-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Human Resource Management Research
p-ISSN: 2169-9607 e-ISSN: 2169-9666
2021; 11(1): 1-5
doi:10.5923/j.hrmr.20211101.01
Received: Aug. 22, 2021; Accepted: Oct. 15, 2021; Published: Nov. 15, 2021

HR Analytics: A Critical Review- Developing a Model Towards the Question “Can Organizations Solely Depend on HR Big Data Driven Conclusions in Making HR Strategic Decisions all the Time?”
H. H. D. P. J. Opatha
Department of Human Resource Management, Faculty of Management Studies and Commerce, University of Sri Jayewardenepura, Sri Lanka
Correspondence to: H. H. D. P. J. Opatha, Department of Human Resource Management, Faculty of Management Studies and Commerce, University of Sri Jayewardenepura, Sri Lanka.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This paper aims to explain that big data in HR analytics which refers to datasets that are not only big, but also high in variety and velocity might not derive the best HR solutions at all the time due to some other considerable factors. Further it describes some important aspects in the literature of HR analytics. Qualitative approach has been utilized to present the facts regarding HR analytics based on the evidences prevailing in the existing literature. Arguments and the conceptual model were developed incorporating author intuition as well in addition to the secondary data sources. Data driven conclusions yielding out of the HR analytics process i.e., identify the objectives/questions, decide metrics, collect data, analyze data and make the final decision, are indispensable to make strategic decisions especially relating to HR issues. However, most of the times, derived solutions/conclusions need to be adjusted considering the factors i.e., financial stability of the organization, current business environment factors, competitive organizations’ behavior, business strategy, capabilities of employees/managers etc. rather accepting the data driven HR solutions as it is. Originality of this paper is high as there is a lack of research papers in the literature supporting this nature of topic “Can Organizations Solely Depend on HR Big Data Driven Conclusions in Making HR Strategic Decisions all the Time?”
Keywords: HR Analytics, Big Data, Human Resource Management, Strategy, Decision
Cite this paper: H. H. D. P. J. Opatha, HR Analytics: A Critical Review- Developing a Model Towards the Question “Can Organizations Solely Depend on HR Big Data Driven Conclusions in Making HR Strategic Decisions all the Time?”, Human Resource Management Research, Vol. 11 No. 1, 2021, pp. 1-5. doi: 10.5923/j.hrmr.20211101.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction to HR Analytics
- Human Resource Management is about managing employees efficiently and effectively to achieve organizational goals and objectives (Opatha, 2009). Sharma and Sharma (2017) have indicated that employees in any organization are significant investment for organizations as they have the power to impact organizational effectiveness. However, it is another perspective that employees are considered as a cost. HR analytics will be useful for an organization to prove that talented employees outweigh the benefits bring to the company over cost. Jhon Sullivan has mentioned that the largest single difference between a great HR department and an average one is the use of metrics (Carlson and Kavanagh, 2018). Human Resource Management International Digest (2017) defines HR analytics as the systematic identification and quantification of the people-drivers of business outcomes, with the purpose of making better decisions. HR analytics is not only about collecting data and reporting them in dashboards. It involves a systematic process of using data, organizing data, analyzing data and reporting conclusions. This goes beyond the concept of metrics and derives meaningful insights for business decision-making. Simply HR analytics is about researching in HRM aspects to achieve competitive advantage for the business organization. HR analytics gives evidence-based advice on how to drive the business from a people perspective (Mondore et al., 2011).Human capital management for the 21st century model (HCM:21) emphasized a framework for analyzing data at an organizational level allowing HR professionals to focus on corporate level strategic issues (Etukudo, 2019). This model supports strategic planners to predict future outcomes while optimizing HR services. The steps of the model are; (a) strategic scan, (b) capability planning, (c) process optimization, (d) integrated delivery, (e) predictive measurement, and (f) analytics. The authors Van den Heuvel and Bondarouk have investigated about HR analytics using 20 respondents from 11 large Dutch organizations and looked at the situation of HR analytics in the 2015 and in 2025 (Human Resource Management International Digest, 2017). As per their conclusions, Human Resource Management International Digest (2017) mentioned that in 2015 HR analytics was relatively unknown in business organizations. Even in present context, 2021 HR analytics is considered as an emerging trend in the field of HRM for developing countries like Sri Lanka. Many business makers were relying on gut feeling rather than using a statistical and analytical approach. HR analytics were mainly used on basic reporting and metrics to derive historical insights to answer the question “what happened?”. In most cases, HR analytics focused primarily on traditional issues in HR, such as absenteeism, not on analytical and strategical issues related to HR. By 2025, HR analytics will be a well accepted and well established practice within developed businesses due to its ability to add value for the organizational strategic aspects. The primary focus of HR analytics will be on predictive analytics (e.g. predicting peaks in staff turnover, predicting future employee needs etc.) rather than simple data reporting on dashboards. In the future HR analytics would become a separate discipline in HRM that continuously supports the business organizations in strategy formulation and implementation.
2. HR Analytics and Organizational Performance
- According to a research done by Etukudo (2019) has found that HR analytics supports business performance. He has found this by interviewing the people working in the field of HR management who have working experience in HRA. As per him, HRA improves company performance through enhancing workforce cost control, delivering more effective HR decisions, increasing employee engagement, and relying HR strategy on business strategy. HRA should not be focused on just gathering information but on addressing a compelling business problem and for this purpose HR professionals should align HR strategy with business goals incorporating HR analytics (Etukudo, 2019). The final outcomes of a strategic business decision might not be fruitful if the decision has not been made based on meaningful data. Data becomes meaningful when analytics is there. Vadakkanmarveettil (2014) has mentioned some key areas that HR analytics can be used to improve a company’s performance:• To identify the suitable candidate for a job vacancy.• To identify which top performers have the intension to leave the company in the foreseeable future and the motivating factors that will help retain them.• To identify successful internal employees who are suitably qualified for promotions (succession planning). • To find out which departments are running too lean while which other departments are overstaffed.• To evaluate HR initiatives like training programs or incentive programs and find out how they will improve performance and employee engagement. • To analyze accident claims to find out what factors and which people are likely to create accidents and submit claims.As per Vadakkanmarveettil (2014) some examples of successful companies that are using HR analytics are:1. Google: Google uses HR analytics mainly to develop management training programs.2. Mindtree: Mindtree uses HR analytics tools in turnover modeling, risk assessment and management profile and productivity index. 3. Microsoft: Microsoft develops statistical profiles of likely leavers and calculate attrition rate and were able to reduce those rates by more than half in each case.4. ConAgra Foods: ConAgra Foods Inc. uses HR analytics to find which key employees are likely to leave the company and why. Based on the above findings in the literature, many companies are using HR analytics to manage key employees’ turnover which has an extensive impact for the business performance. However, in addition to the mentioned facts, HR analytics provides successful implications to manage many more HR related strategic issues. HR analytics is a reason for businesses in gaining competitive advantage, solving HR related problems, improving organizational performance (Tomar and Gaur, 2020). Arellano et al. (2015) did a case study analysis on a quick-service restaurant chain with thousands of outlets around the world and had found that customer satisfaction scores have increased by more than 100 percent, speed of service (as measured by the time between order and transaction completion) has improved by 30 seconds, attrition of new joiners has decreased substantially, and sales have been increased by 5 percent as a result of HR analytics.With consideration to that research, they have found the following conclusions in the restaurant chain thanks to HR analytics.• There was a closer correlation between the ability of employees to focus on their work without distractions and their job performance.• Higher and more frequent variable financial incentives (awards that were material to the company but not significant at the individual level) were not strongly correlated with individual performance.• There was no correlation between length of service of the managers and personality type. • Even though, longer shifts policy (fewer days of work in the week, with more hours of work each day) simplified managerial responsibilities, it was actually damaging productivity.Singh et al. (2017) have found that HR analytics increases the organizational effectiveness and efficiency in higher education institutions. HR analytics is mainly useful for basic HR functions i.e. succession planning., performance evaluation, training and development, compensation management, health and safety, discipline management, labor relations etc. (Opatha, 2020). HR analytics is applicable in following areas (Opatha, 2020).• To find out whether employees’ performance results into profitable consequences.• To investigate whether the performance drives customer satisfaction.• To recognize training needs and solutions. • To identify what T & D methods would have the maximum impact on employees’ job effectiveness.• To check whether the existing remuneration program affects employees’ satisfaction and morale.• To ensure organizational remuneration program attracts talented employees from the industry.• To gather reasons for employee turnover.• To calculate employee accident rate etc.
3. Can Organizations Solely Depend on HR Big Data in Making HR Strategic Decisions?
- Big data refers to gigantic larger datasets (volume) that is consisted with more diversified, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured (variety) data that arrive faster (velocity) than before. Big data analytics refers to the process of collecting, organizing, and analyzing large data sets to discover different patterns and other useful information (Rihai and Rihai, 2018). HR big data includes data sets relating to HR of the organization (eg; employee attendance data, performance evaluation data, training data etc.). HR analytics is suitable to find solutions for many HR related issues. To find better answers for those analytical questions HR professionals must engage in researching with the aid of HR big data. Many top managers still believe that allocating funds and investments for HR might be a waste as traditional HR does not statistically prove its contribution to the strategic aspects of the business. However, with the emergence of HR analytics, evidence less HR is fading away. HR professionals are empowered to present their strategic HR issues to the board of directors and they can find the respective solutions for those issues with the support of HR analytics. Results and conclusions derive from HR analytics reduce different types of subjective biases due to its strong data-based findings. It is always better to keep in mind that we cannot make all the strategic business decisions solely based on the derived data based conclusions from HR analytics. Instead, those decisions and conclusions need to be analyzed again, integrating them with available explicit and implicit knowledge of the decision makers. Further, need to consider financial stability of the organization, current business environment factors, competitive organizations’ behavior etc. As an instance assume that the organizational management has found that employees do like to have gym facilities in the organization as a result of a survey done to identify the welfare facilities needed by the managerial employees to make them satisfy. Even though this was found through data, if the business organization cannot financially afford it then they have to proceed for another solution that is financially affordable to them (giving a certain financial amount monthly in addition to the basic salary to join with a gym). Another example is that in a situation where the economy is suffering from an economic crisis (eg; COVID-19 pandemic), even though the survey results show that the employees like to receive a high salary increment, it might not be possible for the organization to implement it (instead of the salary increment, employees can be motivated by giving them the relevant training to work from home amidst the COVID situation). In addition the organization has to be more careful when making decisions and also has to care about what competitive organizations are doing. Another important aspect that management has to consider about in relation to conclusions yielded from HR analytics/researching is whether the data driven conclusions are aligning with the organization’s strategy or strategies. For an example assume that data shows, there is a scarcity of innovative skills from the employees end and need to invest more on organizing training and development programs to improve innovative skills of the employees, but the organizational strategy is to earn profits through cost reduction strategy instead of differentiation strategy. In this type of scenario investing more on training and development programs to improve employees’ innovative skills might not be useful from the strategic aspect of the business. It would be useful if they are investing on training and development programs that are focusing on cost reduction ways.Kavale (2012) explains the role of data in making strategic decisions. He has mentioned that making decisions based on data is contrast to intuition-based or ‘gut-based’ decision making. Accurate data driven decisions help in gaining competitive advantage, optimization of resources, cost reduction, value creation, accuracy, accountability and hedging uncertainty and finally brings efficiency and effectiveness in the strategic decision making process (Kavale, 2012). Kavale (2012) recommends that management in organizations should attach a lot of importance to data sourcing, analysis, interpretation and should use the data securely to create competitive advantage. As per an empirical research done by Björkman and Franco (2017) in newspaper industry, which is an industry that is going through a crisis with decreasing revenues, emphasizes the cruciality of big data analytics as a way of staying competitive. They have found that the further the organizations are coming their work with analyzing and disseminating big data analytics, the bigger is the effect on the decision-making as it is becoming more transparent, accurate, efficient, and faster. These findings highlight the significance of using big data in making business decisions. In the backdrop of HR analytics, big data plays a major role in extracting HR related conclusions aligning with the business strategy.
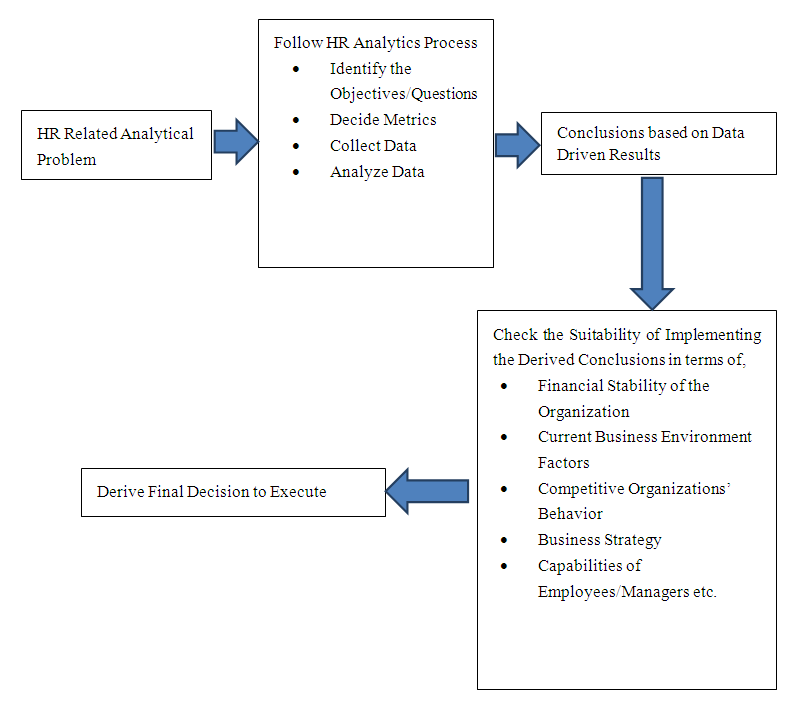 | Figure 1. Conceptual Model Developed by the Author |
4. Conclusions
- HR analytics is the application of research designs and advance statistical tools for evaluating HR data to find out solutions or to make sustainable decisions relating to HR issues aligning with business strategy. Simply it is about researching in HR issues. Big data is highly useful in HR analytics to make accurate conclusions. However, in this paper the author critically argues, emphasizing the fact that data driven conclusions derive from HR analytics process might not be the best solutions for an issue all the time. Those derived solutions/conclusions need to be adjusted considering the factors i.e., financial stability of the organization, current business environment factors, competitive organizations’ behavior, business strategy, capabilities of employees/managers etc.
Funding
- This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of Interest
- The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML