-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Applied Psychology
p-ISSN: 2168-5010 e-ISSN: 2168-5029
2014; 4(6): 240-245
doi:10.5923/j.ijap.20140406.05
Influence of Trait Aggression and Religiosity on Inclination towards Terrorism in Nigeria
Barnabas E. Nwankwo, James U. Aboh, Solomon A. Agu, Chimezie E. Chikwendu
Department of Psychology, Enugu State University of Science and Technology, Enugu, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Barnabas E. Nwankwo, Department of Psychology, Enugu State University of Science and Technology, Enugu, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
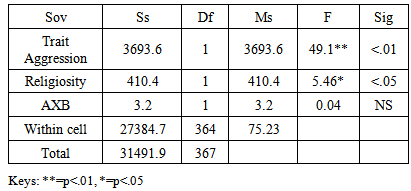
In view of the recent terror attacks by some groups in Nigeria, and the recent bomb blasts, kidnappings, militancy, assassinations, and other religious extremist activities such as bombing of churches, mosque, this study investigated the influence of trait aggression, and religiosity on inclination to terrorism. Utilizing a cross- sectional survey design and purposeful sampling technique, 368 undergraduates with mean age of 22.92 from two Universities in South Eastern Nigeria of who responded to battery of questionnaires designed to measure the variables involved. Two way (ANOVA) result showed that trait aggression significantly influenced the inclination to terrorism, F=49.1, t = (6.76) p<.01 religiosity was also found to significantly influence inclination to terrorism, F=5.46, t=(3.89), p<.05. Interaction effect was not significant, F=0.04, t = (49.1), p<.05. In general, the results showed that trait aggression and religiosity have significant influence on inclination to terrorism. Implications of the study were discussed, and suggestions for further studies made.
Keywords: Aggression, Religiosity, Terrorism, South eastern nigeria, Inclination to terror
Cite this paper: Barnabas E. Nwankwo, James U. Aboh, Solomon A. Agu, Chimezie E. Chikwendu, Influence of Trait Aggression and Religiosity on Inclination towards Terrorism in Nigeria, International Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol. 4 No. 6, 2014, pp. 240-245. doi: 10.5923/j.ijap.20140406.05.
1. Introduction
- Over a decade now, terrorism has become a recurring phenomenon in our society. An average citizen in our society is more security conscious now than ever because of this phenomenon called terrorism. The Nigeria society has been experiencing dramatic changes in every facets of life as a result of terrorism and these changes have also brought some stressful situations to which individual are finding it difficult to cope with. Poland (2002) from his own perspective defined terrorism as the premeditated deliberate systematic murder, mayhem, and threatening of the innocent to create fear and intimidation in order to gain a political or tactical advantage, usually to influences an audience. Rodin (2004) in his own view says that terrorism is the deliberate negligent or reckless use of force against noncombatants, by state or non state actors for ideological ends and in the absence of a substantively just legal process. According to Schmid and Jongman (1988) terrorism is an anxiety-inspiring method of repeated violent action, employed by semi clandestine individual, group, or state actors, for idiosyncratic, criminal, or political reasons, whereby-in contrast to assassination-the direct victims of violence are not the main target. However, there are two common elements usually found in definitions of terrorism:1) That terrorism involves aggression against non combatants.2) That terrorist action in itself is not expected by its perpetrator to accomplish a political goal but to influence a target audience and change that audience’s behaviour in a way that will serve the interest of the terrorist. (Badey 1998: Laquer 1999.)The immediate human victims of terrorism are generally chosen randomly or selectively from a target population, and serve as message generators, threat and violence-based communication processes between terrorist victims, and many targets are used to manipulate the main target, turning it into a target of terror, a target of demands, or a target of attention, depending on whether propaganda, coercion, or intimidation is primarily sought. Terrorism is old as human’s willingness to use violence to effect change in the society. Nigeria has faced her own challenges of terrorism recently. In the Niger Delta region, conflicts started in the 1990’s and generally escalated into a multidimensional resistance in 2005 to 2008. The new dimension saw to the huge destruction of oil installations, kidnapping of foreign (and later) indigenous oil workers, disruption of oil production and illegal oil trade or bunkering. As a country that depends on crude oil earning as a major source of foreign exchange, disruption of oil production resulted in huge national budgetary deficits. Could these fighters be viewed as militants, insurgents, terrorists, revolutionaries, ethnic militias or freedom fighters? Various analysts (Ogundele, 2008, Osaghae, 1995, Dagne, 2006, Cohen, 2008) have used rebels, insurgents, militants, terrorists, freedom fighters etc to describe the crisis and those behind it. Thus, conceptualization is better understood in the context of trends and patterns, and based on the tactic and strategy the perpetuators employ in conflicts. Organizations that employ these tactics include: MEND, -Movement for the emancipation of Niger Delta, NDPVF, the coalition for militant action in Niger Delta and the martyrs Brigade. MEND is about the most visible armed group base in the region (Hazen and Horner, 2007) and the main militant organization attacking oil infrastructure for political objectives (Energy information administration (EIA) 2010). Although most of their attacks have been targeted at oil pipelines and supply terminals on the creeks and swamps of the region, it has created a sense of insecurity and panic many miles offshore at different times in Lagos and Abuja. In what was described as “Al Qaeda – style terrorism” MEND had on July 12, 2009, blown up the receptor pipelines inside the 50 million- inter capacity Atlas Cove Jetty in Lagos, effectively crippling the facility to receive petroleum products. The attack, which left five workers dead, served both the propaganda aim of conviction and using coercion to get the Nigeria state rethink their demand that the delta receive more benefits from its oil (Amaraegbu, 2010; Duffield, 2010). On October 1, 2010, two vehicles full of improvised explosive devices were detonated near Abuja’s Eagle square, venue of the parade, marking the country’s 50years anniversary of independence. After about an hour of threat, vehicles carrying improvised explosive devices were detonated causing substantial damage and fatal causalities. 12 people were confirmed dead and 17 injured in the blasts ((BBC, 2010; Sahara reporters, 2010; Reuters, 2010). The Niger Delta Technical Committee report acknowledged that the “militants have grown from rag-tag opportunistic group into very well- armed and well organized combat forces” (Report of the technical committee on the Niger Delta 2008. 52). It has been argued that the victims or objects of terrorism attack have little intrinsic value to the terrorist but represent a large human audience whose reaction, the terrorists seek (Crenshaw, 1981). The panic its impact produces, and the series of insecurity terrorism created on the population makes more sense to the terrorist than real victims of a terrorist incident. As Kropotkin (1968) noted, by actions which compel general attention the new idea seeps into people minds and wins converts. One such act may, in a few days make more propaganda than thousand pamphlets. Above all, it awakes the spirit of revolt (FEMA, 2009). Terrorism is finally home with us here in Nigeria. Nigeria, the once peaceful nation of about 150 million people is now being rocked by waves of violence, bombing, killings, kidnapping and threats of terror. According to section 1(2(c) (i-iii) of Nigeria terrorism act 2011, terrorism includes attacks upon a person’s life which may cause bodily harm or death, kidnappings, as well as the destruction of government facilities or private properties in a manner likely to endanger human life or result in a major economic loss. This study looks at the acts of terrorism as caused by trait aggression and religiosity. Trait Aggression on TerrorismTrait is a distinguishing characteristic of a person which can also be inherited such as height, age color, etc. trait can also mean distinguishing quality or characteristics, typically one belonging to a person. Santrock (1996), defined trait as an enduring personality characteristic that tends to lead to certain behaviours e.g. aggression, crime etc. Trait theorists believe that personality consists of broad, enduring dispositions that tend to lead to characteristics responses. In other words, people can be described in terms of the basic ways they behave, such as whether they are outgoing and friendly, dominant and assertive, high or low in aggression (Larson & Buss, 2002; Mathews & Dreary, 1998). Allport (1937) believed that each individual has a unique set of personality traits. He argued that if we can determine a person’s traits, we can predict the individual’s behavior in various circumstances. Aggression is a hostile or violent behaviour or attitude towards another. It is also readiness to attack or confront. Aggression is of many types such as; anger and hostility, physical aggression, suspicious and verbal aggression. However, the way in which each individual displays aggression (as a behavior), differs from one individual to the other as a result of their traits on aggression differences, some have high tendency on trait aggression while some have low tendency on aggression (Taylor, 1988). Anderson (2004) investigated how trait aggressiveness can create behavioral hostile social environment which will inadvertently lead to violence. Results suggested that two aggressive motives: hostile and instrumental resulted from high partner aggression during early trait aggressiveness and of early trail aggression on later aggressive behavior and violence. Giumetti and Markey (2007) found that participants who were aggressive were more likely to make hostile attributions to the actions of others after playing violence video games (VVGS) than participants who were not angry or those who had played non VVGS. When aggression was experimentally primed before playing VVGS. It was found that participants tend to use more violent actions during game play and report more hostility than participants who were not primed for aggression (Pane and Ballard, 2002).Religion and TerrorismReligious terrorism is characterized by the legitimization of violence based on religious precepts, a sense of alienation, and the preoccupation with the elimination of broadly defined “enemies”. Terrorist organization often use religious motives to claim stronger sense of superiority, decrease the resistance towards violence in their followers and increase the allegiance with the terrorist group. Terrorist organizations that claim religious inspiration are far more lethal than groups based on secular motives. Hoffmann (1989) also believed that terrorism wants to gain the maximum effect with minimum sacrifice. The actions of terrorists are guided by the values of supporting group. Religious terrorists use methods that are not necessarily accepted with their supporters, such as mass killing. Nigeria is made up of many religious groups such as: Islam, Christian, Traditional religion, etc that helps to accentuate regional and ethnic distinctions. Islam dominates northern and some part of Yoruba, while Christianity dominate eastern, south and other parts of Yoruba. The 1963 census indicated that 47 percent of Nigerians were Muslim, 35 percent Christian and 15 percent member belong to other religions in Nigeria. Now, according to the association of religious and data archives, the Nigeria population is divided into two great groups: Christians (45.5%), Muslims (45.4%) and others (9.1% mostly ethnic religions). Inter-ethnic conflict in Nigeria has generally had a religious element. Recently, in Nigeria, there has been an upsurge in attacks and reprisal attacks targeting Christians and Moslems in northern Nigeria, culminating in the Christmas day massacre at a catholic church near the federal capital territory. Ammerman (1981) examined the relationship between religiosity and Christian fundamentalism, a system of beliefs and practices rooted in liberal interpretation of the bible and strict adherence to norms, on aggression among college students. The result indicated that religiosity and fundamentalism is positively associated with violence. There is no single explanation of the reason why individuals engage in terrorism. Therefore, this, study tends to evaluate the roles which trait aggression and religiosity play on individuals’ tendency to incline to terrorism. Moreover to assume a conservative position this study intends to investigate the following questions;Will trait aggression significantly influence inclination to terrorism?Will religiosity significantly influence inclination to terrorism?HypothesesThe following hypotheses were tested.There will be a significat influence of trait aggression on inclination to terrorism.There will be a significant influence of religiosity on inclination to terrorism.
2. Method
- Design/StatisticsThe design of the study is cross-sectional survey method. The study involves two (IV- independent variable, with two levels each. Therefore a 2-way ANOVA was employed for data analysis. Participants368 undergraduates of Enugu State University of Science and Technology (ESUT) and University of Nigeria Nsukka (UNN) all in Enugu, South East Nigeria participated in the study. Participants comprised of 180 males and 188 females within the age range of 17-40 years of age. All the participants were all in second, third and fourth years of study respectively. Random and convenient sampling techniques were both used in the study. InstrumentReligiosity ScaleThe religiosity scale is a five item scale by Agbo (2010) which assesses an individual’s view of his/her life as inseparable from his or her religious belief. It is anchored on a 5-point response format. All the scales were anchored on a likert-type response format, ranging form 5-strongly agree, to 1-strongly disagree. Sample items on Religiosity Scale include; “my religion is my life” and “I always evaluate myself on the bases of my religious beliefs”. It has a reliability coefficient of 0.89. Before the main study, a pilot study was carried out by the researchers using one hundred (100) undergraduate students drawn from the department of psychology, Enugu State University of Science and Technology to ascertain the reliability of the instrument. These fourteen (5) items loaded .30 and above and the scale yielded a crombach’s alpha level of .84 and a mean score of 64.38. Hence, the questionnaire is reliable. A total score is obtained by adding all the items and all items were positively worded. High scores indicated high religiosity. It is important to note that this scale has been used extensively for studies in Nigeria.Trait Aggression ScaleThe trait aggression scale is a 29-item scale by Buss and Perry (1992). The scale has four dimensions with the following internal consistency coefficients: anger, 0.70; hostility, 0.66; physical aggression, 0.78; and verbal aggression, 0.73. The composite scale AQ has a reliability 0.84. It is important to note that these sub scales make up the composite scale which is the sum total that measures trait aggression as a construct. Before the main study, a pilot study was carried out by the researchers using one hundred (100) undergraduate students drawn from the department of psychology, Enugu State University of Science and Technology to ascertain the reliability of the composite scale. The composite scale(which is made up of the four dimensions) yielded an internal consistency of .80. Sample of items on the questionnaires include; “Once in a while, i can’t control the urge to hit another person” and “I am an even tempered person”. The scale was therefore accepted for this study considering its reliability. The participants were required to respond to every item the way he/she feel’s about it. All items were directly scored (worded). The researchers were not interested in studying the participants’ responses to the different dimensions of trait aggression. Therefore we did not analyse them independently as it was not necessary at this time. A total score was obtained by summing all the numbers assigned to each response anchor. Higher scores indicated high trait aggression.Terrorism Inclination ScaleTerrorism inclination scale (TIS) was developed by Agbo and Ezeuduji (2010) to measure the inclination to engage in the act of terror. The items were constructed using five point scale that include; (1) strongly disagree, (2) disagree, (3) somewhat agree, (4) agree and, (5) strongly agree. This scale is made up of 10 items. Sample items from the scale include; “if putting fear in people will make item believe in my ideas, I don’t mind doing it; I can damage property and endanger life of civilians to stop the government or organization from carrying out their plan.” The developers of terrorism inclination scale reported a crobach’s alpha reliability of .78. A pilot study was conducted by the researchers using 100 undergraduates year one students of Psychology, Enugu State University of Science and Technology to make the scale usable in Nigeria context. We obtained an alpha reliability of .68. All the items in this scale have a direct scoring format. A composite score of Terrorism inclination scale will be obtained by summing up the responses of the respondent to all the items. Higher scores represent higher inclination to terrorism and vice versa. It is important to note that this scale has been used extensively for studies in Nigeria.ProcedureFour hundred and fifty (450) copies of these instrument were distributed to different faculties and departments based on how they were randomly selected. The questionnaire was administered to those respondents that were found in the class waiting for their lectures. Before the administration of the questionnaires, the researcher introduced himself to the students, solicited that they should respond to all items in sincerity. This introduction was made again for further clarification, owning to the fact that the researcher had initially introduced himself on the questionnaire. Researcher also convinced the respondents on handling the information given with utmost confidentiality. Respondents who accepted to fill the questionnaire were the only people that received the questionnaire. When each participant finished completing his or her own questionnaire, the researcher collected it and thanked him or her.
3. Results
- The results of the analysis are presented below:
|
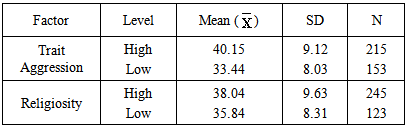
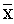 = 40.15, SD=9.12) compared with their counterparts with low trait aggression (
= 40.15, SD=9.12) compared with their counterparts with low trait aggression (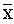 =33.44, SD=8.03). The result equally indicated that participants with high religiosity reported higher means score of (
=33.44, SD=8.03). The result equally indicated that participants with high religiosity reported higher means score of (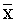 = 35.8, SD=8.31). However, a two way ANOVA was employed to test the significance of these mean differences (see table 2).
= 35.8, SD=8.31). However, a two way ANOVA was employed to test the significance of these mean differences (see table 2).
|
4. Discussion
- This study aimed at finding the influence of trait aggression and religiosity on inclination to terrorism. Two hypotheses were tested: hypothesis I stated that that there will be a significant influence of trait aggression on inclination to terrorism; Hypothesis II stated that there will be a significant influence of religiosity on inclination to terrorism. The first hypothesis was accepted hence the result indicated that trait aggression was significant at p<.01. This result also related to the study of Anderson et al (2006) who found that trait aggressiveness increased punishment intensities (violence) unleashed by different groups of participants in their study. Carnage and Anderson (2007) supported the result of this study by finding a strong relationship between experiencing violence and trait physical aggression. The findings of this study can be linked to the frustration aggression theory of Dollard et al. (1989) which posits that aggression is an inborn part of human nature and the social cognitive model of Bandura (1978) which states that individuals interact with their environment based on how they perceive and interpret it.The second was accepted because the result of the study showed that religiosity had a significant influence on inclination to terrorism. This result has empirical backing from the finding of Ammerman (1981) who found that religiosity is positively associated with violence. Day and Maltby (2000) also found that there is a significant association between religious orientation and death obsession. The findings of Duriez et al (2000) showed that a religious attitude (religiosity) was related to value orientation which can imply terrorism. Based on these findings, it is obvious that trait aggression and religiosity have strong influence on student’s inclination towards terrorism in Nigeria. This means that factors such as trait aggression no matter the shape it may take, which can be in form of physical verbal, suspicious etc can directly or indirectly influence students’ inclination to terrorism. Also religiosity can as well be seen as another factor responsible for involvement in terrorist activities. This is so because from the result findings, every religion has fanatics who will go extra mile in fighting for what they believe in. Terrorism irrespective of where it was committed and by whom, is a serious cause of death or bodily injury characterized by violence and threat of violence which cause social disharmony in our society. Since trait aggression, such as anger and hostility, physical aggression, suspicious, and verbal aggression are all types of aggression and this finding indicated that trait aggression is very significant to terrorism, therefore, humans should be very cautious over the type of behavior they manifest towards one another so that it may not lead to violence and social disequilibrium. The finding of the study also implies that individuals who have trait aggression could be prone to inflicting harm on other persons. Therefore, if individuals are assessed with a view to discover the existence of this high trait aggression, measures should be taking for some behavioral changing initiatives. Also the general public should be mindful of how they express themselves (verbally or through suspicion) so that it will not be taken up and thus returned with open hostility and anger which in the short or long run may lead to physical violence. According to Thomas (2000), religious resurgence is not simply defined by the growth of fundamentalism-rigid adherence to a particular set of rituals and doctrines but is occurring through a variety of renewed rituals and practices both public and private.
5. Summary and Conclusions
- This study contradicts the popular view that people residing in northern Nigeria are more inclined to religious fanaticm in the country because the finding of this study showed significant relationship between religiosity and inclination to terrorism among Christians that dominate the south eastern part of Nigeria. Therefore religious leaders should make concerted effort to control the religious piousness in their members in order to establish peaceful coexistence. Also parents and school authorities should as well play a vital role in check mating their children, students and their religious activities.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML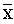 ) and Standard Deviation (SD) Scores on Inclination to Terrorism
) and Standard Deviation (SD) Scores on Inclination to Terrorism