness, so that data from semi-structured interviews were developed so that caregivers feel well and willingness to perform in patient care not feeling or would like to quit care.
12. Restrictions on Research
- 1. The duration of the study is limited the number of samples collected much information about sex. The researchers could not determine the number of samples in each gender are similar can be compared to the burden of care for certain that gender differences affect the burden of care or not.2. The sample used in this research group of family members of patients with symptoms of stroke during the second week of illness with stroke. The illness in its early stages although most patients will require administrators to perform routine matter however, the duration of care that just two weeks ago, only administrators may not feel like a burden. The interview indicates that most administrators feel proud and happy to have fulfilled its role as a responsible administrator.
13. Suggestion
- ResearchThe research next time the sample there should be a similar amount, the severity of the disease (Disability of patients), year of illness, and duration of patient care is important variables that should be studied together.Chief ExecutiveThis study will be useful for hospital administrators, medical personnel, healthcare team, caregivers, and patients. Such information will be made aware of factors affecting the burden of care stroke patients to improve and develop the appropriate care, to reduce the burden of care is happening this will reduce the burden of care for patients, families and society.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- This research study researcher: Thank you all health personnel, patients and their families thank worship Asst. Prof. Dr. Rapin Chayvimol, Prof. Dr. Pennapa Gulnapadol, Prof. Dr. Rungnapa Panitrat, Dr. Doldao Purananon, and Dr. Chompunut Srichannil helps to approved and the study was done well.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML