-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Applied Psychology
p-ISSN: 2168-5010 e-ISSN: 2168-5029
2013; 3(3): 63-73
doi:10.5923/j.ijap.20130303.05
How do Non-clinical Paranoid Vs. Socially Anxious Individuals React to Failure Vs. Success? An Experimental Investigation
Barbara Lopes1, Jose Augusto Veiga Pinto-Gouveia2
1PhD, Lecturer in Psychology, De Montfort University, Leicester, United Kingdom
2M.D., PhD in Psychology, Lecturer in Psychology, Faculdade de Psicologia e de Ciencias da Educacao da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal
Correspondence to: Barbara Lopes, PhD, Lecturer in Psychology, De Montfort University, Leicester, United Kingdom.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
We did a quasi experimental study with 223 college students divided into three groups according to the presence of non-clinical paranoid ideation vs. social anxiety: the paranoia group (PG) vs. the social anxiety group (SAG) vs. the control group (CG). We measured participants’ trait anger, paranoid ideation, external shame, state anxiety, state anger and depressive symptomatology using self-reports at time 1. Afterwards, we randomly assigned participants to a success vs. a failure condition using a computer game task. We then assessed their emotional and paranoid reactions (time 2). Independent sample t tests showed that the PG was more temperamentally aggressive than the SAG. Wilcoxon Sign tests showed that during failure, the paranoia group significantly increased their paranoid ideation, negative emotional reactions to performance, state anger and state social paranoia from times 1 to 2. In contrast, the SAG increased their state anxiety and external shame from times 1 to 2. The PG didn’t significantly decrease in paranoid ideation but they showed a significant increase in positive emotional reactions while significantly decreasing in state anger during success. The SAG increased significantly in their positive emotional reactions during success but they also significantly increased in paranoid ideation. The negative impact of failure for PG and of success for the SAG alerts us to key individual differences and the importance of managing anger, anxiety and paranoid feelings during evaluation.
Keywords: Non-clinical Paranoia vs. Social Anxiety , Success, Failure, Paranoid Ideation, Emotional Reactions
Cite this paper: Barbara Lopes, Jose Augusto Veiga Pinto-Gouveia, How do Non-clinical Paranoid Vs. Socially Anxious Individuals React to Failure Vs. Success? An Experimental Investigation, International Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol. 3 No. 3, 2013, pp. 63-73. doi: 10.5923/j.ijap.20130303.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- There is a growing consensus in the literature that psychotic symptoms such as delusions are on a continuum with normal experience[1]. Indeed, there is emerging evidence to support this argument as paranoid thoughts build upon common social anxieties such as fear of criticism and rejection from others[2]. It is assumed that there is a skewed distribution of clinical and non-clinical paranoid thoughts (i.e. a quasi-continuous distribution) in the general population. Many people do not have delusions whereas other people have persecutory ideas about conspiracy[2,3]. Therefore, for the purpose of research, it is important to understand non-clinical paranoid phenomena in order to inform our understanding of clinical phenomena.There is also evidence suggesting that both paranoia and social anxiety are two types of fear. On one hand social anxiety is a fear of being negatively evaluated by others and not pleasing them. It is associated with feelings of inferiority whereas paranoia is a fear of what others will intentionally do to harm the self. It is associated with feelings of superiority (when depression is controlled for) and external shame[4]. Although it is assumed that both phenomena share etiological characteristics, because there is evidence suggesting that paranoid thoughts build upon common social anxieties such as fear of criticism and rejection from others[4], research has also presented evidence that non-clinical paranoia is associated with more severe psychopathological symptoms, anger and a predisposition to hallucinate[3].Additionally, literature about cognitive models of social anxiety and paranoia have been suggesting that non-clinical paranoid individuals are particularly sensitive to perceived external threats[3,6]. That usually takes the form of perceived negative evaluations, e.g. criticisms or social put-downs[2] . Non-paranoid individuals feel threatened by others when they have to compete for social status and acceptance[7,8]. Socially anxious individuals on the other hand fear both external negative and positive evaluations[9]. This means that socially anxious individuals fear negative evaluations from others but they also fear positive evaluations. Socially anxious individuals thus attempt to please others who they perceive as possessing more positive qualities and talent than themselves, and they undermine their own qualities out of fear of retaliation and loosing the good grace of others4]. Hence, socially anxious individuals’ fear of positive evaluations has to do with the fact that success puts them in the spotlight and raises the bar, which according to evolutionary psychologists makes them feel that they have to compete with powerful others, which leads to even more anxiety[7,8]. Indeed research has found that individuals that present social anxiety and/or depressive symptoms coupled with low self esteem may blame themselves for criticism and rejection, especially if they attribute such aversive social outcomes to their own inadequacy or inferiority. They also tend to behave submissively and downplay their own successes[2]. In contrast to this, research has found that individuals that present paranoid traits and both low levels of depressive symptomatology and normal explicit self-esteem not only show the belief that the malevolence of others is unjustified but also display a tendency to be overtly aggressive[3,4]. Hence the purpose of this study was on one hand to examine the psychological profiles of non-clinical paranoid and socially anxious students and on the other hand to measure their emotional reactions to socially-induced stress. We used an experimental method because most studies use questionnaires[5] that do not provide cause-effect explanations for the data. This means that people who report paranoia in a general population may be reporting these ideas because they perceive themselves to be targets for hostility at that present moment[4].Theoretical models about persecutory delusions such as the threat anticipation model has been proposing that paranoid delusions are the result of an interaction between vulnerability factors (e.g. traits of paranoia), emotional processes (anxiety) and reasoning biases[3]. This model has been tested during virtual social situations depicting ambiguous scenarios but not during situations of “pretense” evaluation and criticism from others.Indeed, there has been a growing body of research about paranoid and anxious reactions in an experimental setting using virtual reality[4,6]. Virtual social situations that mimic real life ones show avatars of people that do not behave in a hostile manner towards the participants. Therefore, when they present paranoid interpretations it is because of other variables (e.g. negative affect) rather than being a target for hostile behaviour.For example, a randomized experiment showed that stress induced by noise and questions about knowledge led to an increase in state paranoia and depression in the general population. The impact of stress was particularly pronounced in individuals with higher baseline levels of sub-clinical psychosis-prone symptomatology[10]. Furthermore, the effect of stress on paranoia was mediated by an increase in anxiety, regardless of the level of individual vulnerability, but anxiety was clearly more related to high state paranoia in more vulnerable participants. Thus, these findings supported cognitive models of psychosis that claim paranoia to be a function of stress and vulnerability[11].Since, to our knowledge, there are not many studies in the literature that address both non-clinical paranoid and socially anxious phenomena using an experimental method, this study set out to explore the impact of a stressful condition of induced failure vs. success on individuals that show non-clinical paranoid ideation versus individuals that show social anxiety and controls. Because there is evidence to suggest that social anxious individuals are particularly prone to situations of social evaluation and criticism we have used day to day experiences of college students being evaluated by others, failing in a task and being criticized condition of stress to create the condition of failure[2].
1.1. Hypotheses
- 1) The Paranoia Group (PG) should present more severe psychological vulnerabilities than the Social Anxiety Group (SAG). The PG should present an aggressive temperament.2) Failure should be problematic for both the PG and the SAG. Failure should induce a higher frequency and higher conviction of paranoid thoughts, stress symptoms, paranoid feelings, and more anger control for the PG. On the other hand, it should induce more anxiety feelings, state anxiety, external shame and anger control for the SAG.3) Success should protect both groups against negative emotional reactions. On one hand, success should decrease state anger for the PG while still inducing an increase in paranoid ideation. On the other hand, success should be particularly threatening for the SAG; it is expected to induce higher conviction and distress of paranoid thoughts in this group.
2. Materials and Method
- 223 College Students were recruited voluntarily in lectures and via ads from the degrees Psychology, Sociology and Education at the University of Coimbra, Portugal. This sample comprises 196 females and 27 males with an age range of 17-46 (M=19.81, SD=3.65). Mostly were single (98%), with an average of 13 years spent in education.We asked students to fill in a battery of screening measures of paranoia, depression and social anxiety and devised two experimental groups and one control group by applying researchers’ standardized norms in the literature for cut off scores on measures of paranoia and social anxiety [3,12,13,14,15,16].We point out that all the instruments used in this study were translated into Portuguese by a bilingual translator and the compatibility of content was verified through stringent back-translation procedures.
2.1. Experimental and Control Groups
2.1.1. Paranoia Group (PG)
|
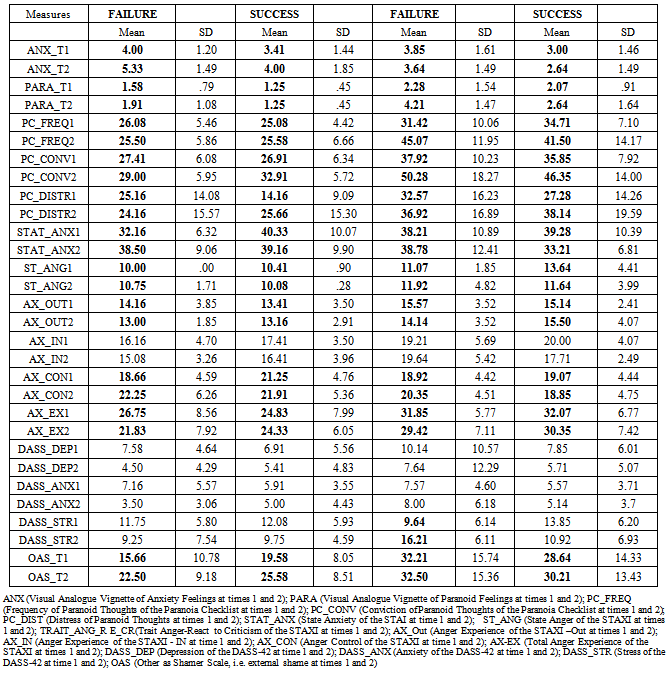
- This group consisted of 28 participants that were selected according to the following standardized norm of a cut-off score plus a standard deviation in the General Paranoia Scale (GPS≥53; + 1 SD)[13]. Also, all participants had to show clear paranoid beliefs in the Portuguese version of the Personal Experience of Paranoia Scale (PEPS) that measures the acknowledgement of personal experiences of paranoia and key cognitive, behavioural and affective dimensions of paranoia[14]. 22 participants were women (78.6%) and 6 were men (21.4%). Females reported statistically significantly more distress of paranoid thoughts of the PC (t (26)=-2.429, p=.020) and more symptoms of anxiety (t (26)=-2.725, p=.018) than males. Depressive symptoms were controlled for with the Portuguese version of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-42)[15] and this group did not present signs of clinical depression and or anxiety (table 1).
2.1.2. Social Anxiety Group (SAG)
- This group consisted of 28 participants that were selected according to the standardized norms for the following cut-off scores in the Social Interaction Perfomance and Avoidance Scale’s (SIPAAS) “Anxiety /Distress subscale” (>115) and “Avoidance subscale” (>105), together with > 110 in the Portuguese version of the Fear of Negative Evaluations Scale (FNE) that measures the fear of being negatively judged by others (peers, superiors)[16] (there was Cronbach alpha of .91 in this study). The SAG also mainly comprised females, n=22, with only 6 males. Females were both older and presented a higher educational level than males (t (26)=-4.161, p<0.001; t (26)=-3.161, p=.005). This group showed the highest levels of social anxiety’s behaviours and of the fear of negative evaluations coupled with medium to low trait paranoia (see table 1). Depression and anxiety symptoms were controlled for and the group did not present signs of clinical depression and or anxiety (table 1).
2.1.3. Control Group (CG)
- This group comprised 28 participants that were selected according to the following cutt off scores GPS <30; SIPAAS-anxiety and avoidance <70; FNE <80; DASS-42: depression, anxiety and stress <10 (see table 1).
2.2. Group Differences
- There were no statistically significant differences between the three groups concerning age, F(2,75)= 1.578, p=.213, and on the female to male ratio (χ2 (1 , 76)= .421, p=.810). There were more females than males in all groups.
2.3. Instruments
- Participants were required to fill in a battery of instruments at times 1 (one week before the experiment) and 2 (seconds after the experiment). Participation in the study was voluntary and confidentiality was assured.Paranoia Checklist (PC)[3. 17]The PC is a 18-item self-report multidimensional scale developed to measure paranoid ideation. Items range from mild interpersonal anxieties e.g. “There might be negative comments being circulated about me” to paranoid ideas “There is a possibility of a conspiracy against me”. Each item is rated on 5-point Likert scales for frequency, degree of conviction, and distress and has excellent internal consistency (Cronbach’s α>0.90) and good convergent validity. This study presented the following Cronbach’s alphas: 0.89 (frequency), 0.95 (conviction) and 0.95 (distress).State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI)[18, 19]State anxiety is measured by 20 items that evaluate current level of anxiety (e.g. “I feel nervous”). Each item is rated on a 4 point scale (1=Not at all, 5=Very much so). Higher scores indicate higher levels of anxiety. Trait anxiety was measured using the Trait anxiety subscale (20 items) of this inventory. STAI scores range from 20 (almost never anxious) to 80 (almost always anxious). This questionnaire is widely used in the literature to control for anxiety induced by the experimental situation and a general tendency to be anxious. The Cronbach alpha for the STAI in this study was α=.92.Other as Shamer Scale (OAS)[20, 21]The OAS is a 18 items scale that asks respondents to indicate the frequency of their feelings and experiences to items e.g. “I feel insecure about others opinions of me” and “Other people see me as small and insignificant” on a 5-point Likert scale (0—4). This scale offers a measure of beliefs of ‘‘being looked down on’’ (seen as low-rank) shame or stigmatizing shame. Higher scores indicate high levels of shame about how others view oneself (i.e. external shame). This scale has shown satisfactory internal consistency[20]. In this study the Cronbach’s alpha for this scale was of .94.The State- Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXI)[22]The STAXI is a 44-item inventory which measures the experience and expression of anger in a 4 point response scale. Higher scores correspond to high levels of anger. State Anger corresponds to current subjective feelings of anger that vary from irritability to intense rage. The chronic trait anger refers to a tendency to perceive situations as annoying and irritating. The “Trait Anger (total)” measure has two sub-scales. First, anger resulting from temperament and requiring no provocation, called “Trait Anger (Temperament)”. Second, the disposition to express anger when criticised or treated unfairly, here called “Trait Anger (react to criticism)”. There are three anger expression scales (AX) to assess how respondents behave when angry or furious. “Anger in” measures the frequency of anger suppression (8 items), “Anger out” measures the frequency of anger expression (8 items), and “Anger control” measures the frequency of attempts to control the experience of anger (8 items). The “Total Anger Expressed” measures the frequency of anger expression regardless of direction. The literature reported good psychometric characteristics for this questionnaire and subscales (Spielberger, 1988). We obtained the following Cronbach alphas of .94 for “State Anger”, .90 for “Trait anger” and .64 for” Anger In” and -.85 for “Anger out” respectively.Aggression questionnaire (AQ)[23]This scale tackles several components ofan aggressive temperament. Participants have to rate in a 5 point Likert scale how much each statement reflects their character and behaviour (1= not at all to 5= very much). The scale has four subscales: Physical Aggression, Verbal Aggression, Anger and Hostility. Higher scores indicate more anger (experiences of anger such as flaring up), hostility (resentment) and aggressive behaviours (such as hitting and shouting). These factors have shown good internal consistency and stability over time. In our study the Cronbach’s alphas for each dimension were the following: 0.84 (physical aggression); 0.69 (verbal aggression); 0.80 (anger) and 0.81 (hostility).State Social Paranoia Scale (SSPS)[24]The SSPS is a 20-item self-report questionnaire devised to measure the occurrence of persecutory thoughts about virtual-reality characters. For the purpose of this study we use the SSPS as a measure of “state social paranoia”, that is the occurrence of persecutory thoughts about “real” people present in the experiment. This questionnaire has three subscales: “Persecution” that presents 10 items assessing paranoid thinking that fulfill the criteria of an established definition of persecutory ideation; “Neutral” that measures neutral ideation about people in the experimental setting and “Positive” that measures positive ideation about the people present in the experimental setting . Each of the 20 items is rated on a 5-point-scale (1=Do not agree, 5=Totally agree). Higher scores indicate higher endorsement. The original version of the scale showed good internal reliability (α=0.90) and clear convergent validity[24]. In our study the scale showed a Cronbach alpha of α=0.60.
3. Experimental Design and Procedure
- The study is quasi-experimental and tried to mimic real-life situations where people are evaluated by others.Participants from the three groups were randomly assigned to two experimental conditions: Success (n=14) vs. Failure (n=14) and then seated in front of separate computers in a laboratory. Participants were informed that they would play a computer game that tested their reasoning, visual-spatial and concentration abilities. The game comprises cards with different geometric features (SET GAME).To rule out any administration biases, the experimenters followed a clear protocol. Participants were warned that they would be evaluated by the researcher on their performance abilities. Before going to the practice session, participants were asked to fill in visual analogue vignettes that assessed their state feelings of anxiety and paranoia in a 7 point response scale from 1= not at all to 7=very much. They were also required to fill in the first part of a questionnaire of self-perceptions (5 positive adjectives e.g.” I am intelligent” versus 5 negative adjectives “I am unintelligent”)[25].The researcher explained orally the rules of the game and how to compose a set. Participants had the opportunity to practice for 5 minutes. After practice, participants were asked to answer by writing in a 7 point response scale: a) how well they expect to do in comparison to their colleagues; b) how good they consider their visual spatial abilities to be; c) how many times they play these types of computer games and d) how important is their performance in this game. They also had to write down their expectations about their performance by selecting from a range of 10% (top, excellent), 50% (average) to 90% (bottom, very bad). After answering these questions, they would play the game for 15 minutes, timed by the researcher.During Success the version of the SET GAME was the easiest (version for primary school children) and the game was set into “easy” whereas during Failure the version of the SET GAME was advanced and the game was set into “very difficult”. Also during Failure, participants were required to play against the computer, which did not happen in Success therefore, this manipulation was an added stressor.Success did not put pressure on participants because they were informed that the goal of the game would be to find as many groups of cards they could whereas during Failure they would be informed that they had to achieve 14 groups and that this was to be expected because it was given the false information that this was the average performance of a college student (it was tested beforehand to be impossible to attain). After playing the game, each participant was debriefed by the researcher about his or her capacity, ability to concentrate, to engage and disengage attention, about their visual-spatial abilities and overall performance. During Success, the researcher would praise their performance with standardized positive feedback e.g. “very good at engaging and disengaging attention; the performance was very good, etc.” while during Failure, the researcher would give negative standardized feedback e.g. “very bad performance, difficulties in engaging and disengaging attention, etc.”.After receiving feedback, participants had to a): fill in the same visual analogue vignettes of anxiety and state paranoid feelings; b) describe their perceived performance (how well they did compared to what they expected before playing the game and compared to other college students in a scale of 10% - top excellent to 90% - very bad) and to write down the number the groups they obtained; c) describe their emotional reactions to the game (positive e.g. joy vs. negative emotions e.g. discontent) in a 7 point response scale (1= totally agree to 7 =totally disagree) (e.g. “the game made me feel stupid”)[25]. Finally participants were asked to fill in the time 2 post experiment battery of questionnaires that was composed by the following measures: the PC (frequency, conviction, distress); the STAI (state anxiety); the STAXI; the OAS, the DASS-42 and the State Social Paranoia Scale. At the end of the experiment participants were debriefed and we made sure they understood that the feedback was not real.
4. Results
- Mean scores according to group membership are presented in table 2. Our analyses focused on the paranoia vs. social anxiety group. All measures showed acceptable levels of Kurtosis and Skewness (i.e values between +/-1) prior to statistical analysis.
4.1. Groups’ Psychological Vulnerabilities
- Independent sample t tests showed that the PG showed significantly more “Physical Aggression”( t (50)= 3.194, p<.005); “Verbal Aggression” (t (50)= 2.348, p=.023); “Anger” (t (50)= 4.262, p<.001) and “Hostility” (t(50)= 3.732, p<.001) than the SAG. The PG demonstrated more aggressive traits and behaviour than the SAG. The PG also demonstrated statistically significantly higher scores on “State Anger” (STAXI) at time 1 than the SAG (t (50)= 3.112, p=.004) and of “Trait Anger Total” (STAXI) at time 1 (t (50)= 3.639, p=.001). The PG not only showed more state anger before the experiment took place but also showed more trait anger, i.e. a tendency to be permanently angry. Further analyses showed that the PG also showed statistically significantly more “Trait Anger- Reaction to Criticism” than the SAG at time 1 (t (50)= 4.118, p<.001). Results thus suggested that generally the PG reacts more angrily to criticism that they perceive as unfair or unjustified than the SAG. The PG also showed statistically significantly more positive expectations about their performance success than the SAG (t (50)= 2.270, p<.028). This meant that the PG showed a bias to over-estimate their chances of success when compared to other people (see table 1).
4.2. Differences within the Non-clinical Paranoid Group Vs. Socially Anxious Group during Success Vs. Failure
- Independent sample t tests with Bootstrap method 95% confidence interval revealed as expected that both the PG and the SAG showed statistically significantly more positive emotions during success vs. failure (M=18.21, vs. M=12.00; t (26)=3.523, p=.002; boostrap standard error = 1.70p=.004; M=16.64, vs. M=11.92; t (26)=2.313 p=.030; boostrap standard error = 1.98, p=.038 respectively), which meant that our method was reliably inducing correct and adequate emotions in the correct condition.FailureWilcoxon Sign ranks tests showed that the PG statistically significantly increased both the frequency and the conviction of paranoid thoughts (PC) from time 1 (Mdn=31.50; Mdn=36.00) to time 2 (Mdn=42.00; Mdn=42.30) during failure (Z=-2.986, p=.003, r=.798 and Z =-3.298, p=.001, r=.881 respectively) (see figures 1 and 2). The PG statistically significantly increased as well the subjective state paranoid feelings (visual analogue vignettes) from time 1 (Mdn=2.00) to time 2 (Mdn=4.00) (Z=-2.925, p=.003, r=.781). Results thus suggested that failure induced in the paranoia group more frequent and higher conviction of paranoid ideation and more paranoid feelings.
|
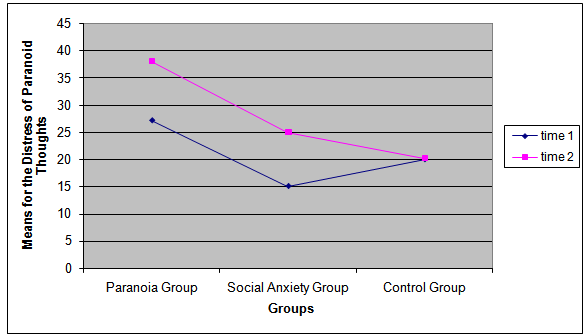 | Figure 1. Group’s Means of the Distress of Paranoid thoughts at times 1 vs. 2 during Success |
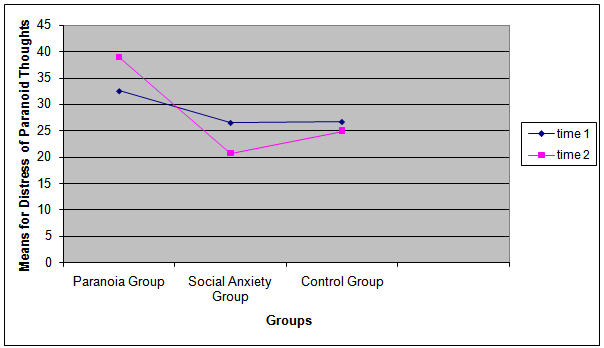 | Figure 2. Group’s Means of Distress of Paranoid Thoughts at times 1 vs. 2 during Failure |
5. Discussion
- Recent developments in the literature in paranoia have been suggesting that there are two types of anxieties in the general population, “the paranoid” type vs. “the socially anxious”[2]. While the paranoid type is preoccupied with what other people can do to harm oneself, the “socially anxious” is worried about pleasing others.Our study attempted to explore how the two types react to social stress provoked by a difficult computer task and negative vs. positive feedback. First of all we expected to see differences in the psychological vulnerabilities of the two experimental groups. We hypothesized that the paranoia group would show more severe psychological vulnerabilities, namely an aggressive temperament. Results supported our hypothesis. The PG when compared to the SAG showed more aggressive traits, hostility, and a higher preoccupation about what other people could do to hamper their success. On the other hand, the SAG seemed to view other people under an exaggerated positive light. This meant that contrarily to non-clinical paranoid individuals, socially anxious individuals showed a positive bias regarding other people’s intentions and behaviours towards them. Furthermore, non-clinical socially anxious individuals also expected to do less well than others whereas paranoids thought they would do much better.This fits with the notion that socially anxious individuals present a “fear of doing well”, i.e. a fear of success, because they worry not only that they cannot maintain and defend social gains but they also feel that positive evaluation from others raise standards by which they will be evaluated in the future[7,8]. Furthermore, another aim of the study was to explore how the different individuals react to positive feedback and praise (success) vs. negative feedback (failure). Results from a Wilcoxon Sign Rank tests showed a negative the impact of failure for the PG. As expected the PG increased the frequency, conviction and distress of their paranoid thoughts and associated paranoid feelings related to performance in the condition of failure. They also showed more state anger but they did not express their anger in this condition. Indeed, results in general showed a decrease of the expression of anger during the experimental conditions. Therefore, although non-clinical paranoid individuals have a generalized tendency to react angrily towards criticism, when they fail and are criticized for it, they do not show their anger overtly; instead they try to control their aggressive feelings[14]. This result is interesting because suggested that non-clinical paranoids were showing submissive behaviours towards a perceived higher rank authority (the experimenter) and although they felt anger during failure, they also entrapped it[26]. In contrast to this, the PG showed less state anger during success. In spite of being less angry during success, non-clinical paranoid individuals continued to show much more state anger than socially anxious individuals. Thus, it seemed that anger and aggression are not only behavioural outcomes of paranoia but also traits and attitudes towards certain social situations. Non-clinical paranoid individuals are in general significantly more angry and aggressive than others. Indeed, results showed that they expressed significantly more anger than socially anxious individuals. Hence it is likely that non-clinical paranoid individuals may also overtly express more trait anger in other situations rather than during the experimental sessions because they are angry all the time[2].On the other hand, as expected, non-clinical socially anxious individuals reacted differently from paranoid individuals on a difficult computer task. The Social Anxiety Group (SAG) comprises non-clinical social anxious individuals that usually focus their attention on their defective self[2, 27]. They did not present traits of anger as much as the Paranoia Group (PG) did. Indeed, non-clinical socially anxious individuals of the SAG showed less state anger in both success and failure than paranoids.Results also showed that socially anxious individuals, when faced with criticism and performance failure showed much more external shame, and thus started to shift their attention from inwards to outwards and focused on what other people would think about their performance. Also, the SAG showed more state feelings of anxiety but not more paranoid feelings during failure as the PG did. More importantly, results showed that success produced an interesting effect on socially anxious individuals. Although both non-clinical paranoid and socially anxious individuals present negative emotions towards failure, success was more menacing to socially anxious individuals than to paranoid individuals. Being praised on a difficult computer task made socially anxious individuals experience more conviction and associated distress of their paranoid thoughts, which did not happen when they failed. Thus, although socially anxious individuals in general showed more positive feelings concerning other people’s intentions towards them in the experiment than the PG, when they were told that they were successful and were praised they tended to show more persecutory ideas about other person’s intentions towards them and more conviction and distress in their paranoid ideas. These results can be explained by the idea that socially anxious individuals have a negative view of the self and view themselves as inferior to others[7, 8, 27]. It seemed that socially anxious individuals expect to fail because they see themselves as being less capable than others, so having other people praising their effort induces a negative emotional effect and produces fear. Indeed, the praise from others seemed to be perceived by the socially anxious individuals as being incongruent to their views of themselves and low expectations about their abilities to perform well. Hence to the socially anxious individual the praise of others is actually perceived as an attempt to “mock” him/her[27]. In other words, the positive views of others regarding the socially anxious individual and their congratulations for his/her success were perceived under a “paranoid light” e.g. as them “laughing at him/her behind his/her back”. Since socially anxious individuals apparently do not to believe their performance will get better because they perceive themselves as not possessing the right qualities to be succesful, they would disqualify the positive and instead pay attention to the negative[9].In contrast to this, the SAG as well as the PG demonstrated a tendency to show less state anger in failure. Moreover, both groups increased the control of their anger during both experimental conditions, although the SAG controlled anger significantly more than the PG. This may be explained by the fact that socially anxious and paranoid individuals act as subordinates towards a perceived higher rank authority that criticizes them, hence both control their anger in order to avoid harm and social put down[7, 8, 28].
5.1. Limitations
- There are several limitations to this study. The sample size was small, and there were mainly females, making it difficult to generalize results. Even so, the literature suggests that there are no significant differences between males and females for their paranoid thoughts[3]. The experimental setting was not ideal and there might have been extraneous effects that could have had an impact on variables from time 1 to time 2, e.g. noise.There was also the problem with inducing failure versus success. Since the computer task was extremely difficult it may well have been the case that praising vs. criticizing and making the computer game easier in the condition of success was not enough to control for individual differences on performance. Indeed, some individuals might have been plainly better than others at the computer game independently of the condition that they were in and thus they may perceive their performance in accordance to their reasoning capacities and abilities on playing games and not according to praise or criticism. We tried to control for the effects of individual differences by asking questions that controlled the effects of parasite variables such as practice and experience on this type of games. All individuals confirmed that they did not have experience in playing this game. Thus, although some individuals showed a relatively good performance in failure, in spite of not obtaining 14 groups and struggling with the task, they showed less positive emotional reactions in this condition. The key question lies with how people deal with failure and whether they perceive criticism about not being able to play a computer game well as a personal failure.
5.2. Conclusions
- This study suggested that non-clinical paranoid individuals seem to fear failure because it induces higher paranoia and anxiety ideation. In contrast, socially anxious individuals fear success the most, because it is incongruent with their negative views of the self. This has important clinical implications: it is important to teach non-clinical individuals who have socially anxious tendencies how to deal with praise and success. Without intervention, their negative self view, anxiety about social situations and their fear of others may induce paranoia in the face of praise[3,4].
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- We would like to thank Sónia Gregório for her help during data collection.Declaration of interest: We do not have any declaration of interest.Funding: Research was funded by PhD Grant by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) - Portugal
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML