-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry
p-ISSN: 2165-882X e-ISSN: 2165-8846
2014; 4(5): 394-401
doi:10.5923/j.ijaf.20140405.08

Economic Valuation of Environmental Resources in Hamoon International Wetland, Using the Choice Experiment Method
Majid Dahmardeh 1, Javad Shahraki 2
1Department of Agricultural Economics, University of Sistan and Baluchestan, University of Payame Noor, Iran
2Department of Agricultural Economics, University of Sistan and Baluchestan, Iran
Correspondence to: Javad Shahraki , Department of Agricultural Economics, University of Sistan and Baluchestan, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

For implementing the conservation project of the wetlands in Iran, Hamoon wetland and its satellite wetlands were selected as one of the sample sites in partnership with UNDP. It aimed to reduce the major threats facing this wetland using a comprehensive management plan. This study examines and explores the citizens' preferences and willingness to pay in Sistan plain to improve the environmental characteristics of Hamoon wetland using the choice experiment method. Required data and information were achieved from the citizens of Sistan in 2013 and the mixed logit model was used for analyzing them. The results showed that the maximum willingness to pay belongs to improvement of water level of the current crisis to the desired level (26,000 Rials per year for each family). Achieving optimum water quality (straw rate), the number of ducks and Amur fish in the wetland (23,000, 14,670, and 11,300 Rials / year per family, respectively) are placed in the next rows of people’s willingness to pay.
Keywords: Choice experiment, Willingness to pay, Hamoon wetland, Mixed logit model
Cite this paper: Majid Dahmardeh , Javad Shahraki , Economic Valuation of Environmental Resources in Hamoon International Wetland, Using the Choice Experiment Method, International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, Vol. 4 No. 5, 2014, pp. 394-401. doi: 10.5923/j.ijaf.20140405.08.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- From the perspective of economists and ecologists, valuation of natural resources and environmental systems follows some goals such as knowledge and understanding of ecological and environmental benefits by human, presentation of the environmental issues of the country to decision-makers and planners, link between economic policies, and natural income. It also seeks for modification of national measures such as GDP and avoidance of damage and uncontrolled exploitation of these resources [16]. Attempts done to estimate the monetary value of environmental resources such as wetlands and lakes has a double role in caused by a mutual management of human and natural systems. at the micro level, valuation studies provides an access to information related to the structure and function of ecosystems and their diverse and complex role in supporting human well-being. In the macro level, valuation of ecosystem can create and modify the parameters that contribute to human welfare and sustainable development [20]. The choice experiment has mostly developed in economics and marketing to determine consumer preferences for products with multiple features [24].Recently, the application of this method has expanded more than other fields such as environmental management and now it has become a common tool for environmental valuation [6, 17]. In some studies, due to lack of data and real markets for public goods, it is difficult to quantify in monetary units, so the risk of ignoring them increases in decision-making process. In most cases, the contingent valuation method [6] is used to estimate consumer willingness to pay for nonmarket goods. In this situation, valuation of each feature in multi-attitude goods is almost impossible [5]. For example, CV damage incurred by the use of Hamoon wetland has some impacts on wetland water levels as well as wildlife. Here, contingent is able to evaluate and estimate the overall value of wetland conservation, but it cannot avoid their effects on its own. Therefore, the choice experiment as an alternative approach for the stated preference approach can identify the value of any individual characteristics [5].In environmental economic studies, choice experiment has had several applications in the field of forests, wetlands, energy, water resources, seas, and air quality in recent years some of which are mentioned in wetlands. In order to reflect the preferences of people on the ways used for developing a wetland in southern Sweden, Carlsson et al. [12] used the choice experiment. The results obtained from estimating the Conditional logit model [1] and the random parameter logit [2] show that biodiversity and convenient walking facilities have the greatest positive impact on the utility and people’s willingness to pay, whereas construction of sea walls and presence of king prawns in a wetland leads to reduction of welfare among people. Othman et al. [30] determined willingness to pay among Malaysian households to set optimal management strategies for Matang- mangrove wetlands in Perak state, Malaysia as Euro 2.7- 3. Birol et al [8] used the choice experiment to estimate the value of economic, social, and ecological functions in Cheimaditida wetlands in Greece. The results show that from the Greeks point of view, biodiversity and retraining people had the most and the least importance, respectively. Smyth et al. [34] also used the choice experiment to assess individuals' preferences regarding management scenarios for Champlain Lake, the U.S., and Canada. The findings show that healthy fish consumption encompasses the bulk of the respondents’ utility. In another study, Eggert and Olsson [13] attempted to estimate the economic benefits obtained from improved water quality in west coast of Sweden. They found out that environmental concerns are highly significant for the responders and have the highest value to avoid the loss of biodiversity and fish stocks. Westerberg et al. [38] used the choice experiment to facilitate decision- making process for policy makers in the managing Marais Des Baux wetland in southern France. The results of estimating the logit model for random parameters and calculating the willingness to pay show that one-third restoration of the wetland, biological control of insects, dense vegetation, recreational facilities, and high levels of biodiversity are among the most important factors. In their research, Liu and Wirtz [23] considered the management practices of the oil spill in the North Sea of Germany. They also observed that environmental attributes including quality of the beaches (Euro 0.7/ km), sea birds (Euro 0.0069/ bird), and the ratio of oil collected from the sea (Euro 1.23/ ton) had a greater impact on household utility than the seawater quality (Euro 0.32/ km2). Wallmo and Liu [37] analyzed the optimization value of endangered and threatened marine species in terms of American households in a national level. The results show different preferences of people for recovery of fish species and seals. It was recognized that differences in WTP depend on the species and its recovery level. Firouz Zare and Gorbani [3] used the time data collected through field survey in Mashhad and employed the choice experiment approach and overlapping logit model to examine welfare effects of policy changes on air pollution. The results referred to high importance of health effects and air pollution from the perspective of the citizens.Hamoon wetland is one of the most important international wetlands and the largest freshwater lake throughout the Iranian plateau. Its area is about 5,700 square kilometers and its depth ranges from 1 to 5 m in desert and arid areas of the East of the country, Sistan, within E6039 to E 633535 and N3115 to N3132. It has significant economic, cultural and aesthetic, recreational, scientific, and protective and ecological values. Its rich biodiversity is one of its most evident values. In fact, it is the hometown of a freshwater fish species (Amur) and the habitat of thousands of seasonal migratory birds [1]. The recent drought periods have dropped the wetland’s water level dramatically and a vast area of the land is subject to wind erosion, which has brought a sharp decline in fish population and consequently, has reduced acceptance of the migratory birds. These factors have lowered the quality of ecosystems and have threatened its capacity and ability to provide ecological, economic, and social functions. Regarding the importance and the specific and critical ecological conditions of the wetland, Hamoon Comprehensive Management Plan was codified to create a unified frame for planning and implementing of the national and provincial institutions within the catchment area. It also considered the principles of ecosystem management. This program consists of three managerial objectives: (1) Increasing awareness of the wetland values and enhancing community participation in its management (2) establishing sustainable management of water resources and agricultural land (3) Biodiversity conservation and sustainable use of the wetland resources. For each of these objectives, the main priorities and related measures are defined [1]. Regarding the point that resources available for the management of Hamoon wetland are limited just the same as any other similar ecosystem and since designing such a wide program of management requires a demand for intense competition in various fields, analysis of social tendency about managerial decision between multiple scenarios seems quite necessary. International experience shows that sustainability of natural resources such as wetlands and lakes primarily depends on the level of community participation in their management. Therefore, local communities should be involved in Hamoon wetland conservation and management [1]. In this research, the preferences and citizens’ willingness to pay are evaluated, using the choice experiment, to improve the environmental characteristics of Hamoon wetland in Sistan. Undoubtedly, reflecting the obtained information and results will contribute to the formation of efficient and sustainable management policies accepted and supported by the public.
2. Materials and Methods
- The choice experiment, a subset of the stated preference methods, is a multi-attitude selection and selection modeling. In a multi-attitude approach, it is believed that in order to understand a person's willingness to perform transactions and balances, it is possible to use environmental attitudes and features characteristics of products. CE can be considered as a multi- option version of the conditional valuation in which goods and services are described by the attitudes of these attributes and levels. In this method, there are several selection series. Each of them has two or more options. These choices are presented to the respondents and they are asked to select their preferred option. A number of attributes or characteristics of goods describe each choice and these attributes can have different levels by themselves. One of these attributes in most cases is price in which a basis that is consistent with the status quo can be observed [33]. Like contingent valuation, the choice experiment is able to estimate the total economic value of environmental goods and services. CE has greater flexibility in estimating the value of environmental services than CV and in comparison with CV, it provides more information with a much smaller sample size. Moreover, some common CV biases such as Strategic bias, Positive response bias, and Effects of surrounding are removed [9]. The choice experiment is founded based on Lancaster value features’ theory [22] and Random utility theory (RUT) [26, 29]. Lancaster believes that desirability of a product can be analyzed into desirability resulted from the features of the product. Random utility models are Econometric models of discrete choice in which it is assumed where all respondents have accurate and thorough understanding whereas the analyzer does not have enough information and inevitably, he will face the problem of uncertainty [28]. According to Random utility theory, the resulted desirability is composed of a selection, a particular component, and a disturbing component. So an indirect utility function M can be divided into two parts: (1) a certain element (agent) which is selected as a linear function from the attributes (Xi) of Jth choice in the selection series, and (2) a random element (e)which shows imperceptible impacts on individual choices [15, 27, 29].
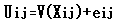 | (1) |
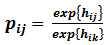 | (2) |
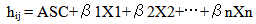 | (3) |
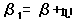 the desirability of each option will be: [18 and 35]
the desirability of each option will be: [18 and 35]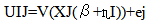 | (4) |
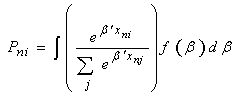 | (5) |
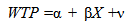 | (6) |
 | Table 1. Evaluated Attitudes and Levels in Hamoon Wetland |
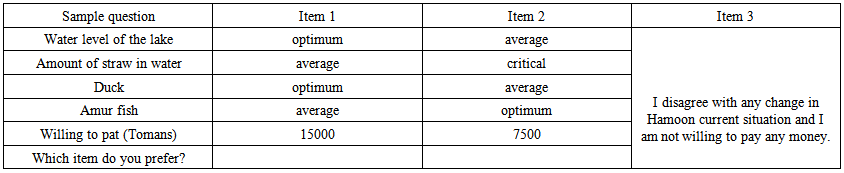 | Figure 1. A Sample of Selection Series |
3. Results and Discussion
- According to the available statistics (Table 2), the average years of residence of the respondents in Sistan was 18.25 years of which %76 had visited Hamoon wetland more than 3 times. The average household size was 4.9 people, average monthly household income was 5,655,000 Rials, and the number of years of education was 13 years. Assessment of environmental trends used a series of statements such as interest rate of reading environmental publications, watching videos and programs related to the environment, wishing to visit the natural aqua scenery, and choosing eco-friendly products while purchasing. The respondents were asked to express their interest rate for the above- mentioned topics in Likert’s five scopes. During data extraction, five codes were used, 0 as the least and 4 as the most favorite. The population’s environmental trends were determined by using the mean and standard deviation showing that % 16, %46, %20.8, %16.8 of people had strongly negative, negative, positive and strongly positive tendencies.
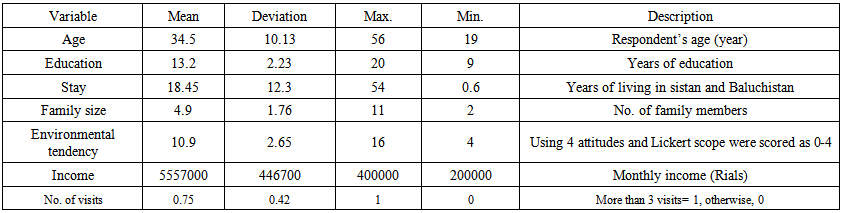 | Table 2. Results of Descriptive Statistics of Respondents |
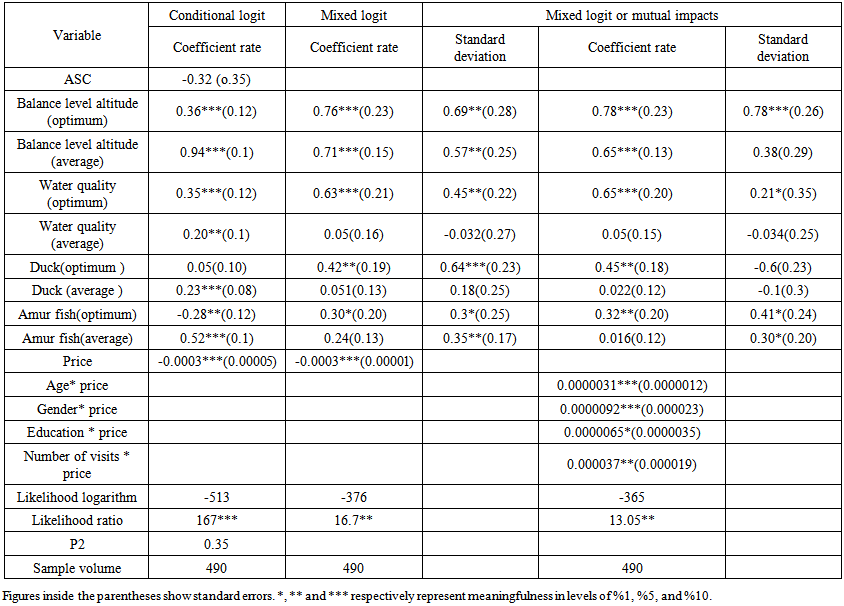 | Table 3. Results of Mixed and Conditional Logit Models |
4. Results of Mixed Logit Model
- In this model, all attitudes with a normal distribution, except price, were considered based on resources [32, 35]. The results are shown in the second column of Table 3. It shows that there is no conprehensive preference in average levels of attitudes such as water quality, ducks, and Amur fish. Signs of the coefficients supply theoretical expectations, and quite reasonably increase higher levels of attitudes and the possibility of selecting the managerial scenarios. The negative sign of price means that items with higher bids reduce people’s utility and compared with other options, it has lower selection probability. Statistical significance of the calculated standard deviations for high levels of qualitative and quantitative features of water, number of ducks and both feature levels of Amur show their unequal preferences. They also focus on the possibility of reverse preferences for these attitudes, i.e., some respondents with lower levels of these attitudes have more utility, whereas they are not enough to overcome the views and preferences of majority of the samples; therefore, the estimated standard deviations are not so high to change the overall marks of the coefficients. Ultimately, it is worth to note that the samples preferred high levels of these environmental attitudes, whereas the mixed logit model considers the unobserved inconsistency of the preferences and it cannot recognize those who are not affected any political changes. In other words, this inconsistency is unclear [11]. In order to get a general view of the reasons and resources of these inconsistencies and determining social, economic, and population attitudes that may underlie these inconsistencies , the mixed logit model is evaluated considering these variables.
5. Results of Mixed Logit Model with Mutual Effects
- To estimate the mixed logit model with mutual effects, numerous states of available multiplication relations among personality attitudes and specific attitudes of the alternatives were tested. Finally, those variables such as age, gender, education, and total number of visitors multiplied by price have significant impact. The results of this model are shown in column 3, Table 2. They show that females (like the previous studies [12 & 39]), people with higher education (like the previous studies [7, 13, 8, 10]) and older people (like the previous studies [31, 39]) and those who had visited the wetland more than 3 times (like the previous studies [8, 10]) selected the wetland managerial scenarios with higher prices.
6. Calculation of Tendency toward Final Payments
- The rates of coefficients have a direct interpretation ability to determine meaningful levels. In order to make it more practical, the final price is calculated as an alternative for environmental attitudes and price fluctuation (Eq. 6). These ratios represent the tendency to final; payment for changes in the above-mentioned attitudes. Given the normal distribution of attitudes and stability of price variable, the tendency for final payment will possess normal distribution. Table 4 represents the resulted obtained from final payments for different levels of environmental attitudes in accordance with the mixed logit model and mutual effects. As it can be seen in the table, changing the current critical state of the wetland and its balance surface height to normal state requires the respondents to pay 26000 Rials/ family annually and be willing to pay 22670 Rials to reach to an average level. In addition, in order to elevate the water quality in spite of little straw into normal state (straw rate of more than 300mg/ L) and the average level, the estimated amount is 23000 and 2000 Rials per year. Tendency to pay among these citizens for improving the current state of ducks to optimum and average levels is 14670 and 770 Rials per year. To increase the reservoirs of Amur fish and move from the current state into the optimum and average levels, the respondents were willing to pay 11330 and 600 Rials per year. It can be inferred from Table 4 that the obtained results for tendency to pay is in accordance with the preference theory in which the attitudes which have improved more have higher tendency to pay.
 | Table 4. Results of Calculating Willingness for Final Payment (Unit: Rials) |
7. Results and Recommendations
- Hamoon wetland is selected as one of the sample sites for implementing protection plan for Iran wetlands with assistance of the development program of the UN (UNDP/ GEF). This plan attempts to reduce the major current threats of this protected wetland by using ecosystem management and implementing a comprehensive managerial program. This article estimates the financial benefits of Hamoon managerial scenarios and tries to enrich the available literature. As far as the choice experiment enforces people to make a balance among these attitudes, they have to choose the most important ecological attitudes. The results obtained from the mixed logit model with mutual impacts not only inform the related managers, but they also represent the public’s support from the ecosystem management plan. These findings show several positive and significant benefits of Hamoon environmental attitudes. As mentioned earlier, attitudes such as water quality (balance level height), water quality (rate of straw available in water), number of ducks, and reservoirs of Amur fish have the most and the least rates of willingness for payment. Likewise, they show the highest importance and preference i the managerial management among people of Sistan. So that based on people’s preferences, the quality of water is the most important and effective factor in people’s utility, so it needs further attention i managerial policy- making processes.The quality of water and the number of ducks in Hamoon are the subsequent effective factors and the last place is given to Amur fish. Moreover, the results show that there is an imbalance state in preferences derived from variables such as gender, age, education, and frequency of visits. Based on the obtained results, it can be concluded that willing to pay for various attitudes of Hamoon wetland mostly depicts the public’s tendency to support the wetland and save it from the current critical situation. It shows that one of the best approaches for improvement of the environmental condition of the wetland is the public participation of the citizens. On the other hand, codifying a uniform basin program for allocating percentages of water to this wetland and optimizing water consumption- especially in agriculture section as a major factor may control the falling trend of the water balance level. Undoubtedly, the present paper is a pilot study that aims to provide more precise information about expenses and benefits gained from the environmental improvement in Uremia Lake, and it requires a more comprehensive study for analyzing the expense benefits.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML