-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Applied Psychology
p-ISSN: 2168-5010 e-ISSN: 2168-5029
2014; 4(3): 81-85
doi:10.5923/j.ijap.20140403.01
Job Related Tension, Interactional Justice and Job Involvement among Workers of Dangote Cement Company Gboko
Mase Judith A. , Aondoaver Ucho
Department of Psychology, Benue State University, P.M.B. 102119, Makurdi, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Aondoaver Ucho , Department of Psychology, Benue State University, P.M.B. 102119, Makurdi, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The study assessed job related tension, interactional justice and job involvement among workers of Dangote Cement Company Gboko in Benue State, Nigeria. 173 (94 males and 79 females) workers participated in the study. Their ages ranged from 20-55 years with the mean age of 32.80 years. Job-related Tension Scale was used to assess workers job related tension. Interactional Justice Sub-scale was used to measure respondents’ perceptions of interactional justice. Job involvement was measured using Job Involvement Scale. Results showed that job related tension has significant influence on job involvement. Interactional justice has no significant influence on job involvement. Results further show that job related tension and interactional justice have interactive effect on job involvement. It is therefore recommended that industries wanting to improve workers job involvement should consider multi-factorial approach of reducing job related tension and increasing interactional justice.
Keywords: Job related tension, Interactional justice, Job involvement, Cement company
Cite this paper: Mase Judith A. , Aondoaver Ucho , Job Related Tension, Interactional Justice and Job Involvement among Workers of Dangote Cement Company Gboko, International Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2014, pp. 81-85. doi: 10.5923/j.ijap.20140403.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Job involvement has always been of great interest to both private and public organizations. Part of the reason for this interest is the fact that researchers have continued to explain that involved employees are what organizations and institutions need to achieve their goals and objectives [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] as well as individual motivation [6]. These links stem from the theoretical notion that being immersed in one’s work increases motivational processes which in turn influence job performance and other relevant outcomes like turnover and absenteeism [1].Job involvement as a concept refers to a state of psychological identification with work or the degree to which a job is central to a person's identity [7]. He considered job involvement in two dimensions which include from organizational and individual perspectives. From an organizational perspective, it has been regarded as the key to unlocking employee motivation and increasing productivity. From an individual perspective, job involvement constitutes a key to motivation, performance, personal growth, and satisfaction in the workplace. Job involvement is also defined as an individual’s psychological identification or commitment to his / her job [8]. It is the degree to which one is cognitively preoccupied with, engaged in, and concerned with one’s present job. Job involvement involves the internalization of values about the goodness of work or the importance of work in the worth of the individual [9]. In this light, individuals who display high involvement in their jobs consider their work to be a very important part of their lives and whether or not they feel good about themselves is closely related to how they perform on their jobs. In other words, for highly involved individuals performing well on the job is important for their self-esteem. Because of this, people who are high in job involvement genuinely care for and are concerned about their work [10].Job involvement as a construct is similar to organizational commitment. This is because they are both concerned with an employee’s identification with the work experience. However there is a significant difference between the two. Job involvement is more closely associated with identification with one’s immediate work activities whereas organizational commitment refers to one’s attachment to the organization [7]. It is possible for example to be very involved in a specific job but not be committed to the organization or vice versa [11]. Research has shown that job involved persons are those who actively participate in job [12]. They are whom work is a very important part of life and as one who is affected by responsibilities of his whole job situation, the work itself, his co-workers, the company etc.Similarly, prior research has found that job involvement positively influences other attitudinal and behavioural outcomes such as organizational commitment [7], turnover [13] and absenteeism [14]. On the contrary, low levels of job involvement contribute to employees’ feelings of alienation of purpose, alienation in the organization or feeling of separation between what the employees see as their ‘life’ and the job they do [15]. It is therefore clear that fostering high levels of job involvement is very significant in enhancing the effectiveness of an organization.Previous research into job involvement indicated that there has been a groundswell of research on factors affecting employees’ job involvement. Some of these factors include job related tension [16, 17, 18] and fairness in organizations [19, 20]. Further investigations show that most of these studies were done in developed countries like United Kingdom and United States of America neglecting African sample, making job related tension and interactional justice and job involvement to emerge as an important set of variables for research in Africa. The study investigated both independent and joint effects of job related tension and interactional justice as predictors of job involvement. Job related tension here refers to feelings of stress, discomfort, uncertainty and tension arising from role conflict and role ambiguity. Research has indicated that job related tension has a negative influence on job involvement. In a study employees perceive characteristics of their jobs and control as a big source of stress, and as a result perceive the organization as less committed to them; they therefore also become less committed to the organization [18]. In another study, job related tension affects workers by bringing about forgetfulness, lack of creativity, concentration and emotional symptoms (such as headaches, pondering of the heart) which lead to low organizational commitment and job involvement [16]. Also an individual faced with job related tension in terms of role conflict and ambiguity has his or her commitment and performance and overall behavior affected [21].Similarly, results suggest that role conflict and ambiguity are valid constructs in organizational behavior research and are usually associated with negatively valued states such as low job involvement [22]. Beehr, Walsh, and Taber expectancy theory of 1976 also has explanations on the effects of job tension arising from role ambiguity and conflict on job involvement. These authors argue that role ambiguity decreases motivation to perform (e.g., involvement or commitment) because it decreases the employee's expectations that effort leads to performance and that performance leads to outcomes. In the same vein, role stress lead employees to reduce organizational commitment and job involvement [23].Research has also linked interactional justice with job involvement. Interactional justice refers to the quality of interpersonal treatment received during the enactment of organizational procedures [24]. In general, interactional justice reflects concerns about the fairness of the non-procedurally dictated aspects of interaction. It includes various actions displaying social sensitivity, such as when supervisors treat employees with respect and dignity. A considerable proportion of perceived injustices did not concern distributional or procedural issues in the narrow sense, but instead referred to the manner in which people are treated interpersonally during interactions and encounters [25]. For instance, where a high degree of interactional justice does not exists, subordinates hold feelings of resent towards either the supervisors or the organization and will therefore seek to even the score [26]. This may be through reduced involvement in work. Furthermore, a victim of interactional injustice will have increased expression of hostility towards the offender which can manifest in actions of counter-productive work behavior and reduce the effectiveness of organizational commitment and invariably work involvement [26]. On the other hand, supportive relation with superiors and co-workers is known to be conducive for job involvement [7].Similarly, report suggests that organizational justice which refers to people's perceptions of the fairness of treatment received from organizations is important as a basic requirement for the effective functioning of organizations [20]. This is due to the fact that perceptions of organizational justice meaningfully affect a number of attitudes and behaviours in a workplace such as sentiments toward job and workplace [19]. From the above therefore, the following hypotheses were stated:i. Job related tension will significantly influence job involvement.ii. Interactional justice will significantly influence job involvement.iii. Job related tension and interactional justice will jointly influence job involvement.
2. Method
2.1. Participants and Sampling
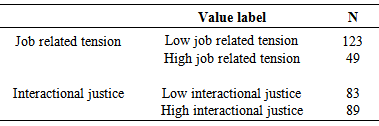
- The researchers employed convenience sampling method for data collection. Many organization studies have used convenience approach in sampling respondents making it common and more prominent than probability sampling. Researchers have argued that the method is more feasible in the study of organizational behaviour compared to probability sampling method [27]. 193 copies of the questionnaire were distributed among employees of Dangote Cement Company located in Gboko. 173 (89.64%) of the 193 copies of the questionnaire completed and returned were used for data analyses. Despite the fact that the researchers used convenience sampling approach, employees were sampled across different job positions and departments of the company.Analyses shows that 94 (54.3%) of the participants were males and the remaining 79(45.7%) were female employees. Majority (35.80%) of the participants were Tiv, a dominant ethnic group in Benue State, Nigeria while 22.0% were Idoma. Hausa and Igbo constitute 11.0% each and the remaining 20.2% of the participants were from other tribes in Nigeria. The mean age of the respondents was 32.80 years.
2.2. Instruments
- The instrument used for data collection was a questionnaire and it consisted of two main parts. Part one was an informed consent form which participants were to read and indicate (by ticking in the appropriate box) their acceptance for participating in the study. Part two of the instrument had four sections. Section A assessed the demographic characteristics of participants in terms of sex, age, tribe and job position. Sections B and C measured participants’ job related tension and interactional justice respectively while section D measured participants’ job involvement.Job-related Tension Scale (JTS) was used in measuring employees’ job-related tension [28]. JTS is a 15-item inventory and it was validated in Nigeria in 1988 [29]. Sample items of the scale include: feeling that you have little authority to carry out the responsibilities assigned to you; being unclear on just what the scope and responsibilities of your job are; feeling that your job tends to interfere with your family life. Respondents were asked to indicate on a five point scale ranging from 1= never to 5=nearly all the time the degree of their acceptance on the items. The coefficient of alpha was reported by different researchers as .87 [30] and .81 [29] using Nigerian sample. A concurrent validity coefficient of .01 was found by correlating JTS with rated performance [30] while a coefficient of .46 was reported when JTS was correlated with Chechlist Symptoms Stress [31]. Relatedly, the researcher found alpha reliability coefficient of .72 for JTS. All these coefficients indicate that the scale is dependable. Similarly, factor analysis was carried out to test construct validity of the scale. Then, with varimax rotation and factor loading the minimum of 0.5 as suggested was met [32]. Interactional justice sub-scale was used to measure respondents’ perceptions of interactional justice [33]. Some items of the scale included 1. When decisions are made about me, my supervisor deals with me in a truthful manner 2. When decisions are made about me, my supervisor offers adequate justification. Participants were asked to respond based on a 7-point scale. 1 represented Strongly Disagree and 7 represented Strongly Agree. Reliability (Cronbach’s Alpha) for the scale was also calculated and a coefficient of .71 was found.Furthermore, job involvement was measured in this study using Job Involvement sub-scale contained in the Organization Commitment Scale [34]. The sub-scale has 6 items, some of which included 1. I live, eat and breathe my job 2. The most important things that happen to me involve my work 3. Most things in life are more important than my work. Participants responded on a 7-point scale ranging from strongly disagree (1) to strongly agree (7). Previous research reported a reliability coefficient of .84 [34] and in this study a coefficient (Cronbach Alpha) of .77 was arrived at.
2.3. Data Collection
- Questionnaires were administered to the respondents at their various duty posts by the researchers. Many of the respondents could not complete the instruments immediately due to their work schedule. And as such they were recovered latter.
2.4. Data Analysis
- Data were analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 16.0. Both descriptive (frequencies, mean and standard deviation) and inferential statistics (correlation and two-way ANOVA) were employed. The former was used to summarize the data while the later was used to measure the relationship between the study variables and test the stated hypotheses.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation
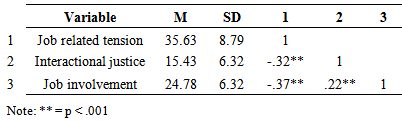
- Table 1 shows the means and standard deviations of the participants on the study variables. The table further indicated that job related tension and interactional justice are significantly but negatively correlated. Job related tension is also significantly but negatively correlated with job involvement. On the other hand, interactional justice and job involvement are significantly and positively correlated.
|
|
|
4. Discussion
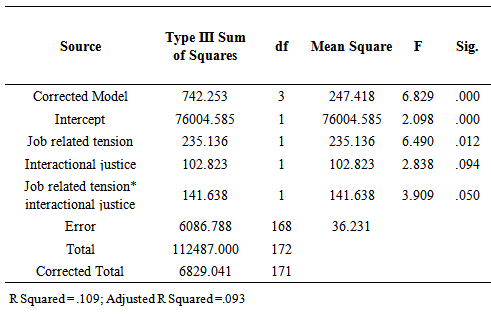
- In this study, we investigated the main and interactive influence of job related tension and interactional justice on job involvement of factory workers in Nigeria. The study revealed that job related tension has significant influence on job involvement of factory workers. Further analysis indicated that the influence is in the negative confirming the previous findings that employees become less committed and involved in their jobs and organization when they perceive the characteristics of their jobs as sources of stress [18]. The finding also agrees with that of other researchers [16, 23, 21]. Particularly, job related tension brings about stress related symptoms such as forgetfulness, lack of creativity and concentration, headaches, pondering of the heart etc. which lead to low organizational commitment and job involvement [16].The research further revealed that interactional justice did not significantly influenced job involvement of factory workers. This result contradicts previous findings that justice perception significantly predicts job involvement [7, 20, 26]. The contradiction between the findings of the current study and that of others may be as a result of differences in sample. Results of previous studies were obtained from participants other than Nigerians. And considering mark differences between European and African workers in terms of socioeconomic background, it is reasonable to report that workers from advanced countries of Europe will value interactional justice more than those of African or Nigerian background whose interest is more on basic resources and how they are distributed (distributive justice).Finally, the research found that job related tension and interactional justice have interaction effect on job involvement of factory workers. Work behavior generally can be simultaneously influenced by many factors. That informed the study of the combined effect of job related tension and interactional justice on workers job involvement. And the implication of this finding is that when workers perceive that there is high level of interactional justice and at the same time there is low level of work related tension they will be more involved in their job compared to when only one of the factors for instance interactional justice is high and there is a poor picture of job related tension.
5. Conclusions
- This study was designed to investigate independent and interactive effects of job related tension and interactional justice on job involvement of factory workers in Nigeria. Job related tension has a significant effect on job involvement. Interactional justice has no significant effect on job involvement. Taken together however, job related tension and interactional justice have significant effect on job involvement. This study suggests that studies of job involvement should adopt multi-factorial approach.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML