-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry
p-ISSN: 2165-882X e-ISSN: 2165-8846
2014; 4(2): 118-123
doi:10.5923/j.ijaf.20140402.12
Assessment of Cowpea Germplasms from Ghana and Mali Using Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers
Ibrahima Z. Doumbia1, Richard Akromah2, James Y. Asibuo3
1Institut d’Economie Rurale (IER), Cinzana Agricultural Research Station, Segou, P.O. Box 214, Mali
2Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST), Faculty of Agriculture, Kumasi, Telex: 255 USTGH, Ghana
3Legumes Program, CSIR-Crops Research Institutes (CSIR-CRI) Fumesua, Kumasi, P.O Box: 3785, Ghana
Correspondence to: Ibrahima Z. Doumbia, Institut d’Economie Rurale (IER), Cinzana Agricultural Research Station, Segou, P.O. Box 214, Mali.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Characterization of germplasms using molecular markers is very important for gene bank managers, since it allows more efficient sampling of available resources and removing duplicate genotypes. This technique doesn’t depend on environmental factors and shows with accuracy the variability between and within germplasm hence, improved identification of the genetic variation for breeders and better management of the available gene pool. A total of 94 accessions (47 from Ghana and 47 from Mali) were investigated in this study using 20 SSR markers to determine polymorphism within the germplasm. Among the 20 SSR markers screened, only 6 primer pairs were polymorphic. Seven to 27 alleles per primer were detected with polymorphic information content (PIC) varying from 0.61 to 0.92 with a mean of 0.83; allele frequency from 0.17 to 0.45 with a mean of 0.28; genetic diversity from 0.66 to 0.92 with a mean of 0.84; heterozygosity from 0.00 to 0.97 with 0.47 as a mean. The diversity observed can be exploited by breeders from the two countries (Ghana and Mali) for cowpea improvement.
Keywords: Cowpea, Germplasm, Cluster analysis, SSR markers
Cite this paper: Ibrahima Z. Doumbia, Richard Akromah, James Y. Asibuo, Assessment of Cowpea Germplasms from Ghana and Mali Using Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers, International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 118-123. doi: 10.5923/j.ijaf.20140402.12.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] is an important legume grown worldwide from Latin America, India to Africa. This legume is a major food crop in these areas because of its high protein content and low cost of production ([1], [2]). Total protein content in seed ranges from 23%-32% seed dry weight [3]. Cowpea grows quickly and covers the soil to prevent weed spreading; it also possesses the capacity to fix atmospheric nitrogen in poor soils and is very adapted to arid areas. Dry haulms of cowpea are often used for livestock feed, particularly in the dry season, when animal feed is scarce. Area grown with this legume was estimated at 11.8 million ha with an annual production of 5.4 million tons of dried grains. With 91% of the global production from West Africa and a record 10.7 million ha, Nigeria and Niger are the leading cowpea growing countries [4]. In Mali, annual production of cowpea is estimated at 161,338 tons of dried grains and it is produced in large parts of the country [5]. According to MoFA [6] cowpea is an important source of vegetable proteins and minerals for over 70% of Ghana’s population and it is currently a food security crop. The mean cowpea production in this country ranges from 340 kg/ha to 400 kg/ha whilst it is 300 kg/ha in Mali ([6], [5]).In these two countries, farmers grow local varieties as well as introduced or improved varieties. They characterize their seeds based on some physical traits such as seed coat colour, seed size, growth habit, maturity time of the variety, and other agronomic traits. Soil physical and chemical properties, diseases, pests, drought, heat can affect these physical traits; and hence, schemes established for characterization will be inherently flawed.Assessment of local and regional cowpea germplasms is important because of identification of diversities between and within germplasms which can help breeders to improve some local varieties and increase farmer’s production and productivity [7]. It also helps to remove duplicate varieties foe efficient germplasm conservation and evaluation. The use of genetic diversity in breeding program is important to decrease crop vulnerability to abiotic and biotic stresses. Cowpea varieties which have large variability will be good candidates for varietal improvement.Several works have been done on germplasm comparison and most of them were based on morphological characterization. The long time of selection using morphological attributes is among the constraints of cowpea breeding in the two countries (Ghana and Mali). The use of new tools of molecular biology like diversity studies can overcome some of the breeding program limitations and speed up selection time of new varieties for crosses. Different molecular techniques were used for diversity study of wild and cultivated cowpea which included Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphisms (AFLP; [8], [9]); Chloroplast DNA Polymorphisms [10]; Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD; [11], [12]) Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLP; [13]); DNA Amplification Fingerprinting (DAF; [14]); and analysis of Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs; [15], [16]) or Sequence Tagged Microsatellite Sites ([17], [18]). Of these techniques, analysis of SSRs has proven to be particularly useful since these sequences are abundant and distributed throughout eukaryotic genomes. Through simple screening requirements, they are highly polymorphic and inherited co-dominantly and reproducible [19]. SSRs have also been extensively used in genotype identification, seed purity evaluation and variety protection [20], pedigree analysis ([21], [22]), genetic mapping of simple and quantitative traits and Marker Assisted Selection (MAS) ([23], [24]). Molecular assessment of cowpea germplasms from Ghana and Mali is necessary. Knowledge of genetic diversity and relatedness among cowpea germplasms will be useful for breeding in the two countries to solve cowpea production constraints by providing index parental lines for crosses. Objective of this study was to complement the results generated from morphological characterization.
2. Materials and Methods
- Ninety-four genotypes (47 from Ghana and 47 from Mali) were used in this investigation at the Biotechnology Laboratory of CSIR-Crops Research Institute (CSIR-CRI), Fumesua, Ghana in 2011. Materials from Mali collected from Cinzana Agricultural Research Station gene bank of Institut d’Economie Rurale (IER) were made up of 30 local varieties, 9 improved varieties from cowpea breeding program and 8 introduced varieties. Thirty-nine local varieties from Plant Genetic Resource Research Institute (PGRRI), Bunso; 7 improved varieties from CSIR-CRI and 1 introduced variety from IITA constituted the Ghanaian materials.
2.1. DNA Isolation and Quantification
- Young leaves of each variety were sampled from the field three weeks after sowing. Total DNA was extracted using DNrasyR Plant Handbook [25] slightly modified by CSIR-CRI Biotechnology Laboratory. DNA quality and quantity were assessed with Spectrophotometer Biochrom Libra S12.
2.2. PCR Amplification of DNA and Electrophoresis
- Twenty (20) oligonucleotide primers taken from [16] were used to amplify samples in PCR based on protocol established by [26] and modified by CSIR-CRI Biotechnology Laboratory and reactions contained 5.12 μl Sterile water, 1.0 μl of 10x Buffer, 0.9 μl of 25nM Mgcl2, 0.4 of 10nM dNTPs, 1.0 μl of each forward and reverse primer, 0.08 μl of Super Therm. 250u Taq DNA polymerase and 10 ng/μl temple DNA in final volume of 10 μl PCR mixture. PCR amplification was carried out using Applied Biosystems (GeneAmpR PCR System 9700 thermocycler) with the following settings: initial denaturation at 94°C for 2 mins, final denaturation at 94°C for 1 min, annealing at 55°C for 1 min and elongation at 72°C for 2 mins (35 cycles). 72°C for 10 minutes for final extension and PCR products were stored at 4°C until analysis was done. PCR products were resolved on 6% (w.v) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) for 2 h in 1 X Tris/borate/EDTA buffer using MS (Major Science) 2 liters. Protocol established by [27] and modified by CSIR-CRI Biotechnology Laboratory was used to stain gels and photo-documented with Alpha Innotech MultimageTM Light Cabinet. The size of DNA bands in base pairs was determined using the 100 bp Ladder DNA marker (Axygen Biosciences).
3. Data Analysis
- Each SSR fragment was scored for their presence/absence, size and polymorphism. Data were analysed using XLSTAT Statistical Analysis Software [28] based on Jaccard test with SAHN (Sequential, Agglomerative, Hierarchical and Nested) Unweighted pair-group average method to classify accessions in accordance with their similarity. PowerMarker program [29] according to [30] was used for SSR analysis.
4. Results
4.1. Cluster Analysis
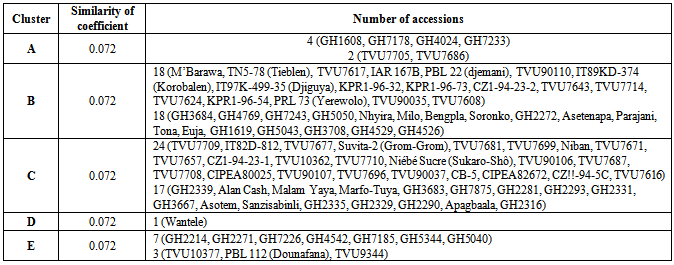
- The dendrogram (Figure 1) illustrated the combined data of six polymorphic primers which delineated the 94 accessions into five major clusters (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E) around 0.072 similarity coefficient (Table 1). Cluster A was made up of six accessions, four from Ghana and two from Mali. Majority of materials from Mali were found in clusters B and C with 18 and 24 accessions respectively. At 0.143, these clusters were divided into sub-clusters with 4 for cluster B whilst 5 belong to cluster C. Few of studied accessions grouped together in cluster E; among them three were from the Malian germplasm whereas seven were from Ghana. Only one variety (Wantele) was in cluster D.
|
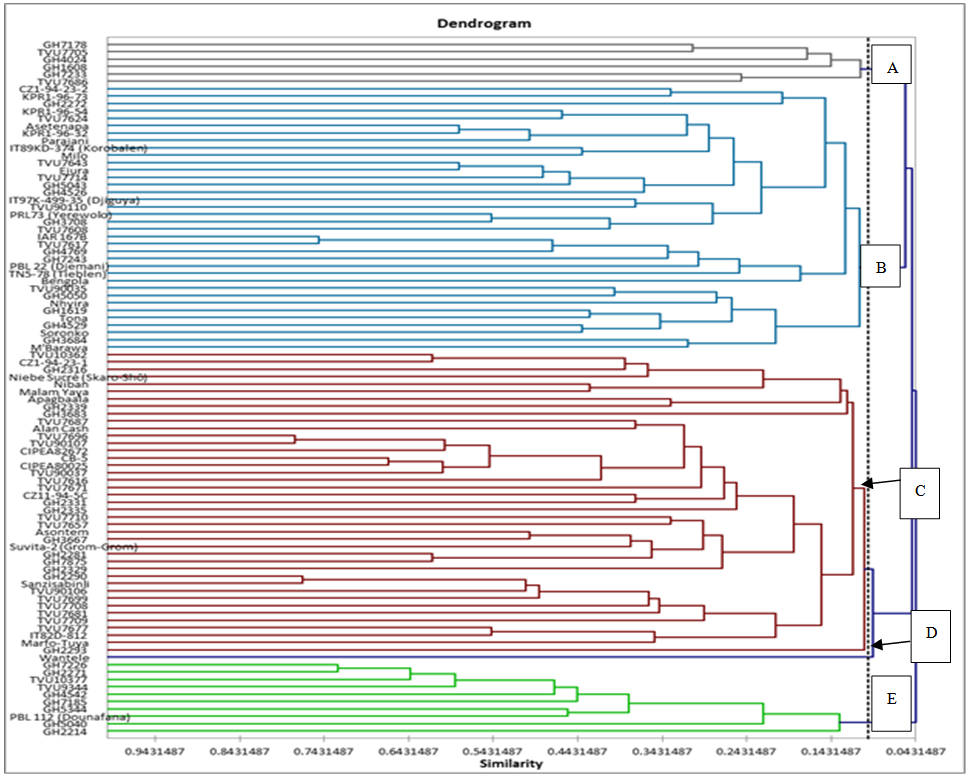 | Figure 1. Dendrogram generated from six SSR markers screened 94 cowpea accessions |
4.2. Genetic Characterization Based on SSR Markers
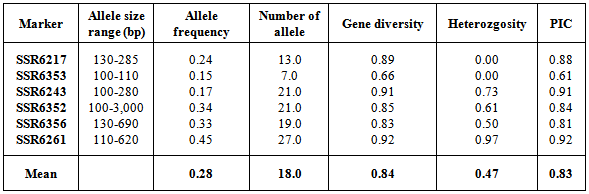
- Twenty pairs (forward and reverse) primers were used to analyse genetic diversity of 94 cowpea varieties. These primers generated a total of 386 bands across the selected genotypes. Fourteen SSR primers did not show any polymorphism between varieties, and therefore, they were excluded from the analysis. Size of amplified alleles ranged from 100 to 3,000 bp as shown in Table 2. Primers SSR6261 and SSR6356 amplified the highest (108) and lowest (34) number of polymorphic bands respectively across the DNA samples. Number of alleles varied form 7 (SSR6353) to 27 (SSR6261). Allele frequency ranged from 0.15 (SSR6353) to 0.45 (SSR6261) with a mean of 0.28. Polymorphic information content (PIC) representing the allele diversity for a specific locus varied from 0.61 (SSR6353) to 0.92 (SSR6261) with a mean of 0.83. Gene diversity ranged from 0.66 in SSR6353 to 0.92 in SSR6261 with an average of 0.84. Variation in heterozygosity among cowpea SSRs increased from 0.00 (SSR6217 and SSR6353) to 0.97 (SSR6261) with an average occurrence of 0.47.
|
5. Discussion
5.1. Cluster Analysis
- The selected microsatellites significantly differentiated cowpea accessions; they clustered accessions differently from the morphological classification reported earlier by [31]. These results showed lower levels of similarity between and within the germplasms from Ghana and Mali. From 1 to 0.80 level of similarity, accessions were different from each other, their high level of similarity started around 0.34 genetic distances. Lots of accessions from the two germplasms which were clustered based on morphological data belonged to different cluster or different sub-cluster using SSR markers. The results from this study were different from those obtained by [16] who reported lower level of genetic variability among Ghanaian cultivated genotypes. According to [32], high degree of homogeneity was also examined using Ghanaian collection on the basis of stored seed protein banding patterns by SDS-PAGE techniques.
5.2. Genetic Characterization Based on SSR Markers
- SSR markers have been used to evaluate genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships of cowpea genotypes ([17], [33]). In this study, all the 20 SSR primer combinations used gave amplification products with 26% being polymorphic. SSR primers were used by [34] to assess genetic similarities and relationships and detected between 4 and 13 alleles among 48 wild lines with an average of 7.5 alleles per primer. According to [35], the number of alleles ranged from 1 to 9 per SSR primer combination in cowpea germlasm from Senegal. Sixteen SSR primers generated a range of allele between 5 and 12 fragments with an average of 8.2 bands per primer combination among cowpea genotypes [36]. Combination of 25 informative SSR primers were used to analyse Ghanaian germplasm and yielded 1 to 6 alleles per primer pair with a mean of 3.8 [16]. The results from this study were in agreement with recent reports on the number of alleles detected using SSR markers in other legumes, such as 14 to 67 alleles in chickpea [37] and 11 to 26 in soybean [38].Data reported by [39] showed polymorphic information content (PIC) ranging between 0.09 and 0.87 with a mean of 0.34. The mean PIC value (0.83) recorded in the current study compared favourably with results obtained from previous reports. Genetic diversity, in [16] study, has showed a range from 0.12 to 0.68 with an average of 0.44; and 0.01 to 0.84 for variation in heterozygosity (0.47) among the accessions were twice of the values obtained by [16]. High level of heterozygosity was observed ranging from 0.50 (SSR6356) to 0.97 (SSR6261) whereas some of the markers never detected any heterozygosity.SSRs data were able to separate accessions into different genotype groups to show low level of similarity between and within both germplasm. Results from this study were different from those reported by [39] who found low level of genetic diversity among cowpea accessions in Kenyan using molecular markers. For them, the resemblance of cowpea types among regions is an indication of both high levels of gene flow between regions and inadequate time for significant genetic differentiation along geographical lines. Twenty of our study materials, from Ghana, were used by [16] which supported some of the recent study results. For example, GH2316, GH2329 and GH2339 were found to belong to the same cluster. The difference between the two studies may be due to the use of materials from two countries (Ghana and Mali), or large number of materials from Ghanaian gene bank used in [16] study collected from nine geographical regions of Ghana and some of them may be duplicated with different name according to their collection area.In this study, molecular data indicate there is enough genetic diversity within and between Ghanaian and Malian cowpea germplasms which could be exploited to improve genotypes for cowpea production. The current study also found that morphological descriptors, even though easy to use and readily available, may lead to mislabelling, particularly where certain varieties were identified as the same on the basis of morphological data.It will be therefore better, if morphological characterization backed by DNA markers for accuracy and reliable genetic diversity assessment and germplasm management. More SSR markers should be used for validation of these results.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- This work was supported by grant from Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa (AGRA). The author is grateful to Institut d’Economie Rurale (IER) of Mali and CSIR-Crops Research Institute of Ghana for supplying the seeds used in this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML