-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Applied Psychology
2012; 2(4): 43-52
doi: 10.5923/j.ijap.20120204.02
The Emotion of Admiration Improves Employees’ Goal Orientations and Contextual Performance
Elisa Maria Galliani , Michelangelo Vianello
University of Padova, Padova, 35131, Italy
Correspondence to: Michelangelo Vianello , University of Padova, Padova, 35131, Italy.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Admiration is the other-praising emotion elicited by the display of outstanding skills, talents, or achievements. Most leadership theories state that effective leaders are admired role models that followers emulate. Nevertheless, no demonstration has been provided so far about the actual role of admiration in the leader-follower relationship. This paper shows that leaders who display technical and managerial competences motivate employees by means of the positive emotion of admiration they elicit. Specifically, we hypothesized and demonstrated that admiration elicited in employees by their leader’s skills increases both their goal orientation to prove and improve their own skills and their contextual performance. In a first field experiment on 137 sales representatives we observed an indirect positive relationship between leader’s skills and followers’ state-goal orientations. Admiration mediated the positive effect of leader’s skills on employees’ motivation. In this study, we also observed a direct and detrimental impact of leaders’ skills on employees learning and proving goal orientations. In a second, cross-sectional, study on 146 full-time teachers we observed that admiration –compared with happiness and gratitude– is the best predictor of state-learning-goal orientation and organizational citizenship behaviors. Implications and limits are discussed.
Keywords: Admiration; Goal Orientation, Organizational Citizenship Behavior, Leader Competence
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Emotions give rise to specific motivations, or action tendencies, that in turn activate behaviors[1]. Understanding and describing the motivational link between emotion and behavior helps to define the emotion itself, to understand its functions and, ultimately, to give an account of individual behavior. In this article, across two studies we demonstrate that the other-directed positive emotion of admiration can increase employees’ motivation to prove and improve their skills and their intention to help and respect colleagues and supervisors.According to Affective Events Theory (AET,[2]), people react emotionally to job events that occur day by day in their workplace, and such emotional responses directly influence their attitudes and behavior. The leader-follower interaction represents a typical class of those situations in which affective events occur (see[3]), because “leadership is an emotion-laden process, both from a leader and a follower perspective”([4], p. 1046). Despite the increasing research interest that in recent times has concerned the positive emotions involved in the leadership processes (see e.g.[3,5,6,7], the examination of the role of positive other-directed emotions involved in the leader-follower relationship has been undeservedly neglected. Especially, if some exceptions are related to the study of empathy (8), gratitude[9], and moral elevation[10], there is a nearly complete lack of research concerning leadership and admiration. This might appear quite odd, considering that the perceived competence of leaders is not only at the basis of their legitimation by followers, but also the foundation of their abilities to motivate followers. Leadership and admirationLeaders’ display of competence is at the centre of most leadership theories, from the early “pre-contingency theory” to the latest transformational approach. In his functional integration of current knowledge on leadership effectiveness, Chemers ([11], p. 40) argues that “leaders must first establish the legitimacy of their authority by appearing competent and trustworthy to their followers”. Hollander’s seminal research[12,13] pointed out that leaders’ legitimacy is rooted in their perceived competence and trustworthiness. A decade later, cognitive models of leadership stressed the centrality of leader legitimacy –which directly depends on followers’ perceptions of leader competence– in understanding the bases of leadership effectiveness (see[14,15]). Even the application of social identity theory to leadership perception[16] confirms the tendency of followers to value leaders who show task-relevant competence and embody group values. Lastly, research on charismatic and transformational leadership considers leader competence and trustworthiness to be at the root of the influential power of leaders[17-18]. It is through their charisma/idealized influence that charismatic/transformational leaders are admired, respected, and trusted by their followers, and it’s through their inspirational motivation that they encourage and motivate followers. Charismatic and transformational leaders are seen as admired and trusted role models such that followers identify with them and seek to emulate them (19) Nevertheless, any clear demonstration has never been provided of the link between the affective response of the followers to their leaders’ charisma and competence and the effectiveness of the motivational influence of charismatic/transformational leaders. McCann, Langford, and Rawlings [20] showed the mediational role played in the leadership process by two feelings of follower appreciation (inspiration and awe), but the authors operationalized them as cognitive rather than affective variables, i.e. follower’s beliefs about leader’s competence and charisma.In this paper, we test the hypothesis that leaders who display technical and managerial competences motivate employees by means of the positive emotion of admiration they elicit. Admiration is typically elicited by the perception of others’ excellence. Ortony, Clore and Collins[21] include admiration within the family of the appreciation emotions, together with appreciation, awe, esteem, and respect. Haidt and colleagues ([22-24]) conceived admiration as the peculiar emotion elicited by the extraordinary display of any skill, talent or achievement by others that motivates people to improve and become skilled. This definition is built on the concept of freely-conferred prestige and sees its phylogenetic evolution as a part of human capacity for culture (see[25]):“Once humans began to do most of their learning by copying others, it became important to find the best role models to copy.”Individuals who excel in any culturally valued skill therefore draw attention and draw followers.[…] Followers feel admiration and a desire for proximity towards prestigious people, not fear and a desire for avoidance, as is typical in dominance relationships” ([24], p. 5).Admiration is thus meant as the emotional basis which gives rise to the motivational state of inspiration (see[26,27]). Individuals displaying outstanding achievements or abilities act as role models that inspire those who admire them to increase their own skills and accomplish higher goals.In Haidt’s[28] conceptualization, admiration belongs to the family of the other-praising emotions, which are elicited by other persons’ excellence that typically give rise to self-enhancing and prosocial behaviors([21,28]). The family also includes gratitude, which is the emotional response to other people’s acts that benefit the self, and elevation, which is the emotional response to the display of moral virtue (see also[24,29,30]). In contrast, admiration is elicited by any display of non-moral excellence (i.e. academic, professional or sport-related skills, talents or achievements) that doesn’t directly benefit the observer. Admiration motivates people to emulate the admired person, improve themselves, and work harder on their own goals[22,24].Following AET[2] and drawing on Haidt’s conceptual view on admiration, we believe that each demonstration of a great deal of competence – both technical and managerial – by a leader acts as an affective event that elicits the specific affective response of admiration in employees.Hypothesis 1. Leader competence elicits admiration in followers.Admiration and state-goal orientationsThe construct of goal orientation (GO) refers to an individual’s dispositional or situational goal preference in achievement settings. Originally developed in educational psychology[33], it was later introduced into organizational psychology[34]. Currently, GO appears to play an important role in many work-related topics such as personnel selection[35], training[36], performance[37], goal setting[38], organizational change[39], and organizational climate and culture[40].GO was initially conceptualized as a bipolar construct that distinguished individuals with a preference for learning or mastery goals over performance goals[33,41]. More recently, learning and performance GOs have been found to be independent, though correlated, dimensions[42], and performance GO turned out to be multidimensional and constituted by ‘prove’ and ‘avoid’ dimensions[43]. Even more recently, a three-factor model of GO was suggested[44]. A Learning GO focuses on the development of competence by acquiring new skills and mastering new situations, a Proving-Performance GO focuses on the demonstration of one’s competence by seeking favorable judgments from others, and an Avoiding-Performance GO focuses on the fear of displaying lack of ability in order to avoid negative judgments from others[44,45]. The avoiding dimension of performance GO negatively affects self-regulation, learning strategies, task performance, and intrinsic motivation[46]. In contrast, both Learning GO and Proving-Performance GO positively impact learning strategies and job performance, with a significant incremental validity over and above cognitive ability and the Big Five[47]. When temporal stability is concerned, most authors agree in conceptualizing GO at both trait-level and state-level, with the trait-GO having a direct effect on the state-GO, but with a number of other psychological and situational variables operating concurrently[48].We predict that the emotional state elicited in followers by the perception of their leader’s competence will enhance their actual motivation to both develop and demonstrate competence in achieving situations. It has been shown that admiration motivates people to improve and become more skilled[22,24]). Thus, it is reasonable to hypothesize that it will boost followers’ state-Learning GO, increasing their actual preference for acquiring new skills and improving themselves. Admiration also motivates people to emulate the role models and strengthen the relationship with them[24]. This leads us to expect that admiration elicited by a competent leader will also boost followers’ state-Proving-Performance GO, increasing their desire to show their value and gain favorable judgments from the leader.Hypothesis 2. Admiration for a competent leader increases followers’ state-Learning GO and state-Proving-Performance GO.Basically, leadership is a matter of influence[49]. In a social learning perspective, leaders influence the behavior of their followers via modelling processes, i.e. through psychological processes like observational learning, imitation, and identification (50,51). Shamir, House, and Arthur[52] have defined role modeling as a class of leader behaviors that leads to the motivational processes entailed in transformational leadership: The leader provides a point of reference and focus to followers’ emulation. Admiration has been proven to be the unique emotional response to any upward assimilative social comparison to a warm and competent role model and the mediator between competence judgments and the consequent motivation to contact, cooperation, and positive approach behaviors[53,54]. Considering admiration as a source of motivation to emulate the role models, and strengthen the relationship with them, we predict that admiration mediates the relationship between followers’ perception of their leaders as competent inspiring role models and their state-GOs.Hypothesis 3. Admiration mediates the effects of leader perceived competence on followers’ state-GOs.
2. Study 1
2.1. Participants, Design and Materials
- 137 sales representatives of a leading European direct selling organization active in the automotive sector participated in the study for no reward. Participants were all men. Their mean age was 36.42 years (SD=7.14). We conducted a field experiment manipulating leader competence by means of 2 scenarios: High Skill and Low Skill (control). Participants were invited to participate in the research on a voluntary basis and for no reward. A questionnaire was sent to each potential participant by standard mail, preceded by a letter in which researchers introduced themselves and the research. Participants were asked to return their anonymous questionnaires in a box placed in the main entrance of the office. The questionnaire asked participants to identify themselves with an employee of Max Castle, a fictitious leader presented in the scenarios. In the High Skill group, Max Castle was depicted as a very skilled leader: “Max Castle obtained 10 years ago a Master’s degree at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, after which he built a brilliant career in financial brokerage. Max Castle is known for his professional talent and for his sensitivity in interpersonal relationships.In his first two years in this company, he gained 36 new corporate clients, raising the company’s assets by 10%”. In the control condition, nothing was said about Max Castle’s achievements or education. He was depicted as a normal leader, who became director in virtue of his seniority.
2.2. Measures
- Manipulation check. After participants had read the scenarios, which took them on average three minutes, the first question asked: Do you think Max Castle exceeds normal standards of competence and skills?Admiration. Drawing on[24], admiration’s peculiar affective reactions were measured by three items: Admiration, Respect, and Inspired. Responses were given on Likert scales ranging from 0 to 7 and were summed to form an overall scale (α=.73). With the same scale we also measured admiration’s typical physical sensations (Energy, Increased Heart Rate, and Chills; α=.69) and action tendencies (Know Max Castle, Work with Max Castle, Be like Max Castle α=.74).State Goal Orientations. VandeWalle’s 12 items[44,55] were adapted to measure state-Learning GO (4 items, α=.84), state-Proving-Performance GO (4 items, α=.74), and state-Avoiding-Performance GO (4 items, α=.76). Participants were asked to think about the present time and report how well each of the 12 items describes their current state with regards to their own job.
2.3. Results
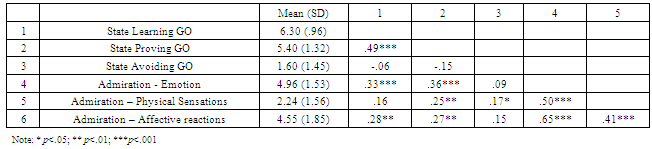
- Descriptive statistics and intercorrelations among study variables are presented in Table 1. To test our hypotheses, we estimated three ordinary least squares regression models with one independent variable (experimental group: 0=control, 1=high skill leader), three mediators (Admiration feelings, physical sensations and action tendencies) and one dependent variable for each model (state-learning, state-proving and state-avoiding goal orientations).
|
|
|
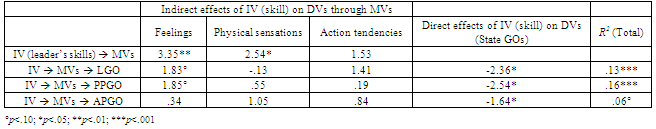
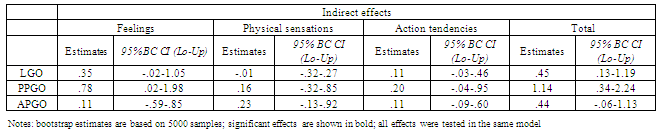
- Furthermore, we computed bias-corrected confidence intervals (95% BC CI) of the indirect (mediated) effects[56]. The direct effects of leader’s skill on the emotion of admiration and on its peculiar physical sensations are high and significant (see Table 2). Our manipulation had no effect on admiration’s action tendencies. Interestingly, the total effect of leader’s skill on state goal orientations is always close to zero (R2LGO=.013, p=.18; R2PPGO=.014, p=.17; R2APGO=.018, p=.12), but the decomposition of this effect highlights that the direct effect of leader’s skill on learning and proving GOs is strong and negative, whereas the indirect component of the total effect on learning and proving GOs is strong and positive (see Table 3). Taking a closer look at standardized regression coefficients (Table 2) we can see that the impact of admiration on learning and proving GO is mainly due to its peculiar feelings (βL=1.83, βP=1.85, p<.10), rather than to its typical physical sensations (β<1.05, n.s.) or action tendencies (β<1.41, n.s.).
2.4. Discussion
- This study provided empirical support to our predictions that leader competence elicits both feelings and physical sensations of admiration in followers (H1), that the feeling of admiration for a competent leader increases followers’ state -Learning GO and state-Proving-Performance GO (H2) and that admiration mediates the effects of leader perceived competence on followers’ state learning and proving GO. Interestingly, the decomposition of direct and indirect effects highlighted that the direct effect of leader skill on learning and proving GOs is negative, whereas the indirect (mediated) effect is positive. In other words, leader’s skill has a positive effect on followers’ motivation to prove and improve their job performance if and only if admiration is felt for the leader. Importantly, we found that the mediation effect of admiration’s feelings was stronger than those of physical sensations and action tendencies. Study 2 will investigate the incremental validity of admiration in a natural workplace, measuring the levels of this emotion elicited in employees by their actual leaders. Its impact on state-GOs and contextual performance will be compared to those of two other positive emotions: happiness and gratitude.
3. Study 2
- Happiness is undoubtedly the most studied discrete positive emotion in the organizational literature. It has been shown that it improves workers’ productivity[57] and evidence has also been provided that income[58,60], organizational citizenship[60] and prosocial behavior(61) are positively affected by happiness. A close test of the incremental validity of admiration at work would be given by a direct comparison with an emotion belonging to the same family, whose role in organizations has already been studied. “Gratitude prototypically stems from the perception of a positive personal outcome, not necessarily deserved or earned, that is due to the actions of another person”([62], p.5). The typical action tendency associated with gratitude is to reciprocate the benefactor in the future[63], but its impact extends to prosocial behaviors[64].Algoe and Haidt[24] demonstrated that admiration produces different action tendencies in comparison to both happiness and gratitude. Three categories of motivational consequences were isolated: Positive social relationships (including enhancement, acknowledgement, reciprocation, and affiliation), emulation (including prosocial behavior and self-improvement), and expend energy. Enhancement, emulation and self-improvement help differentiate admiration from both happiness and gratitude, while expending energy further differentiates it from gratitude. Emulation, self-improvement, and expend energy are closely related to individual’s motivation to improve their ability, as well as to strengthen the relation with the role models by proving their own competence. We therefore expect that the effects of admiration on state Goal Orientations will be stronger than those of happiness and gratitude.Hypothesis 4. Admiration predicts state-Learning and state-Proving-Performance GOs over and above happiness and gratitude.Admiration primarily differs from happiness because it is a social[65-67] other-directed[21] emotion which gives rise to specific action tendencies that are social in nature as well. On the other hand, both admiration and gratitude are social, other-directed emotions, but gratitude mainly gives rise to reciprocity intentions, while the motivational effects of admiration easily extend to groups and social systems. Within organizations, the desire to improve, achieve goals, and strengthen social relationships elicited by admiration could easily extend to colleagues, supervisors and collaborators. Indeed, when individuals are moved by inspiring role models they will be motivated to emulate them. If admiration is elicited by leaders who demonstrate a great competence in performing their job, then it will influence the amount of effort, care, and commitment employees decide to invest in the general functioning of their organization. Hence, we hypothesize that the effects of admiration in work contexts will directly affect contextual performance.Contextual performance refers to the construct of Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB), and concerns any discretionary “contribution to the maintenance and enhancement of the social and psychological context that supports task performance”([68], p. 91). The three most widely accepted and studied components of OCB are altruism, courtesy, and compliance. Altruism concerns helping colleagues or others in order to solve or prevent problems; courtesy refers to behaviors aiming at avoiding or preventing problems for colleagues or others; compliance is concerned with working beyond organizational expectations[69]. We expect that admiration will impact altruism, courtesy, and compliance over and above happiness and gratitude.Hypothesis 5. Admiration predicts OCB over and above happiness and gratitude.
3.1. Participants, design and materials
- Participants were 146 full-time school and pre-school teachers (6 men) who participated in the study for no reward. Their mean age was 44.45 (SD=9.1), and they had been in service, on average, for 19.63 years before their participation in the study (SD=9.8). Three well-trained interviewers provided them with a brief introduction to the study and a paper-and-pencil questionnaire. All responses were collected by means of Likert scales ranging from 1 to 6. The first part of the questionnaire measured independent variables. Participants were asked to think back over the last year and to rate how frequently, in their working days, they felt happiness, gratitude, and admiration for their school principal. Lastly, participants were asked to think back over the last year and rate how frequently they were driven in their job by Learning GO, Proving-Performance GO, Avoiding-Performance GO, and how frequently they adopted a series of behaviors relating to altruism, courtesy, and compliance.
3.2. Measures
- Admiration. The on-line measure of admiration used in the previous study was converted in a retrospective measure. The items were the same, but the frequency rather than the intensity of the emotion felt was asked.Happiness. 5 items were used from the PANAS-X[70] to measure happiness.Gratitude. The 2-item version of the Gratitude Adjective Checklist[71] was employed.State-Goal Orientations. Learning GO, Proving-Performance GO, and Avoiding-Performance GO were measured with the same items used in study 1.OCB. Altruism was measured with 3 items developed in[72], courtesy with 3 items developed in[73], and compliance with 3 items from[74].
3.3. Results
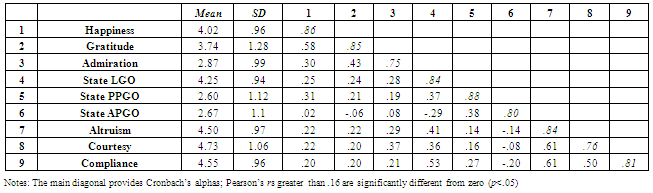
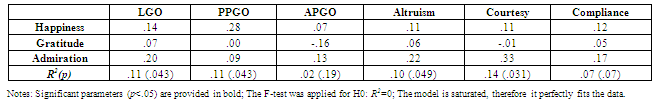
- As can be seen in Table 4, the correlations between admiration and happiness (r=.30) and between admiration and gratitude (r=.42), are lower than the correlation between happiness and gratitude (r=.58; .21<Δz’<.35; p<.05). This result confirms previous evidences that admiration is different and relatively independent from other positive emotions[24].
|
|
- To test our hypotheses, we estimated a saturated SEM for observed variables using positive emotions (happiness, gratitude and admiration) as predictors and our dependent variables (state-Learning GO, state-Proving-Performance GO, state-Avoiding-Performance GO, altruism, courtesy, and compliance) as criteria. Altogether, the model included 3 independent variables and six dependent variables, hence we estimated 18 relationships. In contrast with a series of zero-order Pearson correlations, which might express an undefined amount of redundant relations, in such a model each regression path represents the unique contribution of a predictor (or a moderator) to a dependent variable, controlling for measurement error and for all other relevant relations in the model, such as correlations between predictors. Standardized regression coefficients (Table 5) show that admiration significantly predicts LGO (γ =.20) and OCB (γ1 =.22; γ2=.33, γ3=.17). Our hypotheses can be accepted for all dependent variables except Proving-Performance GO, whose best predictor is happiness (γ=.28).This model was then compared to six other nested models in which regression paths of the three different predictors (and those of their combinations) were sequentially fixed at zero. Results, which are provided in Table 6, show that the impact of happiness and gratitude on our criteria is not significantly different from zero. On the contrary, any time admiration paths are fixed at zero the model does not fit the data. Across criteria, the predictive power of admiration alone (R2=.20) is higher than the sum of the effects of happiness and gratitude on our outcome measures (R2=.17).
3.4. Discussion
- This study confirms the relationships between admiration and state goal orientations that have been found in study 1, and extends them to self-reported actual motivation and prosocial organizational behavior. Furthermore, we directly tested the predictive power of admiration against happiness and gratitude. While happiness is very different from admiration both in terms of elicitors, feelings, and consequences, gratitude is much more similar. Admiration and gratitude are both other-praising emotions, but they are different in nature. Admiration is felt for the display of outstanding talents or achievements and promotes social behavior and self-improvement. Gratitude is a response to a benefactor and motivates reciprocation. In this study, we observed that the motivational consequences of admiration and happiness are different. Admiration motivates to improve one’s own skills in order to master the problem at hand, while happiness motivates people to prove their abilities. As far as self-reported actual prosocial behavior, admiration is by large the best predictor of altruism, courtesy and compliance. Its effects on these prosocial organizational behaviors are much larger than those of happiness and gratitude.
4. Conclusions
- Individual skills, talents and achievements are the foundations of any organizational success. The results of our studies showed that skilled, talented and successful leaders elicit a specific and intense positive emotion in followers – admiration – which in turn motivates them to improve their own skills and to perform better. Admiration was observed to directly impact employees’ organizational citizenship behavior (OCB), and to mediate the positive influence of leaders’ perceived competence on followers’ state-goal orientation in achievement situations. The motivational and behavioral effects of admiration in organizational settings were also compared to those of happiness and gratitude, with admiration being the strongest predictor of employees’ state learning goal orientation and organizational citizenship behavior.Theoretical and practical implicationsAn interesting question arises from our results. We found that the direct effect on motivation of the perception of leaders’ competence is negative. In other words, when no admiration is felt, a skilled leader has the detrimental effect of decreasing employees’ motivation to prove and improve their performance. At this regard, it has been suggested that leaders are perceived as role models to whom employees socially compare themselves[75], but the motivational consequences of these social comparisons can be surprising. For instance, Lockwood and Kunda[76] showed that outstanding models can both provoke self-enhancement and self-deflation, depending on the perceived attainability of their success and on the self-relevance of the domain in which the role model achieved their successes. In addition, the accessibility of one’s best selves – one’s highest hopes and achievements – was found to undermine the inspiration derived from an upward comparison[77]. Also the emotional reactions to outstanding role models seem to vary as a function of both the attainability of the result and the perception of control in achieving it. Manipulating participants’ beliefs about self-improvements, Van de Ven, Zeelenberg, and Pieters[78] found that those who were primed with the idea that self-enhancement is easy felt more (benign) envy toward a fictitious outstanding model than those primed with the idea that self-enhancement is difficult. On the contrary, admiration was marginally stronger when self-improvement was thought to be difficult. As the leader-follower relationship is concerned, it is very likely that the domain in which leaders achieve their successes is relevant for followers’ self-concepts. Instead, what can actually vary between followers is the subjective attainability of the success, as well as the perceived control over the possibility to achieve it. Our findings suggest a wider and deeper analysis of the cognitive and affective processes underlying the variety of motivational consequences of the social comparison that employees make with their leaders. In addition, it is our opinion that the individual moderators of the relationship between leader’s competence and followers’ motivation should be explored. For example, people differ from each other in their dispositional tendency to compare with others[79], and the social comparison orientation was found to moderate the impact of role models on performance[80]. Similarly, the elicitor-emotion and the emotion-motivation relationships might be moderated by many individual and situational variables. Individuals might differentiate one another for the intensity at which they feel envy and admiration in response to the same situation. At the same time, other moderators might influence the relationship between admiration and state GOs. For example, it is reasonable to hypothesize that individuals respectively high in trait-Proving-Performance or trait-Learning-Performance GO will react differently to upward social comparisons, because these two individuals make a very different use of self- and external-referent feedbacks. Indeed, while the latter use self-referent information to appraise and evaluate their progress toward valued goals (e.g., the perception of mastery), the former makes a larger use of external-referent information such as feedbacks from their boss[81], which are perceived to be likely negative if the boss is very skilled. This reasoning might also explain why we in the second study we did not observe a relationship between admiration and state-Proving-Performance GO: It might be very hard to prove others that we are good at something when they are much better than we are. A second important result concerns the theory of admiration itself. Admiration, measured in actual work settings, was shown to outperform both happiness and gratitude in fostering not only the individual motivation to improve job performance, but also some important organizational citizenship behaviors. This result is very clear if we think that admiration is a social emotion, whose motivational consequences typically extend to the social context. Current results provide evidence that in organizational settings admiration produces two main behavioral effects: Self-improvement and prosocial behavior[24]. This finding demonstrates the necessity of carefully considering admiration and positive other-directed emotions in order to explain and promote virtuous organizational behavior.In addition, our results offer an original contribution to the flourishing research literature regarding leadership and positive emotions. They support and extend findings of[82], providing evidence that leaders influence followers’ emotions by their acts and behaviors, and not only by the contagion of their own affect. Competent leaders are role models who inspire their followers. The motivational state of inspiration originates from admiration, which therefore represents the emotional link between leaders’ skills and followers’ achievements. A link that is even more important because the direct effect of leaders’ skill on employees motivation is indeed negative. When no admiration is felt, the more a leader is skilled, the less employees are motivated to prove and improve their job performance.Finally, this paper contributes to the debate regarding the influence of leaders on followers’ goal orientation. This effect has already been theorized, but has never been actually tested. Dragoni[83] hypothesized that a leader’s achievement pattern orientation shapes followers’ state-GO through the mediation of team climate. Specifically, the author argues that when leaders display an ability-oriented achievement pattern orientation, followers feel encouraged to develop their proving goal orientation. We found that the leader’s display of competence increases both proving and improving goals. These effects can be explained by the mediation of admiration, whose peculiar motivational consequences are emulation, self-improvement, and achievement. Any time individuals feel admiration, both their improving and proving goals are likely to increase, as the emotional response to the perception of outstanding talents cause them to emulate the admired role model. Limits and directions for future researchAs regards methodological limitations, the risk of a common-source bias might have affected some results of our studies, so we recommend that future research extends these initial findings by using multiple sources of data (e.g. using supervisor’s evaluations as a measure of leader competence). However, study 2 is much less exposed to such a bias because if we assume that a common source biased our data, we also have to assume that it equally biased all the relationships among our variables (typically inflating them). Hence, a direct comparison such as one that investigates incremental validity (based on differences between strengths of associations) would not have been affected.Also, the two samples are heavily unbalanced in terms of gender. This limits the generalization of our results to a more balanced sample and prevented us to investigate whether gender moderates the relationships we identified in this article. Both the mediators and moderators of the relationship between leaders’ perceived competence and followers’ motivation deserve more research. One clear limit of these studies is that we did not consider competing emotional mediators such as envy, which has recently been found to be more related to task performance than admiration[78]. Envy might explain the detrimental effect of leader’s perceived competence on followers’ motivation. Envy is an unpleasant emotion characterized by feelings of inferiority, hostility and resentment that can arise when we compare unfavorably with others[84]. A wide variety of personal and contextual variables probably interact in determining whether a positive – admiration – or a negative – envy – emotion is triggered by the perception of an outstanding leader. Some of the most important are the actual and perceived distance between the leader’s and the follower’s skills, follower’s personality and motivational traits, and leader’s specific characteristics and behaviors. The latter might not only favor the feeling of envy, but also inhibit admiration. For example, a skilled but unfair leader might negatively impact employees’ motivation[85]. Further research is necessary to replicate our findings, to identify interactions between leaders’ features and their impact on employees, and to establish whether admiration can improve employees’ task performance.
References
| [1] | Frijda, N. H. (1986). The emotions. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. |
| [2] | Weiss, H. M., & Cropanzano, R. (1996). Affective Events Theory: A theoretical discussion of the structure, causes and consequences of affective experiences at work. Research in Organizational Behavior, 18, 1-74. |
| [3] | Dasborough, M. T. (2006). Cognitive asymmetry in employee emotional reactions to leadership behaviors. Leadership Quarterly, 17(2), 163-178. |
| [4] | George, J. M. (2000). Emotions and leadership: The role of emotional intelligence. Human Relations, 53(8), 1027-1055. |
| [5] | Damen, F., Van Knippenberg, B., & Van Knippenberg, D. (2008). Affective match in leadership: Leader emotional displays, follower positive affect, and follower performance. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 38(4), 868-902. |
| [6] | Pescosolido, A. T. (2002). Emergent leaders as managers of group emotion. Leadership Quarterly, 13(5), 583-599. |
| [7] | Ashkanasy, N.M., & Humphrey, R.H. (2011). Current emotion research in organizational behavior. Emotion Review, 3(2), 214-224. |
| [8] | Sadri, G., Weber, T.J., & Gentry, W.A. (2011). Empathic emotion and leadership performance: An empirical analysis across 38 countries. The Leadership Quarterly, 22, 818-830. |
| [9] | Luthans, F., Youssef, C. M., & Avolio, B. J. (2007). Psychological capital: Developing the human competitive edge. New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [10] | Vianello, M., Galliani, E. M., & Haidt, J. (2009). Elevation at work. The Effects of Leaders’ Moral Excellence. The Journal of Positive Psychology. 5(5), 390-411. |
| [11] | Chemers, M. M. (2000). Leadership research and theory: A functional integration. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research, and Practice, 4(1), 27-43. |
| [12] | Hollander, E. P. (1964). Leaders, groups, and influence. New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [13] | Hollander, E. P., &. Julian, J. W. (1970). Studies in leader legitimacy, influence, and innovation. In L. Berkowitz (Ed), Advances in experimental social psychology (pp. 33-69). New York: Academic Press. |
| [14] | Calder, B.J. (1977). An attributional theory of leadership. In B.M. Staw, & G.R. Salancik (Eds), New directions in organizational behavior (pp. 179–204). Chicago: St. Clair. |
| [15] | Staw, B. M. (1975). Attribution of the “causes” of performance: A general alternative interpretation of cross-sectional research on organizations. Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 13(3), 414-432. |
| [16] | Hogg, M. A., Hains, S. C., & Mason, I. (1998). Identification and leadership in small groups: Salience, frame of reference, and leader stereotypicality effects on leader evaluations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75(5), 1248-1263. |
| [17] | Avolio, B. J., & Bass, B. M. (1990). Developing potential across a full range of leadership. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc. |
| [18] | House, R.J. (1977). A 1976 theory of charismatic leadership. In J.G. Hunt & L.L. Larson (Eds.), Leadership: The cutting edge. Carbondale, IL: Southern Illinois University Press. |
| [19] | Bass, B.M., & Avolio, B.J. (1990). The implication of transformational and transactional leadership for individual, team, and organizational development. In R.W. Woodman, & W.A. Passmore (eds.), Research in Organizational Change and Development. Greenwich, CT: JAI Press (pp. 231-271). |
| [20] | McCann, J. A. J., Langford, P. H., & Rawlings, R. M. (2006). Testing Behling and McFillen's Syncretical Model of charismatic transformational leadership. Group & Organization Management, 31(2), 237-263. |
| [21] | Ortony, A., Clore, G. L., & Collins, A. (1988). The cognitive structure of emotions. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. |
| [22] | Haidt, J., & Keltner, D. (2004). Appreciation of beauty and excellence. In C. Peterson, & M. E. P. Seligman (Eds), Character strengths and virtues (pp. 537-551). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. |
| [23] | Keltner, D., & Haidt, J. (2003). Approaching awe, a moral, spiritual, and aesthetic emotion. Cognition and Emotion, 17(2), 297-314. |
| [24] | Algoe, S. B., & Haidt, J. (2009). Witnessing excellence in action: the “other-praising” emotions of elevation, gratitude, and admiration. Journal of Positive Psychology, 4(2), 1-23. |
| [25] | Henrich, J., & Gil-White, F. (2001). The evolution of prestige: Freely conferred deference as a mechanism for enhancing the benefits of cultural transmission. Evolution and Human Behavior, 22, 165-196. |
| [26] | Thrash, T.M., & Elliot, A.J. (2003). Inspiration as a psychological construct. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(4), 871-889. |
| [27] | Thrash, T.M., & Elliot, A.J. (2004). Inspiration: Core characteristics, component processes, antecedents, and function. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 87(6), 957–973. |
| [28] | Haidt, J. (2003). The moral emotions. In R. J. Davidson, K. R. Scherer, & H. H. Goldsmith (Eds), Handbook of affective science (pp. 852-870). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. |
| [29] | Tangney, J.P., Stuewig, J., & Mashek, D.J. (2007a). What’s moral about the self-conscious emotions? In. J. L. Tracy, R. W. Robins, & J. P. Tangney (Eds), The self-conscious emotions: Theory and research (pp. 21-37). New York: Guilford Press. |
| [30] | Tangney, J.P., Stuewig, J., & Mashek, D.J. (2007b). Moral emotions and moral behavior. Annual Review of Psychology, 58, 345-372. |
| [31] | Avolio, B. J., & Bass, B. M. (1993). Manual: the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologist Press. |
| [32] | Bass, B.M. (1985). Leadership and performance beyond expectations. New York: Free Press. |
| [33] | Dweck, C. S. (1986). Motivational processes affecting learning. American Psychologist, 41(10), 1040-1048. |
| [34] | Farr, J. L., Hoffman, D. A., & Ringenbach, K. L. (1993). Goal orientation and action control theory: Implications for industrial and organizational psychology. International Review of Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 8, 193-232. |
| [35] | Roberson, L., & Alsua, C. J. (2002). Moderating effects of goal orientation on the negative consequences of gender-based preferential selection. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 87(1), 103-135. |
| [36] | Brown, K. G. (2001). Using computers to deliver training: Which employees learn and why? Personnel Psychology, 54(2), 271-296. |
| [37] | VandeWalle, D., & Cummings, L. L. (1997). A test of the influence of goal orientation on the feedback-seeking process. Journal of Applied Psychology, 82(3), 390-400. |
| [38] | Phillips, J. M., & Gully, S. M. (1997). Role of goal orientation, ability, need for achievement, and locus of control in the self-efficacy and goal-setting process. Journal of Applied Psychology, 82(5), 792-802. |
| [39] | Gully, S. M., & Phillips, J. M. (2005). A multilevel application of learning and performance orientations to individual, group, and organizational outcomes. In J. J. Martocchio (Ed), Research in personnel and human resources management (pp. 1-51). US: Elsevier Science / JAI Press. |
| [40] | Potosky, D., & Ramakrishna, H. V. (2002). The moderating role of updating climate perceptions in the relationship between goal orientation, self-efficacy, and job performance. Human Performance, 15(3), 275-297. |
| [41] | Dweck, C. S., & Leggett, E. L. (1988). A social-cognitive approach to motivation and personality. Psychological Review, 95(2), 256-273. |
| [42] | Button, S.B., Mathieu, J.E. & Zajac, D.M. (1996). Goal orientation in organizational research: A conceptual and empirical foundation. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 67(1), 26-48. |
| [43] | Elliot, A. J. (1994). Approach and avoidance achievement goals: An intrinsic motivation analysis. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Wisconsin - Madison. |
| [44] | VandeWalle, D. (1997). Development and validation of a work domain goal orientation instrument. Journal of Educational and Psychological Measurement, 57(6), 995-1015. |
| [45] | Dweck, C. S. (1999). Self-theories: Their role in motivation, personality, and development. Philadelphia: Psychology Press. |
| [46] | Cron, W., Slocum, J., VandeWalle, D., & Fu, Q. (2005). The role of goal on negative emotions and goal setting when initial performance falls short of one’s performance goal. Human Performance, 18(1), 55-80. |
| [47] | Payne, S. C., Youngcourt, S. S., & Beaubien, J. M. (2007). A meta-analytic examination of the goal orientation nomological net. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(1), 128-150. |
| [48] | DeShon, R. P., & Gillespie, J. Z. (2005). A Motivated Action Theory Account of Goal Orientation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(6), 1096-1127. |
| [49] | Yukl, G.A. (2002). Leadership in organizations (5th edition). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall. |
| [50] | Bandura, A. (1969). Social-Learning Theory of identificatory processes. In D.A. Goslin (ed), Handbook of socialization. Rand McNally & Company (pp. 213-262). |
| [51] | Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundation of thought and action. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall. |
| [52] | Shamir, B., House, R. J., & Arthur, M. B. (1993). The motivational effects of charismatic leadership: A self concept based theory. Organization Science, 4(4), 577-594. |
| [53] | Cuddy, A. J. C., Fiske, S. T., & Glick, P. (2007). The BIAS map: Behaviors from intergroup affect and stereotypes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 92(4), 631-648. |
| [54] | Cuddy, A., Fiske, S., & Glick, P. (2008). Warmth and competence as universal dimensions of social perception: The stereotype content model and the BIAS Map. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 40, 61-149. |
| [55] | VandeWalle, D., Cron, W. L., & Slocum, J. W. (2001). The role of goal orientation following performance feedback. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(4), 629-640. |
| [56] | Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling methods for estimating and comparing indirect effects. Behavior Research Methods, 40, 879-891. |
| [57] | Zelenski, J. M., Murphy, S. A., & Jenkins. D. A. (2008). The happy-productive worker thesis revisited. Journal of Happiness Studies, 9(4), 521-537. |
| [58] | Graham, C., Eggers, A., & Suckhtanker, F. (2004). Does happiness pay? An exploration based on panel data from Russia. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, 55, 319-342. |
| [59] | Lucas, R. E., Clark, A. E., Georgellis, Y., & Diener, E. (2004). Unemployment alters the set point for life satisfaction. Psychological Science, 15(1), 8-13. |
| [60] | Thoits, P. A., & Hewitt, L. N. (2001). Volunteer work and well-being. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 42(2), 115-131. |
| [61] | George, J. M. (1991). State or trait: Effects of positive mood on prosocial behaviors at work. Journal of Applied Psychology, 76(2), 299–307. |
| [62] | Emmons, R. A. (2004). The psychology of gratitude: An introduction. In R. A. Emmons, & M. E. McCullough (Eds), The psychology of gratitude (pp. 3-16). New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [63] | McCullough, M. E., Kilpatrik, S. D., Emmons, R. A., & Larson, D. B. (2001). Is gratitude a moral affect? Psychological Bulletin, 127(2), 249-266. |
| [64] | McCullough, M. E., & Tsang, J. A. (2004). Parent of the virtues? The prosocial contours of gratitude. In R. A. Emmons, & M. E. McCullough (Eds), The psychology of gratitude (pp. 123-141). New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [65] | Buck, R. (1985). Prime theory: An integrated view of motivation and emotion. Psychological Review, 92(3), 389-413. |
| [66] | Buck, R. (1989). Emotional communication in personal relationships: A developmental-interactionist view. In C. Hendrick (Ed), Close relationships (pp. 144-163). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. |
| [67] | Weiner, B. (2005). Social motivation, justice, and the moral emotions: An attributional approach. Lawrence Earlbaum: Mahwah, NJ. |
| [68] | Organ, D.W. (1997). Organizational citizenship behavior: It’s construct clean-up time. Human Performance, 10(2), 85–97. |
| [69] | Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Paine, G. B., & Bachrach, D. G. (2000). Organizational citizenship behaviors: A critical review of the theoretical and empirical literature and suggestions for future research. Journal of Management, 26(3), 513-563. |
| [70] | Watson, D., & Clark, L. A. (1994). The PANAS-X: Manual for the positive and negative affect schedule-expanded form. Iowa: The University of Iowa. |
| [71] | Emmons, R. A., & McCullough, M. E. (2003). Counting blessings versus burdens: An experimental investigation of gratitude and subjective well-being in daily life. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(2), 377-389. |
| [72] | Konovsky, M. A., & Organ, D. W. (1996). Dispositional and contextual determinants of organizational citizenship behavior. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 17(3), 253-266. |
| [73] | Smith, C. A., Organ, D. W., & Near, J. P. (1983). Organizational citizenship behavior: Its nature and antecedents. Journal of Applied Psychology, 68(4), 653-663. |
| [74] | Pond, S. B. III, Nacoste, R. W., Mohr, M. F., & Rodriguez, C. M. (1997). The measurement of organizational citizenship behavior: Are we assuming too much? Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 27(17), 1527-1544. |
| [75] | Bass, B. M., & Avolio, B. J. (1994). Improving organizational effectiveness through transformational leadership. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. |
| [76] | Lockwood, P., & Kunda, Z. (1997). Superstars and me: Predicting the impact of role models on the self. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 73(1), 91-103. |
| [77] | Lockwood, P., & Kunda, Z. (1999). Increasing the salience of one’s best selves can undermine inspiration by outstanding role models. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76, 214-228 |
| [78] | Van de Ven, N., Zeelenberg, M., & Pieters, R. (2011). Why envy outperforms admiration. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 37(6), 784-795. |
| [79] | Gibbons, F. X., & Buunk, B. P. (1999). Individual differences in social comparison: The development of a scale of social comparison orientation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76, 129-142. |
| [80] | Buunk, A. P., Peiro, J. M., & Griffioen, C. (2007). A positive role model may stimulate career-oriented behavior. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 37, 1489-1500. |
| [81] | Nicholls, J. G. (1975). Causal attributions and other achievement-related cognitions: Effects of task outcome, attainment value, and sex. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 31(3), 379-389. |
| [82] | Bono, J. E., Foldes, H. J., Vinson, G., & Muros, J. P. (2007). Workplace Emotions: The Role of Supervision and Leadership. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92, 1357–1367 |
| [83] | Dragoni, L. (2005). Understanding the emergence of state goal orientation in organizational work groups: The role of leadership and multilevel climate perceptions. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(6), 1084-1095. |
| [84] | Smith, R. H., & Kim, S. H. (2007). Comprehending envy. Psychological Bulletin, 133, 46-64 |
| [85] | Weaver, G. R., Treviño, L. K., & Agle, B. (2005). “Somebody I look up to”: Ethical role models in organizations. Organizational Dynamics, 34(4), 313-330. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML