-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Applied Psychology
p-ISSN: 2168-5010 e-ISSN: 2168-5029
2014; 4(2): 73-80
doi:10.5923/j.ijap.20140402.05
Exploring the Incorporation of Executive Functions in Intelligence Testing: Factor Analysis of the WAIS-III and Traditional Tasks of Executive Functioning
Loes van Aken1, 2, 3, Roy P. C. Kessels2, 4, 5, Ellen Wingbermühle1, 2, Marloes Wiltink1, Paul T. van der Heijden2, 6, Jos. I. M. Egger1, 2, 3, 7
1Centre of Excellence for Neuropsychiatry, Vincent van Gogh Institute for Psychiatry, Venray, The Netherlands
2Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behaviour, Radboud University Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
3Behavioural Science Institute, Radboud University Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
4Department of Medical Psychology, Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
5Centre of Excellence for Korsakoff, Vincent van Gogh Institute for Psychiatry, Venray, The Netherlands
6Centre for Adolescent Psychiatry, Reinier van Arkel Psychiatric Hospital, ‘s-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands
7Pompe Institute for Forensic Psychiatry, Pro Persona, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between subtests of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – third edition (WAIS-III) and executive functions. The Behavioural Assessment of the Dysexecutive Syndrome, Wisconsin Card Sorting Test, and Stroop Color-Word Test were administered to a heterogeneous group of 234 psychiatric patients and 24 healthy volunteers. Maximum likelihood procedures with promax rotation were applied to two, three and four factor solutions. The four factor model fitted the data best, confirming the four factor indices of the WAIS-III. All three executive tasks had their highest loading on the factor corresponding to the perceptual organization index (POI) of the WAIS-III. Results confirm the overload of crystallized intelligence in the subtests and EF involvement in the POI of the WAIS-III. Results are discussed as to the need for an integrated, multifaceted view on cognitive disorders and intellectual (dis) abilities.
Keywords: Fluid and Crystallized Intelligence, Executive Functions, Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – Third edition, Neuropsychology, Factor Analysis
Cite this paper: Loes van Aken, Roy P. C. Kessels, Ellen Wingbermühle, Marloes Wiltink, Paul T. van der Heijden, Jos. I. M. Egger, Exploring the Incorporation of Executive Functions in Intelligence Testing: Factor Analysis of the WAIS-III and Traditional Tasks of Executive Functioning, International Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 73-80. doi: 10.5923/j.ijap.20140402.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
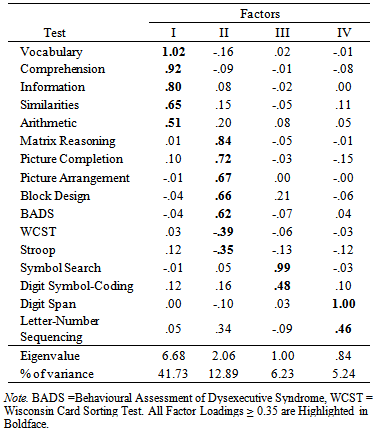
- The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Third Edition (WAIS–III; Wechsler, 1997a; Wechsler, 1997b) is a frequently used measure of intelligence. The development of subtests of the original WAIS occurred based on Wechsler’s clinical experience. Empirical research led to modifications of the test, and factor analytical research on the subtests revealed a four factor structure. According to the recurrent findings, the WAIS-III structurally identifies four indices, i.e., the Verbal Comprehension Index (VCI), the Perceptual Organization Index (POI), the Working Memory Index (WMI), and the Processing Speed Index (PSI). These index scores provide better profile interpretation as compared to the verbal-performance (VIQ-PIQ) dichotomy (Kaufman & Lichtenberger, 1999). Moreover, they show a much better fit than the VIQ-PIQ factor solution in diverse clinical and nonclinical samples (Arnau & Thompson, 2000; Ryan & Paolo, 2001; Taub, 2001; Van der Heijden & Donders, 2003a; Van der Heijden, van den Bos, Mol & Kessels, 2013). Unfortunately, the WAIS-III held on to the dichotomy next to the four indexes, resulting in perseverance in the use of the VIQ and PIQ among clinicians. Therefore, the latest revision of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale, the WAIS-IV (Wechsler, 2008) does not provide VIQ and PIQ scores any longer. Although structures were re-evaluated in the development of the WAIS-IV (mainly by eliminating VIQ and PIQ and replacing them with four index scores and a full scale IQ score), the WAIS-III is still widely used in clinical practice. Therefore, its structure and applicability to neuropsychological assessment should be reconsidered. The usefulness of the index scores, especially PSI and WMI, in neuropsychological evaluation is reasonably well established [Hawkins (1998); Martin, Donders and Thompson (2000), Fisher, Ledbetter, Cohen, Marmor & Tulsky, 2000; Taylor & Heaton (2001); Van der Heijden and Donders (2003)], but the overall structure of the WAIS-III lacks theoretical ground. Therefore, the WAIS-III research findings have been subject to discussion within a framework of existing neuropsychological and factor analytical theories of intelligence (Ardilla, 1999; Duncan, 2010, Duncan, Burgess & Emslie, 1995; McGrew, 2009; van der Heijden & Donders, 2003b).One of the most influential theories is the Cattel-Horn-Carroll (CHC) theory of cognitive abilities. The CHC theory arose from the distinction between fluid (Gf) and crystallized (Gc) intelligence made by Horn and Cattell (1966) and Carroll’s (1993) three striatum theory of cognitive abilities. The CHC theory consists of both a general component of intelligence (g; stratum III), broad abilities (stratum II, e.g. fluid reasoning, crystallized knowledge, visual and auditory processing, short-term memory, long-term storage retrieval, processing speed, decision and reaction speed, reading and writing and quantitative knowledge) and narrow abilities (stratum I), providing a complete and comprehensive taxonomy of human intelligence. See Kaufman, Kaufman & Plucker (in press), and McGrew (2009), for further reading on contemporary theories of intelligence. A disadvantage of the Wechsler scales in general (and most other current intelligence test) is that they do not cover the complete CHC taxonomy. Only five broad abilities (crystallized knowledge, visual processing, short-term memory, processing speed and fluid reasoning) are measured in both the WAIS-III (Alfonso, Flanagan & Radwan, 2005) and WAIS-IV (Grégoire, 2013; Weiss, Keith, Zhu & Chen, 2013). Furthermore, multiple subtests can show loadings on the same ability, and specific abilities may not be completely covered by the subtests. In other words, CHC provides a rather complete structure of human intelligence, but it is challenging to develop tasks which are pure measures of those abilities. Describing and developing new intelligence tests within the CHC taxonomy would be advisable. The WAIS-III does not fit the theory well, and therefore describing the test only in terms of the CHC does not necessarily contribute to clinical evaluation of patients.Another persisting criticism of the WAIS-III is that it disproportionately assesses Gc, in comparison to Gf (Blair, 2006, Duncan et al., 1995). Duncan et al. (1995) found unchanged WAIS-IQs in patients with frontal-lobe damage, while performance on a Gf task (Cattell’s Culture Fair Task) was significantly impaired. Looking at the nature and location of the lesions, they also concluded that Gf was in fact a reflection of executive functioning (EF). EF can be defined as abilities which enable us to produce independent, purposive, self-directed and self-serving behavior (Lezak, Howieson, Bigler & Tranel, 2012). This includes (mental) adaptivity and flexibility, planning and problem solving capacities as well as (social) decision making skills. Many studies suggest an extensive overlap between Gf and EF (Ardilla, 1999; Duncan et al., 1995; Duncan, Schramm, Thompson & Dumontheil, 2012; Van Aken, Kessels, Wingbermühle, van der Veld & Egger, submitted; Roca et al., 2010), given the fact that both are related to effective performance in complex or novel situations, as well as frontal lobe functioning. For instance, all WAIS-III subtests added to enhance the measurement of Gf (Matrix Reasoning, Symbol Search, Letter-Number Sequencing) are related to EF performance (McGurk et al., 2000; Oosterman & Scherder, 2006; Sweet et al., 2005). This was studied using imaging techniques in both clinical and healthy samples. The subtest Digit Symbol Coding is also related to EF (Davis & Pierson, 2012). At the level of index scores, research showed affected PSI, WMI and, to a more limited extend, also POI in patients with brain injury and EF dysfunctioning (Ferry et al., 2004; Fisher et al., 2000; Hawkins, 1998; Martin, Donders & Thompson, 2000; Taylor & Heaton, 2001, Van der Heijden & Donders, 2003). This raises the question to what extent EF is incorporated and distributed in the factor structure of the WAIS-III.Both Wood & Liossi (2007) and Davis, Pierson & Holmes Finch (2011) examined the relation between intelligence and EF using the WAIS-III in a brain injured and healthy sample, respectively. Both studies demonstrated that EF is to some extend comparable to parts of global intelligence (g) measured by the FSIQ of the WAIS-III, next to unique variance which seems to reflect more specific executive requirements (‘e’; see Wood & Liossi, 2007). In 2001, Kaufman, Lichtenberger & McLean suggested a three-factor model solution for the WAIS-III, including verbal comprehension (factor 1), perceptual organization (factor 2) and a third factor labeled EF. For determining this third factor, they assumed that EF and working memory were interrelated, since the third factor was based on high loadings of Digit Symbol Coding and Letter Number Sequencing. They interpreted the third factor as being a blend of WM and PS. The aim of the present study is to gain insight in the degree to which EF is included in the WAIS-III in a heterogeneous sample consisting both psychiatric patients and healthy volunteers. All 13 subtests of the WAIS-III are administered, except for Picture Assembly given the poor low reliability of this subtest. To assess the broad construct of EF, Dutch versions of multiple traditional EF tasks were included: the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST; Heaton, 1981), the Stroop Color Word Test (Stroop; Hammes, 1971) and the Behavioural Assessment of the Dysexecutive Syndrome (BADS; Wilson, Alderman, Burgess, Emslie & Evans, 1996; Krabbendam & Kalff, 1997). Based on earlier factor analytical studies of the Wechsler scales, in compliance with the four index scores, we expect a four factor structure to best fit the data. Nevertheless, since little research is done with all 13 WAIS-III subtests combined with different measures of EF, models with 2 (according to the VIQ-PIQ dichotomy) and 3 (according to Kaufman et al., 2001) factors will also be evaluated. In line with Wood & Liossi (2007), we expect the executive tasks to load high on the factors analogous to the PIQ scale (consisting of the POI and PSI) of the WAIS-III. More specific, we expect the BADS to load high on the factor corresponding to the POI, the WCST to load on either of the factors representing the POI or WMI, and the Stroop on the factor comparable to the POI or PSI.
2. Method
2.1. Participants
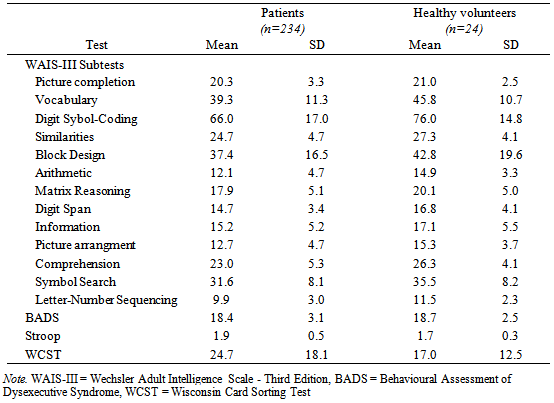
- Included were 258 participants, (mean age 33.0 ± 14.1, 64.3% male), consisting of 24 community-dwelling volunteers (mean age 37.2±15.7, 45.8% male) and 234 inpatients and outpatients (mean age 32.55 ± 13.81, 66.2 % male) of the Dutch Vincent van Gogh Institute for Psychiatry. In accordance with the guidelines of the institutional review board, records were drawn from a large electronic database, containing test results of patients admitted in the period from 2005 to 2013. Data were obtained as part of the standard neuropsychological assessment. Exclusion criteria for healthy volunteers were use of narcotics or sedatives and a presence or history of alcohol abuse, psychiatric illness or neurological disease. All participants were Dutch-speaking. Psychiatric patients had a FSIQ between 61 and 131 (M = 95.9; SD = 13.6). Healthy volunteers had a FSIQ scores between 79 and 141 (M = 106.6; SD = 15.4). Patients were diagnosed according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR, 2000). Diagnoses included major affective (including bipolar) disorders (22.6%), anxiety disorders (7.8%), substance related disorders (5.1%), psychotic disorders (4.7%), dementia and other cognitive disorders (1%), developmental disorders (32.9%), adjustment disorders (7.3%), other disorders (3%; mainly identity and relational problems), and no diagnosis on axis I (7.8%). In some patients (8.1%) the formal diagnosis was unknown. Comorbidity with personality disorders was diagnosed in 24.3% of the patients, or diagnosis on axis II was deferred (29%).
2.2. Materials
- The Dutch version of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale - third edition was administered (except for the subtest Object Assembly) according to standard procedures (Wechsler, 2000). Reliability statistics are comparable to those found in the US version with internal consistency coefficients ranging from .72 for the subtest Picture Arrangement to .93 for the subtest Vocabulary. The factor structure of the Dutch WAIS-III is similar to the US version, except for Arithmetic, which has high loadings on both the VCI, POI and WMI, instead of a specific high loading on the WMI (Van der Heijden, Van den Bos, Mol & Kessels, 2013; Van Ravenzwaaij & Van Hamel, 2006). Raw scores of all subtests were included in analyses.The Dutch version of the BADS (Krabbendam & Kalff, 1997), WCST (Heaton, 1981, Heaton, Chelune, Talley, Kay & Curtiss, 1993) and the Stroop (Hammes, 1971) were included as a comprehensive reflection of different EF sub functions. The BADS contains six subtests (Rule shift cards, Action Program, Key Search, Temporal Judgment, Zoo Map and Modified Six Elements), which measure planning, problem solving, set-shifting, monitoring behaviour and the use of strategy (Lezak et al., 2012; Wilson et al., 1996). The overall profile score, computed out of standard scores of each subtest (not corrected for age, gender or education), was included in analysis. The WCST is a test of abstract reasoning, requiring mental flexibility (set-shifting), problem solving skills and working memory (Heaton et al., 1993). Subjects have to sort cards with symbols, varying in shape, color and number, and achieve categories predetermined by the examiner, who gives feedback after each sorted cared (‘right’ or ‘wrong’). Rules of how to sort cards are changed without warning after ten correct placements of the cards, and the participant has to adapt his strategy to the new rule and change his responses. As an overall performance index (Lezak et al., 2012), the total number of errors was used in analyses. The Stroop is a test of response inhibition and cognitive flexibility. Subjects have to read colors out loud on three cards. The first card shows the name and print of the color, card two shows only colors and the third card shows a color in words with an incongruent color print, in which the latter has to be read out loud. To measure the concept of response inhibition, the element of speed is eliminated by using the interference score (response time on card III divided by the average response time of card I + II) for analysis.
2.3. Analyses
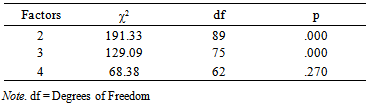
- Factor analysis was conducted using PASW Statistics (version 18). The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy (KMO) was used to determine the appropriateness of the factor analysis (Field, 2009). Maximum likelihood procedures with promax rotation were used to examine the model fit of two, three and four factors. The chi-square statistic was used to determine the goodness of fit of all three factor solutions. Taking a conservative approach (Field, 2009), only factor loadings ≥ .35 were interpreted.
3. Results
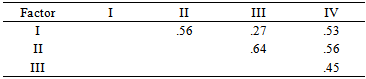
- Descriptive statistics of all tests are presented in Table 1. Intercorrelations of the WAIS-III and the measures of EF are shown in Table 2. The KMO score is .91, which can be considered excellent (Field, 2006).
|
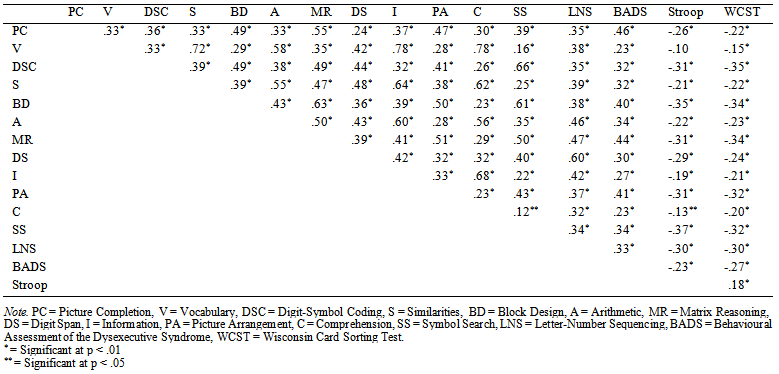 | Table 2. Intercorrelations of the 13 WAIS-III Subtests and BADS, WCST and Stroop |
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- The goal of the present study was to gain insight in how executive functioning is incorporated in the WAIS-III, examined in a large heterogeneous group of both psychiatric patients and healthy volunteers. Exploratory factor analysis using maximum likelihood procedures was conducted to examine the model fit of two, three and four factor models. Both three and four factor models fitted the data. The three factor model was almost identical to the model found by Kaufman et al. (2001), and consisted of a combined POI/PSI factor, and a second and third factor which were completely comparable to the VCI and WMI of the WAIS-III, except for Arithmetic. The four factor model was almost completely identical to the four factor indices of the WAIS-III. The BADS, WCST and Stroop loaded all on factor two, corresponding to the POI of the WAIS-III. This model fitted the data best, and therefore was selected for interpretation. Contrary to expectation, Arithmetic rather loads on the VCI than on the WMI in the American WAIS-III manual. This is also in contrast with the Dutch manual of the WAIS-III, in which Arithmetic loads on all index factors except PSI. This emphasizes the unstable structure of this subtest (Grégoire, 2013; Ravenzwaaij & Van Hamel, 2005; Van der Heijden, Van den Bos, Mol & Kessels, 2013). Furthermore, the intercorrelation of the VCI and PSI was low (.27), which differs from the intercorrelation of the two index scores in the Dutch WAIS-III manual (.50). According to Hawkins (1998), and Taylor & Heaton (2001), PSI can be considered the most sensitive factor for various clinical disorders and VCI the least. This is probably due to the fact that VCI is a measure of ‘hold’ tasks, which means that VCI performance stays relatively uninfluenced by brain disease or impairment, and this may explain the low correlation between VCI and PSI in the current sample.Results support the hypothesis that components of g can be measured by EF tasks (Duncan, 1995, Wood & Liossi, 2007). The BADS, WCST and Stroop have loadings of respectively .62, -.39 and -.35 on the POI, implicating that this index accounts at least for some part for variance in EF performance. These results are similar to results found by Wood & Liossi (2007), who concluded that performance on all neuropsychological tests of executive function correlated with the WAIS-III FSIQ and PIQ scores. The partial reflection of EF performance in the POI is in line with the upcoming evidence of a great overlap between EF and Gf, since (subtests) of the PIQ scale are often associated with Gf (Duncan, 2010; Roca et al., 2010; Van Aken et al., submitted). The explained variance by the POI accounts for 12.89% in the model, compared to 41.73% by the VCI. Given the importance of executive functions in neuropsychological evaluation of patients as well as their relation to intellectual (dis)abilities, these results contribute to the already persisting criticism that the WAIS-III is mainly a test of crystallized intelligence (Blair, 2006). Since g for the greater part can be explained by Gf (Duncan et al., 1995), this should translate to the distribution of more Gf and EF subtests, instead of an overload of Gc subtests. In terms of CHC, this is in agreement with the suggestion of Ward, Bergman & Hebert (2012) and Grégoire (2013), who propose a more hierarchic structure in the description of CHC abilities. More specific, they state that fluid reasoning should go upwards in the hierarchy, given its influence on g and its impact on overall (cognitive) functioning. As to the relation between Gf and EF, it is suggested that they co-exist through a general Gf factor next to more specific EF sub processes like set shifting, inhibition or processing speed (Duncan et al., 2008; Miyake et al., 2000; Wood & Liossi, 2007). In Duncan (2010), Gf is hypothesized as being a reflection of the efficiency in which complex behavior (consisting of different EF processes) is set up. The more complex or novel the task demands, the more interference of Gf is required. Therefore, including task complexity as an important variable in intelligence studies, more insight in the relation of intelligence and EF will be gained. Nevertheless, contemporary research should keep in mind that in the current, but nearly all factor analytic studies on intelligence, covariance between both subtests and factors exists, just like they will interact in daily life. Therefore, interpreting cognitive disabilities within the context of the individual is essential for both assessment and treatment of cognitive disorders. A limitation of the current study might be the use of explorative factor analysis, which makes it less unequivocal to compare with many other studies on intelligence, which tend to utilize confirmative methods (Bowden, 2013). This decision was made based on the fact that little (confirmative) research is done combining the WAIS-III subtest and additional (EF) tasks. Nevertheless, using the maximum likelihood procedure, results could still be interpreted within the four-factor structure known from the WAIS-III. In the future, a consideration would be to include executive tasks with higher reliability and validity statistics, using more robust statistical analysis to support the theory. Moreover, it is evident that, if available, the use of the WAIS-IV in future research is preferred given the more prominent influence of (especially) Gf in the development of the subtests.
5. Conclusions
- The current study gives more insight into the distribution of EF in the WAIS-III. Limited performance on the POI gives direction to further examination of different EF aspects, which in turn could account for disharmonic distributions in intellectual abilities. Although current models on intelligence and EF tend to describe process pure abilities to find an overall theory of abilities, the assessment and treatment of cognitive disorders requires a multifaceted and integrated view in which cognitive disorders can be understood through the interaction of an individual and the environment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Correspondence can be directed to J.I.M. Egger, PhD, Centre of Excellence for Neuropsychiatry, Vincent van Gogh Institute for Psychiatry, Stationsweg 46, 5803 AC Venray, The Netherlands. E-mail: J.Egger@psych.ru.nl, telephone: +31.478.527.339.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML