-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry
p-ISSN: 2165-882X e-ISSN: 2165-8846
2012; 2(5): 257-261
doi: 10.5923/j.ijaf.20120205.09
Effect of Density on Thermal Conductivity of Bamboo Mat Board
M. C. Kiran , Anand Nandanwar , M. Venugopal Naidu , K. Ch. Varada Rajulu
Indian Plywood Industries Resarch and Training Institute IPIRTI, P. B. No 2273, Tumkur road, 60022, Bangalore
Correspondence to: K. Ch. Varada Rajulu , Indian Plywood Industries Resarch and Training Institute IPIRTI, P. B. No 2273, Tumkur road, 60022, Bangalore.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Bamboo mat boards (BMB) is a plywood-like wooden board produced from woven mats of bamboo that are soaked inadhesive resin and then pressed firmly together in a hot press.BMB is becoming popular as an eco-friendly material in housing applications such as panelling, ceilings, prefabricated shelters, roofs, doors and door panels etc., hence information on thermal properties of BMB is desired to access it’s heat insulating value, in addition to other physical and mechanical properties.Investigations were carried out to evaluate the thermal conductivity of bamboo mat board (BMB) and to study the effect of density on thermal conductivity of BMB. The thermal conductivity of BMB was determined by a steady-state guarded hot-plate method keeping temperature at 30°C and 50°C considering Indian climatic conditions during summer at bulk densitiesof 0.75 to 1.65 g/cm3. Thermal conductivity increased from 0·121W/m-Kfor bulk density 0·765 g/ cm3 to0.384W/m-K for bulk density1.61 g/cm3. Linear trend line relationship between density and thermal conductivitywas derived with correlation coefficient value of 0.92. From the results, it was found that thermal conductivity of BMB increased with increasing bulk density.
Keywords: Thermal Conductivity, Guarded hot plate, Density, BMB
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Bamboo mat board (BMB) is a layered composite comprising several layers of woven mats. The decline in timber availability and the emergence of new technologies and product options have spurred interest in bamboo–based composites and wood substitutes. Bamboo mat board is gaining popularity as an alternative to other panel products such as plywood, particle board, etc., in housing applications due to its good strength properties and aesthetic value. Thermal conductivity is the quantity of heat transmitted through a unit thickness in a direction normal to a surface of unit area due to a unit temperature gradient under steady state conditions. Thermal conductivity is generally expressed in W/m-K.Thermal conductivity is the intrinsic property of a material which relates its ability to conduct heat. Heat transfers through a material at a specific rate and the rate which depends on the material itself. Some materials such as metals allow heat to transfer quickly through them,whereas some materials such as wood allow heat to transfer very slowly through them. Information on the thermal conductivity of any panel product is of importance for determining its heat insulating value for specialized uses such as walling, roofing, partitions etc. Thermal properties of BMB concern the way that BMB responds in the presence of heat and it can have considerable effects on energy efficiency and fire safety, among other issues. The energy design of buildings using BMB and the evaluation of their energy performance depends in part on thermal properties of BMB. Thermal insulation of a material is known by its thermal insulating value (R), which is the reciprocal of thermal conductivity and it depend on structure of material and influenced by density and moisture content. The thermal conductivity of materials with low conductivities can be derived from two standard linear heat flow test procedures. One method employs calibrated heat flow meters as described in ASTM[1], in which a steady-state unidirectional heat flux through the specimen is maintained between two parallel plates and measured with a calibrated heat flux transducer. This method provides a rapid means of determining conductivity. Whereas in other methodsthe thermal conductivity is determined by the guarded hot plate as described in ASTM and IS[2, 3]. In these methodsthe test specimens are installed between heating and cooling plates. A constant heat flows through the test specimens in the stationary temperature state and the thermal conductivity is determined by the heat flow and the mean temperature difference between the sample surfaces and the dimensions of the samples. This method is most often used in determining thermal conductivity of wood and wood products.Same method has been employed to determine thermal conductivity of BMB. Thermal conductivity of wood varies considerably with moisture content, temperature, grain orientation, voids, amount of summer wood and spring wood fiber[4]. Thermal conductivity of 56 Indian timbers in transverse direction were investigated at air-dry condition[5] and also established relationship of thermal conductivity with density and porosity of timber.Authors found a linear relationship between thermal conductivity and specific gravity[6,7]for some of the wood species found in South India. The data on seven Indian timber species along longitudinal and transverse direction in dry condition was reported and relationship between thermal conductivity and specific gravity was established[8].Thermal characteristics of wood based panel products viz. plywood of different grades reported that thermal conductivity of plywood increases with increase in density[9].The thermal conductivity of plywood is largely dependent on its density and is likely to be in the range 0.09 to 0.24 W/m-K.Thermal conductivity of various material like Glass (0.8 W/m-K), Concrete (1.0 W/m-K), Steel (46 W/m-K), Copper (401 W/m-K) etc., were reported[10].The thermal behavior of three wood species of the family of combretaceaewas carried out using the modified Lee’s method and reported that within an interval of time, the thermal agitation in the samples increases as the temperature increases, after which thermal stability was attained[11].Thermal conductivity is a critical attribute when offering energy conserving building products. This is due to the fact that wood has excellent heat insulation properties. Lower thermal conductivity values equates to greater heat insulating properties [12]. The prevalence of wood product in construction industries is driven by their high stiffness to weight ratio allowing for the use of lightweight assemblies and innovative design. However, field experience suggests that fire performance on engineered wood products is inferior to traditional timber [13].Wood plastic composites (WPC) is known to have drawn increasing attention over the years. To this end, wood materials had been preferred to inorganic materials like talcum or fiber due to the density of the composite, which is considerable lower and therefore of interest for transportation applications, as well as the renewability and enhanced recyclability of the wood plastic composites [14-16]. The influence of processing parameters of wood plastic composites and bamboo blast were investigated[17]Since, no previous data is available on thermal conductivity of BMB this study was carried out to generate data on thermal conductivity of BMB, which will be useful for engineers, architects and builders in designing housing systems and components for specialized uses where thermal insulation is of importance.
2. Materials and Methods
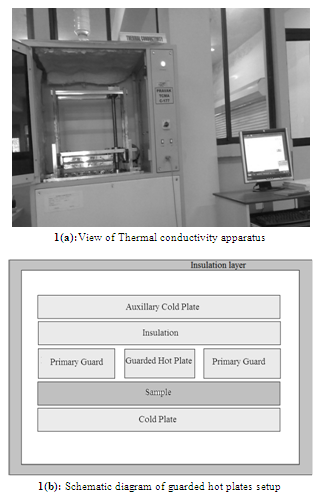
- Bamboo mat boards of different thicknesses varying from 5 mm to 19 mm, drawn from the market and pressed at in-house were randomly selected for this study. Three numbers of samples of size 300 X 300 mm were prepared and conditioned at 27+2ºC and 65+5% RH. The moisture content of the samples was maintained in the range of 8-10%. The density of specimenswere determined by the method specified in IS[18] are given in Table 1. The BMB samples were then grouped in four groups based on their densities viz. Group A (0.75 to 0.85 gm/cm3), Group B (0.85 to 0.95 gm/cm3), Group C (0.95 to 1.05 gm/cm3) and Group D (>1.05 gm/cm3), each group containing BMB samples of different thicknesses. The Group A, B and C were formed to study the effect of thickness (of BMB having similar density) on thermal conductivity. Group D was formed for BMBs which does not fall under category A, B & C with wide range of densities i.e. > 1.05 gm/cm3. All the four groups of BMB were considered for studying the effect of density (irrespective of their thickness) on thermal conductivity of BMB. The thermal conductivity of the samples were determined by the method specified in ASTM[2]using computerized thermal conductivity apparatuswhich works on the principle of guarded hot plate method and uses an absolute method for the determination of thermal conductivity. The View of Thermal conductivity apparatusis as shown in Figure 1(a). The thermal conductivity apparatus consists of a guarded hot plate, primary guard plate, auxiliary cold plate and a cold plate. The guarded hot plate, primary guard plate and the auxiliary cold plate are maintained at the same temperature. Schematic diagram of guarded hot plate setup is as shown in Figure 1(b). The guarded hot plate and the cold plate are used to create a temperature differential across the sample. Considering the Indian extreme conditions at summer season, the temperature of hot plate and cold plate were set at 50℃ and 30℃ respectively for determining thermal conductivity of BMB.Since the guarded hot plate, primary guard and the auxiliary cold plate are at the same temperature, under steady state conditions, all the energy from the guarded hot plate flows through the sample, and there is no lateral heat exchange or flow from the guarded hot plate and the primary guard, as well as no upward heat exchange of heat between the guarded hot plate and the auxiliary cold plate. The amount of energy flowing in the guarded hot plate is measured by measuring the voltage applied to the heater and the current flowing through the heater. The product of the voltage and the current gives us the watts. This metered energy in the guarded hot plate is then used to determine the thermal conductivity of the sample, knowing the cross sectional areas of the guarded hot plate and the height of the sample.The thermal conductivity is computed by the equation as given below:
 Where: Q is the heat supplied through a medium, in WA is the cross-section, in m2∆T is the temperature differential across the medium, in oKD is the length of the medium through which heat flows, in mk is the thermal conductivity of the medium, W/m-KThe thermal conductivity of samples was recorded after steady state condition was observed and the temperature differential between the guarded metered hot plate and the primary guard as well as the auxiliary cold plate was within 0.5℃. Also, this difference was stable for a four consecutive periods of half an hour each. During testing BMB samples, time taken by the apparatus for reaching the steady state was observed after 4hrs, but reading was taken after 8hrs of startingthe test.
Where: Q is the heat supplied through a medium, in WA is the cross-section, in m2∆T is the temperature differential across the medium, in oKD is the length of the medium through which heat flows, in mk is the thermal conductivity of the medium, W/m-KThe thermal conductivity of samples was recorded after steady state condition was observed and the temperature differential between the guarded metered hot plate and the primary guard as well as the auxiliary cold plate was within 0.5℃. Also, this difference was stable for a four consecutive periods of half an hour each. During testing BMB samples, time taken by the apparatus for reaching the steady state was observed after 4hrs, but reading was taken after 8hrs of startingthe test.3. Results and Discussions
- The densities of BMB of different thicknesses are given in Table 1. The densities of BMB was observed between 0.7 to 1.6 gm/cm3, The thermal conductivity of BMBs of different groups viz. Group A (density: 0.75 to 0.85 gm/cm3), Group B (density: 0.85 to 0.95 gm/cm3), Group C (density: 0.95 to 1.05 gm/cm3) and Group D (density: >1.05 gm/cm3) are given in Table 1. Coefficient variation 7.52, 3.03 & 2.64 % of thermal conductivitywas observed for Group A, Group B and Group C respectively, forBMBs of different thicknesses.No considerable effect of thickness on thermal conductivity of BMB (having same density) was observed. Thermal conductivity of BMB varies from 0.12 to 0.38 W/m-K for density range 0.75 to 1.6 gm/cm3 keeping India extreme temperature at summer. The effect of density on thermal conductivity of BMB is shown in Figure 2, in which correlation coefficient of 0.92 is observed between thermal conductivity and density of BMB, which shows that the thermal conductivity of BMB increases with increase in density and it can be expressed in linear trend line relationship as given below:y = 0.328x - 0.143Where, y = is thermal conductivity in W/m-K, x = is Density in gm/cm3.
 | Figure 1. Thermal conductivity apparatus |
 | Figure 2. Effect of density on thermal conductivity of BMB |
4. Conclusions
- Thermal properties of BMB concern the way that BMB responds in the presence of heat and it can have considerable effects on energy efficiency and fire safety, among other issues. From the study, it is observed that the thermal conductivity of BMB varies from 0.12 to 0.38 W/m-Kand it increases with increase in density, since it has lower thermal conductivity as compared to most of the other building material which indicates that it allow heat to transfer very slowly andhence it can be a good alternative for building materials.The data obtained from this study will be useful for architects and engineers in choosing what density BMB is suitable for walling, roofing, flooringand major applications in building construction and also helps in computing its heat insulating value (R) which helps in calculating thermal comfort of the house. Since the thermal conductivity of BMB evaluated is applicable at temperatures of 30 and 50OC. hence there is further scope to evaluate thermal conductivity of BMB at different temperature by taking care of its mechanical properties and its dimensional stability for different humid conditions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to sincerely thank to Director, IPIRTI, Bangalore for permission and for providing necessary research facilities.
References
| [1] | “Standard Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus”, ASTM C518,2010 |
| [2] | “Standard Test Method for Steady State Heat Flux Measurements and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the Guarded Hot Plate Apparatus”, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, ASTMC177, 2010. |
| [3] | “Method of the determination of thermal conductivity of thermal insulation materials”, IS 3346, 1980. |
| [4] | Venkateswaran A, “A note on the relationship between electrical properties and thermal conductivity of woods” Journal of Wood Science,Vol.8, No.1, 50-55, 1974. |
| [5] | Naryanamurthi D, Ranganathan V, “The thermal conductivity of Indian timbers: part-1” Proceedings Mathematical Sciences, Vol 13, No.4, 1941. |
| [6] | Pandey C.N, Kamla B.S, Jain J.C, “Thermal conductivity of some wood species of karnatka”, Indian Academy of Wood Sci., Vol.12, No.1,23-25, 1981. |
| [7] | Jain V.K, Dubey Y.M, “A note on thermal conductivity of wood”, Indian Academy of Wood Sci., Vol.22, No.2,45-47, 1990. |
| [8] | Dubey, Y. M, Jain J. D, Uniyal K. K, “Note on Thermal conductivity of some Indian timbers”, Journal of the Timber Development Association of India,Vol 46, No. 3/4, 14-18, 2000. |
| [9] | Aswathanarayana B.S, Venugopal Naidu M, “Evaluation of thermal characteristics of wood based panels”, IPIRI/RR No.13, 1986. |
| [10] | Tipler, Paul A, “Physics for Scientists and Engineers”, Third Edition, Extended Version 1-42, Worth Publishers, 1991. |
| [11] | Oluyamo Sunday Samuel, Bello Olawale Ramon, YomadeOlabode Johnson, “Thermal Conductivity of Three Different Wood Products of Combretaceae Family; Terminalia superb, Terminaliaivorensis and Quisqualisindica”, Journal of Natural Sciences Research, Vol.2, No.4, 2012. |
| [12] | Daniel, D. P, “Perfect ! Wood Win-Door Profiles”, Trace Laboratories, INC 5 North Park Drive Hunt Valley,MD 21030, USA. Pg. 1-5, 2010. |
| [13] | Mahmood, Tabaddor, “Thermal and Mechanical Finite Element Modeling of Wood-Floor AssembliesSubjected to Furnace Exposure” Underwriters Laboratory, 07CA42520, NC9140, 2008. |
| [14] | Burgstaller, Christopher, “Processing of thermal sensitive materials-a case study of wood plastic composites”Monatschefte fur Chemie 138, 34-346, 2007. |
| [15] | Daniel, M. “Wood Plastic Deposite in Europe Vs USA-processing and product trends” Proceedings ‘Woodplastic composite 2005’. Applied marketing information, Vienna, 2005. |
| [16] | Burgstaller, Christopher, “Investigation on the relationship between wood particle size, wood type and contenton the mechanical and physical properties of wood platic composites”. Doctoral thesis, Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Pg 25, 2006. |
| [17] | Vanchai, Laemlaksakul, “Physical and Mechanical properties of particle board from Bamboo waste” WorldAcademy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 64, 2010. |
| [18] | “Methods of Test for Wood Particle Boards and Boards from Other Lignocellulosic Materials”, IS 2380 (Part 1 to 21), 1977. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML