-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry
p-ISSN: 2165-882X e-ISSN: 2165-8846
2016; 6(3): 103-108
doi:10.5923/j.ijaf.20160603.01

Systematical Identification of Insect Pests and Predator on Crops in Sibut (Central African Republic)
Wango Solange Patricia1, Aba-Toumnou Lucie2, Mpembily Fabrice Procor1, Bolevane-Ouantinam Serge Florent1, Lakouèténé Didier Ponel-Béranger2, Mborohoul Jean Benoit3, Yongo Olga Diane4
1Laboratory of Applied Animal Biologyand Biodiversity, University of Bangui, Central African Republic
2Laboratory of Biological and Agronomical Sciences for Development, Bangui, Central African Republic
3Ministry of Agriculture Development, Central African Republic
4Laboratory of Plant and Fungi Biodiversity, Faculty of Sciences, University of Bangui, Central African Republic
Correspondence to: Aba-Toumnou Lucie, Laboratory of Biological and Agronomical Sciences for Development, Bangui, Central African Republic.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

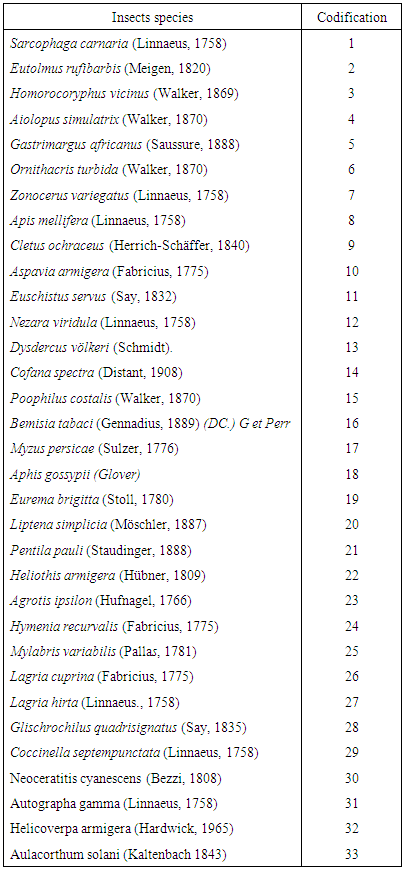
Crop production is constrained by pests and diseases which severely impacts the quantity and quality available in the value chain in the world. The hypothesis of this work was that crop production in Sibut is or not affected by the pests. The data were analyzed by a factor analysis of correspondence formed by two groups of crops/ Insects species. The Group I contained sensitive insects to Lycopersicum esculentum, Abelmoschus esculentus and Capsicum annuun. There were: Sarcophaga carnari, Eutolmus rufibarbis, Homorocoryphus vicinus, Aiolopus simulatrix, Gastrimargus africanus, Ornithacris turbida, Zonocerus variegatus, Apis mellifera, Cletus ochraceus, Euschistus servus, Nezara viridula, Dysdercus völkeri, Cofana spectra, Poophilus costalis, Bemisia tabaci, Myzus persicae, Aphis gossypii, Liptena simplicia, Pentila pauli, Heliothis armigera, Hymenia recurvalis, Mylabris variabilis, Lagria cuprina, Lagria hirta, Glischrochilus quadrisignatus, Coccinella septempunctata, Neoceratitis cyanescens, Autographa gamma and Helicoverpa armigera.The group II contained sensitive insects to Arachis hypogaea and Zea mays. There were: Cletus ochraceus, Eurema brigitta, Agrotis ipsilonand Aulacorthum solani. The result obtained could be useful as a baseline for further research on control of insect pests in the affected areas in Sibut.
Keywords: Biodiversity, Insect pest, Predator
Cite this paper: Wango Solange Patricia, Aba-Toumnou Lucie, Mpembily Fabrice Procor, Bolevane-Ouantinam Serge Florent, Lakouèténé Didier Ponel-Béranger, Mborohoul Jean Benoit, Yongo Olga Diane, Systematical Identification of Insect Pests and Predator on Crops in Sibut (Central African Republic), International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, Vol. 6 No. 3, 2016, pp. 103-108. doi: 10.5923/j.ijaf.20160603.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The Central African Republic (CAR) is situated just north of the Equator with daily temperatures normally reaching at least 30 degrees Celsius. About 80% of CAR’s population lives in rural areas and relies on agriculture for most of its income. Nearly half the country’s 4 million people are poor or unable to meet their daily nutritional requirements [1]. The bulk of CAR agriculture remains traditional land holdings are small, crop production is labour intensive, little or no external inputs are used [2]. Organic agricultural systems are characterized by a large biodiversity and high complexity. Biodiversity is often associated with a wide variety of entomophagous insects [3, 4]. Pests are one of the major constraints to agricultural production in the world and CAR is no an exception [5]. A large number of insect and mite pests attack crops during all stages of growth seedling to storage. Effects of insect pests on crops include reduction of yield, transmission of diseases, reduction of market yield and increase in farm cost [6, 7, 8]. It is important to survey insect pest, because routine use of control measures (i.e. chemical, cultural or both) without taking into consideration the pest density is economically wasteful, also environmentally hazardous chemicals (that destroys natural enemies and other beneficial insects) and toxic contaminants are introduced into the soil thus causing pesticide resistance [9, 10]. The aim of this study is the systematical identification of pests and predator in the farms that devour some common crops to in order to have an informed decision which might be of great benefit to both the farmers as well as the entire for the purpose of food security in Sibut area.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Choice of Surveyed Sites
- The latitude and longitude of Sibut (figure 1) are respectively N: 5° 56' 49" and E: 18° 46' 29". In Sibut, the agricultural system is predominantly a mixed system with livestock and cultivation of annual and perennial crops. The mains crops are cassava, leaf and fruit vegetables, peanut, bean, corn, which covers approximately 80% of the total cropland. Sibut has been considered for this study because of it high production of leaf and fruit vegetables and few study were realized according the pests identification [11].
 | Figure 1. Location of sites for insects’ collection in Sibut |
2.2. Sample Collection and Insect Identification
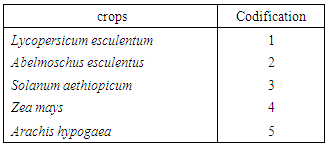
- The 6 farms selected for this study have not suffered any phytosanitary treatment during the entire test period. The plants (Lycopersicum esculentum, Abelmoschus esculentus, Solanum aethiopicum, Zea mays and Arachis hypogaea) were sampled at seedling stage, vegetative stage, flowering stage, fruiting stage and at harvest of the cultivated vegetable crops. The insect trapping was conducted from transplanting stage to fruition and maturity of the fruit. The two different fields that were laid traps had an area of 400 m2 (20m x 20m) at least. Data collection is weekly and for three months. Each farm selected for the survey was divided into four quadrants and from each part four plants were selected at random within the square meter. After quick visual count of the insects on the plants, they were then captured from those plants and taken to the laboratory for identification. Population size of each of the insect species was also taken into consideration. Materials and methods used for collecting insect samples include swoop nets for flying insects, aspirators for collecting tiny insects, pair of forceps and hand picking for larvae and slow moving insects. Polythene bags, specimen tubes and rearing jars were used to transfer the insects to the laboratory and alcohol (70%) was used to preserve them for identification.Morphological identification of pest was done using hand lens and microscope, and utilizing identification keys [12, 13, 14, 15].
2.3. Statistical Analyses
- A factorial analysis of correspondence with the software R (R version 2.15.1) was used to identify the relation between species of crops and species of insects.
3. Results
3.1. Insects Families Identified
- Insects of the families of Pieridae, Aleurodidae, Coccinellidae are the important in the selected farms of experience in Sibut (figure 2).
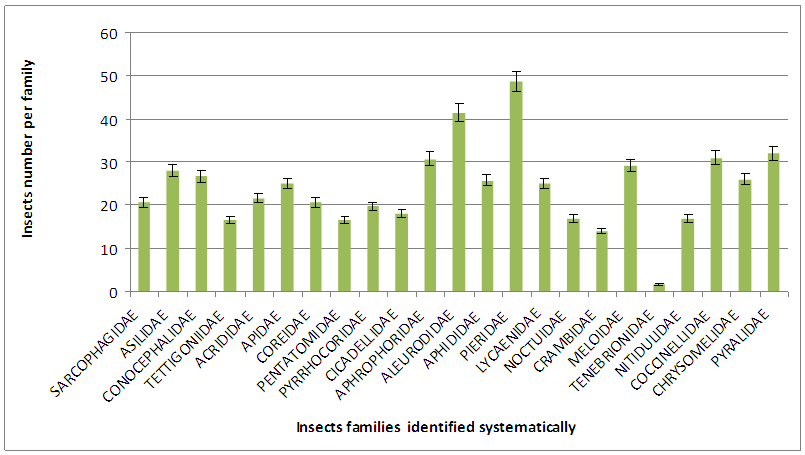 | Figure 2. Insects families identified |
3.2. Insects Species and Crops Relation
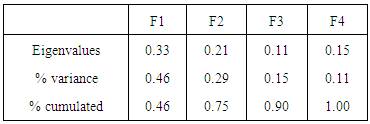
- The eigenvalues of the principal axes extracted from the factor analysis of correspondence indicated that the first two factors explained 75% of the matrix crops / Insects species information (tables 1 and 2). The factorial plane formed by these two axes (component 1 and component 2) defined two groups of crops/ Insects species (figure 3). The Group I contained sensitive insects to Lycopersicum esculentum, Abelmoschus esculentus and Capsicum annuun. There were: Sarcophaga carnari, Eutolmus rufibarbis, Homorocoryphus vicinus, Aiolopus simulatrix, Gastrimargus africanus, Ornithacris turbida, Zonocerus variegatus, Apis mellifera, Cletus ochraceus, Euschistus servus, Nezara viridula, Dysdercus völkeri, Cofana spectra, Poophilus costalis, Bemisia tabaci, Myzus persicae, Aphis gossypii, Liptena simplicia, Pentila pauli, Heliothis armigera, Hymenia recurvalis, Mylabris variabilis, Lagria cuprina, Lagria hirta, Glischrochilus quadrisignatus, Coccinella septempunctata, Neoceratitis cyanescens, Autographa gamma and Helicoverpa armigera (table 3).The group II contained sensitive insects to Arachis hypogaea and Zea mays. There were: Cletus ochraceus, Eurema brigitta, Agrotis ipsilon and Aulacorthum solani (table 3).
|
|
|
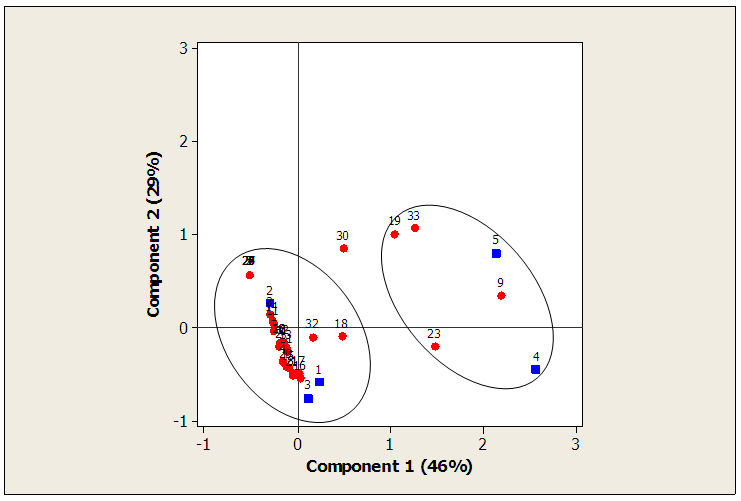 | Figure 3. Crops /insects by a factorial analysis of correspondence (FAC) |
3.3. Discussion
- The aim of this study is the systematical identification of pests in the farms that devour some common crops in Sibut. The study was carried on Lycopersicum esculentum, Abelmoschus esculentus, Solanum aethiopicum, Zea mays and Arachis hypogaea. 33 insects belonging to 23 families were identified. Insects of the families (figure 2) of Pieridae, Aleurodidae, Coccinellidae are more likely than others families in the selected farms of experience in Sibut. Lycopersicum esculentum (tomato), Abelmoschus esculentus and Solanum aethiopicum are the crops were more likely sensitive by the all families of insects than Arachis hypogaea and Zea mays.Some work [16, 17, 18, 19] showed that the tomatoes are subject to attack by a large number of insect pests from the time plants first emerge in the seed bed until harvest. Aphids, flea beetles, leaf miners, and spider mites threaten young plant-bed tomatoes. In the field, flea beetles, aphids, leaf miners, stink bugs, and fruit worms cause minimal damage to the foliage. However, severe damage may result either from their feeding on the fruit or by spreading certain diseases. The first is damage due to biting and chewing of plant materials. The groups of insects concerned are Orthoptera (grasshoppers, locusts, crickets), larvae of Lepidoptera (Caterpillar), adult and larvae of many beetles (Coleoptera) and other dipteran larvae [20, 21]. The second is damage due to sucking of the plant sap from the phloem (or xylem) system or from general tissues of foliage, roots or fruits. The main group of insects concerned is Hemiptera (bugs) and the Thysanoptera (thrips) [17]. Effects of insect pests on crops include reduction of yield, transmission of diseases, reduction of market yield and increase in farm cost. Insect pest with a wide host range will be able to multiply on different varieties of plants, attacking both leafy and succulent types like spinach and tomatoes belonging to Chenopodiaceae and Solanaceae families [22, 23]. In our work, Aphis gossypii (A. gossypii) is sensitive to Lycopersicum esculentum, Abelmoschus esculentus and Solanum aethiopicum. In general A. gossypii is a minor pest of cotton and vegetables in the world [24]. The pest prefers to attack the tender shoots and the lower of the young leaves of the host plant but it can also exist on older leaves. A heavy infestation leads, especially on cotton, okra, cucurbits, to leaf curl and stunting in growth. The honeydew, which is produced by the aphids in considerable amounts, collects on the upper surface of the leaves. The honeydew can also attract the moths of Heliothis armigera, which take it up as food [25].However, locally, it may reach the status of a major pest if the application of unselective insecticides against other pests destroys the natural enemies of the aphids and may increase its fecundity [26]. A. gossypii can also play an important role as vector of viruses especially on cucurbits [27, 28]. Abelmoschus esculentus is subject to attack by White flies (Bemisia tabaci), and Aphids (A. gossypii). These pests infest leaves, stems, branches and pods during the rainy season in CAR.The Coccinellidae family is one of important predator in this work. Augmentative biological control has been performed in open fields with cultivated crops, vegetables and fruits around the world [29]. Many predators and parasitoids of arthropod pests are facultative or obligate omnivores in that they may include plant-derived foods such as pollen, nectar, extra-floral nectar, or honeydew in their immature, and/or adult diet .Dispersal of predators or parasitoids from selected release points should be great enough to allow discovery of potential hosts, on the other hand, a propensity of parasitoids or predators to disperse can result in reduced effectiveness in controlling pests [30]. Many predators and parasitoids of arthropod pests are facultative or obligate omnivores in that they may include plant-derived foods such as pollen, nectar, extra-floral nectar, or honeydew in their immature, and/or adult diet ([30]; [31, 32, 33]. Alternative foods such as lepidopteran and coleopteran immatures [34, 35] and non-prey foods [36] are critical components of optimal diets in most coccinellids, and shape the natural histories of these and other predators [30]. As a group, coccinellids are extremely polyphagous; and it is increasingly apparent that species and individuals are in many instances quite polyphagous as well. The simple fact is that there is not a single species for which the entire dietary breadth is known. The abundance, dispersion, and pest management benefits of Coccinellids are influenced by their suite of natural enemies. Parasitoids, parasites (mites) and pathogens (nematodes, viruses, protozoa, bacteria, and fungi) are widespread in many Coccinellid populations [37], and their geographic and host ranges have expanded with the anthropogenic redistribution of coccinellids used in biological control.
4. Conclusions
- The most important implication of this study is the indication that Lycopersicum esculentum, Abelmoschus esculentus, Solanum aethiopicum, Zea mays and Arachis hypogaea in Sibut might be contaminated with insects pest, which continue to develop and proliferate to varying degrees depending on the type of crops. The predators are also documented. The result obtained could be useful as a baseline for further research on control of insect pests in the affected areas, in order to have an informed decision which might be of great benefit to both the farmers as well as the entire nation economically and for the purpose of food security.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors extend profound thanks and gratitude to the Direction and technical staff of Youth United for the Protection of the Environment and Community Development (JUPEDEC) for providing funding for this research. Studies on insect pests were carried out within the framework of an official agreement between the Laboratory of Applied Animal Biology and Biodiversity of the University of Bangui and JUPEDEC.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML