-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Human Resource Management Research
p-ISSN: 2169-9607 e-ISSN: 2169-9666
2025; 14(1): 1-12
doi:10.5923/j.hrmr.20251401.01
Received: Jul. 17, 2025; Accepted: Aug. 31, 2025; Published: Sep. 21, 2025

The Effect of Applying Organizational Culture on Administrative Creativity among Employees in Higher Education Institutions: Lebanese University-Beirut
Nada Shouman1, Ramez Al Tanbour2
1Ph.D. Candidate, Faculty of Business Administration, Al-Jinan University, Lebanon
2Professor, Al-Jinan University, Lebanon
Correspondence to: Nada Shouman, Ph.D. Candidate, Faculty of Business Administration, Al-Jinan University, Lebanon.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

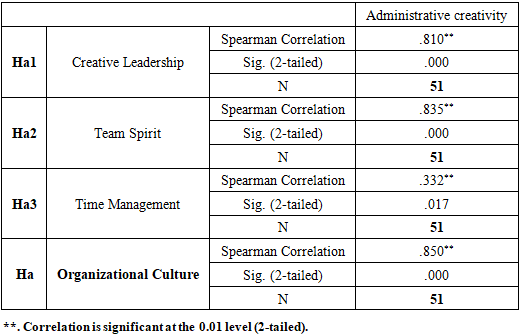
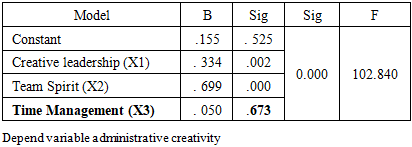
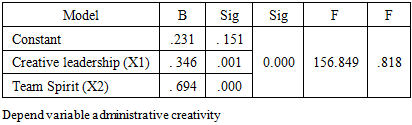
The aim of the research is to identify the impact of the practice and application of the principles of administrative culture in achieving administrative creativity (an empirical study of the opinions of a sample of administrative employees at the Lebanese University in Beirut), and the descriptive analytical approach was used. A questionnaire tool was adopted to collect quantitative data and distributed to the research community consisting of administrative staff at the Lebanese University in Beirut. The total research sample reached 51 employees, and the questionnaire was distributed via e-mail and social media, and after receiving the questionnaires, they were checked and analyzed using the SPSS version 25 statistical program. The researches reached a set of conclusions, the most important of which were: There is a statistically significant relationship between organizational culture with its dimensions and administrative creativity at the Lebanese University in Beirut. The correlation coefficient reached r = 0.85, with a significant degree of Sig = 0.000. The study also showed that the creative leadership and the principles of teamwork followed at the Lebanese University have a strong impact and a strong correlation on the university's ability to achieve administrative creativity. While it was found that time management and discipline have the least effect on administrative creativity.
Keywords: Organizational culture, Creative leadership, Team spirit, Discipline, Administrative creativity, The Lebanese University
Cite this paper: Nada Shouman, Ramez Al Tanbour, The Effect of Applying Organizational Culture on Administrative Creativity among Employees in Higher Education Institutions: Lebanese University-Beirut, Human Resource Management Research, Vol. 14 No. 1, 2025, pp. 1-12. doi: 10.5923/j.hrmr.20251401.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The researchers were interested in the concept of organizational culture and its dimensions as the main focus for the success and development of institutions. An organization with an adaptive and strong culture that enables its members to commit, discipline, creativity, innovation and participate in decision-making drives them to an outstanding individual performance that enables the organization to achieve its goals.Organizational culture draws the organization’s policy, so each worker expresses what is inside him through the beliefs, ideas, and values he has acquired from that culture. This appears in solving problems, dealing with decisions, and achieving goals in more creative ways.Higher education institutions seek to use modern and effective methods in order to develop the performance of their employees and achieve their goals. One of the recent trends of most institutions is the interest in organizational culture, which is an influential part in the organizational behavior of employees, and this culture also contributes to the formation of the organization's identity and mission.Hence, these studies came to clarify the impact of organizational culture on administrative creativity at the Lebanese University, from the point of view of the university's administrative staff. This study has four chapters, the first chapter deals with the background of the study, its importance and the presentation of its methodology, while the second chapter deals with the theoretical aspect of the research and includes presenting the basic concepts of this study. The third chapter will also include the results of the field study. In the last chapter, the results will be discussed and a number of recommendations will be presented.Research Problem:Due to competition and the complexity that surrounds educational institutions today, they face a lot of problems and challenges, and in order to respond to those challenges, they need to change their policies and administrative systems. In order to achieve outstanding performance which contributes to the achievement of the organization's goals and desires, we emphasize the values of innovation and creativity.Based on this, the main question of the subject can be formulated as follows:In the Lebanese University, how does organizational culture, including its elements (creative leadership - team spirit - discipline and time management) influence administrative creativity?- Does creative leadership affect administrative creativity?- Is managerial creativity affected by team spirit values?- Do the values of discipline and time management affect administrative creativity?Research Objectives:The main objective of the research is to know the impact of organizational culture and its elements (creative leadership - team spirit - discipline and time management) on administrative creativity.The sub-objectives of the research are:- Knowing the impact of creative leadership on administrative creativity.- Determining the impact of team spirit values on managerial creativity.- Describing the influence of discipline and time management on administrative creativity.Research Significance and structure:The importance of the research is manifested in two theoretical and practical aspects:From the theoretical point of view: the issue of organizational culture is one of the topics that have received great attention in the field of business management, and organizational culture is the main driver of energy and capabilities. It primarily affects the behavior of individuals, and the achievement of high productivity by choosing the means, patterns, and methods of effective movement.As a result, the findings of this study will help us understand the nature of relationships between organizational culture and administrative creativity at the Lebanese University from a practical perspective in a way that involves the university in the process of development.
2. Literature Review
- The first requirement: The concept of organizational cultureOrganizational culture is an essential element in contemporary organizations. Therefore, leaders and managers in institutions had to be aware of its dimensions and elements, as it is the environmental medium in which organizations live. Organizational culture is the product of what workers have acquired of habits, values, ways of thinking, and technical skills before joining the organization in which they are currently working. “The culture of the organization is similar to the culture of the community, as the organization consists of values, beliefs, perceptions, assumptions, rules, standards and things made by man, common behavioral patterns. The culture of the organization is its personality, its climate or feeling, and the culture of the organization determines the behavior and appropriate links and motivates individuals...” [1] There are several definitions of the concept of organizational culture, and the following is a presentation of some of them:Organizational culture is defined as “a system of values and beliefs shared by the employees of the organization so that this system grows within the same organization.”It is also defined as a model of shared values that shows how to control attitudes and behavior and establish what is important to the organization's members.The second requirement: The Types and Dimensions of Organizational CultureThe researchers looked at the types of organizational culture from multiple angles, and some of them like Al-Mursi [2] classified it into four types: the culture of power, the culture of the role, the culture of tasks and the culture of the individual. As for Al-Amyan [3], he referred to two types of culture, namely: a strong culture and a weak culture. He explained [4] its dimensions are: bureaucracy and exclusionary and supportive, and in this regard Al-Khashali and Al-Tamimi [5] adopted the following four dimensions in their study: Cooperation innovation, coherence, and effectiveness.The third requirement: the importance of organizational cultureSome believe that the importance of culture stems from the three functions it provides to organizations, which are:A- Through it, the organization and its employees are provided with a sense of belonging and vitality.B- Creating a spirit of commitment, dealing and discipline among the employees with the mission of the organization.C- It helps clarify the standards adopted within the organization.The role of organizational culture in individuals and organizations can also be summarized as follows:The organization works to make the behavior of individuals within its conditions and characteristics, and culture has an effective role in addressing everyone who aims to change the conditions of individuals in organizations from one situation to another.Culture directs the behavior of individuals, so when faced with a certain situation or certain forms, it acts according to culture, and without it will be difficult to predict the behavior of the individual. [6]The fourth requirement: the elements of organizational cultureFirst: creative leadership. Creative leadership is that leadership practice that works to achieve the highest quality standards by using skills, experiences, and qualifications to achieve strategic and desired goals. Creative leadership is the ability to collect and link new ideas with each other in a way that organizes their unconnected relationship and makes them a focus of creativity, and the creative leader is the one who sees the problem and recognizes it in a completely different way. [7]Leadership has been defined as “the academic leader’s ability to develop, change, or produce new and useful ideas through individuals, technical means and systems to achieve the institution’s current and future goals and functions in unconventional ways characterized by fluency, originality, and flexibility.” [8]Because of its great importance, creative leadership has become an important requirement for several reasons:Creative leadership increases the quality of decisions made to address problems and situations at the level of the institution or at the level of its various sectors.- Administrative creativity in institutions is the effective force to move towards exceeding the expectations of societies or individuals, and this is what creative leadership seeks, which encourages creativity to generate new and developmental ideas.Creative leadership works on developing personal skills in thinking and interacting on a collective creativity through brainstorming. [9]Second: Team Spirit (Teamwork)Individual work differs from group work by a number of characteristics that must be shared by all members of the group, where the work team works with one hand with the presence of trust and affiliation between them, with greater ideas and capabilities, effort and less time, thus achieving better results at the lowest cost.Abu Jarjoa quoting from West [10] defined it as “a group of individuals within an institution or organization who perform many tasks that contribute to achieving the goals of the organization. These individuals participate in all work tasks and possess the authority, independence, and resources necessary to achieve their goals.” Characteristics of teamwork:1- Commitment to the members of the group.2- Orientation towards the spirit of the group.3- Clarity of the relationship between the roles of members and the goals of the group.4- Acknowledgment of each member's opinion and experience.5- Full interaction between members.6- Group performance.7- Responsibility.Third: Time managementTime is known as a measure of the hour and that it runs in a straight line, and time is a unique commodity that is given to all people regardless of age and location... And because we cannot create more time than we have been given it, we must use, conserve, control, and manage it. useful. Organizing, arranging, and programmed daily work procedures are important elements in maintaining and managing time, and time is divided into three sections [11].A- Creative time: It is the time a person spends thinking and planning for the future, in addition to assessing and directing the level of achievement, and then developing logical solutions to ensure the effectiveness and results of decisions.B- Preparatory time: It is the time during which the individual collects information and data and prepares the necessary supplies before starting to perform his work.C- Productive time: It is what the individual takes in execution to complete the work for which he was prepared. [12]The fifth requirement: The Lebanese University, a historical overview:On December 11, 1948, the idea of establishing the Lebanese University appeared in the speech of former Foreign Minister Hamid Franjieh when he said, "Lebanon is working to see in this place a Lebanese university whose spirit is the spirit of UNESCO."As for the establishment of the university, it came after the popular student movement, which lasted for a long time, when the movement witnessed clashes with the security forces, forcing the Council of Ministers to meet in February of 1951.In 1953, a center for financial and administrative studies was created and attached to the university.In 1959, the university’s organizational decree was issued, which stated that “the Lebanese University is an institution that carries out the tasks of formal higher education in its various branches and degrees.” After that, the university’s financial system was established on 4/14/1970. Until 1975, the faculties and institutes of the university were concentrated in Beirut and its suburbs, but after the Lebanese war, branches were established in the Bekaa, the north, the south, Nabatiyeh, as well as Mount Lebanon.Until 2018, the number of students at the university reached 79,000, making the Lebanese University one of the largest and most important universities in the Middle East.Sixth requirement: The concept of managerial creativity:The concept of administrative creativity is one of the general concepts of creativity itself. Administrative creativity means launching new ideas to develop products, improve services for customers, lead work teams...As administrative creativity mainly depends on innovation and initiative, and that is based on new ideas and knowledge through which new and innovative things are created that were not previously through the processes of interaction and blending. [13]Defining creativity:Among the definitions of creativity is "the successful stabilization of new processes, programs or products that appear as a result of decisions within the organization." [14]It was also defined as “a departure from the ordinary and typical, taken in a number of different forms and dimensions, at different times and places, depending on the subject, and as an administrative strategy or an entirely different management style. [15] as it was defined as “creativity that refers to changes in the structure of The organization or its operations” [16] Elements of administrative creativity: There are many elements of administrative creativity, including:1- Fluency: It is producing as many ideas as possible about a particular topic at a given time.2- Flexibility: the ability to change the state of mind by changing the situation.3- Originality: It means that the creative person does not think about the ideas of those around him, but that his ideas are new and unique.4- Sensitivity to problems: It is represented in the individual's ability to discover different problems in different situations. The creative person can see many problems at the same time. He is aware of mistakes and feels the problems delicately.5- Analysis: It means creative or innovative production that includes the process of dividing any new work into simple units to be reorganized.6- Risk: It means taking the initiative in adopting new ideas and methods and searching for solutions to them at the same time that the individual is able to bear the risk resulting from his actions and is ready to assume full responsibilities.7- Deviating from the ordinary: It means liberation from traditional tendency and common developments and the ability to deal with rigid regimes and adapt them to the reality of work, and this requires sufficient courage. [17]Organizational culture and creativity:There is a very strong relationship between organizational culture and administrative creativity so that if there is organization, there is creativity also because the role of creativity is for the individual to do his best at work so that the culture of the organization becomes a school that supports creativity in a large and continuous way. But there are also some obstacles that prevent the achievement of creativity in the organization, due to the lack of an appropriate organizational culture that encourages and supports administrative creativity, which leads to the failure to appropriately exploit the creative abilities of individuals. [18]The superior organizational culture is the one that is creativity, keeping pace with the times, development and encouragement from the beliefs of its employees, so that this culture is translated into transactions and policies within the organization, and for the organization to reach that stage, it must take into account several things:1- To cooperate with the innovators in the organization to develop its visions for the future.2- That its developmental steps be accompanied by reinforcements for the developed behavior, and that the workers feel the results of their creativity and ideas, by giving them rewards and bonuses for that.3- Allow all employees to communicate their ideas or reservations by providing open communication channels.4- Support from the administrative leaders for those with specializations, to remove fear and anxiety from their souls, and to reassure them that they are on their side and not alone, and that failure, even if it is achieved, is the step that precedes the successes in the institution. [18] and adapting it to the reality of work, and this requires sufficient courage. [17]The relationship between organizational culture in its dimensions and administrative creativity.
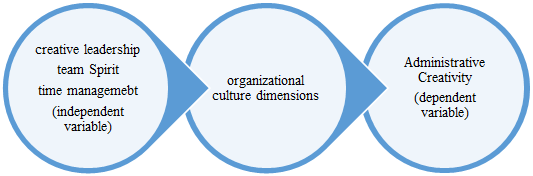 Previous studies:The researcher reviewed many studies related to the subject of the study, which is (the impact of organizational culture on administrative creativity), and it was found that there are several studies related to the issue of organizational culture, some of them studied its impact on performance, some on affiliation and loyalty, others on commitment and organizational discipline, and others studied its impact on Developing the creative behavior of employees We will mention here several studies according to the research chronology:• Dr. Abdul-Baqi, Amira (2020) Entitled: The impact of organizational culture on creative behavior.This study aimed to identify the impact of organizational culture on the creative behavior of workers in the Industrial Maintenance Corporation.The study also showed a strong correlation between organizational expectations and creative behavior, and a medium between organizational values and creative behavior. [19]• Dr. Bassis, Hamza, 2019 Entitled: The impact of organizational culture on job performance in private institutions (a field study at the Tescoba Foundation for the weaving of blankets and flip-flops - Ghardaia-).This study aimed to identify the impact of organizational culture on job performance in the Tescoba Foundation for Food Textiles and Castles in Al-Qarra, Ghardaia Province, where the study was applied to a sample of 60 workers. There is a statistically significant effect between organizational culture and job performance, and its most prominent suggestions were: Working to spread a clear organizational culture among all members of the organization and the need to promote and develop this culture by involving workers in making decisions and listening to their opinions. [20]• Dr. Hisham Ahmed Al-Ashery, 2018 Entitled: The impact of organizational culture on the job performance of government agency employees in the Kingdom of Bahrain.This study aims to know the impact of organizational culture on the job performance of employees of government agencies in the Kingdom of Bahrain and to study the impact of years of practical experience on their performance. Job performance, motivation to work, discipline, team spirit, and human relations. As for the influencing factors, it was found that the administration has the greatest impact on the organizational culture of the governmental body, where the management style came first. [21]• Dr. Tariq bin Khalaf School, 2021 Entitled: The contribution of organizational culture to the development of creative behavior. D case study of the State Property Directorate in Djelfa.This study aimed to emphasize the importance of the contribution of organizational culture to the development of creative behavior through great attention to the organizational culture of the organization.The level of perception of creative behavior among employees in the State Property Directorate was average.There is an impact of the organizational culture of the dimension (organizational norms) on the creative behavior from the point of view of workers in the State Property Directorate.There is no impact of the organizational culture dimension (values, job, organizational beliefs, organizational expectations, policies and procedures) on creative behavior. [22]• Dr. Shamar Selim, 2019 Entitled: The impact of organizational culture on administrative creativity. Field study: the financial control of Biskra province.This study aimed to identify the level of organizational culture among the financial control employees in the Wilayat of Biskra, and also to identify the level of administrative creativity prevailing among them, in addition to knowing the impact of organizational culture with its various dimensions on administrative creativity.Among the most important findings of this study were:The level of employees' awareness of the dimensions of organizational culture was at a high level, and the level of their awareness and view of managerial creativity was also high.Also, a statistically significant effect was found for the dimension of organizational culture represented (beliefs - expectations) in administrative creativity. [23]• Dr. Ruba El-Kang, 2017 Entitled: The Role of Organizational Culture in Achieving Administrative Creativity for the Organization. A field study on administrative workers at Tishreen University.This research aims to identify the level of organizational culture prevailing at Tishreen University and the level of administrative creativity among its administrative staff. Among the most important findings of the study were:The level of culture prevailing in the University is a high level and of relative importance (75.16%), and the level of administrative creativity among the administrative workers at Tishreen University is a high level with regard to solving problems, making decisions, susceptibility to change and encouraging creativity. [24]• The study of Farid Qawasmeh, 2013 Entitled: The role of organizational culture in achieving organizational excellence.This study aims to renew the role of organizational culture in achieving institutional discrimination at Jiddar University (Jordan).The results also confirmed the existence of a strong correlation between the overall university culture and organizational excellence. And the middle of the study was the necessity for the senior management to provide training and development opportunities for all university employees and to conduct future studies for them. [25]• Dr. Muhammad bin Amer, 2006 Entitled: Organizational variables and their relationship to the level of administrative creativity in the security services: A field study on officers working in the Riyadh police, Master's thesis in Administrative Sciences, Naif Arab University for Security Sciences, College of Graduate Studies, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.This study aimed to:- Demonstrating the creativity level of the officers working in the city of Riyadh police.- Identifying the degree of centralization prevailing in the Riyadh city police environment, according to the working officers' point of view.The study found: the high level of administrative creativity among the officers working in the city of Riyadh, and the low degree of centralization prevailing in the environment of the city of Riyadh police. [26]• Al-Sarirah study, Aktham Abdul Majeed, 2003 Entitled: The Relationship Between Organizational Culture and Administrative Creativity in the Two Jordanian Public Shareholding Potash and Phosphate Companies: Mashiyo Study, Journal of Administrative Sciences, Jordan, Volume 8, 53.This study aimed to find the relationship between organizational culture and administrative creativity in Jordanian industrial companies, and reached the following results:The dominant organizational culture pattern is (personal) does not correspond to creativity to a large extent, and (strength) came in the second degree, which corresponded to a lesser degree, after which the culture of (role) and the task came in the third and fourth order, which are less compatible with creativity. Creativity was measured in the study sample companies Through its dimensions, the variable of change and the ability to solve problems were more evident than the rest of the variables. [27]After surveying the previous 9 studies, we note that the current study is a continuation of the previous studies in terms of its handling of the issue of organizational culture and its impact on administrative creativity. This study agreed with the study (King, Amer, Al Majeed, Salim).In the adoption of administrative creativity is a dependent variable, and the study of (Qawasma, Hamza, Al-Ashiri, Khalaf, Amira) differed in their adoption of another dependent variable. Also, this study agreed with all studies by following the descriptive analytical approach, and also agreed with them in the research tool, the questionnaire. To collect information related to the study, it also differed with all these studies in the place and sample of the research, as the Lebanese University (Beirut) chose to be a place for research.Hypotheses:Based on the research problem and its questions, the following hypotheses are tested:Main premise:There is a positive, statistically significant relationship between organizational culture in its dimensions and administrative creativity at the Lebanese University-Beirut.As for the sub-hypotheses:- There is a positive, statistically significant relationship between creative leadership and administrative creativity.- There is a positive, statistically significant relationship between the values of team spirit and administrative creativity.- There is a positive, statistically significant relationship between discipline, time management and administrative creativity.
Previous studies:The researcher reviewed many studies related to the subject of the study, which is (the impact of organizational culture on administrative creativity), and it was found that there are several studies related to the issue of organizational culture, some of them studied its impact on performance, some on affiliation and loyalty, others on commitment and organizational discipline, and others studied its impact on Developing the creative behavior of employees We will mention here several studies according to the research chronology:• Dr. Abdul-Baqi, Amira (2020) Entitled: The impact of organizational culture on creative behavior.This study aimed to identify the impact of organizational culture on the creative behavior of workers in the Industrial Maintenance Corporation.The study also showed a strong correlation between organizational expectations and creative behavior, and a medium between organizational values and creative behavior. [19]• Dr. Bassis, Hamza, 2019 Entitled: The impact of organizational culture on job performance in private institutions (a field study at the Tescoba Foundation for the weaving of blankets and flip-flops - Ghardaia-).This study aimed to identify the impact of organizational culture on job performance in the Tescoba Foundation for Food Textiles and Castles in Al-Qarra, Ghardaia Province, where the study was applied to a sample of 60 workers. There is a statistically significant effect between organizational culture and job performance, and its most prominent suggestions were: Working to spread a clear organizational culture among all members of the organization and the need to promote and develop this culture by involving workers in making decisions and listening to their opinions. [20]• Dr. Hisham Ahmed Al-Ashery, 2018 Entitled: The impact of organizational culture on the job performance of government agency employees in the Kingdom of Bahrain.This study aims to know the impact of organizational culture on the job performance of employees of government agencies in the Kingdom of Bahrain and to study the impact of years of practical experience on their performance. Job performance, motivation to work, discipline, team spirit, and human relations. As for the influencing factors, it was found that the administration has the greatest impact on the organizational culture of the governmental body, where the management style came first. [21]• Dr. Tariq bin Khalaf School, 2021 Entitled: The contribution of organizational culture to the development of creative behavior. D case study of the State Property Directorate in Djelfa.This study aimed to emphasize the importance of the contribution of organizational culture to the development of creative behavior through great attention to the organizational culture of the organization.The level of perception of creative behavior among employees in the State Property Directorate was average.There is an impact of the organizational culture of the dimension (organizational norms) on the creative behavior from the point of view of workers in the State Property Directorate.There is no impact of the organizational culture dimension (values, job, organizational beliefs, organizational expectations, policies and procedures) on creative behavior. [22]• Dr. Shamar Selim, 2019 Entitled: The impact of organizational culture on administrative creativity. Field study: the financial control of Biskra province.This study aimed to identify the level of organizational culture among the financial control employees in the Wilayat of Biskra, and also to identify the level of administrative creativity prevailing among them, in addition to knowing the impact of organizational culture with its various dimensions on administrative creativity.Among the most important findings of this study were:The level of employees' awareness of the dimensions of organizational culture was at a high level, and the level of their awareness and view of managerial creativity was also high.Also, a statistically significant effect was found for the dimension of organizational culture represented (beliefs - expectations) in administrative creativity. [23]• Dr. Ruba El-Kang, 2017 Entitled: The Role of Organizational Culture in Achieving Administrative Creativity for the Organization. A field study on administrative workers at Tishreen University.This research aims to identify the level of organizational culture prevailing at Tishreen University and the level of administrative creativity among its administrative staff. Among the most important findings of the study were:The level of culture prevailing in the University is a high level and of relative importance (75.16%), and the level of administrative creativity among the administrative workers at Tishreen University is a high level with regard to solving problems, making decisions, susceptibility to change and encouraging creativity. [24]• The study of Farid Qawasmeh, 2013 Entitled: The role of organizational culture in achieving organizational excellence.This study aims to renew the role of organizational culture in achieving institutional discrimination at Jiddar University (Jordan).The results also confirmed the existence of a strong correlation between the overall university culture and organizational excellence. And the middle of the study was the necessity for the senior management to provide training and development opportunities for all university employees and to conduct future studies for them. [25]• Dr. Muhammad bin Amer, 2006 Entitled: Organizational variables and their relationship to the level of administrative creativity in the security services: A field study on officers working in the Riyadh police, Master's thesis in Administrative Sciences, Naif Arab University for Security Sciences, College of Graduate Studies, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.This study aimed to:- Demonstrating the creativity level of the officers working in the city of Riyadh police.- Identifying the degree of centralization prevailing in the Riyadh city police environment, according to the working officers' point of view.The study found: the high level of administrative creativity among the officers working in the city of Riyadh, and the low degree of centralization prevailing in the environment of the city of Riyadh police. [26]• Al-Sarirah study, Aktham Abdul Majeed, 2003 Entitled: The Relationship Between Organizational Culture and Administrative Creativity in the Two Jordanian Public Shareholding Potash and Phosphate Companies: Mashiyo Study, Journal of Administrative Sciences, Jordan, Volume 8, 53.This study aimed to find the relationship between organizational culture and administrative creativity in Jordanian industrial companies, and reached the following results:The dominant organizational culture pattern is (personal) does not correspond to creativity to a large extent, and (strength) came in the second degree, which corresponded to a lesser degree, after which the culture of (role) and the task came in the third and fourth order, which are less compatible with creativity. Creativity was measured in the study sample companies Through its dimensions, the variable of change and the ability to solve problems were more evident than the rest of the variables. [27]After surveying the previous 9 studies, we note that the current study is a continuation of the previous studies in terms of its handling of the issue of organizational culture and its impact on administrative creativity. This study agreed with the study (King, Amer, Al Majeed, Salim).In the adoption of administrative creativity is a dependent variable, and the study of (Qawasma, Hamza, Al-Ashiri, Khalaf, Amira) differed in their adoption of another dependent variable. Also, this study agreed with all studies by following the descriptive analytical approach, and also agreed with them in the research tool, the questionnaire. To collect information related to the study, it also differed with all these studies in the place and sample of the research, as the Lebanese University (Beirut) chose to be a place for research.Hypotheses:Based on the research problem and its questions, the following hypotheses are tested:Main premise:There is a positive, statistically significant relationship between organizational culture in its dimensions and administrative creativity at the Lebanese University-Beirut.As for the sub-hypotheses:- There is a positive, statistically significant relationship between creative leadership and administrative creativity.- There is a positive, statistically significant relationship between the values of team spirit and administrative creativity.- There is a positive, statistically significant relationship between discipline, time management and administrative creativity.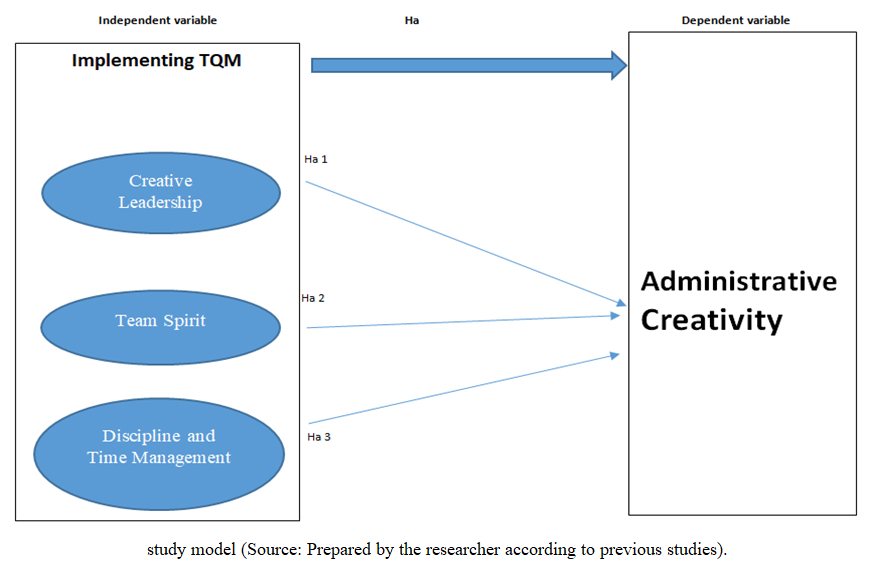 | Figure 1. Conceptual Framework |
3. Statistical Analysis and Hypothesis Testing
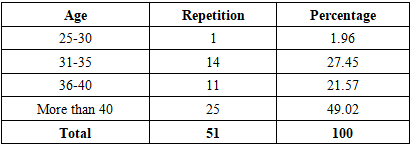
- First: The validity and reliability of the tool:To ensure the stability of the tool, the internal consistency "Cronbach's alpha" coefficient was extracted, and the percentage was high for all study variables (95.3%), which is a good percentage compared to the acceptable minimum of 60%.Second: the study sample's characteristicsThe study sample consisted of 51 administrative employees at the Lebanese University in Beirut. The characteristics of the individuals in the research sample were determined in the following personal information: gender, age, and number of years of experience.1- Gender:The data analysis showed that the study sample consists almost equally between females and males, with 51% of females (n=26) and 49% of males (n=25). It is clear from the results that there is no dominant gender on employee positions. administrators at the Lebanese University.2- Age:The study indicates that the age group (above 40 years) constitutes nearly half of the sample with a percentage of 49% (n = 25), and in the second place came the age group (31-35 years) with a rate of 27.45%. Table 1 shows the distribution of participants in the questionnaire according to their age group.
|
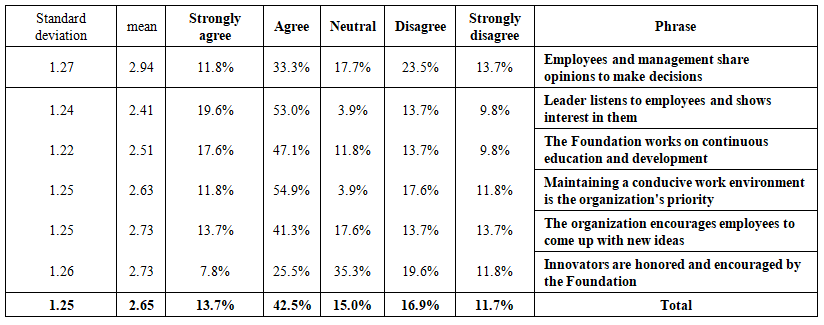 | Table 2. Description of the Phrases of Organizational Culture: Creative Leadership |
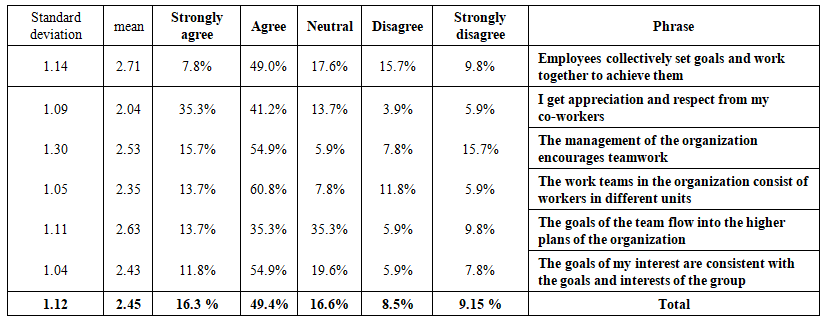 | Table 3. Description of organizational culture phrases: Team spirit |
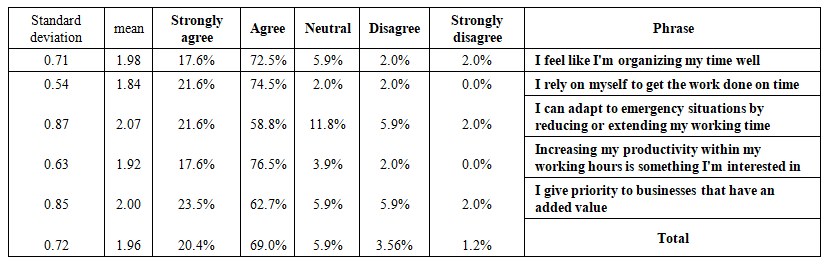 | Table 4. Description of organizational culture phrases: Discipline and Time management |
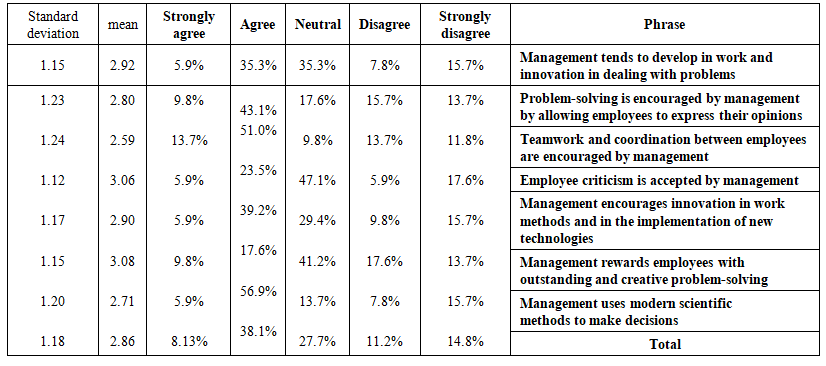 | Table 5. Responses of the study sample to the presence of administrative creativity at the Lebanese |
|
|
|
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
- Through the study and analysis of the relationship between the application of organizational culture with its various standards and the achievement of administrative creativity at the Lebanese University in Beirut according to its administrative staff, and after conducting statistical analyzes, this study produced the following results:1- The study showed that there is a statistically significant relationship between organizational culture with its dimensions (creative leadership, team spirit, discipline and time management) and administrative creativity at the Lebanese University in Beirut. For the majority of administrative staff at the Lebanese University, there is an organizational culture followed in The university and accordingly, administrative creativity is achieved.2- The study showed that the creative leadership and the principles of teamwork followed at the Lebanese University have a strong influence and a strong correlation on the university's ability to achieve administrative creativity. While it was found that time management and discipline have the least effect on administrative creativity.The study recommends the following:Encouraging the spirit of leadership from a creative point of view.The need to work to increase the awareness and knowledge of employees of the organizational culture prevailing in the institution.The need for senior management to encourage any new ideas presented by employees and support them at all administrative levels.Developing a spirit of cooperation and teamwork.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML