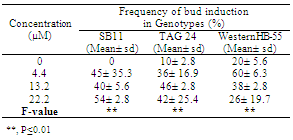-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry
p-ISSN: 2165-882X e-ISSN: 2165-8846
2012; 2(4): 171-174
doi: 10.5923/j.ijaf.20120204.07
Evaluation of Indian Peanut on the Induction of Caulogenic Buds in Vitro
Sujatha Raman 1, Dina Ermias Dagne 1, Nutan P Malpathak 2, W.N. Gade 1
1Department. of Biotechnology, University of Pune, Pune, 411007, India
2Department. of Botany, University of Pune, Pune, 411007, India
Correspondence to: Sujatha Raman , Department. of Biotechnology, University of Pune, Pune, 411007, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The present work has been undertaken to study the in vitro response in widely used cultivars WesternHB-55, TAG 24 and SB11 of peanut having desired agronomic characteristics. The mature embryo derived leaflet explants of all three peanut genotypes were found morphogenic in vitro. When comparing the effects of TDZ and BA with respect to caulogenic response, it can be inferred that TDZ is a more potent inducer of caulogenesis in vitro than BA. All genotypes responded equally to different concentrations of BA. WesternHB-55 responded better than others which results in high proliferation rate in vitro. The present study emphasizes on the usage of WesternHB-55 germplasm through adventitious organogenesis pathway in transformation studies (biolistic gun approach), for the production of proteins, vaccines enzymes etc.
Keywords: Peanut, Westernhb-55, TDZ, Adventitious, Organogenesis, TAG 24, SB 11
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is the major oilseed crop of India. India is the second largest peanut producer after China. Many of the important agronomic traits high yield and quality, earliness, resistance to major pests, diseases, high protein and oil content have yet to be improved through gene transfer technology[1]. To exploit the existing germplasm for improvement, various genotypes need to be studied for their desired agronomic characteristics as well as their in vitro response. In vitro regeneration, a key requisite in the development of transgenic peanut plants is highly genotype dependent. Differences in the in vitro response among the non Indian genotypes belong to Spanish, Runner, Virginia, and Valencia types had been extensively studied and reported [2]. Though in India, more than a hundred varieties of peanut are released for cultivation based on its agronomic importance (SB11, JL 24, WesternHB-55, TAG 24, ICGS 1, GG 20, K134 etc), literature pertaining to in vitro studies is very much limited to SB11 and JL 24. Cultivars like TAG 24 (semi dwarf, early maturing and high yielding), WesternHB-55 (early maturing and high oil content) belong to Spanish type with desired agronomic characteristics are widely used in the central region of India, but theirgermplasm was not exploited for peanut improvement. Chengalrayan et al. studied the genotype-specific response at each stage of somatic embryogenesis in 16 Indian genotypesincluding SB- 11 and TAG 24[3]. However, there are no reports available on the genotype-specific response in the direct adventitious organogenesis pathway. This pathway is useful in gene transfer techniques and well suited for many transient expressions involved in the production of proteins, enzymes, vaccines etc[4]. Differences in response observed in vitro by peanut genotypes is possibly due to the complex interaction of genes controlling morphogenesis in the genotype with the culture protocol[5]. Irrespective of the pathway, the major difference lies in the initial induction phase.Hence, the present study was carried out to evaluate the agronomically important peanut cultivars belong to Spanish groups like TAG 24, WesternHB-55 including SB 11 as control, for the direct induction of caulogenic buds in mature zygotic embryo derived leaflets. Also, the interaction of plant growth regulators during induction phase was studied.
2. Materials and Methods
- Pods of mature seeds of three cultivars of peanut were collected in the month of December from Agricultural College, Pune, India. WesternHB-55 is early maturing high oil yielding cultivar. TAG 24 is a semi dwarf early maturing and high yielding groundnut variety. Its pedigree is TGS 2 x TGE 1 and is of the Spanish variety which has a high harvest index and is tolerant to bud necrosis disease[6]. The yield is 2000 kg/ha. The cultivar SB11’s pedigree is Ah 4213 x Ah 4394, belong to Spanish variety. The dates of release are 1991 and 1965 respectively[6].To initiate the cultures, the embryoaxes from the dehusked seeds of TAG 24, SB 11 and WesternHB-55 were excised. Then it was rinsed with tap water twice after the addition of two drops of 1% liquid detergent. Mercuric chloride treatment (0.1%) treatment was given for 2 min. followed by rinsing with sterile distilled water for 4-5 times and kept in little sterile water for 12-16 hrs (over night incubation) and cultured on to MS basal medium for germination. The explants were incubated in dark for 3 days and transferred to tubes. Data on shoot length root length and number of leaves were collected after 30 days of culture. Thirty explants per treatment were taken and the experiment was repeated thrice. To induce direct adventitious organogenesis, the explants were sterilized as mentioned but after overnight incubation in sterile distilled water for the opening up of the MZEDL, the leaflets were carefully excised without any damage and were cultured on to MS medium supplemented with different concentrations of BA and TDZ (4.4 µM, 13.2 µM, and 22 µM) with MS basal medium as a control. Fifty explants per treatment were tested and the experiment was repeated thrice. Data on caulogenic bud induction was collected after 30 days of culture. All cultures were incubated to 25 ± 2C light conditions in irradiance of 32 μmol m-2s –1, 16 h photoperiod. For optimization parameters, Completely Randomized Designs were used. The data was subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and treatment means were compared using F test[7]. To differentiate morphogenic cells from non- morphogenic cells, a double-staining procedure described by Gupta and Holmstrom was followed[8].
3. Results and Discussion
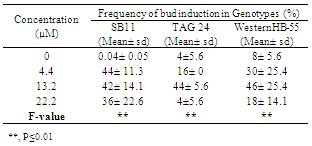
- Before studying the morphogenic responses, it is imperative to determine viability of the seeds by germinating in vitro. Instead of seeds, embryo axes were the explants used in order to minimize the occurrence of contamination i.e. to establish an aseptic culture. Radical emergence was considered as sign of germination. The genotype TAG 24 showed the highest germination frequency with approximately 90% (90.0 ± 9.43) of the explants inoculated had germinated while SB 11 and WesternHB-55 showed equal frequency of about 73% (73.3 ± 14.1 & 73.3 ± 1.00). Germination parameters like shoot length, root length and number of leaves showed no significant difference in response among the genotypes (Table 1).
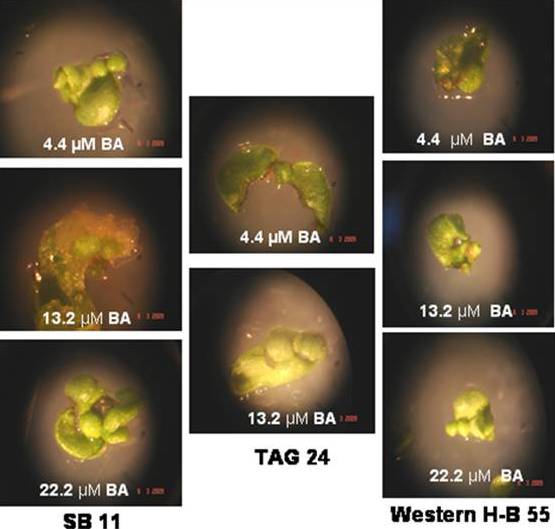 | Figure 1. Caulogenic bud induction in MZEDL explants of peanut genotypes with different concentrations of BA |
|
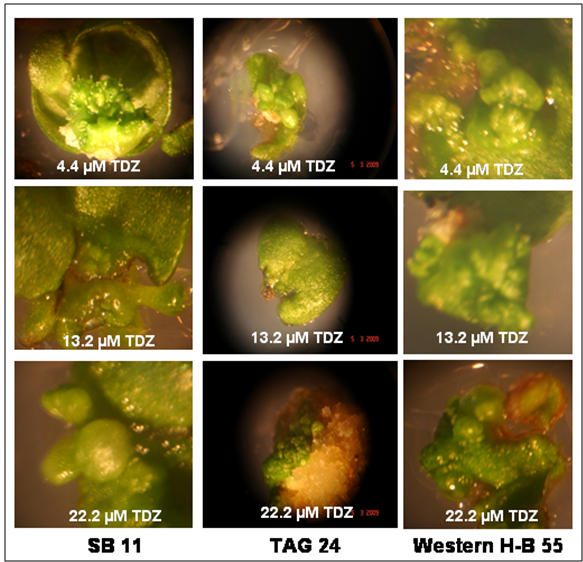 | Figure 2. Effect of different concentrations of TDZ in caulogenic bud induction in MZEDL explants of peanut genotypes |
|
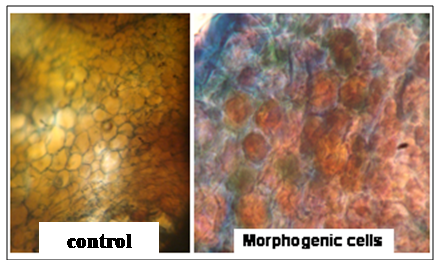 | Figure 3. Histological sections of cells obtained by double staining of cells in control and morphogenic mass obtained in TDZ |
4. Conclusions
- It can be stated from this study that Spanish varieties TAG 24 and WesternHB-55 have in vitro morphogenetic potential similar to SB 11. Inoculating the MZEDL of these varieties in MS media fortified with the growth regulators BA or TDZ induced caulogenesis in all genotypes, which appeared to be direct de novo organogenesis in BA. Indirect caulogenesis in TDZ was observed to some extent however direct caulogenesis was mostly observed. The morphogenic nature of the cells was confirmed with histological staining methods.When comparing the effects of TDZ and BA with respect to caulogenic response, it can be inferred from these values that TDZ is a more potent inducer of caulogenesis in vitro than BA by producing more buds. All three genotypes responded equally to different concentrations of BA. In the MS media supplemented with varied concentrations of TDZ, the variety WesternHB-55 responded better than SB 11 and TAG 24 in terms of number of buds. Its maximum response at lower concentrations of TDZ (4.4 µM) ensures the proper growth avoids the impairment of growth due to high exposure. Among the Spanish varieties only SB 11 has been exploited for transformation studies.The present study emphasizes on the usage of other cultivar like WesternHB-55 whose in vitro response similar to SB 11 in tested BA concentration and better than SB 11 in TDZ supplemented media. The explants of WesternHB-55 produced caulogenic buds through direct organogenesis pathway compared to other germplasm. These explants can be targeted through biolistic gun delivery for desired protein or vaccines expression in their caulogenic buds. More the production of caulogenic buds proportional to protein expression not even requiring regeneration procedures. With regeneration protocol, WesternHB-55 germplasm can be used for nuclear transformation studies. Also, it can become an effective target for breeding approaches in peanut improvement.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors acknowledge Department of Biotechnology, University of Pune for financial assistance.
References
| [1] | Sharma HC, Sharma KK, Seetharama N, Ortiz R “Genetic transformation of crop plants: Risks and opportunities for the rural poor”, Curr. Sci. 80, 1495-1508, 2001. |
| [2] | Kalyand Matand, Prakash CS “Evaluation of peanut genotypes for in vitro plant regeneration using Thidiazuron” J. Biotechnol. 130, 202-207, 2007. |
| [3] | Chengalrayan K, Mhaske VB, Hazra S, “Genotypic control of Somatic Embryogenesis”, Plant Cell Rep. 17, 522–525, 1998. |
| [4] | Pittman RN, Banks DJ, Kirby JS, Mitcchell ED, Richardson PE, “In vitro culture of immature peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.)”, Peanut Sci. 10, 21-25, 1983. |
| [5] | Kris MHS, Bingham ET, “Interactions of highly regenerative genotypes of alfalfa(Medicago sativa) and tissue culture protocols”, In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol.-Plant, 24, 1047–1052, 1988. |
| [6] | Alpa J, Mungala T, Radhakrishnan, Jayanti R. Dobaria, “In vitro Screening of 123 Indian Peanut Cultivars for Sodium Chloride Induced Salinity Tolerance”, World J. Agri. Sci. 4(5), 574-582, 2008. |
| [7] | Panse VG, Sukhatme PV, Statistical Analysis for Agricultural Workers, ICAR, New Delhi, India. 1967. |
| [8] | Gupta, Holmstrom, “Double Staining Technology for distinguishing Embryogenic Cultures” In “Protocol for Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants”(eds) NM Jain, PK Gupta, Springer Publishers, pp 573-575, 2005. |
| [9] | Chandra A, Pental D, “Regeneration and genetic transfor mation of grain legumes: An overview”, Curr. Sci. 84, 381–387, 2003. |
| [10] | Banerjee P, Maity S, Maiti SS, Banerjee N, “Influence of genotype on in vitro multiplication potential of Arachis hypogaea L.” Acta Bot. Croat. 66, 15-23, 2007. |
| [11] | Matand, Prakash, “Evaluation of peanut genotypes for in vitro plant regeneration using thidiazuron”. J. Biotechnol. 130, 202–207, 2007. |
| [12] | Joshi M, Sujatha K, Sulekha Hazra, “Effect of TDZ and 2, 4-D on peanut somatic embryo-genesis and in vitro bud development”. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. cult. 94, 85-90, 2008. |
| [13] | Visser C, Qureshi JA, Gill R, Saxena PK, “Morphoregulatory role of thidiazuron”. Plant Physiol. 99, 1704-1707, 1992. |
| [14] | Malik KA, Saxena PK. “Regeneration in Phaseolus vulgaris L; High frequency induction of direct shoot formation in intact seedlings by N6-BAP and Thidiazuron”. Planta, 186, 384-389, 1992. |
| [15] | Gill R, Ozias-Akins P, “Thidiazuron induced highly morphogenic callus and high frequency of regeneration of fertile peanut(Arachis hypogaea L.) plants”. In Vitro Cell Develop Biol. Plant, 35, 445-450, 1999. |
| [16] | Murty, Saxena, “Thidiazuron: A potent regulator of in vitro plant morphogenesis”. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant, 34, 267-275, 1998. |
| [17] | Murthy BNS, Victor J, Singh RP, Saxena PK, “In vitro regeneration of chickpea(Cicer arietinum l.): stimulation of direct organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis by TDZ”. J. Plant growth regul. 19, 233-240, 1996. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML