-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry
p-ISSN: 2165-882X e-ISSN: 2165-8846
2014; 4(2): 94-99
doi:10.5923/j.ijaf.20140402.08
Understanding the Vermicompost Process in Sewage Sludge: A Humic Fraction Study
Paulo R. Dores-Silva1, Bruno M. Da Silva2, Túlio C. Zozolotto1, Maria D. Landgraf1, Maria O. O. Rezende1
1Institute of Chemistry of São Carlos – University of São Paulo. São Carlos, SP, Brazil
2Faculty Padre Anchieta. Jundiaí, SP, Brazil
Correspondence to: Maria O. O. Rezende, Institute of Chemistry of São Carlos – University of São Paulo. São Carlos, SP, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
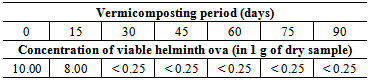
The objective of this research was the characterization of the humic substances isolated from domestic sewage sludge (DSS) in natura and after three months of vermicomposting, treated with Eisenia foetida, in order to help the understanding about the main differences between the maturation degree of both organic residues. Elemental analysis, infrared and UV-Vis spectroscopy were used for the characterization of the humic substances. By comparing both humic substances, those from DSS in natura presents a great potential as fertilizer, whereas the humic substances from DSS vermicompost produced in three months shown a satisfactory percentage of humic acids, thus being able to be incorporated into the soil as a conditioner or fertilizer and thereby offering an adequate environmental destiny for this residue, transforming an unwanted material into a valuable product. It is notable to mention that the number of viable helminth ova is reduced during the process of vermicomposting. It has shown that vermicomposting process is a powerful tool to increase the stability of this residue.
Keywords: Fulvic acids, Humic acids, Vermicomposting, Domestic sewage sludge
Cite this paper: Paulo R. Dores-Silva, Bruno M. Da Silva, Túlio C. Zozolotto, Maria D. Landgraf, Maria O. O. Rezende, Understanding the Vermicompost Process in Sewage Sludge: A Humic Fraction Study, International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 94-99. doi: 10.5923/j.ijaf.20140402.08.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
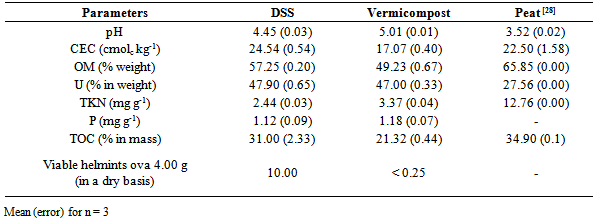
- Domestic sewage sludge (DSS) is an organic residue generated during the treatment of wastewater stations in the Wastewater Treatment Plant [1-3]. Among many processes of final disposal of DSS (after being stabilized), it is worth to consider the agriculture recycling of this residue due to the adequacy for agricultural and environmental health [4,5]. Among of several sources of organic matter applied to the agriculture, the use of vermicompost has been considered as a great alternative to sustainability, therefore it is presented as a material rich in macronutrients, consequently, it can be used as fertilizer or conditioner of soils [6,7]. Vermicomposting is the process of transformation of recent organic matter in stabilized organic matter through the action of earthworms along to the flora that lives inside their digestive dealings [8-11]. In the gut of earthworms, the not digested organic matter along to those organic matter that was not assimilated are expelled together with earth particles in the form of an organic compound rich in nutrients, easily assimilated by plants, which receives the name of coprolites [6,5,12]. Humic substances are formed through chemical and biological degradation of organic matter and metabolic activity of microorganisms and consist of humic acids, fulvic acids and humin [13]. The physical and chemical characteristics of humic acids and fulvic acids extracted from different locations are dependent on many factors, such as the merits of the original material. In nature the process of humification is slow and gradual and may take thousands of years to occur, leading to humic substances with different structural characteristics [14,15]. The process of composting through the metabolism of the earthworms occurs in a short period of time - about 3 months -, leading the recent organic matter to a state of stabilization similar to what occurs in the environment if compared to humic substances originated from peat or soil, thanks to several enzymes that live inside the earthworms and are able to accelerate the humification process [16,17].This research had as main objective the comparison between the domestic sewage sludge in natura and the humic substances generated after 3 months from the same domestic sewage sludge vermicomposted to be used as fertilizers or soil conditioners. For sample characterization, techniques such as elemental analysis and spectroscopy in UV/Vis and infrared regions were used. The physicochemical characterization of the DSS in natura and after 3 months of vermicomposting was done in order to assess the fertilizing potential of the residue. In addition, one sample of humic acids from peat was submitted to the same analysis in order to compare the humification degree of the DSS in natura and of the vermicomposted DSS. The quantification of the number of viable helminth ova during the vermicomposting process was done in order to evaluate the sanitary conditions of the material. For its determination, the Yanko method was used [18-20].
2. Materials and Methods
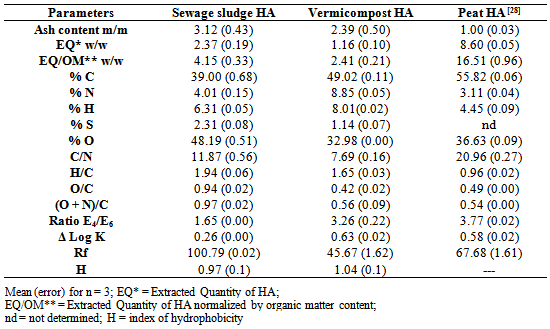
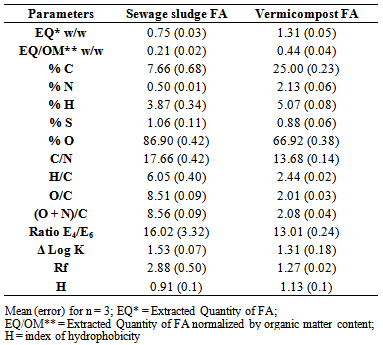
- Samples Preparation Samples were collected in the Wastewater Treatment Plant of São Carlos city, SP, Brazil. The samples were from DSS previously dried at 50℃, with about 40% moisture, without being stabilized by any process, the sludge was collected in natura. For the vermicomposting process approximately 60 kg of the same material were used.Preparation of the vermicompostsTo prepare the vermicomposts, boxes of 0.70 m length, 0.70 m wide and 0.70 m height were constructed. These boxes were filled up with DSS, and then approximately 1,000 worms of the specie Eisenia foetida per m² were inoculated in controlled conditions of humidity and temperature for the adaptation of the earthworms [21]. After the inoculation of the earthworms, the material was composted for three months. At the end of the vermicomposting process, the vermicomposts so obtained were collected and divided into samples of 100.00 g, and submitted to extraction and purification of humic acids (HA) and fulvic acids (FA). For the samples of DSS in natura the FA and HA were immediately extracted and purified after the collection of the material at the Wastewater Treatment Plant.Analytical MethodsThe chemical characterization of the domestic sewage sludge and of the vermicompost from domestic sewage sludge were based on the following parameters: pH in CaCl2; a microwave furnace was utilized to prepare the samples for determination of both nitrogen Kjeldahl total (NKT) and phosphorus by Hach® method 399 and Hach® method 480, respectively; organic carbon (TOC) via Shimadzu® TOC-V OHC; cation exchange capacity (CEC), through the occupation of active sites to exchange with hydrogen ions in solution 1 mol L-1 of glacial acetic acid; organic matter content (OM) and humidity (U); and concentration of viable helminth ova, using the method of Yanko. The samples were collected each 15 days, up to 90 days, and compared to the DSS in natura.Extraction, purification and characterization of HA and FAThe extraction and purification of HA and FA were performed according to the conventional methodology suggested by the International Humic Substances Society (IHSS) [22]. The HA ash content was determined by burning up the samples in a crucible of platinum, at 550℃ for 4 hours. The levels of ash were below 5%, indicating an acceptable degree of purification for subsequent use of the samples for elemental analysis. Elemental analysis were performed in a Carbo Erba Instruments® EA 1110 CHNS-O. The oxygen content was obtained by difference in an ash-free basis [23]. The ratio between the absorbance at 465 and 665 nm, E4/E6 ratio, was measured in NaHCO3 0.025 mol L-1 solution. Approximately 5.00 mg of HA and FA were dissolved in 50.00 mL of solution with pH 8.40. A spectrometer for UV/Visible Hitachi U3501® with a quartz cuvette of 1 cm optical path was used. The infrared spectra were obtained in tablets of KBr, with about 0.50 mg of sample to 200.00 mg of KBr. The spectra were analyzed in a Bomem MB-102® spectrophotometer with Fourier transform, making up 32 scans from 4000 to 400 cm-1 with resolution of 4 cm-1. Measurements were made in triplicate, and the error for a confidence interval of 95% calculated by the Equation 1:
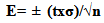 | (1) |
3. Results and Discussion
- Characterization of the Domestic Sewage Sludge and of Its VermicompostFor understanding which of the two materials possess a greater fertilizer potential, the physicochemical characterization of the DSS in natura and of the obtained vermicompost from the DSS was performed (Table 1). For comparison purposes two peats are also presented, once peat usually presents a higher fertilizing potential.The vermicompost from the sewage sludge showed up a slender increase in the pH value, reflecting the earthworm action. According to Bidone [24], from the earthworms esophagus the calcific glands secrete calcium carbonate, controlling its content in the animal organism. The CO2 produced through breathing is eliminated with the excess of absorbed calcium from the soil, making up CaCO3, which is released outside along with the non-digested particles such as excrements.
|
|
|
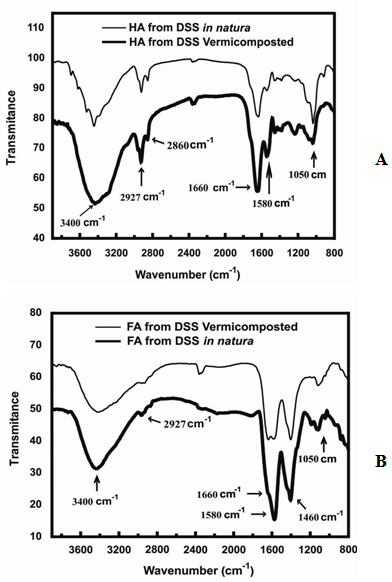 | Figure 1. FT-IR spectra of (A) HA from DSS in natura and HA from DSS vermicomposted; (B) FA from DSS vermicomposted and FA from DSS in natura |
|
4. Conclusions
- From the FT-IR spectra strong bands at 1450 cm-1 for HA and FA extracted from the DSS in natura and for the vermicomposted DSS were observed. The bands prove the high degree of aliphatic compounds for the studied samples.The properties of the analyzed vermicompost were similar to the established values from the Brazilian legislation [37], which determines the criterions for the agriculture use of DSS in the São Paulo state, mainly the concentration of pathogen microorganisms, signalizing that the DSS vermicompost is able to be used as a soil conditioner or fertilizer.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- This work was supported by the financial agencies FAPESP and CNPq and by the University of São Paulo through the program “Teaching with Research” and through the program NAP-BioCiTec.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML