-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Human Resource Management Research
p-ISSN: 2169-9607 e-ISSN: 2169-9666
2016; 6(3): 73-81
doi:10.5923/j.hrmr.20160603.03

Ambiguity: A Critical Factor that Affect Leadership
Khairi Mohamed Omar
College of Administrative Science, Applied Science University, Bahrain of Kingdom
Correspondence to: Khairi Mohamed Omar, College of Administrative Science, Applied Science University, Bahrain of Kingdom.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This paper aims to address the ambiguity as one of the most important factor that plying a significant role in leadership. It is conducted based on reviewing several related manuscripts such as examination documents, conceptual and empirical work in which the researcher made his review. The paper addressed the ambiguity as one of most important factor that affect organizational leadership. A concepts model has been suggested for future research. The ability to manage ambiguity has been introduced as moderators the relationship between followers, leader and organization as independent variables and leadership as dependent variables. Conceptual framework has been presented for better understanding of the topic science leadership which formed the basis for the topic under study. The paper is more in understanding the contexts in which organizations could move forward towards achieving its aims whether increase of the performance, productivity or profit.
Keywords: Ambiguity, Followers, Leader, Organization, Leadership
Cite this paper: Khairi Mohamed Omar, Ambiguity: A Critical Factor that Affect Leadership, Human Resource Management Research, Vol. 6 No. 3, 2016, pp. 73-81. doi: 10.5923/j.hrmr.20160603.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The concept of leadership is no longer new in virtually in any field of research and study. This is because virtually all field of human endeavour have one way or the other referred to leadership during their studies. However, the gathering of two or more people have created the need for leadership. Thus, someone must play that role in order for them to achieve their anticipated or stated goal. Therefore, it is better to examine leadership in its totality (principles, traits, types etc.) for a better understanding of the topic since leadership formed the basis for the topic under study.Several definitions of leadership have evolved over the past decades by different authors. For instance, leadership has been seen as a process that deal with social influence whereby a person can play a part of supporting and aiding in order to achieve a stated goal or organizational. Some definitions actually view leadership with respect to followers. For instance, Alan Keith (2015), viewed leadership as making ways for other people in order for them to contribute to the success of the organization. Thus, it will better to deferential leadership from posture as noted by Tom De Marco. Therefore, leadership can be totally seen as a process that a person follows with the aim of influencing others so as to achieve organisational task or goal and also try to pilot the organization in the right way by being more coherent and cohesive. This is definition could be said to be consistent with that of Northouse (2015), where his perspective of defined leadership as a process a person attempt to influence a group of persons with the aim of achieving their stated goals.Furthermore, the important or role of leadership cannot be over emphasized. Its importance can be seen in almost every area of life that involves human being, in as much as their two or more people in that place. Accordingly, the same can be said of animal kingdoms. Animals also have leaders among themselves. This is to enable them to achieve unity and be more organized, and equally achieve their aims. According to Curtis, Vries, and Sheerin, (2011), they argued that, leadership should be seen as an essential factor that can help team to become more effective. Based on this, several authors have argued that; it is the most essential ingredient and critical factor that can make orgainsation to survive.However, past studies and as well as past experience have shown that several factors affect leadership, therefore, making it effective or ineffective. For instance, the followers, communication and a host of others have been noted in this regard. However, the most critical factor of these is the ambiguity in leadership (Jeffrey, 1977). Actually, for the best knowledge of the researcher, so far it is quite unfortunate that until this time no optimal solve has been offer to address this problem. This formed the major issue in this write up. The problem of ambiguity cannot be overemphasized. First, it tends to create disagreement among researchers on the concept. Secondly, causes researchers to produce bag of mix findings and lastly produces inconsistency in research results. Therefore, there is need to examine the ambiguity as a critical factor that affect leadership and possibly suggest a way out. Taking followers for example, experience and studies have shown that whenever the followers are ready and willing to support and obey the lead then there is every tendency that both the leader and his/her followers will like to achieve a greater success. However, if otherwise is the case then both the leader and his/her followers are likely to achieve nothing. Thus, no leader no followers and on the other hand no followers and no leader.
2. Principles of Leadership
- In order to make leadership effective, certain principles have advanced. According to the U.S Army in 1983, eleven principles of leadership have been provided, this is to assist and guide leaders in their effort to pilot the organization, hence, it helps you be, know, and do all that are required in the course of leading.a) Know yourself and seek self-improvement: knowing yourself involves understanding of your be, know, and do, attributes. This will help you to discover your weaknesses and strengths and consequently help you to capitalize on your strengths and work on your weaknesses. Again, it pretty good for a leader to ensure a constant upgrading and improvement of himself in order to meet up with the new challenges cause by the dynamic nature of the environment. Several ways he can do this; self-study, formal classes, reflection, and interacting with others.b) Be technically proficient: as a leader professionalism is needed or expected from you by the entire organization. Professionalism deals with a leader differentiating himself from amateur. Therefore, a leader should be able to have a solid knowledge about know his job, not only that but also familiarize himself with employees in the organization.c) Seek responsibility and take responsibility for your actions: it is often said that a good leader always takes responsibility for his actions whether good or bad. Thus, a leader should devour from blaming others most especially when things go wrong. Hence, proper analysis of situation should be done and action should be taken to correct to avoid future occurrence and proceed to the next task. Another thing that is important for a leader to do is to always found responsibilities that could take your organization to new heights.d) Make sound and timely decisions: one of the biggest tasks of a leader is to make decisions concerning the organization and as well as the employees. It is not just making decision but it is all about making sound decision and these decisions must be timely that at the time they are required for the effective, efficient and smooth running of the organization. These decisions must be able to solve the organisation’s problems and become a tool for effective planning of the business activities of the organisation.e) Be example to others: the usual saying which goes like this, “leadership by example” meaning that leadership is all by being example to others- your followers. Therefore, be a good role model to your workers is very essential and crucial. If you want people to good and act in a certain way therefore, you as a leader must and should act the same. Thus, ones they see you acting in that manner they will act same. This is in line with the word of Mahatma Gandhi who said that for your employees. We must become the change we want to seef) Know your people and look out for their well-being: there is no doubt that workers will like and obey a leader that is ready care for them and willing to fight for their well-being in the organization. Successful leaders have been known to be concern about their employee’s welfare and well-being. Naturally this is true of human being.g) Keep your workers informed: past experience has shown that different works or employees demand different form of communication. The way you communicate to the senior employees may differ in the way you communicate to the junior employees. Therefore, leaders should ensure that each employee is being communicated within his capability and task. Also, other major people in the organization deserve a suitable means of communication.h) Develop a sense of responsibility in your workers: in developing the sense of responsibility in them, you are equally developing character traits in them. The essence of this, is to assist each individual worker develop professional responsibilities that is making them to be responsible to their task and action.i) Always make people to understood task, supervised, and accomplished: people may not understand their task if the tasks are not properly communicated or transmitted to them. Thus, it is observed that communication maybe the major key to this responsibility. However, it is not ensuring that people are well communicated but also ensure that you as leader must supervise them so as to ensure that each of them carry out their task accordingly. When this is done, there is tendency that the work or task would be accomplished.j) Train as a team: so many leaders have failed in this respect because they never regard their people in the organization as a team. They see them as just individual working in the organization or individual doing their own assigned task. The leaders need to train a team and work with them; this is the most probable way of achieving organization goal more effectively and efficiently.k) Maximize the full capabilities of your organization: every organization is capable of doing anything, because it has the capability of doing so. Therefore, a leader needs to make use of these capabilities provided by the organization to develop a team spirit. However, to do this, a leader needs to involve his section, organization, department etc. this will help me to achieve the capabilities to its fullest.
3. Traits of a Good Leader
- Several authors have listed various leadership traits. However, this is based on their studies and situation coupled with their experience in relation to the environment in their study were conducted. According one author, he noted that they are many traits to be discussed, hundreds of them for that matter as far as leadership is concern, however, they all tend towards one direction, and that is, trying to distinct one person’s characteristic from another person. he suggested that is more better some concentrate on those one that are critical to his/her discourse since the more a leader shows these traits the more likely the followers may trust and believe in his leadership or way.However, below are some leadership traits suggested and listed by in Santa Clara University and the Tom Peters Group:• Intelligent: this involves thinking fast and also thinking strategically in a way that it will help the organization to achieve it stated goals. To be able to do this you must have a right thinking frame of mind and attitude. To possess this, a leader should be able to read, seek challenges and study very hard. This is what actually differentiates a good leader from bad leaders and followers. Reading and studying makes a leader thinks fast and smart.• Competent: competent is another area a leader must not play with. So many other skills are required in this regard. For instance, Diamond, Thomas, and Munro (2007) have suggested and listed the following competence skills in their study of competence; dedicate to make the venture work whenever possible, refuse to let the venture fail whenever appropriate, possess an extremely strong internal drive, commit to long-term business goals, learn from a variety of means, learn proactively, learn as much as I can in my field, keep up to date in my field, apply learned skills and knowledge into actual practices, maintain a high energy level, motivate self to function at optimum level of performance, respond to constructive criticism, plan the organisation of different resources, keep the organization run smoothly, organize resources, coordinate tasks, Supervise subordinates, lead subordinates, organize people, motivate people, delegate effectively, maintain a positive attitude, Prioritize tasks to manage my time, Identify my own strengths and weaknesses and match them with opportunities and threats, manage my own career development and many others. Your competence should be guide you in making sound decisions which are not based on emotions and childlike.• Forward-looking: it is said that forward ever and backward never. A leader must have a vision and also set goals that are future oriented. The vision should reflect the entire goal of the organization.• Inspiring: this is like setting example and be a role model for others. It tasks the leader to be confidence about himself and in what he can do. Here, more maturity in both mental capacities, physical and spiritual person is needed in this regard. With this, the followers will be highly inspired. Thus, you have succeeded in building confidence and acceptance in them.• Broad-minded: within this context, it is advised that a leader should be limited in his mind. He should be broad minded that be diverse in his responsibilities. This would help his understand and manage the both the organization and as well as the employees. Thus, there is for him to seek out diversity.• Fair-minded: this calls equally and fair treatment to all people in the organization. The leader should endeavour to ensure justice all the time. Thus, prejudice should be avoided at all cost. As suggested by author that empathy should be replaced prejudice and injustice. Empathy implies that a leader should be sensitive towards the values, feelings, interests, and well-being of others.• Courageous: this takes a lot of strength and effort. However, it is one of the best ways to deal with hard and difficult situations. When the going get though, courage is the answer. It also deals with stress and obstacles that seem insurmountable. Hence, a leader is expected to show perseverance and total confident calmness during a difficulty and stressful situations.• Straightforward: this is similar to be honest. However, it calls that a leader should be sound in making his decisions and judgment. Having good knowledge of judgment would help the leader to judge himself in term of every decision he is making. It also helps the leader in assessing himself in whatever action and decision on both the organisation and on the employees.• Imaginative: this involves visualizing things and later bringing them into reality when possible. Be visualistic helps the leader to effect any needed and necessary changes that could occur in the organization’s strategies, plans, and changes that have to deal with departments, sections, etc. therefore, creativity and innovation are also needed in this regard. The presence of these two aforementioned would help the effectively achieve the organizational goals.• Honest: as a leader, you must ensure that all actions are sincere most especially in business dealings. Apart from that your integrity should follow your sincerity. Bad habit and behaviour like deception must be avoided. People should be able to believe your word and every statement that come from your behaviour should be able to inspire others.Apart from the above listed, the U.S Army in 1973 has also contributed by suggesting and listing some of the attributes of leadership. They argued that contended that attributed make a leader. Thus, every leader needs some of these attributes in order to excel. Some of these attributes the include the following;• Standard Bearers: this is involves establishing and building openness as well as trust into your workers or the people in the organization. To achieve this, an ethical framework for the organization needs to be put in place. A leader must therefore be committed towards ensuring that the organizational culture is being protected. Ones these are done, the leader will soon discover that he has succeeded in establishing ethical behaviour for the organization which in due time may become a lay down rule and examples for people to follow. In this manner employees may decide to be learning the culture and the ethical behaviour of the organization via listening and observing and role model of the leader.• Builder: this is the leader try to develop and build others via series of activities like coaching, teaching and training. Here, the leader strongly believe that the only way of making people to becoming active, productive and more dedicated and committed to their work is by giving them a proper training and development, when this is done, it highly believe to produce a positive atmosphere that motivate the employees to put in their best in order to help in achieving the set or organizational goals. Again, the leader try to afford the employees with opportunity of learning and at the same time understand that they are capable of making mistake and give room for their corrections.• Integrators: organization consists of many departments, sections and units. All of them are working towards accomplishing the same objective. The leader should be able to integrate and harmonize all the departments and as well as the employees working across these departments so as to create unity among them. As has been noted that the success an organization accomplished depends highly on the amount unity obtained among each department that make up the organization including the employees also. Without contradiction, the leader should be able to allow the employees to work on their own without much supervision, this will actually help to bring the best from the employees, hence, they will work within a vision-based framework which they leader has established earlier in the organization.The style of leadership: generally, leadership has been divided into three major parts, these include the following;a. Autocratic: according to Feldman (2003), he noted that authoritarians always found to be using strong desire in attempt to curtail uncertainty situations. There is every possibility that the followers in authoritarian will tend to resist change, this will automatically make them to reject innovation and put up negative work habit. For instance, ambiguous (that’s unclear) and new experience will be ejected ones perceived. Therefore, Feldman (2003), against this direction, claimed that his argument is in line with that of general logic within the management literature context, as noted in the work of Covin and Slevin, (1988), they stated that “For example an ‘‘entrepreneurial management style” is assumed to result from management’s general propensity to take risks, to innovate, and to compete”. In this same vein, one should be able to perceive and reason that a likely situation where firm’s leadership that prefers to curtail uncertainty situation could succeed in producing a pattern of behaviour that could produce or yield authoritarian leadership. In line with this, Feldman (2003); Stellmacher and Petzel (2005), conceptualized authoritarian management leadership “as employees’ perceptions of their organization’s management’s actions and decisions as rigid, dogmatic, and rule-bound”. From this argument, one could conclude that organizations that are pruned to authoritarian leadership in making decisions equally behave in manner that make decisions are predictable. Agreeing with this, Mitchell and Ambrose, (2007), reported that authoritarians organizations are found to inflexible, rigid and adhere to rule accordingly. They asserted that behaviours in this manner produce an uncertainty situation. Thus, followers are bound to experience uncertainty or become unsafe in their workplace or environment. Here, the leader proves to be in total control and sometimes he does not give room for followers to ask questions when necessary.b. Democratic: the exact opposite of the authoritarian leadership. This leadership type gives the followers the opportunities to participate in the decision making of the organization. Thus, followers are fully involved in the decision making. This leadership highly believes in team players, thus, making team members-followers to feel a sense of belonging since their input were recognized in the decision making. The followers are ready to be highly committed and dedicated in solving the organization problem since they believed that they were part of the decision.c. Lesser faire: As the name suggests, free and no control. This leadership involves those who are known not be leading. The followers in this type of leadership are believed to be full of experience. Thus, little or no supervision is therefore needed in this regard. The leader here lacks control over his followers, thus giving room for situation such as unacceptable behaviours among followers. There is no rules and regulations guiding followers. Followers do want they feel like. Therefore, it is called free leadership.
4. The Critical Factor: Ambiguity
4.1. The Concept of Ambiguity
- Several definitions have put forward by various writers in the attempt to define the concept of ambiguity. For instance, it has been defined to mean a situation that is characterized by the presence of two or more possible meanings of a word. In another definition, it is perceived to involve the use of a term in more than one way, this is by Richard Nordquist. Therefore, ambiguity can be regarded as characteristics of a word having more than one meaning. It is been argued that ambiguity is totally different from vagueness because ambiguity could be precise and applicable to terms while vagueness is applied to concept.Gerald et al (2005), in their attempt to define ambiguity has come up with types two ambiguity which they named; patent and latent. They asserted that it could be regarded as patent if the ambiguity in the word or concept is very noticeable and on the other hand, it is latent if the ambiguity in it is perceived to be hidden. One could conclude that ambiguity simply means a word in which is meaning becomes uncertain and doubtful. Similarly, in the field of psychology and sociology, the term has been associated with uncertainty and much of the researches in these fields have been noted to be directed towards “ambiguity tolerance”. The findings have noted that quite a number of correlations exist between a range of factors and individual tolerance and reaction’. In a likewise manner, the leadership field is not left out. For instance, David (2006) reported that correlation exist between the modes of leadership and individual’s reaction to ambiguous situations. Similarly, Kirton (2003), has reported correlation between modes of leadership and creativity.Furthermore, as noted earlier, several studies have been advanced with regard to leadership. However, their definitions and dimension of the concept still remain unsettled among various researchers in this filed as noted by one study (Jeffrey, 1977). Hitherto, one of the major problems facing leadership as a concept is that of ambiguity in definition and measurement of the concept itself.This implies that they seem to be disagreement between authors and researchers on the actual definition of leadership and its particular dimension which it be studied. Thus, ambiguity exists as in the concept of leadership. Based on this, study has argued that they seem not to be a concrete content on the construct or concept of leadership, hence many researches have adopted the model of behaviour in the study of leadership. Similarly, many have also adopted the line of social influence concept while others looked at it in the perspective of social power and authority. Meanwhile, these three perspectives will examine;Social influence: it has been greatly argued that to regard leadership as a separate entity it must be distinguished from the social influence construct. Past study has reported little differences between leadership and social influence concepts. However, it is also argued that some agreement exist between leadership and social influence phenomenon. Thus, they both relate in to some extent. Yet, both agreement and disagreement are still a matter of concern till this day. A critical examination will reveal that a person with a high social influence may not be a good leader and on the other hand, a good leader may posses some sort of social influence which form part of his leadership traits, and as such they leadership and social influence may continue to be in variance.Social power and authority: first, leadership must be differentiated from power and authority. Leadership is all about the lead and the led and therefore it involves the willingness of the followers to follow and obey the commands and instructions of the leader. On the contrary, power involves coerce or force in order to achieve a desire goal. Authority means the responsibility is being given to the leader. Form the forgoing one could foresee that leadership and power and authority cannot be likened. As it is argued that power itself is not aimed at achieving goal, hence it is not compatible to goal. It is just a mere subordinate. However, leadership involves achieving some sort of objectives between the led and the leader. In the case of leadership followers follow or comply voluntarily while involuntary compliance is present in power and to assess goal compatibility. Past study has reported that leaders who tend to apply or use the authoritarian-democratic in leadership position have not be able to achieve performance. Thus, small or little inconsistent exist in this regard.Model of behaviour: Two things are very crucial within this context. First, more disagreement have continue to more evolve with regard to the actual dimension of leadership model of behaviour. Secondly, more proliferation of on the dimension of leadership continues to emerge. However, it is perceived to be one of the researcher’s tricks and approaches adopted when embarking on research work. In the argument of leadership dimensions, two things are paramount with respect to the task to be achieved by the group namely; task performance and the group maintenance. Based on this, some authors have argued in this direction. Similarly, the Ohio State leadership study has also produce structure initiating and consideration as a dimension. Within this argument, some other dimensions have suggested, they include the following; in terms of punitiveness and closeness of the supervision, the least-preferred-co-worker scale which is also called (LPC) and discretion subordinates and authority. However, the cruz of the matter is that no answer has been found in this regard to solve this controversy. One author noted “but the meaning and behavioral attributes of this dimension of leader-ship behavior remain controversial”.
4.2. Problems of Ambiguity
- The major problem of ambiguity in leadership can be traced in the following;1. Disagreement: first ambiguity creates several meanings and definitions to a concept. Thus, making each individual to view that particular in several ways. This therefore consequently gives room for individual researcher to disagree with another. For instance, is argued that researchers have attempted to define leadership in terms of social influence, power and authority including mode of behaviours.2. Inconsistency in findings: ambiguity in doubt produces mix bag of findings. While some findings are positive others are negative. This is as a result of different views being argued by different authors within this context. Except researchers come to agree, more mix findings will continue to be reported by the authors in this field.3. No acceptable direction: because several definitions exit, there is therefore no acceptable direction to the concept since each research tends to claimed superiority over another researcher’s directions. Thus, there is need to set up standard and one acceptable direction so that the findings or results present in this field could be seen as concrete.
5. Other Non-critical Factors of Leadership
5.1. Leader
- A leader could be a led or lead leader, depending on his style and capabilities, and power to command people. Therefore, a leaders’ style of leadership affects the leadership. For instance, it is argued that a leader who adopts the democratic style of leadership is likely to achieve more result than leader who adopts other leadership style most especially the authoritarian leadership style. It is noted that a leader should be able to posses certain leadership characteristics and principles as discussed above, this help a leader lead the follower in the right direction and also make the followers to contribute and support the leader very well. With regard to the leadership qualities mentioned above, as a leader you should be honest in the area of understanding your capabilities that is, knowing who you are, what you can do and what your knowledge is. One author puts it this way “the followers, not the leader or someone else who determines if the leader is successful. If they do not trust or lack confidence in their leader, then they will be uninspired. To be successful you have to convince your followers, not yourself or your superiors, that you are worthy of being followed”.
5.2. Followers
- Experience has shown that much about leadership is dependent on the type of leadership style. The reason is that, the followers are ready to comply, obey and follow any leader that tend to be good, trusted, friendly, goal getter and who believe in himself. It has been noted that different followers demand different type of leadership style. There are also followers who ready and willing to follow and some are also not willing to follow. Therefore, it calls for the leader to master and understand the type of followers he is leading. Again, you should to motivate, know their needs and emotions, this will help the leader to achieve a great result. Finally, a leader “must come to know your employees' be, know, and do attributes”.
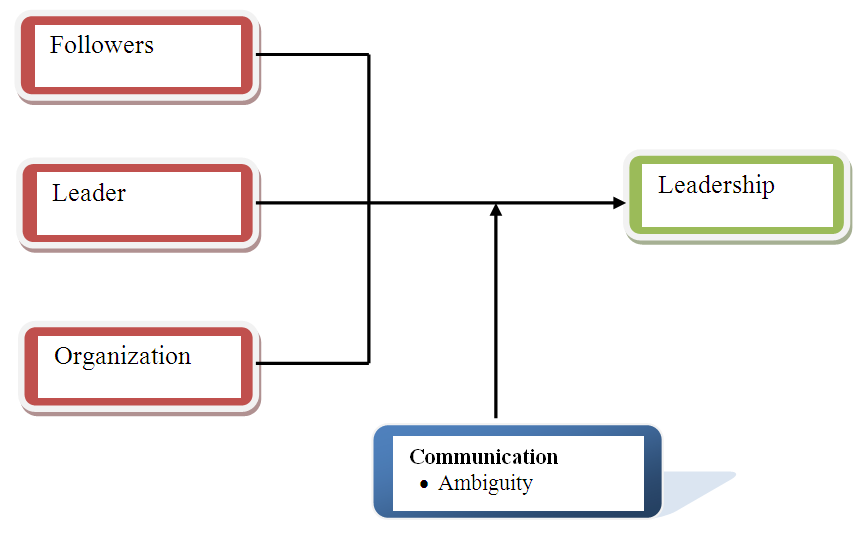 | Figure (1). The Framework of reference |
5.3. Communication
- Various communication methods exist when one talk about communication. For instance, some communication methods could be one-way while other could be two-ways. However, a good leader should adopt two-ways communication methods since in many cases feedbacks are needed from the followers by the leaders on their duties or work assigned to them. For example the followers will always like to report back to the leader on the assignments you asked to perform or complain about their work, fellow employees or want to ask questions about what they do not understanding. What and how you communicate either builds or harms the relationship between you and your employees.
5.4. Situation
- This can be aligned to the work of William Richard, who argued greatly on the contingency theory. Study has asserted that situation greatly affect a leaders’ actions than the leadership characteristic. Thus, it argued that it is the current or present situation that determines the kind or type of style to be adopted. Therefore, a leader should be able to assess, evaluate and analysis his current environment and as well as his followers. It has been reported that contingency theory always looks for best way within the present situation in achieving its goals. For example, you may need to confront an employee for inappropriate behavior, but if the confrontation is too late or too early, too harsh or too weak, then the results may prove ineffective. Apart from the factors mentioned and discussed above, some other factors play a role. These factors include the following; the skill of the leaders’ followers, senior employees relationship, informal, how the leader manages the organization and many more.The below framework indicated that the dependent variable, leadership is being affected by the three independent variables of follower, leader and organisation in the framework. These independent variables are being suggested by the past studies. For instance, Gabriel et al (2007) has reported the influence of leader’s personal value and style, organizational culture etc… on the leadership. Similarly, the important of communication has also been reported by various researchers like, Dwyer (2005) and Corvette (2007).Furthermore, the framework has established that there is a relationship between the independent variables which has been mentioned above with the dependent variable, leadership. However, their level of influence is still subject to the presence of the moderating variable, communication. Thus, it means that communication in the dimension of ambiguity could become an obstacle or good vehicle a good leadership. Also good or bad leadership is being determined by the independent variables in the framework. Therefore, it argued here that, the independent variables are likely to bring about good or bad leadership depending on the influence of the moderating variable-communication-ambiguity. For instance, the leader’s style, attitude, his/her personal value and characteristics such as honesty, commitment, goal getter, friendly and others could affect the leadership of the organization, though, this is also influence by the communication ambiguity, meaning that the lines of communication need to be thoroughly defined in such a way that it will avoid ambiguity between the leader and the followers, if this is done, the leadership of the organization will achieve a great success and if not otherwise will be the case. Similarly, the type of organization, its nature and organizational culture is a greater influence of leadership. For instance, some organizations are not well structured therefore, giving room for ambiguity which now automatically becomes a determinant in the relationship of both organization and leadership. Thus, poor organizational culture, value and the size of the organization whether big or small could bring about ambiguity or on the other hand ambiguity bring about poor organizational culture which invariably lead to poor leadership and consequently cause organizational failure or poor performance. Again, unmotivated and uncommitted followers could also negative impact on the leadership (Robert et al, 2004). Therefore, a leader should ensure that his followers are always being motivated, this will consequently make the followers to more committed to their duties or tasks and therefore, produce a good result. Ambiguity can also make the followers to be demotivated and uncommitted. Thus, leader needs to avoid communication gap between them and the followers by being friendly and defining the lines of communication very clear in order to ensure a positive leadership.
6. Underpinning Theory to Support the Issue
- So far, there are some highlighted theories that considered to be the best theory to underpin the issue in this context such as the use of contingency or situational theory of leadership. The situational leadership is propounded by William Richard. The theory proposes that no single leadership style is good or best or effective in all situations. Adopting this theory into this present issue in this study, it therefore implies that no single definition could be effective in the study of leadership concept hence, the presence of several definitions. This is also contributed by the situations or the environment in which the researchers found themselves or the objective they tend to achieve in their studies.
7. Types of Leadership
- Several authors have tried to classified leadership in different ways. However, this write up follows the classification made by Vipin et al (2004), since his classification suit present discussion. Three classes of leadership which the study made include;
7.1. The Transformational Leadership
- The theories prominent within this type of leadership include; the operant conditioning and the path- goal. Here, the leadership role or function has been perceived to instrumental and not to be seen as inspirational. Therefore, it is argued here that a transformational leadership tends to transform the followers. In line with this, the transformational leadership as noted by Vipin et al (2004), concentrates on the behaviour of the followers through their self-interest though using persuasion means to achieve his aim. Thus, it believed that this kind of leadership aimed at ‘‘binding leader and follower together in a mutual and continuing pursuit of a higher purpose. One of the areas you can easily found this kind of leadership, is in the entrepreneurship leadership. Here, the entrepreneurs try to persuade the followers in order to perform their task thereby achieving their results. The essence of persuading the followers is to get their maximum performance. Hence, the entrepreneur tries to create and get the followers willingness.
7.2. The Team-oriented Leadership
- This type of leadership place more emphasis on the relationship and interactions between the groups and leaders. Thus, there is need for a leader to involve a team or call it team participation in attempt to achieve his objective. Therefore, the leader–member exchange theory is much applicable within this context. Study has reported that this kind of approach, leader–member exchange could produce result such as team performance and managerial progress. This leadership type could be a little bit similar with that of entrepreneurship leadership in the area of highly levels of employees or workers participation and involvement.
7.3. Value-based Leadership
- Within this type of leadership, three key things are very essential. They include; the leader, vision and mission. Here, the make known to the followers both the vision and the mission of the organization, again display some sort of belief and confidence they posses and in addition to that try also to create example for the followers to follow. This example could be better appreciated if it personal examples of the leaders. In return, the followers will be more committed and much involvement to the organization’s mission and vision.
8. Conclusions
- Leadership has been reported to be influenced by several factors such as situation, follower, leader etc. however, the ambiguity in leadership in terms definitions, and social influence and mode of behaviours have posed a great worries and challenges to every researcher in this field. Thus, no agreement in terms of the above mentioned. Therefore, there is need to find or come up with a workable definition(s) and also with the mode of behaviour. Secondly, another best way to solve or put an end to this matter as suggested by this write up is to apply the theory of contingency which formed the underpinning theory of this write up. It therefore means that researchers should be guided by the situation under study in the defining of the concept in order to avoid the problem of ambiguity.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML